Environmental factors (L14)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
main causes of congenital abnormalities (environmental)
maternal/placental infections (e.g. rubella virus)
maternal nutrition and disease (folic acid deficiency, diabetes)
chemicals and drugs (alcohol, retinoic acid)
transcervical (ascending) infections - what
can pass up the cervix into the uterus
mostly acquired from the cervicovaginal route
how fetus gets infected in transcervical infections
inhaling infected amniotic fluid into the lungs shortly before birth or
from the infected birth canal during delivery
what is a common result of infection and how is it caused
preterm birth
damage/rupture of amniotic sac due to inflammation
or infuction of labour by prostaglandins released from infiltrating neutrophils
premature birth as result of infection can cause
neonatal respiratory distress syndrome and other complications
what can inhalation of amniotic fluid cause
pneumonia, sepsis or meningitis
transplacenta infections - what type of pathogen
mostly viral and parasitic
few bacterial
how do transplacental infections cross the placenta
access the fetal bloodstream via the chorionic villi
occasional during delivery by maternal to fetal transfusion - placenta haemmorrhage (e.g. hepatitis B and HIV)
when do transplacenta infections occur
can occur at any time during gestation
occassionally during deliivery
consequences of transplacental infections
can interfere with early development or destroy structures that have already been formed
viruses crossing the placenta
can pass into trophoblast cells which surround the villi
can also get into the hofbauer cells (type of macrophages in the placenta) and replicate inside these, then released and cross into the fetal capillaries
rubella virus
RNA virus, mild disease in children and adults, most serious impact is its teratogenic efect
congential rubella syndrome = neonatal menifestation of infections
when rubella infection
in first trimester - infection rate of fetus is around 85%
after 16 weeks infection rate drops to around 50%
by third trimester fetal ifnections are low and resulting abnormalities are rare
infection at birth does not appear to cause CRS
consequences of maternal rubella infection
abortion, still birth, foetal growth restriction and CRS
congenital malformations in CRS
occular defects - cataract, glaucoma, retinopathy, iris hypoplasia etc
auditory defects - sensorineural deafness
cardiovascular defects - persistent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosi, ventricular septal defect, myocarditis
CNS defects - microcephaly, psychomotor retardation, meningoencephalitis
occuluar defects from CRS
cataract, glaucoma, retinopathy, microphthalmia, iris hypoplasia, cloudy cornea
auditory defects from CRS
sensorineural deafness
cardiovascular defects from CRS
persistent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis, ventricular septal defect, myocarditis
CNS defects
microcephaly, psychomotor retardation, meningoencephalitis
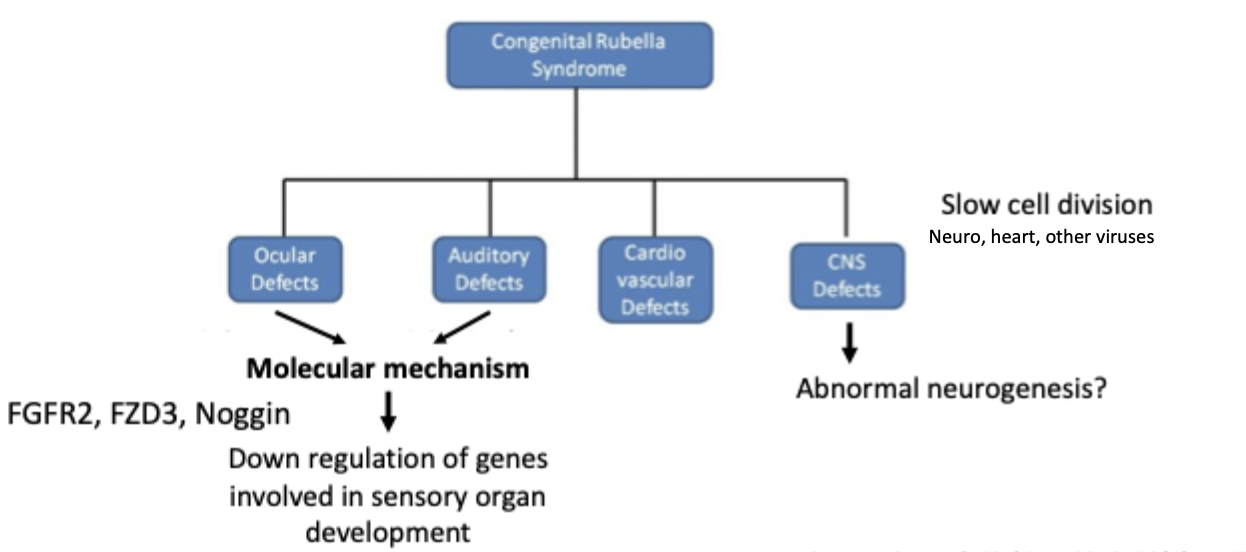
molecular mechanisms of CRS
rubella virus infection during critical stages of organ development can result in CRS
RV causes apoptosus in adult cells, vs in feotal fibroblasts no apoptosis so infection persists
downregulation of genes in fetal cells involved in sensory organ development (FGFR2, FZD3, Noggin, MYO7A)
these genes are required for ear and eye development - hence ocular and auditory impairment
disrupts actin filament assembly and can slow cell division in fetal cells
molecular mechanisms od CRS diagram
prevention of rubella
immunisation
universal screening and vaccinaion pre-pregnancy
MMR vaccine for kids at 12 and 15 months
incidence has drastically decreased since vaccine, no reported cases of congenital rubella in NZ since 1998, but still high in developing countries - no vaccine
pregnancy and covid
pregnant women at higher risk of ICU and ventilation
higher rate of preterm birth and c section - electively to improve respiratory condition
chances of vertical transmission is low
no reported teratogenicity so far, but prelimanry evidence that maternal covid may be associated with neurodevelopmental sequalae in some offspring (from dif paper)
covid vaccines safe while pregnant
neural tube
formed from neural ectoderm by week 4
neural tube becomes spinal cord, spine, brain and skull
neural tube - what days do pores close on
anterior pore closes on day 25 - posterior on dat 28
neural tube defects - what
failure of neural tube pores to fuse
connection between amniotic fluid cavity and spinal canal
anencephaly and spina bifida
what causes neural tube defects
genetic mutation or exposure to environmental factors
maternal infection, irradiation, maternal diabetes, low folic acid
anencephaly
underdeveloped brain and incomplete skull
anterior pore doesnt close
spina bifida
spinal cord fails to develop and close normally
range of symptoms depending on the defect - occulta, meningocele, myelomeningocele
mild or no symptoms to paralysis or bowl ddysfunction
can treat with pre or post natal surgery
may still be disabled due to nerve damage
when susceptible to neural tube defects
first month of gestation because this is when the neural tube is forming and closing
spina bifida occulta
gap in vertebrae but spinal cord is normal - this could be completely invisible or have a dimple or patch of hair
meningocele
just have a fluid filled sac which will likely have no effect and can easily be surgically corrected
myelomeningocele
spinal cord protrudes and becomes damaged which can cause paralyss which may even be too severe to correct surgically
how does folic acid deficiency cause NTD
folic acid is a B vitamin needed for synthesis of nucleotides (DNA synthesis, repair, methylation
essential for mitosis in rapidly proliferating cells e.g. neuroectoderm cells - deficiency during gestation can result in neural tube defects
higher incidence in spring pregnancies
folic acid supplementation significantly reduces neural tube defect incidence
conclusions of report about folic acid
fortification of foods with folic acid reduces the prevelance of NTDs
no known adverse effects
the beneficial effects arent limited to pregnant women
in NZ flour now has to be fortified with folic acid
this is during first trimester, now doing research to see if it is also beneficial at second and third trimester
glucose in healthy people
increase glucose = increase from pancreas
so increase in uptake of glucose by cells for energy OR if hyperglycemia increase storage of glucose in liver, muscle and fat cells
glucose levels are controlled
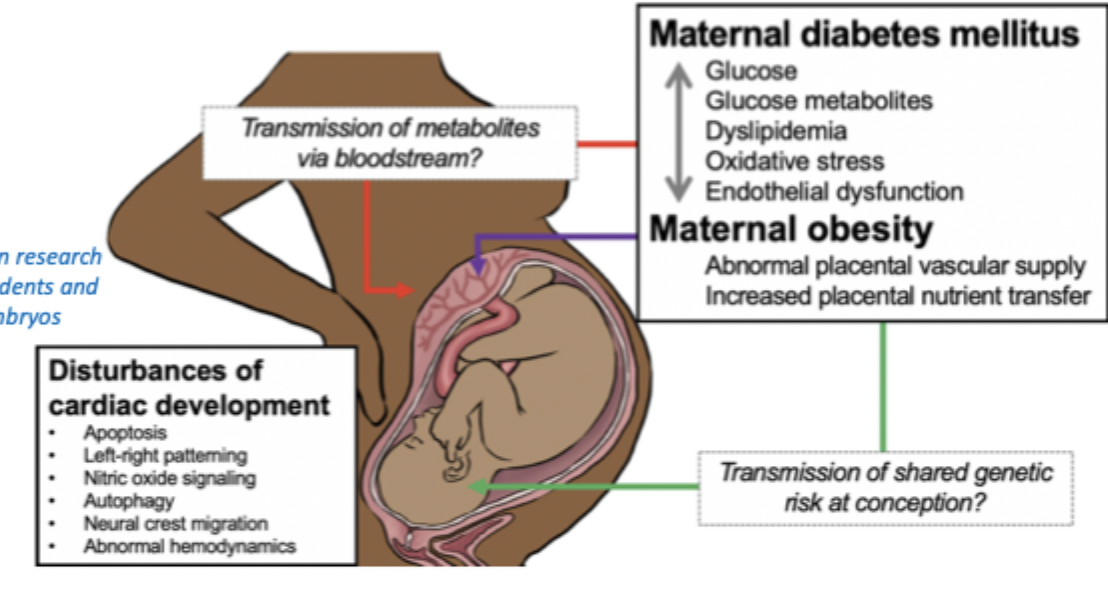
maternal diabetes - what happens
even in normal pregnancy metabolic changes are induced including increased insulin resistance
pre-existing diabetes prevents increasing insulin secretion causing hyperglycemia
high blood glucose causes increased insulin in fetus = fetal hyperinsulinaemia
what can pre-existing diabetes cause in fetus
duration and degree of hyperglycemia and time of onset effect outcome (early is more severe for fetus)
exposure to abnormal mixture of metabolites alters phenotype of cells in developing fetus
can cause: stillbirth, heart defetcs, kidney defects, diabetes, obesity, hypertension, higher risk of attention-dficit hyperactivity disorders and autism
overal maternal diabetes
gestational diabetes mellitus - when
second or third trimester
organs already formed - no major developmental defects
consequences of gestational diabetes
fetal macrosomia
birthing complications
50% of mothers with GDM develop type II diabetes
foetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) - what disorders
group of disorders caused by prenatal exposure to alcohol include:
foetal alcohol syndrome
alcohol related neurodevelopmental disorder
alcohol related birth defect
foetal alcohol syndrome
most severe effects
minor facial anomolies, growth deficiency, brain abnormality, cognitive or behavioural impairment
alcohol related neurodevelopmental disorder (ARND)
cognitive or behavioral development
alcohol-related birth defects (ARBD)
other systemic malformation
FASD when
exposure during first trimester more severe - causes more anatomical defects
later exposure can cause more subtle neurological defects as brain development continues throughout gestation
FASD rates
~3% of births but this varies per country
probably more in NZ as we have higher rates of alcohol drinking and reporting is not very reliable
plus defects may occur early before the person knows they are pregnant
FASD clinical features - physical
discriminating craniofacial anomalies:
microcephaly
short palpebral fissures
smooth philtrum
thin upper lip
associated features:
epicanthal folds
minor ear anomolies
low nasal bridge
micrognathia
FASD - other physical features
minor physical anomalies: railroad track ears, altered pa,mar creases, clinodactyly
number of minor features correlates with magnitude and timing of alcohol exposure
sensory and cognitive processing impariment
eye development impairments - microphthalmia (small eye), reduced palpebral fissure length, coloboma, retinal dysplasia
shorter than average height - greoth retardation
FASD clinical features - neurological
hearing, speech and language disorders
developmental delay
cognitive deficits
fine motor deficits
hypoplasia of brain structures e.g. corpus callosum, cerebellum, brainstem
behavioural and emotionl disturbances (e.g. hyperactivity, poor impule control, aggression, poor social skills)
compromises schoola dn work performance and can lead to criminal behaviour
FASD in NZ
leading preventable cause of non-genetic intellectual disability
FASD mechanisms
outcomes depend on amount, frequency, duration and gestational timing of alcohol consumption
ethyl alcohol metabolised by alcohol dehydrogenase enzyme and CYP2E1 which the fetus has low amounts of
EtOH and acetaldehyde are toxic to cells - affect the survival and migration of cranial neural crest cells that form craniofacial structures
EtOH inhibits retinol metabolism to retinoic acid - retinoic acid signalling important for early embryogenesis and patterning of structures
steps of FASD mechanisms
ethanol metabolism generates reactive oxygen species (ROS)
ethanol metabolism competes for same enzymes as retinol - reduces retinoic acid
retinoic acid essential for development of many early embryonic structures
acytl-CoA modifies gene expression
depleted neural stem cells incluse neural crest cells (craniofacial abnormalities)
disrupted neuronal migration (altered brain development)
retinoic acid as a teratogen
when given orally (for acne)
defects related to cranial neural crest cells - e.g. facial structures, outflow tract of the heart, thymus
so when taking this medication have to be careful to not get pregnant