Financial Accounting
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Accounting definition
The process of identifying, measuring and communicating information to permit informed judgements and decisions by users of the information
Financial accounting
Information for the users on the outside of a business. Regulated by company law, is always about the past, not very specific information. Balance sheet of big PLCs
Management accounting
Used for people inside the company. Concerns the future and helps make decisions. Highly technical and specific info, no laws to regulate and helps control resources
Types of organisation
Sole trader - still must file accounts but less regulated
Partnerships- usually law firms and if accounts are reported wrong the liability stands with all partners
Not for profit sector - Charities, Council, Government
Companies - Private Limited Companies (LTD) and Public Limited Companies (PLC)
Limited when regarding business
Means they’re only limited to what their shares are worth in the business when they were purchased
3 financial statements
Statement of financial position (Balance sheet)
Statement of Income (Profit or Loss)
Statement of Cash Flow
Who would use accounting info?
Competitors, Regulators, Shareholders, Employees, Government, Investors, Bank etc
Qualities of Financial Statements
Relevant and Reliable
Comparability, Timelines, Verifiability, Understandability
Statement of Financial Position
Assets= Equity + Liabilities
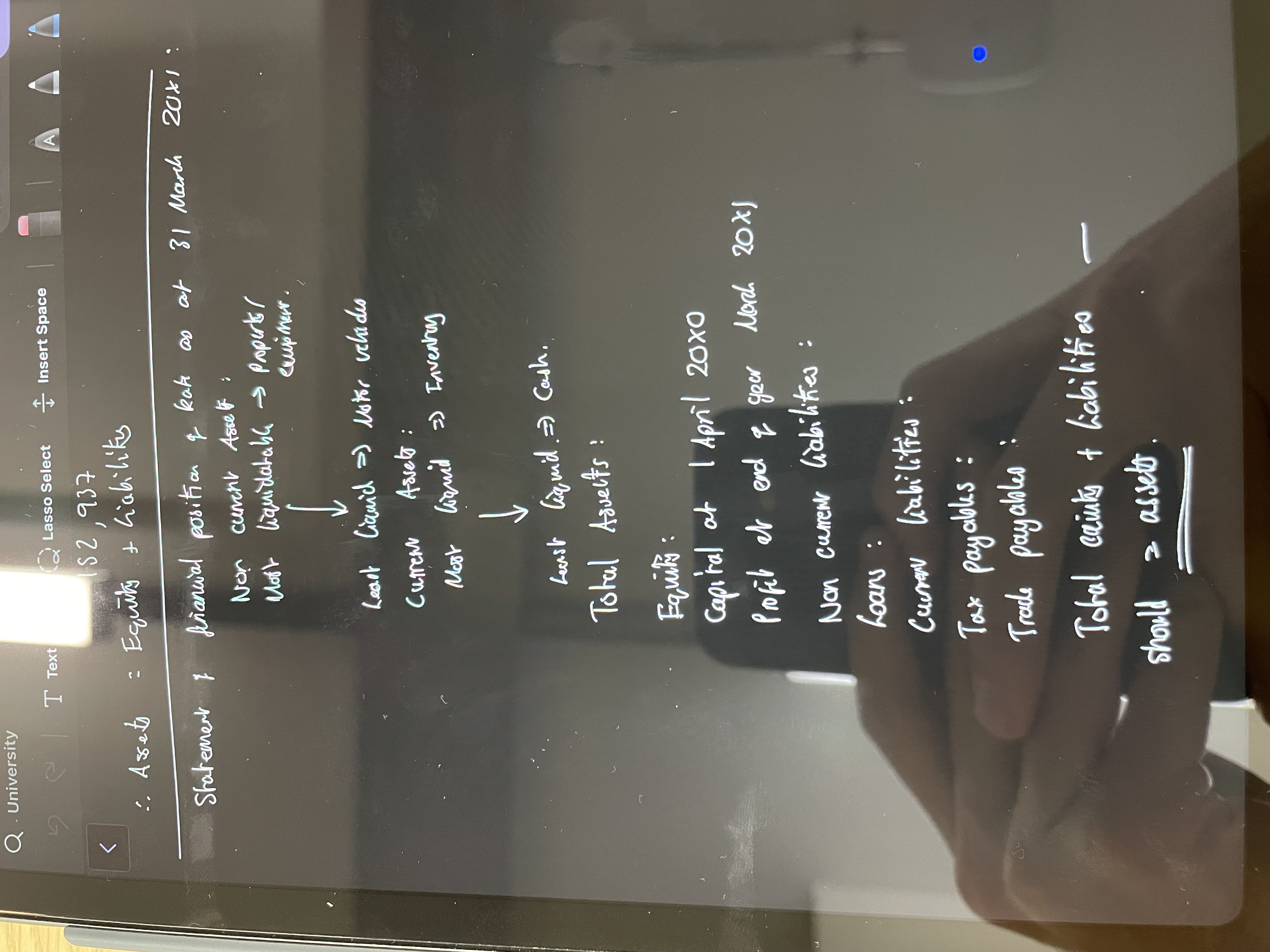
Assets
Non-Current- Generate income in the long term or must by sold over a long period of time (property)
Current - Cash, can be sold within the next 12 months or near cash
Equity
The amount the owner has invested and is able to claim from the business
Liabilities
Claims from organisations or businesses from outside the business that they cannot avoid.
Current - Settled within 12 months
Non Current - Long term loans
4 Accounting conventions
Business Entity Convention
Prudence
Going concern
Matching
Business entity convention
The owner and the business are treated as separate and distinct
Prudence
Financial statements should err on the side of caution. Should not be approximated without knowing true figures
Going concern
The business will continue operation for the foreseeable future without reasonable doubt of otherwise
Matching
The expenses should match the revenues that they helped generate in the same accounting period as the revenues are released
The Income statement
Measures profit or losses over an accounting period
Revenue
Measure of the inflow of assets or reduction in liabilities which arise from a result of trading activities
Usual source of revenue comes from the sales of goods by retail or manufacturing businesses or the provision of a service in the service industry
Criteria for Revenue
Amount can be measured reliably
Probable that the economic benefits will be received
Ownership and control of the items should pass to the buyer (when the goods are being sold)
Expenses
Measure of the outflow of asset (or the increase of liabilities) that is incurred as a result of generating revenues
This may include salaries, wages, rent etc
The accounting equations
Assets= Equity + Liabilities
This can be extended to
Assets = Equity at start of period + profit at end of period + Liabilities
Profit = Revenue - Expenses
Assets + Expenses + Drawings= Equity + Liabilities + Revenue
On left is debits, on right is credits
Debits and Credits
DEAD CLIC
Debits are expenses, assets and drawings
Credits are liabilities, income, capital
Setup of the Income Statement

Th trial balance
The debits and the credits listed, they must equal one another to be valid
Accruals
A business has not paid all of its expenses for an accounting period.
increase expenses and create a current liability
Prepayments
A business has paid amounts towards purchases in the future past the current accounting period
Decrease expenses and create current assets
Closing inventory
The amount you have left in inventory at the end of the accounting year.
This follows over to the opening inventory the next year
This should always be the lower of two options: what you paid for it and what you can sell it for
Cost of sales adjustment
Cost of sales = open inventory + purchases - closing inventory
Methods of depreciation
Straight line depreciation
Reducing balance depreciation
Unit of production
Straight line depreciation
Simple interest, reducing by the same amount each year
Depreciation is taken as an expense in the income statement
Net book value
Historic cost- accumulated depreciation
This is labelled as an asset in the SFP
Reducing balance depreciation
Compound interest
Cost - accumulated depreciation x n%
How is depreciation recorded
Income statement has a depreciation expense
SFP has accumulated depreciation under non current assets next to the historic cost of the asset
Calculating Trade receivables
Take original amount- irrecoverable debt like ones that will never be paid then take the percentage off of that
5 different adjustments
Accruals
Prepayments
Cost of sales
Depreciation
Bad debts
Scrap/ Residual value
The amount of money you could get from selling the item at the end of its useful life (must be estimated but is usually 0)
Amortisation
Depreciation for intangible assets
Choosing a depreciation method
Accouting regulations don’t tell you what one to use
Difficult to measure how much an asset actually wears out during a year
Unpredictable factors effect wear and tear: how careful operation is, maintenance, intensity and variety of use
Choose and apply consistently and disclose what method you use
Perpetual life
A company will continue to exist regardless of changes in shareholders and employees until its existence is legally ended
A company has a separate legal existence away from shareholders
Legal safeguards for companies
Plc or limited after the name to designate that is it a company
Limitations to withdrawals of equity (limited to how much you put in)
Produce financial statement
Have financial statements reviewed by an auditor
Public Limited Companies (plc)
Able to raise capital by selling shares to the public
Minimum issued share capital of £50000
Subject to strict regulations
Shares may be listed on the stock exchange for trading overseas
Private Limited Companies (LTD)
Cannot offer shares to public
Usually shares are held by family members or larger companies
Only need 1 shareholder
Large % of UK companies are LTD
Directors (3 things they must do)
Appointed by shareholders
Report annually about their management
Disclose all material information
Accountability for their actions
Fairness in directors dealings with shareholders
3 different law and regulation centres
Statutory regulation (layout of financial statements)
Financial reporting council (UK accounting standards)
Stock exchange rules
Financial reporting council
There is the international financial reporting council (all companies in EU) and The Financial Reporting Standards which operate in the UK
Corporate Governance
We need governance over the corporate world to ensure that scandals cannot be covered up by dishonest accounting
The 2008 financial crisis triggered widespread re-appraisal of governance systems in the UK and internationally
UK corporate governance code
Published in May 2010, latest version in Jan 2024
Code sets out good practice in relation to
Board leadership
Division of responsibilities
Board composition
Audit, risk and Internal control
Remuneration
Company accounting features
Equity
Dividends
Borrowings
Corporate tax
How a company raises capital
Uses shares
For example to raise £50000, they may release 50000x£1 shares or 100000×£0.50 shares
This is the nominal, face or par value
Types of shares
Ordinary shares- pay dividends which are out of the residual income= profits after all other claims have been met
Dividends will obviously depend on profits
Preference shares - pay a fixed dividend so do not depend profits. They get paid before ordinary shareholders but not after all claims have been dealt with
Shares are placed under assets (bank balance) and equity (share capital)
Profit and reserves
Usually for a sole trader, profit is recorded as capital on the balance sheet however for a company they have profit shown as a reserve called retained earnings
2 types of reserves
Revenue reserves - retained earnings (profits made by the company and not yet distributed to dividends)
Capital reserves - Share premium account arises when shares are issued at more than the nominal value. Revaluation reserve occurs when assets are re valued at higher than their historical cost
What do companies do with this profit
Retain to provide funds for growth
Pay dividends - usually happens twice a year (half way through and at year end)
Borrowings
Normally labelled as non-current liabilities
This may be loan notes which are paid at a fixed interest rate every 6 months
If all or part of the loan can be repayed within the next 12 months then it becomes a current liability
Taxation
Companies pay tax on their profits
Tax charge is based on profit before tax and it is displayed in the balance sheet as a current liability
Companies are taxed under corporation tax whereas sole traders are taxed under personal tax
Statement of Cash Flow
Split up into 3 main sections:
Operating activities
Investing activities
Financing activities
At the end you consider your net change in cash (3 sections added together)
Difference between cash and profit
Profit = revenue - expenses and this can include non cash items like depreciation
Cash measures liquidity not profitability
Profit is an idea , cash is reality (you only record cash when it physically comes to you)
Accrual basis
You record revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred not when the cash arrives
Net operating cash flows
Cash from revenues minus payments for inventories, expenses, interest, taxe
Cash flows from investing activities
Usually negative cash flows, as it comes from cash payments to acquire new non current assets
Cash flows from financing activities
Issue or repayment of shares, receipt or repayment of borrowings
This is followed by net cash change
Stakeholders
People who have an interest in the business.
This is an umbrella term for all the people that would be interested in financial statements
Company profiling
Companies with similiar financial statements are likely to behave in a similiar way. You can usually tell what type of company they are based off of their financial statement
Financial ratios
Help you compare against previous performance or performance against other businesses
Essentially analyse how well a company is performing
5 most common ratios:
Profitability
Efficiency
Liquidity
Financial gearing
Investment
Benchmarking ratios
They’re only useful when compared to a benchmark, this can be past periods, similiar businesses, or performance targets
Profitability ratio (1) Return on Ordinary shareholders funds (ROSF)
Profit after tax / Ordinary share capital and reserve
A high value for this figure is desirable as long as it is not at the expense of future returns
Profitability ratio (2) return on capital employed (ROCE)
Operating profit / Capital employed
Capital employed = share capital + reserves + non current liabilities
Profitability ratio (3) Gross profit margin
Gross profit / sales revenue
Usually effected by selling prices, sales volume reducing, cost of goods purchased increasing etc
Profitability margins (4) Operating profit margin
Operating profit / sales revenue
Same as gross profit calculation
Efficiency ratios (5) Inventory turnover
Inventory / cost of sales x 365
Indicates how many days it would take to sell inventory
Builders usually have a long turnover as it may take a year or 2 to build a house, retailers have very short
Efficiency ratios (6) Trade receivable days
Trade receivables / credit sales revenue x 365
Efficiency ratios (7) Trade payables days
Trade payables / Credit purchases x 365
Efficiency ratios (8) Sales revenue to capital employed
Sales revenue / capital employed
Indicates how efficiently a company is using its assets
Liquidity ratios (9) Current ratio
Current assets / Current liabilities
Indicates how many times current assets cover current liabilities or can the company pay the liabilities by using their assets
Liquidity ratio (10) Acid test ratio
(Current assets - Inventory ) / Current liabilities
Usually a better measure of how well they can pay their liabilities off
Sources of internal finance
Retained earnings
Better credit control (being proactive and reactive to ensure all payments are made punctually)
Reduction in inventory (handling costs and storage costs will reduce money)
Deferring payments to suppliers
Sources of external finance
Ordinary shares
Leases
Loans
Loans
Must be paid back at the agreed interest rate over the agreed time period
Fixed rate or variable rate
Appear as finance cost or finance expense
When is high gearing better than low gearing
High gearing means you have high levels of interest bearing debt which should be good during expansion as profits should be rising
Low gearing is optimal when profits are falling and you cannot pay off as much debt