ENSP 2341 FINAL Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/162
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:54 PM on 5/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
1
New cards
Atom
smallest particles of any element that is still an element
2
New cards
Molecule
groups of 2 or more atoms
3
New cards
Compound
groups of 2 or more different elements
4
New cards
Biogeochemical cycle
track the flow of matter and energy through the different “spheres”
5
New cards
Reservoir, pools, fluxes
**Reservoir/pools -** “pools”, major compartments that contain the substance
\
**Fluxes -** rates at which substances moves between reservoirs (mass per unit time)
\
**Fluxes -** rates at which substances moves between reservoirs (mass per unit time)
6
New cards
Mycorrhizal fungus
* Mycorrhizae - Fungi that form symbiotic association with plant roots
* plays a big role in plant uptake of phosphorus
* plays a big role in plant uptake of phosphorus
7
New cards
Humus
dark, organic material that forms in soil when plant and animal matter decays
8
New cards
Cation/ Anion
* **Cation:** Positively charged ions - hydrogen, magnesium, aluminum
* **Anion:** Negatively charged ions - sulfate, phosphate, nitrate, chloride, etc.
* **Anion:** Negatively charged ions - sulfate, phosphate, nitrate, chloride, etc.
9
New cards
Cation exchange capacity
Quantity of cations that can be **adsorbed** by a soil expressed in milliequivalent of negative charge per 100 g dry soil (1 meq = the ability to adsorb and hold one milligram of H+)
10
New cards
Soil formation
* Soils begin to form when sediment, organic matter, or rock—(1) parent material—is first deposited or exposed, often by water, wind, or ice.
* Soils develop as parent material ages in place, changed by (2) climate, (3) soil organisms, and the (4) terrain over (5) time.
* Soils develop as parent material ages in place, changed by (2) climate, (3) soil organisms, and the (4) terrain over (5) time.
11
New cards
Lithosphere
outer layer \~ 100 km deep
12
New cards
Weathering (phys,chem, biol)
* **Physical Weathering:** Manual fragmentation of rocks through the action of wind, water, ice, temperature fluctuations, etc, without chemical change
* EXAMPLE:
* Water enters the joints in a rock
* Water freezes in the crack as temperatures fall at night and increase 9% in volume put pressure on the crack
* Thawing occurs, followed by subsequent freezing the following night. Freeze-thaw cycles gradually widen the crack
\
* **Chemical Weathering:** Chemical reactions between minerals and the environment (air, water)
* Main chemical weathering reactions are dissolution (also called carbonation), hydrolysis, and oxidation
* Weathering increases with more water, O2 and CO2
* **Biological Weathering:** When roots penetrate the cracks, breaking up rocks, usually a mix of physical and chemical weathering
* EXAMPLE:
* Water enters the joints in a rock
* Water freezes in the crack as temperatures fall at night and increase 9% in volume put pressure on the crack
* Thawing occurs, followed by subsequent freezing the following night. Freeze-thaw cycles gradually widen the crack
\
* **Chemical Weathering:** Chemical reactions between minerals and the environment (air, water)
* Main chemical weathering reactions are dissolution (also called carbonation), hydrolysis, and oxidation
* Weathering increases with more water, O2 and CO2
* **Biological Weathering:** When roots penetrate the cracks, breaking up rocks, usually a mix of physical and chemical weathering
13
New cards
Soil pH
\
* **Soil pH:** Measure of H+ ion activity in soil solution
* The mineral content of the soil is what primarily determines the pH
* Carbonate minerals tend to increase pH
* When significant aluminum iron are present, the pH is lowered
* **Soil pH:** Measure of H+ ion activity in soil solution
* The mineral content of the soil is what primarily determines the pH
* Carbonate minerals tend to increase pH
* When significant aluminum iron are present, the pH is lowered
14
New cards
Soil salinity
\
* **High concentration of salts in soils - Salinization:**
* Caused by irrigation in arid systems - water evaporates and salt crystals left behind
* **Electrical Conductivity (EC) - Measures Salinity:**
* Salts increase a solution’s ability to conduct electrical current because the separation of charges provides a “pathway” for the current’s flow
* Units are in decisiemens per metre (dS/m)
* Low salinity = low dS/m ratings
* **High concentration of salts in soils - Salinization:**
* Caused by irrigation in arid systems - water evaporates and salt crystals left behind
* **Electrical Conductivity (EC) - Measures Salinity:**
* Salts increase a solution’s ability to conduct electrical current because the separation of charges provides a “pathway” for the current’s flow
* Units are in decisiemens per metre (dS/m)
* Low salinity = low dS/m ratings
15
New cards
Nitrogen fixation
Occurs when inert N (N2) is transformed to ammonium (NH4+)
16
New cards
Biological N fixation
Uses enzyme “nitrogenase”
* High-energy requirement, only occurs where bacterium has abundant carbohydrate supply
* High-energy requirement, only occurs where bacterium has abundant carbohydrate supply
17
New cards
Haber-Bosch process
Converts hydrogen and nitrogen to ammonia
18
New cards
Denitrification
Process by which specialized bacteria break down NO3− and NO2− to N2 or N2O
19
New cards
Reactive nitrogen
**Nitrous oxide -** reactive nitrogen compound
20
New cards
Labile vs recalcitrant carbon
* **Labile:** most rapid turnover times
* **Recalcitrant:** resistant to decomposition
* **Recalcitrant:** resistant to decomposition
21
New cards
Soil organic matter
(SOM) is the portion of soil that is composed of living and dead things in various states of decomposition, such as plant roots and microbes.
22
New cards
Decomposition
\
break-down of organic molecules
\n “CH2O” + O2 → H2O + CO2 + Nutrients
break-down of organic molecules
\n “CH2O” + O2 → H2O + CO2 + Nutrients
23
New cards
Photosynthesis
CO2 is removed from the atmosphere by primary producers
CO2 + 6 H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
CO2 + 6 H2O + sunlight → C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2
24
New cards
Cellular respiration
all animals, plants, many fungi and some bacteria obtain \n energy through cellular respiration by breaking down sugars, fats, and amino acids with oxygen as part of their metabolism \n
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 → CO2 + 6 H2O + chemical energy (ATP) and heat
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 6O2 → CO2 + 6 H2O + chemical energy (ATP) and heat
25
New cards
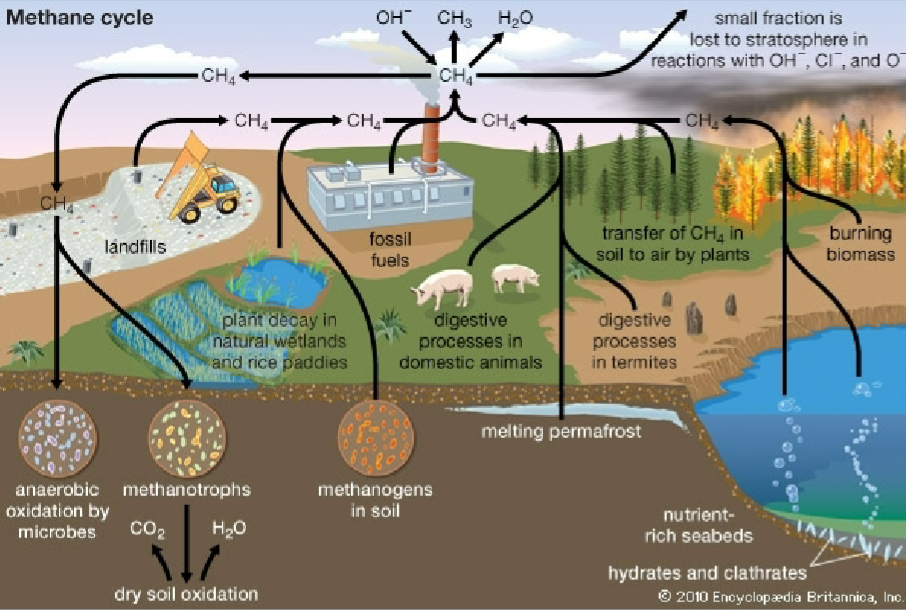
Methane cycle
* Wetlands are the major natural source of methane to the atmosphere
* Methanogens use CO2 or acetate in place of O2 as their terminal electron acceptor during metabolism, and produce methane in the process
* Methanogens use CO2 or acetate in place of O2 as their terminal electron acceptor during metabolism, and produce methane in the process
26
New cards
Ocean acidification
The impacts of altered carbon cycle such as with land-use changes and fossil fuel emissions.
Increased CO2 + CH4 in the atmosphere has led to Ocean Acidification
Increased CO2 + CH4 in the atmosphere has led to Ocean Acidification
27
New cards
Properties of water
Water has many unusual properties due to its **hydrogen bonding**
* Water is polar
* Water is an excellent solvent
* Water has high heat capacity
* Water has high heat of vaporization
* Water has cohesive and adhesive properties
* Water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid.
* Water is polar
* Water is an excellent solvent
* Water has high heat capacity
* Water has high heat of vaporization
* Water has cohesive and adhesive properties
* Water is less dense as a solid than as a liquid.
28
New cards
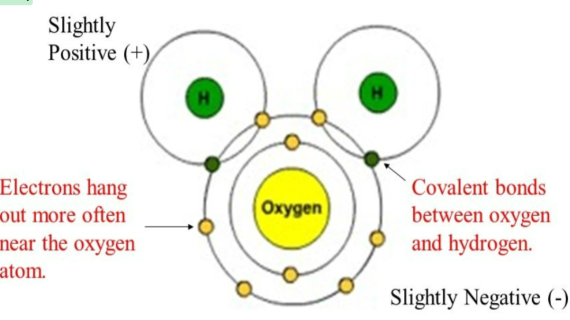
Hydrogen bonding
* Special type of dipole-dipole attraction between molecules, not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom (Hydrogen is positive and oxygen is negative)
* Occur when H is covalently bonded to a small, highly electronegative atoms - **N, F, O**. This H can form an H- bond with another electronegative atom
* H bonds hold together double helical chains of DNA!
* Occur when H is covalently bonded to a small, highly electronegative atoms - **N, F, O**. This H can form an H- bond with another electronegative atom
* H bonds hold together double helical chains of DNA!
29
New cards
Polarity
separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end
30
New cards
Polar covalent bonding
Slight difference in electronegativity (unequal sharing of electrons)
31
New cards
Ionic bonding
Ionic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that involves the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions, or between two atoms with sharply different electronegativities
32
New cards
Point source pollution
\
* Single large source
* Can be traced back to the spot it came from
* Single large source
* Can be traced back to the spot it came from
33
New cards
Non-point source pollution
* Diffuse source or many smaller point sources
* Can not be traced back to a point
* **Nonpoint source water pollution from agriculture:** The largest source of water pollution in the U.S. (64% of pollutants into streams & 57% of pollutants entering lakes)
* Can not be traced back to a point
* **Nonpoint source water pollution from agriculture:** The largest source of water pollution in the U.S. (64% of pollutants into streams & 57% of pollutants entering lakes)
34
New cards
Dissolved oxygen
An indicator of water quality
* High dissolved oxygen = Good water quality
* **Sources of D.O in a body of water = photosynthesis, diffusion from atmosphere, wind cycling**
* Salinity affects DO, the higher the salinity, the lower the DO concentration
* **Temperature and elevation affect DO**
* **Cold lakes can hold more dissolved oxygen than warm lakes**
* **Low elevation lakes and rivers hold more oxygen than those at high elevation**
* High dissolved oxygen = Good water quality
* **Sources of D.O in a body of water = photosynthesis, diffusion from atmosphere, wind cycling**
* Salinity affects DO, the higher the salinity, the lower the DO concentration
* **Temperature and elevation affect DO**
* **Cold lakes can hold more dissolved oxygen than warm lakes**
* **Low elevation lakes and rivers hold more oxygen than those at high elevation**
35
New cards
Oxygen-consuming wastes
* **Sources:** Human and animal feces; Industrial wastes from \n paper mills, tanneries, food processing plants, slaughterhouses, meatpacking plants
* **Fate:** Bacteria and fungi break down organic detritus through \n aerobic decomposition. When overloaded with org matter, \n aerobic decomposers proliferate and DO consumed more \n rapidly than can be replaced from atmosphere
* **Fate:** Bacteria and fungi break down organic detritus through \n aerobic decomposition. When overloaded with org matter, \n aerobic decomposers proliferate and DO consumed more \n rapidly than can be replaced from atmosphere
36
New cards
Biological oxygen demand
**BOD =** capacity of organic material in a sample of water to consume the DO
Amount of dissolved oxygen needed by **aerobic decomposers** to break down **organic materials** in a certain volume over a 5–day incubation period at 20°C \n \n The higher the **BOD**, the greater the amount of reactive organic compounds in the water
Amount of dissolved oxygen needed by **aerobic decomposers** to break down **organic materials** in a certain volume over a 5–day incubation period at 20°C \n \n The higher the **BOD**, the greater the amount of reactive organic compounds in the water
37
New cards
Cultural eutrophication
Cultural eutrophication occurs when human water pollution speeds up the aging process by introducing sewage, detergents, fertilizers, and other nutrient sources into the ecosystem.
38
New cards
Sedimentation
* Sediments – undissolved particles in water
* Natural erosion of rock and soil leads to sedimentation
* Increased rates of sedimentation due to...
* Development, clear-cutting, strip mining, overgrazing, plowing, etc.
* Natural erosion of rock and soil leads to sedimentation
* Increased rates of sedimentation due to...
* Development, clear-cutting, strip mining, overgrazing, plowing, etc.
39
New cards
Turbidity
cloudiness caused by suspended particles
40
New cards
Redox potential, (Eh)
Redox potential (voltage) is a measure of how easily a metal (or other ion) will give up electrons or retain electrons, not the likelihood for a specific oxidation or reduction reaction occurring.
41
New cards
Anoxic/ Anaerobic
A condition in which the aquatic (water) environment does not contain dissolved oxygen (DO), which is called an oxygen deficient condition.
* the absence of free oxygen
* the absence of free oxygen
42
New cards
Dose-response
A relationship exists between the dose of an agent and the biological response.
43
New cards
Carcinogen
cause cancer – cells reproduce and grow abnormally producing a malignant tumor
\
(PAHs, aromatic amines, vinyl chloride, asbestos, metal compounds)
\
(PAHs, aromatic amines, vinyl chloride, asbestos, metal compounds)
44
New cards
Teratogen
cause birth defects
\
(alcohol, cigarette smoke)
\
(alcohol, cigarette smoke)
45
New cards
Mutagen
chemicals that alter genes and chromosomes to cause heritable abnormalities in offspring
46
New cards
Endocrine disrupter
Synthetic chemicals that block, mimic, or otherwise interfere with naturally produced hormones
47
New cards
Cancer cluster
a greater than expected number of the same or etiologically related cancer cases that occurs within a group of people in a geographic area over a defined period of time.
48
New cards
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study of how often diseases occur in different groups of people and why.
49
New cards
Persistence
EPA calculates persistence as half life of chemical in different media (atmosphere, water, soil, sediments)
50
New cards
Bioavailability (of heavy metals)
Bioavailability of heavy metals in soils is very important for their fate in their environment and uptake in plants
* different metals have different bioavailability
* bioavailability is dependent on metal speciation and on different physio-chem properties of soils
* different metals have different bioavailability
* bioavailability is dependent on metal speciation and on different physio-chem properties of soils
51
New cards
Halogenated hydrocarbon
halogenated meaning a chemical compound containing F, Cl, Br, or I
52
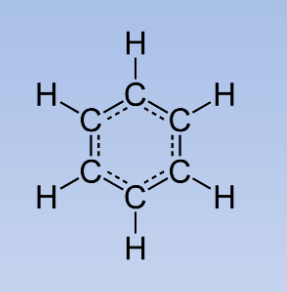
New cards
Aromatic hydrocarbon
Aromatic = cyclic, flat molecule with ring of resonance bonds. Very stable!
* Simplest is benzene
* Can be monocyclic or \n polycyclic (PAH)
* Can be halogenated
* Chemical compound containing F, Cl, Br, or I
* Simplest is benzene
* Can be monocyclic or \n polycyclic (PAH)
* Can be halogenated
* Chemical compound containing F, Cl, Br, or I
53
New cards
Grasshopper effect
**Grasshopper effect, global distillation =** geochemical process by which POPs are transported from warmer to colder regions of the earth (poles, mountaintops) \n
Semi-volatile: compounds are vaporized at high temperature
* Travel to low temperature, condenses repeatedly..
Semi-volatile: compounds are vaporized at high temperature
* Travel to low temperature, condenses repeatedly..
54
New cards
Acid mine drainage
Acid mine drainage is the formation and movement of highly acidic water rich in heavy metals.
* forms through the chemical reaction of surface water (rainwater, snowmelt, pond water) and shallow subsurface water with rocks that contain sulfur-bearing minerals,
* results in sulfuric acid
* forms through the chemical reaction of surface water (rainwater, snowmelt, pond water) and shallow subsurface water with rocks that contain sulfur-bearing minerals,
* results in sulfuric acid
55
New cards
Impacts of heavy metals
* Most heavy metals cause environmental and atmospheric pollution, and may be lethal to humans.
* Heavy metals can become strongly toxic by mixing with different environmental elements, such as water, soil, and air, and humans and other living organisms can be exposed to them through the food chain.
* Heavy metals can become strongly toxic by mixing with different environmental elements, such as water, soil, and air, and humans and other living organisms can be exposed to them through the food chain.
56
New cards
Stratosphere
Absorption of UV radiation by ozone increases temperature
57
New cards
Troposphere
temperature decreases with increasing altitude
* Warmed air that rises from the surface of Earth
* Pressure decreases with altitude, as air rises, it enters zone of lower pressure and expands and cools
* Warmed air that rises from the surface of Earth
* Pressure decreases with altitude, as air rises, it enters zone of lower pressure and expands and cools
58
New cards
Residence time
mean residence time is calculated as the total mass divided by the flux into or out of the atmosphere over a given time
* gases that have short residence times are distributed unevenly
* gases that have short residence times are distributed unevenly
59
New cards
Atmospheric composition
Dry air made up of two major components:
* Nitrogen (N2)78.08%
* Oxygen (O2) 20.95%
Two minor components:
* Argon (Ar) 0.934%
* Carbon Dioxide(CO2) 0.035%
Water vapor:
* Water makes up 0.1 - 5% of the atmosphere by volume, (usually \~1-3%)
* Nitrogen (N2)78.08%
* Oxygen (O2) 20.95%
Two minor components:
* Argon (Ar) 0.934%
* Carbon Dioxide(CO2) 0.035%
Water vapor:
* Water makes up 0.1 - 5% of the atmosphere by volume, (usually \~1-3%)
60
New cards
Mean free path
* Average distance travelled before colliding with another molecule
* Greater at higher altitudes since pressure is so low
* Greater at higher altitudes since pressure is so low
61
New cards
Aerosols /Particulate matter
Aerosols = minute particles, diameter < 10 μm
Particulates = larger particles
Particulates = larger particles
62
New cards
Air pollutant
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials
63
New cards
Primary vs Secondary Pollutants
* Primary pollutant - air pollutant emitted directly from a source
* Secondary pollutant - not directly emitted as such, but forms when other pollutants (primary pollutants) react in the atmosphere
* Secondary pollutant - not directly emitted as such, but forms when other pollutants (primary pollutants) react in the atmosphere
64
New cards
Mobile sources
These are Anthropogenic Sources
\- Motor vehicles
\- Motor vehicles
65
New cards
Stationary sources
These are Anthropogenic Sources
\- Power plants
\- Industrial facilities
\- Power plants
\- Industrial facilities
66
New cards
Acid deposition
Acid rain: rainfall whose pH is less than 5.6; caused by nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ammonia (NH3) which form nitric and sulfuric acid and NH4+ when mixed with water.
4NO2 + 2H2 + O2 → 4HNO3 (nitric acid) → acid rain
4NO2 + 2H2 + O2 → 4HNO3 (nitric acid) → acid rain
67
New cards
Photochemical smog
mix of atmospheric chemicals with anthropogenic emissions derived daily from fossil fuel burning
* Ozone, aldehydes, Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN)
* Ozone, aldehydes, Peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN)
68
New cards
Thermal inversion
…can increase air pollution
* Thermal inversions = cool air at the surface beneath warmer air above
* Restricts movement and dispersal of air pollutants
* Thermal inversions = cool air at the surface beneath warmer air above
* Restricts movement and dispersal of air pollutants
69
New cards

Greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in Earth's atmosphere trap the Sun's heat. This process makes Earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes Earth a comfortable place to live.

70
New cards
Global warming potential
Is a relative measure of how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere compared to CO2.
71
New cards
Albedo
Amount of incident radiation reflected by a surface; does not contribute to the heating of the surface
72
New cards
Radiative forcing
Occurs whenever there is an imbalance in sunlight entering atmosphere and energy radiating back to space.
73
New cards
Infrared radiation
IR radiation is not energetic enough to break covalent bonds, but \n can change the vibrational/rotational motion of the molecule
74
New cards
Dipole moment
To absorb IR, molecule must undergo change in dipole moment
* When atoms in a molecule share electrons unequally, they create a __**dipole moment.**__
* This can occur between two ions in an ionic bond or between atoms in a covalent bond. Dipole moments arise from differences in electronegativity.
* CO2 has no net dipole moment, but it does undergo a change in dipole moment. H2O does both.
* When atoms in a molecule share electrons unequally, they create a __**dipole moment.**__
* This can occur between two ions in an ionic bond or between atoms in a covalent bond. Dipole moments arise from differences in electronegativity.
* CO2 has no net dipole moment, but it does undergo a change in dipole moment. H2O does both.
75
New cards
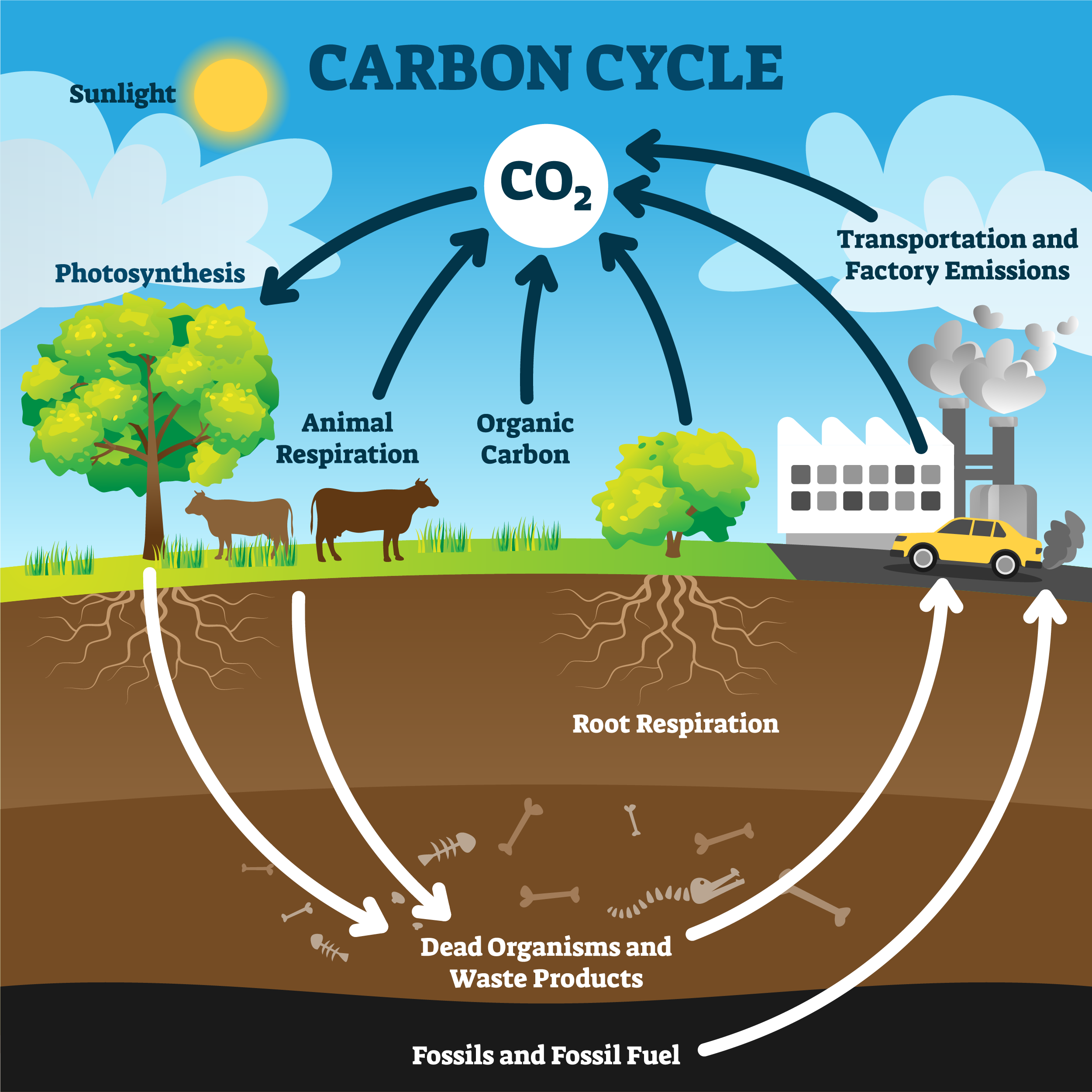
Carbon cycle
Soil organic matter/carbon cycle - based on continuously supplying carbon in the form of organic matter as a food source for microorganisms
76
New cards
Carbon sequestration
Capturing CO2 from the atmosphere for long-term storage
77
New cards
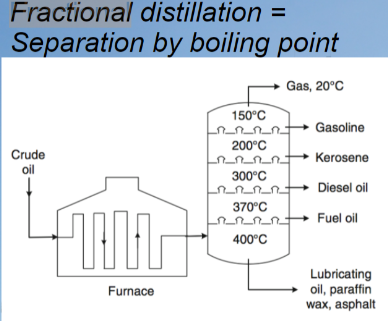
Fractional distillation
the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions.
* Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize
* Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize
78
New cards
Bond energy
energy required to break 1 mole of a particular kind of bond; same energy released if bond reformed
79
New cards
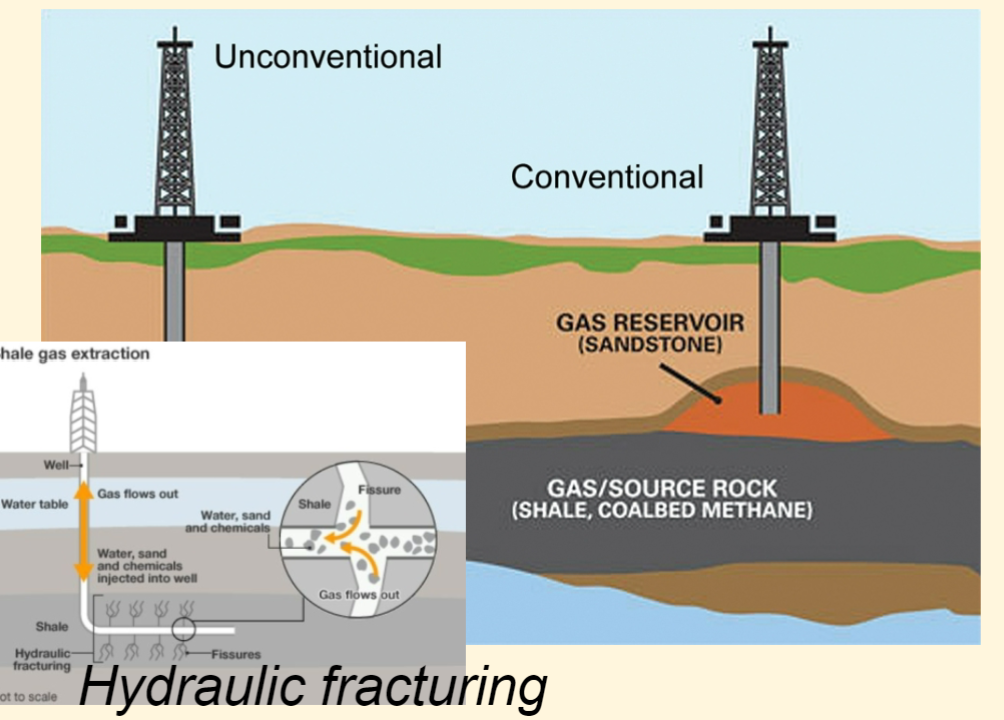
Hydraulic fracturing
technique used commonly in low-permeability rocks like tight sandstone, shale, and some coal beds to increase oil and/or gas flow to a well from petroleum-bearing rock formations.
80
New cards
Tar sands
= Sandstone + bitumen
\
Extraction for oil
* Extraction – Hot water process separates bitumen from sand, water, and minerals – 2 tons tar sands to produce one barrel of oil
\
Extraction for oil
* Extraction – Hot water process separates bitumen from sand, water, and minerals – 2 tons tar sands to produce one barrel of oil
81
New cards
**Porosity, permeability**
Porosity and permeability of soil allow the migration and accumulation of petroleum under adequate trap conditions.
82
New cards
Lithium mining
Lithium used for:
* batteries of electric vehicles, batteries of laptops and cell phones, glass and ceramics industry.
\
Environmental/social side effects include:
* use of large quantities of water and related pollution
* potential increase in carbon dioxide emissions
* production of large quantities of mineral waste
* increased respiratory problem
* alteration of the hydrological cycle
* batteries of electric vehicles, batteries of laptops and cell phones, glass and ceramics industry.
\
Environmental/social side effects include:
* use of large quantities of water and related pollution
* potential increase in carbon dioxide emissions
* production of large quantities of mineral waste
* increased respiratory problem
* alteration of the hydrological cycle
83
New cards
Radioactivity
The release of energy from the decay of the nuclei of certain kinds of atoms and isotopes
84
New cards
Ionizing radiation
Not energetic enough to break covalent bonds, but can change the vibrational/rotational motion of the molecule
85
New cards
Alpha, beta, gamma radiation
* Gamma rays are the most harmful external hazard.
* Beta particles can partially penetrate skin, causing “beta burns”.
* Alpha particles cannot penetrate intact skin. Gamma and x-rays can pass through a person damaging cells in their path.
* Beta particles can partially penetrate skin, causing “beta burns”.
* Alpha particles cannot penetrate intact skin. Gamma and x-rays can pass through a person damaging cells in their path.
86
New cards
Radioactive decay
More unstable = more raid decay, shorter half life
* ΔN/Δt = kt
* N= number of nuclei
* No = initial N
* k= rate constant
* t= time
* ΔN/Δt = kt
* N= number of nuclei
* No = initial N
* k= rate constant
* t= time
87
New cards
Decay rate – ½ life
A half-life is the time it takes for a certain amount of a pesticide to be reduced by half.
Half life t1/2 = 0.693/k
Half life t1/2 = 0.693/k
88
New cards
Nuclear fission
* 1939 - Manhattan Project began to develop atomic bomb
* Einstein sent letter to FDR warning that the Germans were already working on a bomb based on nuclear fission
* Differs from other types of nuclear reactions in that it can be amplified via a nuclear chain reaction
* Neutrons released by each fission event can trigger more events, in turn releasing more neutrons and causing more fissions
* This continues with the release of ever increasing amounts of energy until all the uranium nuclei have been split
* Einstein sent letter to FDR warning that the Germans were already working on a bomb based on nuclear fission
* Differs from other types of nuclear reactions in that it can be amplified via a nuclear chain reaction
* Neutrons released by each fission event can trigger more events, in turn releasing more neutrons and causing more fissions
* This continues with the release of ever increasing amounts of energy until all the uranium nuclei have been split
89
New cards
Isotope
Atoms with the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons and therefore different atomic mass
90
New cards
Fissile isotope
* Most common fissile isotopes are U-235 and Pu-239
* Process by which atoms are split and energy is released
* Process by which atoms are split and energy is released
91
New cards
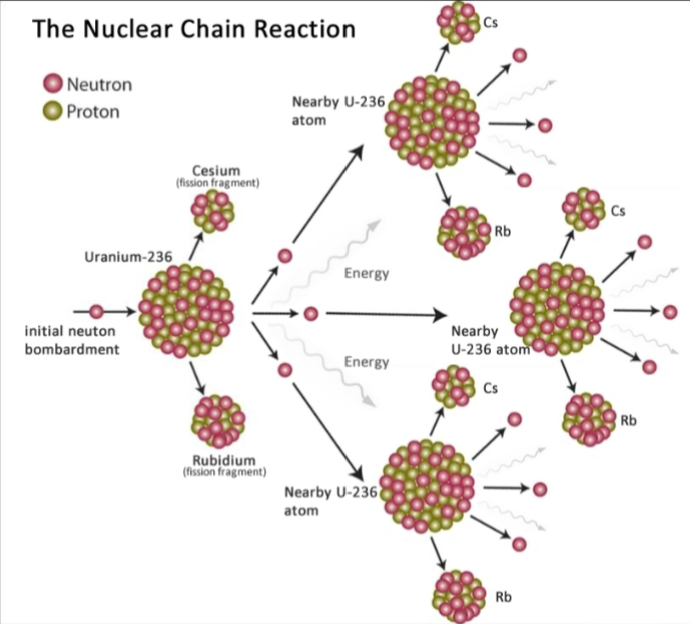
Nuclear chain reaction
\
* Neutrons released by each fission event can trigger \n more events, in turn releasing more neutrons and causing more fissions
* This continues with the release of ever increasing amounts of energy until all the uranium nuclei have been split
* Neutrons released by each fission event can trigger \n more events, in turn releasing more neutrons and causing more fissions
* This continues with the release of ever increasing amounts of energy until all the uranium nuclei have been split
92
New cards
Critical mass
The smallest mass of a fissionable material (U-235) that will sustain a nuclear chain reaction at a constant level.
93
New cards
Radwaste
* Radioactive waste, remains radioactive for up to hundreds of thousands of years
* Four options for dealing with radwaste:
* Cooling ponds – temporary onsite storage
* Dry-cask storage – stored onsite in barrels
* Fuel reprocessing – a nuclear proliferation threat because reprocessed fuel can be used in weapons
* Deep-geological storage – long-term underground storage
* Four options for dealing with radwaste:
* Cooling ponds – temporary onsite storage
* Dry-cask storage – stored onsite in barrels
* Fuel reprocessing – a nuclear proliferation threat because reprocessed fuel can be used in weapons
* Deep-geological storage – long-term underground storage
94
New cards
Life Cycle Analysis
* Developed in the 1960s, motivated by concerns over limitations of raw materials & energy resources.
* Considers everything that goes into the making, using, transporting, and disposing of a product
* Considers everything that goes into the making, using, transporting, and disposing of a product
95
New cards
Cradle-to-Gate
Cradle-to-gate refers to the carbon impact of a product from the moment it's produced to the moment it enters the store.
* some companies prefer to measure cradle-to-gate because they've designed a product that can be easily recycled or composted, avoiding the landfill altogether.
* some companies prefer to measure cradle-to-gate because they've designed a product that can be easily recycled or composted, avoiding the landfill altogether.
96
New cards
**Cradle-to-Grave**
Products made with no contribution to the environment and made to end up as waste.
97
New cards
Cradle-to-Cradle
Industry must protect and enrich ecosystems and nature's biological metabolism while also maintaining a safe, productive technical metabolism for the high-quality use and circulation of organic and technical nutrients.
98
New cards
Technical nutrient
Technical nutrients would be manufactured/created
99
New cards
Biological nutrient
Biodegradable
100
New cards
Upcycling
Making a product better