HD 3700 Prelim 2- Somatic Symptoms Disorders
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Somatic Disorders
characterized by prominent bodily (somatic) symptoms and/or anxiety around illness
Somatic symptom disorders
one or more somatic symptoms that are distressing or result in significant disruption of daily life
somatic symptoms may or may not have a clear cause
can include, pain, swelling, coughing, fatigue, palpitations, dizziness, GI symptoms
somatic symptoms disorders
excessive thoughts, feelings, or behaviors related to the somatic symptoms are associated health concerns as manifested by at least one of the following
disproportionate and persistent thoughts about the seriousness of one’s symptoms
persistently high level of anxiety about health or symptoms
excessive time and energy devoted to these symptoms or health concerns
although 1 symptom may be not be cont present, the state of being symptomatic is persistent
specially if pain is predominant and if symptoms are mild, moderate, or severe
SSD prevalence
relatively common: 5-7% of population
more common in women
more common in people who have tendency to experience bodily sensations intensely and to pay attention to bodily cues
Illness Anxiety Disorder
preoccupation with having or acquiring serious physical illness
somatic symptoms are not present; or if present are only mild
if another medical condition is present, or there is a high risk for developing a medical condition, the preoccupation is clearly excessive or disproportionate
high level of anxiety about health
performs excessive health-related behaviors
present for at least 6 months
illness- related preoccupation not better explained by another mental disorder
disease conviction
strong persistent belief in having a serious physical illness, despite lack of medical evidence and info/ reassurance from health care professionals
often present in illness anxiety disorder
Predictors of SSD and illness anxiety disorder
related to cognition and perception of physical signs
enhanced sensitivity to cues of illness
current stress
belief that severe illnesses are common
disproportionate early life experiences of disease in family members
covid increased these disorders
how this can maybe occur (flow chart)
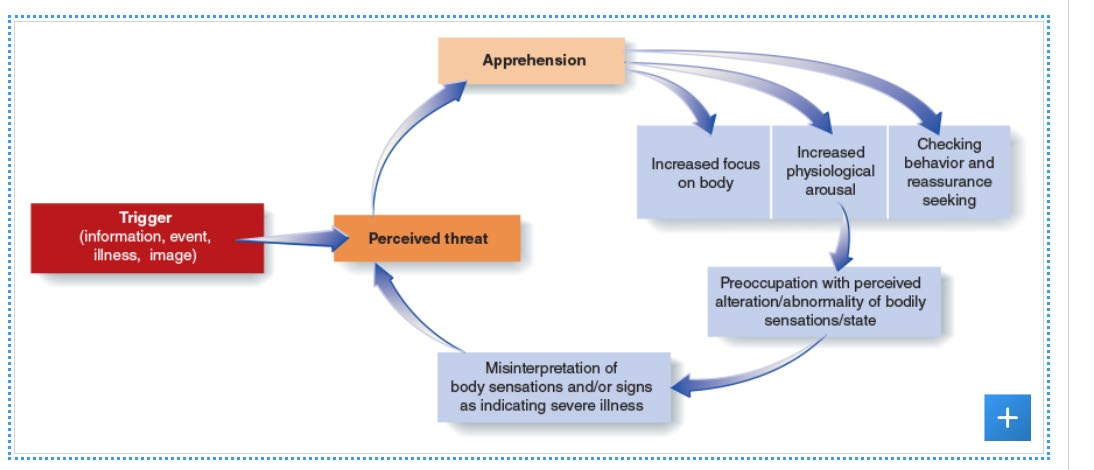
treatment for ILD and SSD
CBT frist
yield strong effects with relatively brief course
modifying thoughts around symptoms or illness
adding behaviors to boost quality of life and relationships
help people interpret physical symptoms without assuming they are dangerous
functional neurological symptom disorder (conversion disorder)
>1 symptoms of altered voluntary motor or sensory function
clinical findings provide evidence of incompatibility between the symptom and recognized neurological or medical conditions
glove anesthesia
neurology, functional: refers to a symptom without an organic cause
people lose all feeling and become numb in one hand
physical damage to ulnar nerve causes numbness (pinky - ½ ring)
physical damage to radial never causes numbness ½ ring -thumb
specify if with
with weakness/ paralysis
with abnormal movement
with swallowing symptoms
with attacks / seizures
with anesthesia / sensory loss
with special sensory symptoms
with mixed symptoms
primary gain
anxiety around an unconscious conflict is reduced by “converting” psychological symptoms to physical ones
secondary gain
symptoms may be prolonged or exacerbated if they result in some kind of benefit, sympathy, attention
prevalence
episodes of unresponsiveness / seizures are the most common functional symptom globally
more common in women
16-20% of new neurology patients
What are some primary environmental risk factors?
achievement- related pressure
trauma and stress
high rates of functional blindness among Cambodian refugees who witnessed war trauma
infections and inflammation
prognosis
long term prognosis of FND is similar to that for multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s
significant decrements in quality of life due to symptoms
course can be waxing and waning
FND over time
prevalence has shifted over history
common in turn of the century europe, particularly in women
increased during WW1&2
Mass Psychogenic Illness
outbreaks of functional neurological disorder within a group of people who share daily activities
spread of symptoms is often very rapid
ex) dancing manias
spread of mass psychogenic illness is exacerbated by…
rumors and misinformation about causes
community pressure to solve problem
lack of attention to psychological explanations
anxiety related to presumed causes (vaccines, chemical exposure)
negative perception of government and health authorities
psychological stressors
media and social media coverage
physical proximity or close-knit group
Factitious Disorder
falsification or physical / psychological signs or symptoms or induction of injury or disease, associated with identified deception
criteria:
individual presents themselves to others as ill, impaired or injured
deceptive behavior is evident even in absence of obvious external rewards
behavior is not better explained by another mental disorder like delusional or psychotic
can occur for oneselfs or be imposed on another by proxy
early life maltreatment, particularly physical and emotional maltreatment
60% experience severe childhood illness
higher prevalence among health care professionals
patients describe uncontrollable urge to maintain behaviors
Falsification of symptoms can be extreme
creating lesions, swelling
ingesting substances to create abnormalities in blood
contamination of medical samples with blood or stool
Munchhausen’s Syndrome
nickname of factitious disorder
Malingering
intentionally presenting false symptoms for personal gain
usually but not always financially motivated
not considered psychological disorder
factitious disorder differs from malingering because the symptoms are not linked to personal gain
treatment for factitious disorder
disorder by proxy is often by legal issue
no standard treatment
frequently DONT consent to treatment
prognosis considered poor
some improvement with CBT and supportive treatments
some improvement documented when comorbid conditions are treated