Adolescent Psychology Final Study Guide
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
123 Terms
What is the most common form of birth control used by adolescents?
Condoms
What are the primary functions of masturbation for adolescents?
Masturbation helps individuals learn about their bodies, respond sexually, develop sexual identity, and achieve sexual release.
What percentage of sexually active American teenage girls get pregnant each year?
About 20%.
What has been the trend in adolescent pregnancy rates in the U.S. since the 1970s and 1980s?
Rates have declined by 15%.
What are some difficulties faced by gay and lesbian adolescents?
They face heightened risks of harassment, victimization, rejection from family and religious groups, mental health problems, and feelings of isolation.
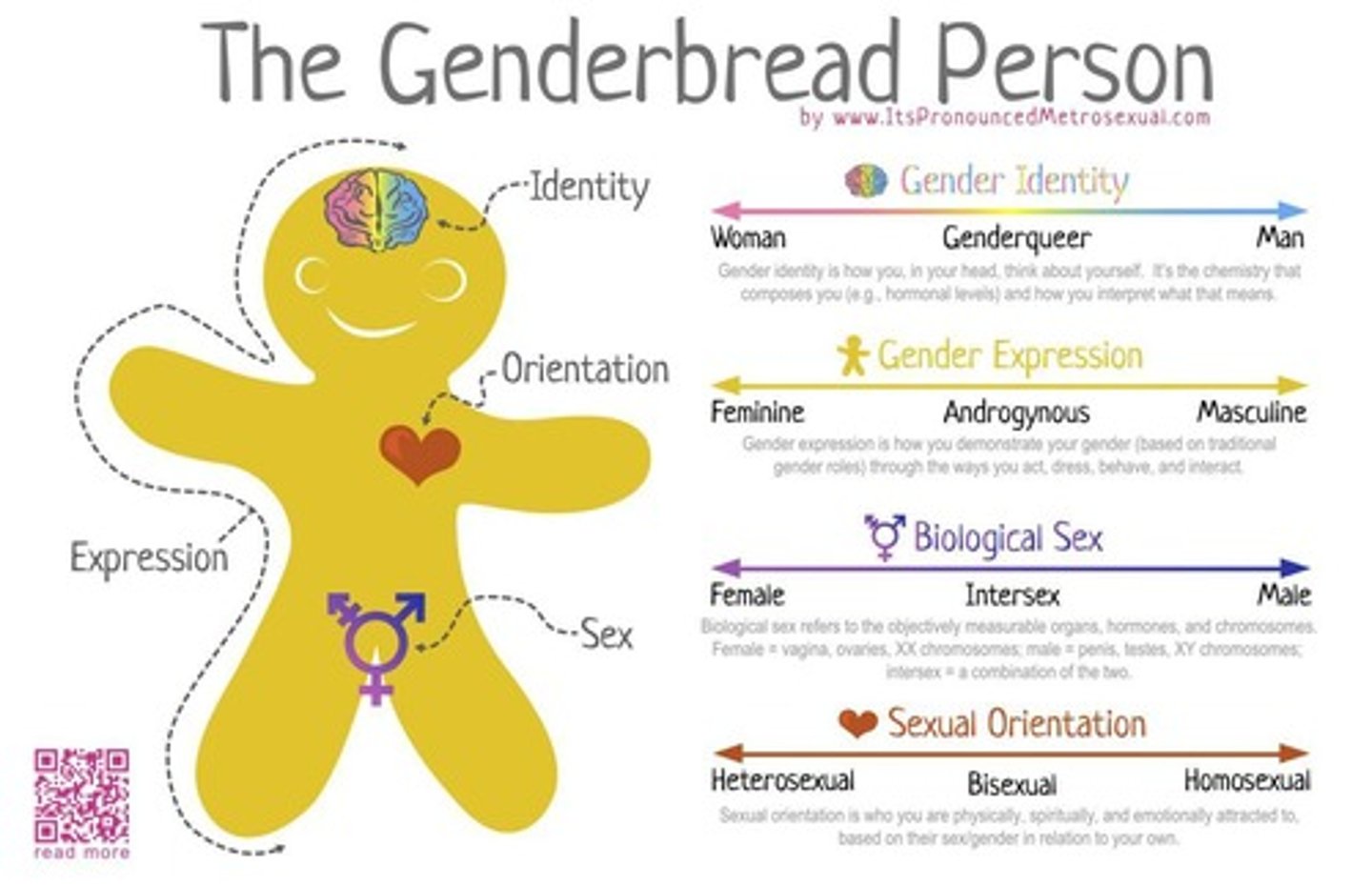
What does comprehensive sex education include?
It includes information on contraception, STDs, and sexual behavior, alongside abstinence as one option.
What has research shown about the effectiveness of abstinence-only programs?
Research finds that abstinence-only programs are not as effective in addressing sexual behavior and preventing teen pregnancy and STDs.
What is the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) scale used for?
It measures childhood trauma based on 10 questions, with higher scores indicating increased risk for various negative outcomes.
What are the two main educational philosophies discussed in the notes?
Traditionalists focus on teaching basics, while progressives emphasize preparing students for life.
What are magnet schools?
Theme schools that serve students within public school systems, focusing on specific areas like performing arts or science.
What is the purpose of charter schools?
Charter schools are public schools funded and run by private entities, accountable to the government but with fewer regulations.
What is the function of vouchers in education?
Vouchers subsidize the cost of private school education and special services for disabled students.
What do tech-prep schools provide?
Technical training and workplace experience, partnering with community colleges for career preparation.
What is open enrollment in the context of education?
A policy allowing students to choose from a large number of public schools, sometimes outside their own district.
What are some reasons for the middle school slump?
Middle schools are larger, more impersonal, and students spend less time with one teacher and close friends.
What was the impact of Sputnik on U.S. education?
It led to an obsession with improving schools to keep pace with technological advances.
What is the significance of the recent Supreme Court ruling mentioned in the notes?
It has led some states to ban abortion, potentially impacting the availability of birth control.
What is the trend in the rate of birth control use among adolescents?
The rate of use has been increasing but is still more sporadic than among adults.
What are the mental health risks associated with high ACE scores?
Higher ACE scores are linked to increased risks of depression, suicide attempts, and substance abuse.
What is the primary argument against comprehensive sex education?
Opponents argue that it may lead to increased sexual behavior among students.
What is the relationship between race/ethnicity and birth control use?
Birth control use is influenced by factors such as race/ethnicity, age, and sexual orientation.
What percentage of adolescent pregnancies are unplanned?
80% of adolescent pregnancies are unplanned.
What are the broader educational goals of progressive education?
To prepare students for citizenship, home living, vocational skills, and personal growth.
What significant legislation did Congress pass to support education in math, science, and foreign languages?
The National Defense Education Act, which provided nearly 1 billion in federal aid.
What are the three dimensions of alienation that students may experience?
1. Powerlessness: feeling disengaged; 2. Meaninglessness: unclear connection between school subjects and future; 3. Normlessness: lack of uniform goals and standards.
What family-related factors can contribute to student dropout rates?
Caring for a family member, including a spouse or child, and teenage pregnancy.
What indicators did Dr. Robert Balfanz identify that predict high school dropout rates in high-poverty schools?
1. Attendance below 80%; 2. Unsatisfactory behavior grade in a core course; 3. Failing math or English.
What is the likelihood of a student dropping out of high school if they meet the indicators identified by Dr. Balfanz?
There is a 75 percent chance of dropping out without effective intervention.
What are the five factors of low socioeconomic status (SES) that influence dropping out of school?
1. Lack of positive parental influences; 2. Teacher prejudice against low SES students; 3. Fewer rewards for low SES students; 4. Lower reading and writing skills; 5. Anti-school peer influences.
How do teachers' backgrounds affect their treatment of low SES students?
Teachers, often from middle-class backgrounds, may show preferential treatment to higher status students and struggle to understand low SES students' goals and behaviors.
What impact does the lack of rewards have on low SES students compared to higher status students?
Low SES students receive fewer academic grades, social acceptance, and opportunities for participation in school activities.
Why do low SES students often struggle academically compared to their middle-class peers?
They frequently lack the necessary reading and writing skills, which hinders their performance across subjects.
What recent trend has been observed regarding educational curriculum in some states?
A movement to ban certain books and remove specific information from lesson plans, particularly related to gender identity, sexual orientation, and diversity.
What is Ginsberg's Compromise with Reality theory regarding vocational choice?
Vocational choice is a developmental process occurring over time, not a single moment.
What are the three stages of Ginsberg's vocational choice theory?
1. Fantasy Stage (up to age 11); 2. Tentative Stage (ages 11-17); 3. Realistic Stage (age 17 and onward).
What characterizes the Fantasy Stage of Ginsberg's vocational choice theory?
Children imagine their future jobs without regard to realistic considerations.
What are the four sub-stages of the Tentative Stage in Ginsberg's theory?
1. Interest period (ages 11-12); 2. Capacities period (ages 13-14); 3. Values period (ages 15-16); 4. Transition period (ages 17+).
What occurs during the Interest period of the Tentative Stage?
Choices are primarily based on personal likes and interests.
What awareness develops during the Capacities period of the Tentative Stage?
Students become aware of job requirements, occupational rewards, and necessary preparation levels.
What synthesis occurs during the Values period of the Tentative Stage?
Students synthesize job requirements with their own values and capacities.
What is the focus of the Transition period in Ginsberg's Tentative Stage?
Making realistic choices influenced by school, peers, parents, and graduation circumstances.
What is the exploration phase in the Realistic Stage of Ginsberg's theory?
An intensive search for greater knowledge and understanding regarding vocational choices.
What is crystallization in career development?
Crystallization is the process where individuals, typically between ages 19 and 21, narrowly define a single set of choices and commit to a general area of employment.
What is specification in career development?
Specification is the process where a general career choice is further limited to a particular choice.
What are the two main processes in Gottfredson's Theory of early career development?
Circumscription and compromise.
What does circumscription involve in career development?
Circumscription involves realizing that some careers require abilities that individuals do not possess or require efforts they are unwilling to expend, leading them to reject certain careers.
What is compromise in the context of career choices?
Compromise refers to modifying career choices to align them with reality, often involving anticipatory compromises made by adolescents.
What are the five traits related to Krumboltz's Happenstance Theory?
Optimism, curiosity, flexibility, persistence, and risk-taking.
What are the three barriers to women's vocational choice?
Structural barriers (gender discrimination), normative barriers (socialization to be feminine), and cognitive differences (psychological differences not supported by research).
Who are the main influences on vocational choice?
Parents, peers/friends, and school personnel.
What are some determinants of vocational choice?
Aptitudes and special abilities, interests, job opportunities and salary, and socioeconomic factors.
What is Holland's Theory of Career Selection?
Holland's Theory posits that people select occupations that match their personality types, leading to greater job satisfaction and stability.
What are the six personality types in Holland's Theory?
Artistic, conventional, enterprising, investigative, realistic, and social.
What characterizes the artistic personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Creative, views self as expressive and independent, with potential careers like composer, designer, or art teacher.
What characterizes the conventional personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Likes structure and order, views self as systematic and organized, with potential careers like bookkeeper or bank teller.
What characterizes the enterprising personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Likes to lead, views self as ambitious and outgoing, with potential careers like lawyer or city manager.
What characterizes the investigative personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Likes math and science, views self as intellectual and exacting, with potential careers like biologist or architect.
What characterizes the realistic personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Likes working with machines or animals, views self as practical, with potential careers like carpenter or police officer.
What characterizes the social personality type according to Holland's Theory?
Likes working with people and helping, with potential careers like counselor or teacher.
What are some feelings associated with adolescent alienation?
Powerlessness, meaninglessness, self-estrangement, cultural estrangement, normlessness, and social isolation.
What are common causes for adolescents running away?
Family dysfunction, family discord, association with deviant peers, poverty, and school failure.
What are some specific reasons youths might run away?
Desertion by parents, being thrown out, issues related to homosexuality, sexual abuse, substance abuse problems, and long-standing health problems.
How can anger or unhappiness manifest in adolescents?
Through acting-out behaviors such as truancy, aggression, promiscuity, theft, or self-harm.
What is the impact of alienation on adolescents?
Distressed youths feel alienated from family and school, leading to dysfunction in mainstream society.
What are the two primary classes of runaways?
Intent runaways, who mean to flee, and transient runaways, who leave spontaneously and do not intend to stay away long.
What percentage of transient runaways return home within two days?
About half of all transient runaways.
What are throwaways in the context of adolescent runaways?
Adolescents who have been pushed out of their homes by their parents, either through encouragement to leave or being thrown out.
How do girls and boys differ in their views of parental control in the context of running away?
Girls generally view their parents as controlling and punitive, while boys report minimal family control, leading to outside influences.
What is the third leading cause of death among adolescents?
Suicide.
How does the suicide rate among adolescent girls compare to boys?
Girls are about twice as likely to attempt suicide, but 85 percent of successful suicides are committed by boys.
What trend was observed in the suicide rate for adolescent females aged 10-14 from 1999 to 2014?
The rate tripled during that period.
What factors contribute to the higher success rate of suicide among males?
Males often use more violent means.
What are status crimes?
Violations of laws that apply only to minors, such as underage drinking, violating curfews, and truancy.
What was the significance of the Gault case in juvenile justice?
It established that minors are entitled to due process rights under the Bill of Rights and the 14th amendment.
What are some environmental causes of juvenile delinquency?
Poverty, high-crime neighborhoods, gang presence, substandard schools, drug availability, and exposure to media violence.
What interpersonal factors can contribute to juvenile delinquency?
Poor relationships with parents, relatives involved in criminal activity, and social learning from peers.
What personal causes can lead to delinquent behavior?
Defiant personality traits, lack of self-control, conduct disorders, substance abuse, and poor school performance.
What is the trend regarding gang membership in the U.S.?
Membership is broadening, with members more likely to engage in antisocial activities.
What are some risks associated with gang membership?
Increased likelihood of stealing, committing assaults, carrying weapons, early pregnancy, drug use, and being involved in violence.
How does depression manifest differently in adolescents compared to adults?
During childhood, boys and girls are equally likely to be depressed, but by adulthood, women are twice as likely to be depressed.
What life events can contribute to depression in adolescents?
Poor academic performance, divorce, ending of romantic relationships, and sexual orientation issues.
What is the typical onset age for schizophrenia?
Late adolescence to early adulthood.
How is schizophrenia typically treated?
It can be managed with medication but is not curable.
What symptoms may be associated with schizophrenia?
Hallucinations, delusions, and thought or movement disorders.
What is the relationship between adolescent depression and gender?
The gender difference in depression emerges during adolescence, with factors such as puberty and genetic predispositions influencing this.
What is the role of school-based support in addressing adolescent issues?
Screenings and programs can be helpful in identifying and supporting adolescents facing mental health challenges.
What are the characteristics of flat affect in mental health?
Reduced pleasure in everyday life, difficulty beginning and sustaining activities, and poor executive functioning.
What brain structure changes are observed in individuals with certain mental illnesses?
MRI scans show somewhat larger ventricles in the brain, but no other major differences.
What barriers do individuals with mental illness face when seeking treatment?
Stigma often prevents individuals from disclosing their condition or seeking help.
What is Restorative Justice in the context of juvenile justice?
An approach that addresses the needs of the victim, community, and perpetrator, focusing on restitution for the victim and personal development for the offender.
What needs does Restorative Justice aim to balance?
The victim's need for reparation and confrontation, the community's need for security, and the juvenile's need for skills and alternatives.
What is self-injurious behavior?
Self-injury or self-mutilation that is not a suicide attempt but may increase future risk.
What are some examples of self-injurious behavior?
Cutting, biting, burning, picking wounds, and purposely falling down stairs.
What are the purposes of self-injurious behavior?
To relieve negative feelings, resolve problems, induce a positive mood, and not to cause death.
What are the patterns of drug use?
Experimental, social-recreational, circumstantial-situational, intensified, and compulsive.
What defines physical addiction?
A condition that develops from drug abuse forming a chemical dependency, leading to withdrawal issues requiring medical supervision.
How is drug abuse defined?
Abuse occurs when there is an increased risk for harm or when drug use interferes with daily life.
What are the most commonly used substances among adolescents?
Alcohol, marijuana, and tobacco.
How has drug use among college students compared to high school students?
College students are more likely to drink alcohol, but rates of illegal drug use are about the same as high school students.
What factors increase the risk of substance abuse in adolescents?
History of sexual abuse, ADHD, and undiagnosed mental illness.