15.4 excretion, homeostasis and the liver
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
main metabolic waste products in mammals
carbon dioxide - one of the waste products of cellular respiration which is excreted from the lungs
bile pigments - formed from the breakdown on haemoglobin from old red blood cells in the liver. They are excreted in the bile from the liver into the small intestine via the gall bladder and the bile duct
nitrogenous waste products (urea) - formed from the breakdown of excess amino acids by the liver. All mammals produce urea as their nitrogenous waste. Fish produce ammonia while birds and insects produce uric acid
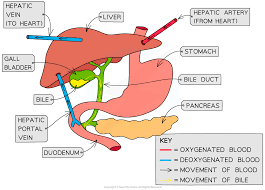
what vessel supplies blood to the liver
hepatic portal vein (blood loaded with products of digestion)
hepatic artery (oxygenated blood)
parts of liver cells (hepatocytes)
large nuclei
prominent golgi apparatus
lots of mitochondria
sinusoids
the spaces where blood from the hepatic artery and hepatic portal vein are mixed
Kupffer cells
act as macrophages in the liver cells - help to protect against disease
secretion of bile
the hepatocytes secrete bile from the breakdown of the blood into spaces called canaliculi
from these, blood drains into the bile bile ductules which take it to the gall bladder
carbohydrate metabolism
when blood glucose levels rise, insulin levels rise and stimulate hepatocytes to convert glucose to the storage carbohydrate glycogen
when blood sugar levels fall, the hepatocytes convert the glycogen back to glucose under the influence of the hormone glucagon
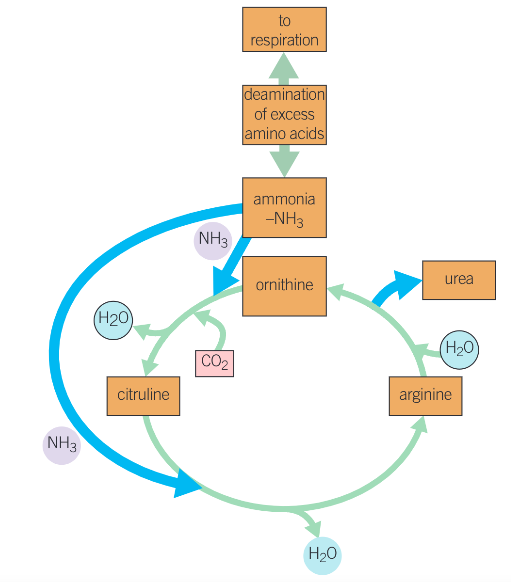
deaminaton of excess amino acids
the removal of an amine group group from a molecule
the body cannot store proteins/ amino acids
the amino group of an amino acid is removed and converted into ammonia
the remainder of the amino acid can then be fed into cellular respiration or converted into lipids for storage
transamination
the conversion of one amino acid into another
the ornithine cycle
detoxification in the liver
eg, breakdown of hydrogen peroxide using the enzyme catalyse
the liver detoxifies ethanol using the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase to break the ethanol into ethanal. Ethanal is converted to ethanoate which may be used to build up fatty acids or in cellular respiration
diagram of the structure of the liver