Climate Change
1/11
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
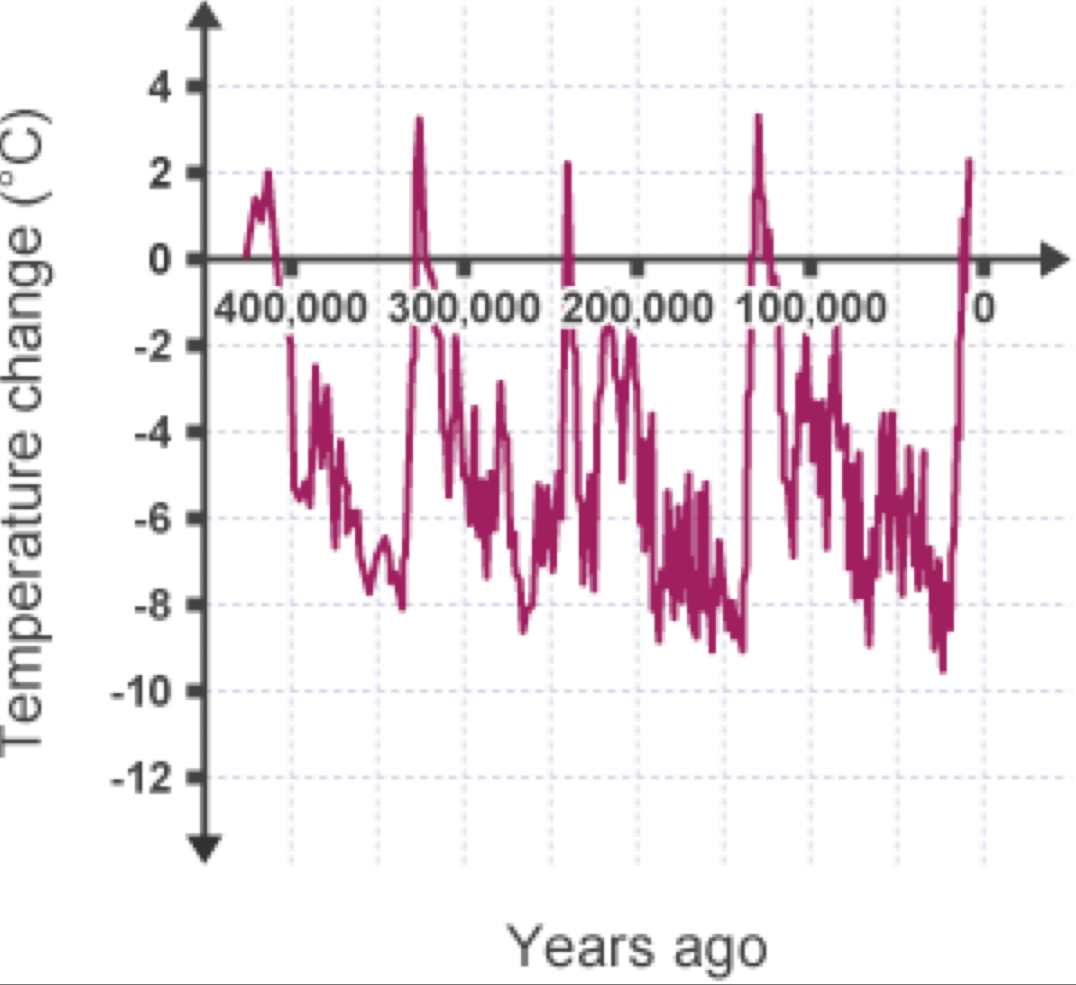
What are the phases of Earth's climate history?
The global climate has phases including interglacial (warmer) and glacial (cooler), with the last major cold period being the Pleistocene, which ended 10,000 years ago, leading to the current warm phase, the Holocene.
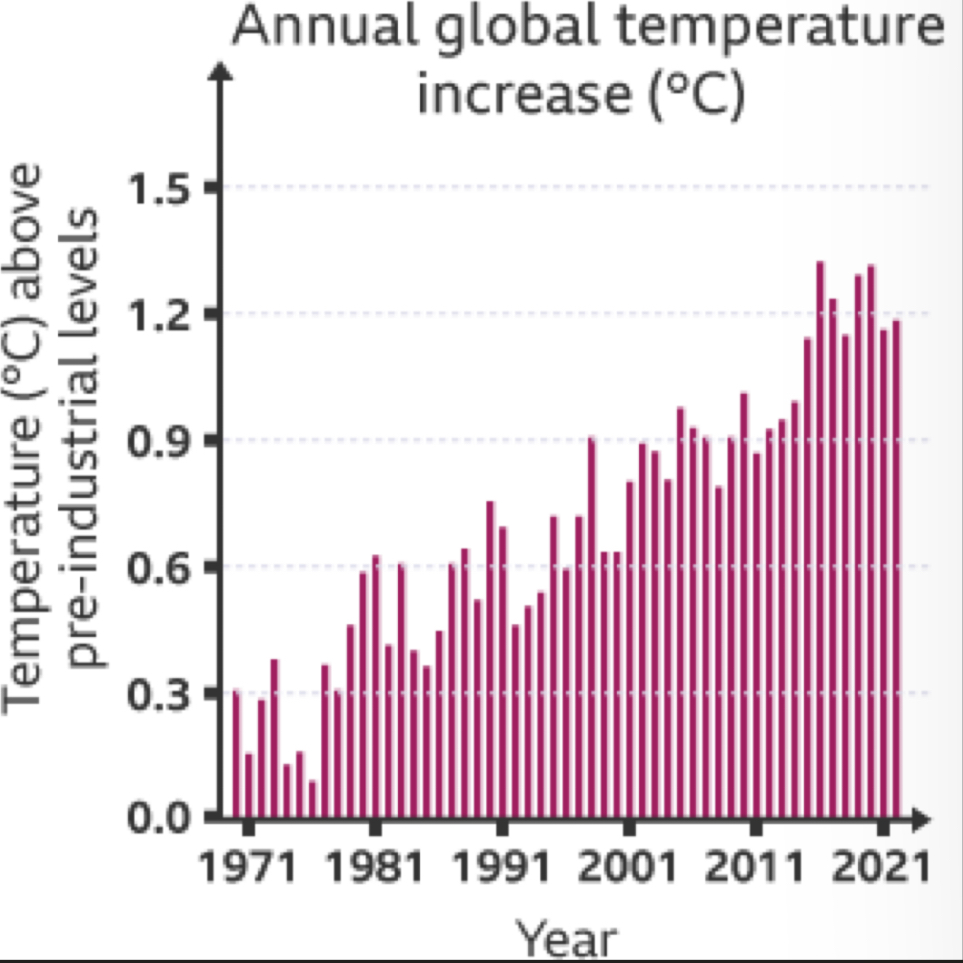
Evidence of climate change (thermometer readings)
The Earth's average surface air temperature has increased by around 1°C since 1900, with the warmest decade being between 2010 and 2020.
What determines the future climate warming on Earth?
The degree to which the climate warms in the future will depend on natural climate variability and the level of greenhouse gas emissions. If emissions continue, average global temperatures will rise, affecting regions differently.
Evidence of climate change (glacial retreat)
Over the past 50 to 100 years, photographic evidence has shown that the world's glaciers have been melting, which has caused them to retreat.
the increase in global temperatures is causing glaciers to disappear and is increasing the melting of sea ice in the Arctic.
Evidence of climate change (ice cores)
scientists use ice cores to detect changes in temperatures
when snow falls it traps air into the ice, so the atmospheric gas concentrations at the time the snow fell can be used to calculate the temperature at that time
ice cores show that there is clear evidence that there has been a rapid increase in temperature in the past decades
Evidence for climate change (early spring)
in recent years there have been signs of a seasonal shift - spring arrives earlier and winters tend to be less severe.
These seasonal changes affect the nesting and migration patterns of wildlife.
Evidence for climate change (rising sea levels)
Between 1900 and 2019, average global sea level rose by 0.21m.
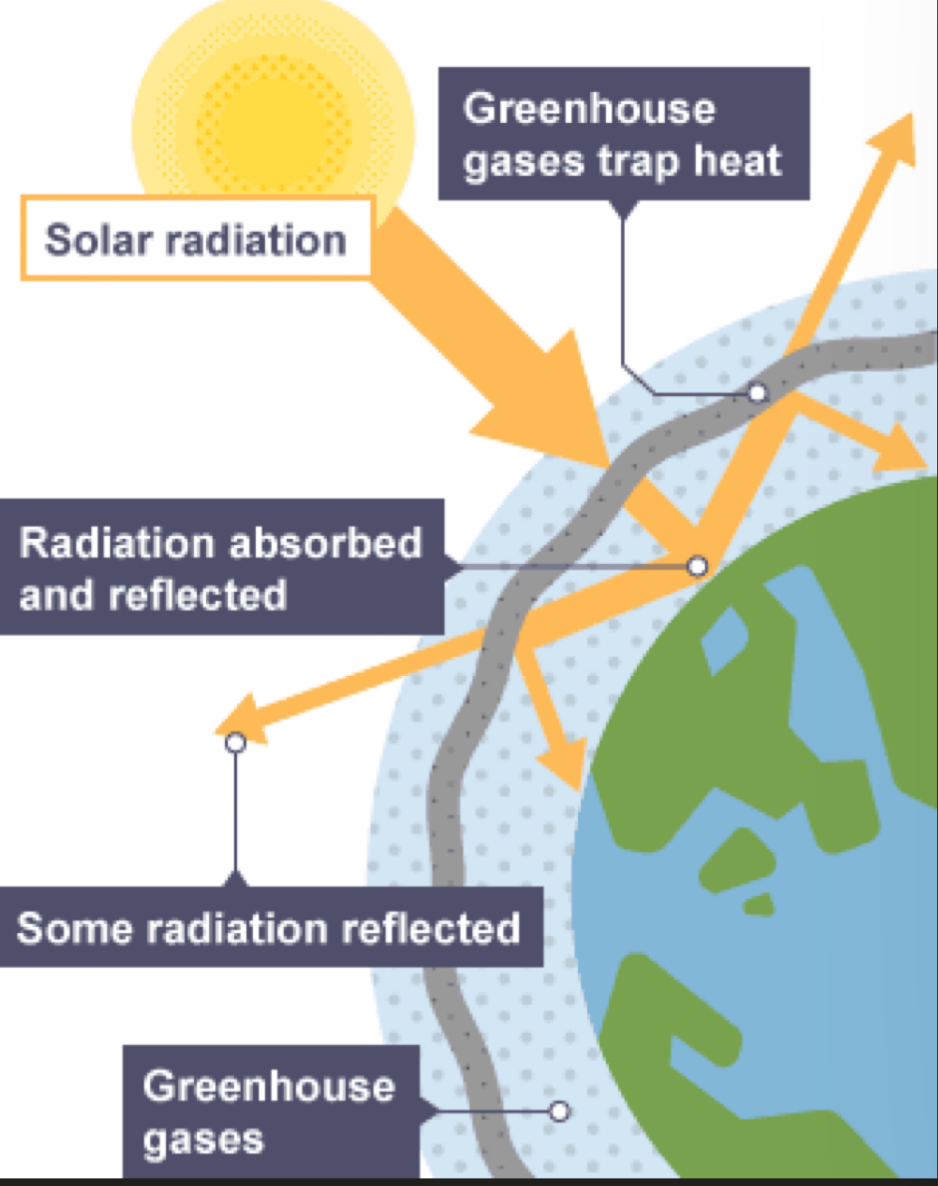
The Greenhouse effect
The atmosphere allows the heat from the Sun (short-wave radiation) to pass through to heat the Earth's surface.
The Earth's surface then gives off heat (long-wave radiation).
This heat is trapped by greenhouse gases (eg methane, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide), which radiate the heat back towards Earth.
This process heats up the Earth
Human factors increasing global warming
Burning fossil fuels, eg coal, gas and oil - these release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation - trees absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. If they are cut down, there will be higher amounts of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Dumping waste in landfill - when the waste decomposes it produces methane.
Agriculture - agricultural practices lead to the release of nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere.
Natural factors increasing global warming
Orbital changes - the Earth has natural warming and cooling periods caused by Milankovitch cycles or variations in the tilt and/or orbit of the Earth around the Sun (known as the Wobble, roll and stretch theory).
Volcanic activity - during a volcanic eruption carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
Solar output - there can be fluctuations in the amount of radiation from the sun. If there is high amount emitted there will be an increase in Earth's temperatures.
Impacts of climate change in the UK
sea levels could rise, covering low lying areas, in particular east England
droughts and floods become more likely as extreme weather increases
increased demand for water in hotter summers puts pressure on water supplies
impact on some industries, eg Scottish ski resorts may have to close due to lack of snow
Impacts of climate change around the world
sea level rise will affect 80 million people
tropical storms will increase in magnitude (strength)
species in affected areas (eg Arctic) may become extinct
diseases such as malaria increase, an additional 280 million people may be affected