Chemistry Photon or a living Room Photon? Let's get on the same wavelength.
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
neutral, N/A
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Photon units
Frequency: Hz or s^-1
Wavelength: nm or m (m is always used in equations)
wavelenngth and Frequency
when frequency increases, wavelentgh decreases
Light spectra
electrons go to excited state than backto groudn state, emit energy and photons
Quantum numbers
Angular Momentum (shape of orbital, based on shell)
Magnetic (use number line, orientation of orbital)
Spin (+ or - 0.5, electron spin)
Electron configuration
1 s2, etc
Pauli’s Exclusion principle
no electrons are the same, excluded
Hund’s Rule
every orbital is slighty occupied
Aufbau principle
electrosn fill orbital starting from nucleus out
Photoelectric effect
KE electron = E photon - photoelectric energy
Effective Nuclear Charge Zeff
Zeff = proton # - core electrons
The Shielding Effect
inner electron repel electron from outer shells
Columbus Law
attraction/ repulsion is tronger when
particles charge is greater
distance is shorter
Isoelectric Series
atoms/ ions with same electron configuration
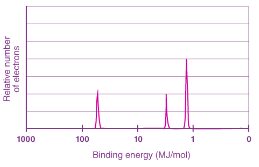
Photoelectron Pectroscopy
A process which measures the binding energy that the nucleus has for its electrons
attraction between charged particles increases as the distance between them decreases