Chapter 7 Textbook
Key Terms
- Socialization: Learning the rules and norms of the group, becoming moralized
- Golden Rule: Do unto others as you would have them do unto you
- Dwellers: Americans who look for religious fulfillment in conventional religious practice.
- Liberals: They are impatient with perceived inequalities and injustices and welcome change using a promotion focus.
- Seekers: Americans who look for religious fulfillment in spirituality.
- Ethic of community: Evolution has shaped humans to respond with anger and moral outrage when somebody betrays the group.
- Conservatives: They manage uncertainty and threat by justifying the system's status quo using a prevention focus.
- Gesellschaft: More modern, impersonal arrangements of civil society reflected in modern markets, urban settings, and complex bureaucratic states - liberal sentiment.
- Morality: is comprised of (intentional) agency + (suffering) patient
- Gemeinschaft: Traditional patterns of social relations based on shared blood, shared place, and shared beliefs - conservative sentiment.
- Motivated social cognition: Human beings formulate social attitudes and values that meet underlying needs and goals.
- Religious instruction: Reinforces a natural tendency to perceive agency nearly everywhere and to assume that what happens in the world is largely dictated by the minds of agents (human or divine)
- Moral motivational agenda: The values and goals people pursue to exert a transformative effect on the world
- Moral conduct: No human group can function without some shared agreement called
- Hero: When an agent is intentionally helpful
- Villain: When an agent is intentionally harmful
- Beneficiaries: When patients are helped by a good agent
- Victims: When patients are harmed by a bad agent
- Sacred canopy: People that are brought together under a common sociomoral barrier through religion
- Conservatives: See positive change as restoration
- Liberals: See positive change as reform
- O: Trait with direct relevance to personal values
- Social affinity: serves as a check on aggression within the group
- Fairness: sharing behaviour and other collaborations depend on this sense in the group
- Moral judgment: involves assigning characters to the roles of hero, villain, beneficiary, and victim
- Moral values: social arrangements that the person imagines to be especially good and praiseworthy
- Political cognitions: express underlying fears, hopes, desires, and wishes regarding social life while also reflecting deep moral concerns
- Religiosity: the tendency to take on religious beliefs and practices
- Authoritative parenting: combines a loving emphasis on the value of children with the establishment of clear norms and standards
- Cohort effects: how people raised in one generation differ from those from another generation
Researchers - Theories
- Jonathan Haidt: suggested that human beings have strong moral reactions to violations of care/harm, fairness/cheating, loyalty/betrayal, authority/subversion and sanctity/degradation
Experiments
- Monkeys respond negatively when resources are distributed in a grossly inequitable manner
- Coyotes that are rejected from play sessions are much more likely to leave the pack than those that are included and it doubles their risk of death
- When an inanimate object moves and the force is imagined inside the object it is seen as an active agent but when the force is imagined outside the object it is due to God or an external agent whose intention is to make the object move
- Most Christian American teenagers ascribe to a watered-down generic brand of religious beliefs reflecting common themes in American culture more generally
- The heritability of religiosity increases with age into adulthood, as people are better able to ignore what others want them to do and follow
- The heritability of religion is connected to the heritability of personality characteristics that specify concerns for community integration and existential certainty
- Religiosity is connected to the dispositional traits of A and C
- High school sophomores who profess strong religious values tend to show larger increases in A and decreases in antisocial traits over the next 3 years
- When people begin to lose faith in the government, people increase their adherence to religion and vice-versa
- Conservatives see the world as a more dangerous place
- People become more conservative when they are faced with serious threats or when they are reminded of their own mortality
- Conservatives imagine government as a strict father who provides rules in order to protect his children (citizens)
- Liberals imagine government as a nurturant caregiver like a mother who provides her children with the nourishment they need in order to grow
- Conservatives focus more on the moral foundations of loyalty/betrayal, authority/subversion and sanctity/degradation
- Liberals focus more on the moral foundations of care/harm and fairness/cheating
- Religiosity is at least moderately heritable
- MZ twins often match on their opinions regarding social/political issues more than DZ twins
- Inhibited and fearful preschool children have a tendency to become conservatives
- Restless preschool children have a tendency to become liberals
- O is positively associated with higher stages of moral reasoning, greater religious searching or quest, and liberal political attitudes
- People high in O tend to move away from religious traditions they grew up with and to sample new faiths and alternative religious perspectives
- High O is associated with involvement in spirituality and “New Age” expressions of religious experience
- Authoritative parenting is associated with higher levels of empathy, conscience, moral development, and prosocial values among children
- Political orientation tends to remain pretty stable after young adulthood
- Age is positively related to prosocial values and negatively related to material values
- Religious values decline from adolescence through late midlife but rebound as people move into their retirement years
Examples
- Mother Teresa: experienced dread and loneliness in her relationship with God but this may have solidified her identification with Jesus
- Andrei Sakharov: advocated for human rights but he did not believe in God so his values were moral and political rather than religious
- Andrei Sakharov: he was a Russian critic of the Soviet political system
- Without morality, we cannot be a eusocial species
- Organized religion and complex political structures are recent human achievements that emerged after the development of language and culture
- Primates and eusocial species have basic social instincts that predispose them to express forms of care and consideration to other group members
- Care/harm and fairness/cheating undergird a basic ethic of autonomy in human groups
- Those who betray others in friendships or love are viewed to have violated a moral principle
- Sanctity/degradation has its roots in humans’ experience with pathogens and toxins where the body reacts with disgust to spoiled food
- A shared sense of sacredness may bind group members together under a moral banner, solidifying loyalty to the group and respect for authority
- The 1st step in becoming a moral agent is to make an explicit moral judgment
- Agents are responsible for what they do because they have intentionality and patients have rights that should be maintained because they are capable of suffering
- Some characters are high on intentionality and experience making them either agents or patients (ex: adults)
- Some characters are high on agency and low on experience making them agents (ex: God, Google)
- Some characters are low on agency and high on experience making them patients (ex: children)
- When we hear stories of heroism we feel inspiration, stories of villains we feel anger/disgust, stories of beneficiaries we feel happiness/relief, stories of patients we feel sympathy/sadness
- You cannot be an agent until you really understand what an agent is
- Autistic individuals may be compromised in moral decisions because they do not fully get agency
- Psychopaths may be compromised in moral decisions because they fail to appreciate what it means to be a moral patient
- The prime function of religion is to build a community
- Religion is pervasive across human cultures
- Religion has evolved to promote cooperation in groups, which strengthens the group’s ability to compete against other groups, which indirectly promotes the inclusive fitness of group members
- Religion can promote self-regulation and health
- The development of religious beliefs depends on the kinds of religious community to which the person belongs
- Religion and politics both spring from moral considerations regarding how people should live together in groups
- The relation between religion and politics is hydraulic; as one begins to ebb the other flows
- Political conservatives score higher on death anxiety, fear of threat/loss, need for order, and self-esteem
- Political liberals score higher on tolerance for uncertainty, sensation seeking, and O
- Conservatives reflect a prevention focus approach to life and liberals reflect a promotions focus approach
- George W. Bush: had the lowest rating of O among all presidents and was really conservative
- Ronald Reagan: was liberal when he was young but then shifted towards conservatism
- People become more conservative during times of war
Table 7.1
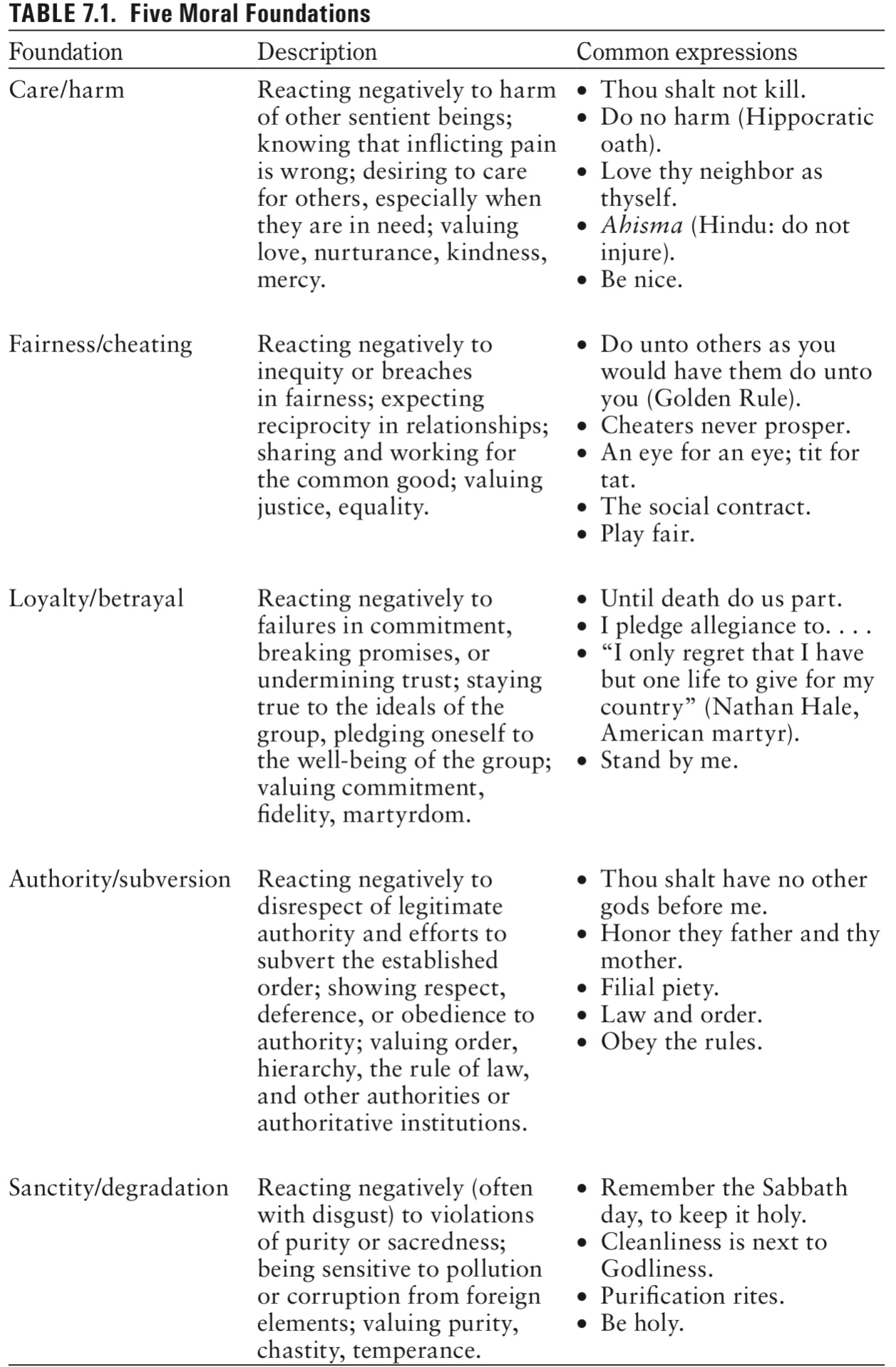
- Care/harm: reacting negatively to harm of other sentient beings
- Fairness/cheating: reacting negatively to inequity or breaches in fairness
- Loyalty/betrayal: reacting negatively to failures in commitment, breaking promises, or undermining trust
- Authority/subversion: reacting negatively to disrespect of legitimate authority and efforts to subvert the established order
- Sanctity/degradation: reacting negatively (disgust) to violations of purity or sacredness
