Rate of Reaction
1/40
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Rate of Reaction
The rate of a reaction is a measure of how quickly a reactant is used up, or a product is formed.
How can the rate of a chemical reaction be found?
By measuring the quantity of a reactant used or the quantity of product formed over time.
Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without itself being used up in the reaction
How do catalysts work?
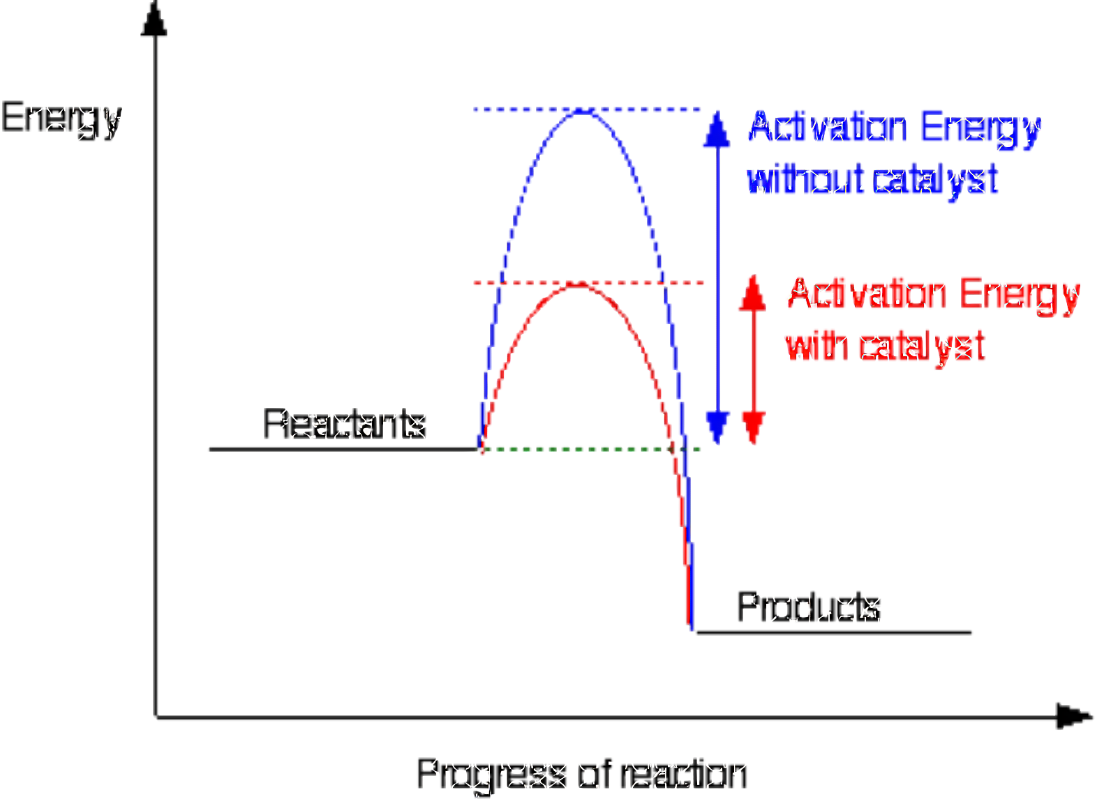
The minimum amount of energy that particles must have to react is called the activation energy
A catalyst provide an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy
Give a type of catalyst
Enzymes - molecules that act as catalysts in biological systems
Collision Theory
Chemical reaction scan only occur when reacting particles collide with each other and with sufficient energy
What is a collision that causes a reaction called?
A successful collision
Activation Energy
The minimum amount of energy that colliding particles must have for them to react.
Equations for mean rate of reaction
mean rate of reaction = quantity of reactant used ÷ time taken
mean rate of reaction = quantity of product formed ÷ time taken
Why is measuring mass useful in a reaction?
This method is useful when eg carbon dioxide is a product which leaves the reaction container. It is not suitable for hydrogen and other gases with a small relative formula mass, Mr.
Units for measuring mass in a reaction
g/s or g/min
Why is measuring volume useful in a reaction?
This method is useful when a gas leaves the reaction container.
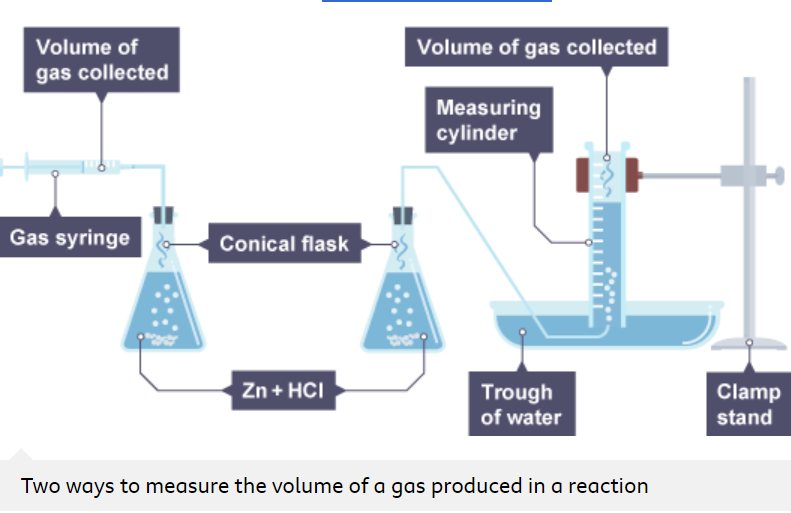
How is the volume of a gas measured in a reaction
The volume of a gas is measured using a gas syringe, or an upside down burette or measuring cylinder
Burette
Long glass tube with a tap and marked with volume measurements, used in titrations.
Units for measuring volume in a reaction
cm3 s-1 or cm3 min-1
What can the rate of a chemical reaction be measured in
g/s, cm³/s, mol/s Mol s-1
How do you use graphs to analyse the rate of reaction?
by plotting a graph of mass or volume of product formed against time
The gradient of the line is equal to the rate of reaction:
the steeper the line, the greater the rate of reaction
fast reactions - seen when the line becomes horizontal - finish sooner than slow reactions
The greater the _____ of ____ ____, the greater the ___ ____.
frequency, successful collisions, rate of reaction
Measuring Rate of Reaction: Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen: Symbol Equation
SE: Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) +H2(g)
Measuring Rate of Reaction: Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen: Apparatus
Delivery Tube
Clamp
Measuring cylinder
trough
water
dilute acid + magnesium ribbon
Conical flask
bung
Measuring Rate of Reaction: Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen: Method
Using a measuring cylinder pour 50cm³ of 1.0mol/dm³ hydrochloric acid into a 100cm³ conical flask
Fit the bung and delivery tube to the top of the flask
Half fill a trough with water
Fill the other measuring cylinder with water and make sure it stays filled when you invert it into the water trough and the delivery tube is positioned correctly
Add a single 3cm length of magnesium ribbon to the flask, put the bung back into the flask and start the stop watch
Record the volume of hydrogen gas collected every ten seconds
Continue timing until the gas does not change
Measuring Rate of Reaction: Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to produce magnesium chloride and hydrogen: Conclusion
Plot a graph with volume of gas, cm on the y-axis and time, s on the x-axis
Draw a line of best fit (curved)
Draw tangents at different point on the graph and create a right-angled triangle to work out the gradient
The steeper the gradient the higher the rate of reaction
How else can you measure the rate of reaction using the volume of gas given off?
By using a conical flask (with the reaction mixture in it), a bung, delivery tube and a gas syringe
Observing the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction: Apparatus
Dilute acid
marble chips
conical flask
bung
delivery tube
water trough
inverted measuring cylinder
clamp
Observing the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction: Method
Set up apparatus using a 100cm³ measuring cylinder
Measure out 25cm³ HCl using a 25cm³ measuring cylinder and pour it into the conical flask
Weigh out 2g of marble chips using a weighing boat and a mass balance
Add the chips to the acid in the conical flask and start the stop watch immediately
Record the volume of water displaced (CO2 is produced) each minute and record in a table
Repeat for different sized marble chips
Observing the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction: Conclusion
Plot a graph with Volume of CO2 collected, cm³ on the y-axis and time, min on the x-axis
Plot two lines - one for small chips and one for large chips
The large marble chips should be lower than the small marble chips because the small marble chips should react faster than larger ones
Observing the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction: Important notes
The steeper the curve, the faster the rate of reaction
The graph levels off because one of the reactants have been used up and so no more gas was produced
Observing the effect of surface area on the rate of reaction: Variables
Independent: The size of the marble chips
Dependent: The volume of gas collected in the given time
Control: Same mass of marble chip used
Same volume of hydrochloric acid used
Same temperature
Same concentration of hydrochloric acid
Investigating the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction: Apparatus
40g/dm³ sodium thiosulfate solution
2.0 M dilute hydrochloric acid
10cm³ measuring cylinder
100cm³ measuring cylinder
100cm³ conical
printed black paper cross
stop clock
Investigating the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction: Method
Use a measuring cylinder to measure out 10cm³ sodium thiosulfate solution into the conical flask
Use the measuring cylinder to add 40cm³ water to dilute the sodium thiosulfate solution to a concentration of 8g/dm³
Put 10cm³ of hydrochloric acid into the 10cm³ measuring cylinder
Put this acid into the flask and swirl gently
Start the stop clock
Look down through the top of the flask and stop the clock when you can no longer see the cross
Record the time taken for the cross to disappear
Repeat steps 1-5 using:
20cm³ sts + 30cm³ water - c16g/dm³
30cm³ sts + 20cm³ water- c24g/dm³
40cm³ sts + 10cm³ water- c32g/dm³
50cm³ sts + no water - c40g/dm³
Investigating the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction: Conclusion
Calculate the mean time for each of the sodium thiosulfate concentrations - leave out anomalous results
Plot a graph with mean time taken for cross to disappear on the y-axis and sodium thiosulfate concentration in g/dm³ on the x-axis
Draw a smooth curved line of best fit
Investigating the effect of changing concentration on the rate of reaction: Equations
Sodium thiosulfate +hydrochloric acid → sodium chloride + sulfur dioxide + sulfur + water
Na2S2O3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → 2NaCl(aq) +SO2(g) + S(s) + H2O(l)
Explain why in the reaction of sodium thiosulfate solution the reaction goes cloudy
Sulfur is produced which is insoluble and this forms a precipitate (an insoluble solid)
in the reaction of sodium thiosulfate which product is a gas
Sulfur dioxide (SO2(g)) is a gas
Why does increasing the concentration increase the rate of reaction?
Increasing the concentration of reactants in the solution results in more reactant particles in a given volume and so this leads to more frequent collisions between reactant particles leading to an increase in rate of reaction
Why does increasing the Pressure of reacting gases increase the rate of reaction?
Increasing the pressure of reacting gases results in more reactant particles in a given volume and this results in more frequent collisions between reactant particles. This leads to an increase in rate of reaction
Why does increasing the temperature increase the rate of reaction?
Increasing the temperature gives the reacting particles more energy and so they move around faster. This results in more frequent collisions between reacting particles.
Increasing the temperature also makes the collisions more energetic. A higher proportion of the reacting particles have energy equal to or greater than the activation energy and so a greater proportion of the collisions will result in a reaction taking place
Why does increasing the surface area increase the rate of reaction?
Increasing the surface area of a solid reactant causes more of the solid particles to be exposed and so there will be more frequent collisions between reactant particles. This increases the rate of reaction
Investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction: Method
Choose a temperature to investigate and use an ice bath or water bath to get the two solutions to that temperature
Use a thermometer to check the temperature of the solutions
Measure 5cm³ of hydrochloric acid and add 50cm³ of sodium thiosulfate solution in a sperate clean measuring cylinder
Place the flask on the centre of the large cross
Add sodium thiosulfate and then hydrochloric acid
start the stopwatch and swirl to mix to solutions
stop the clock when the cross disappears and note the time
repeat the experiment for four more different temperatures
Investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction: Conclusion
Plot a graph with temperature on the x-axis and time taken for the cross to disappear on y-axis
Plot a line of best fit (curved)
As the temperature increases the rate of reaction rapidly increases as the time taken for the cross to disappear decreases
Investigating the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction: Variables
Independent: temperature
Dependent: time taken for the cross to disappear
Control: same volume and concentration of sodium thiosulfate solution
Same volume and concentration of hydrochloric acid