Psych Semester 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/174
Earn XP
Last updated 4:45 PM on 1/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
1
New cards
Key Ideas of Psychology
Organisms, Motivations, Behaviors, Cognition, Competence
2
New cards
Stability vs. Change
Are people born with the ability to change who they are or will that stay the same their entire lives.
3
New cards
Rationality vs. Irrationality
Are we bound for success or failure?
Are we inherently good or bad?
Are we inherently good or bad?
4
New cards
Nature vs. Nurture
Are genetics or your environment the reason you are the way you are?
5
New cards
Empiricism
The idea that knowledge must be found through experience and senses.
6
New cards
Phrenology
The study of the shape and size of the cranium as a supposed indication of character and mental abilities.
7
New cards
Introspection
The examination or observation of one’s own mental and emotional processes (self-reflection).
8
New cards
Structuralism
Structure is more important than function and divided up the mind in to mental parts.
9
New cards
Functionalism
Function is more important than structure and divided up the mind by function.
10
New cards
Gestalt
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts. Focuses on the brain as a whole.
11
New cards
Wilhelm Wundt
Created the first psych lab in Germany.
12
New cards
Sigmund Freud
“Everything is a penis.” Austrian Neurologist who founded psychoanalysis. Developed the concept of the unconscious
13
New cards
Ivan Pavlov
Russian psychologist who studied classical conditioning. Did the dog experiments.
14
New cards
William James
First American psychologist, he established functionalism as a school of thought in psych.
15
New cards
John Watson
American psychologist who founded Behaviorism
16
New cards
Neuroscience/Biology
Medical approach to psychology
17
New cards
Evolutionary
Behavior is dictated by a drive to survive and pass along our genes.
18
New cards
Behavior Genetics
Nature vs. Nurture
19
New cards
Psychodynamic/Psychoanalytic (Freudian)
Freud, the unconscious, trauma.
20
New cards
Behavioral
What we do/observable responses.
21
New cards
Cognitive
How we think and memorize.
22
New cards
Social Psychology
Surrounding environments and cultures and how they influence us.
23
New cards
Humanistic
Self-Actualization (focuses on the good)
24
New cards
Basic Research vs. Applied Research
REsearch for future study or to be applied to solve problems, help people make money, etc.
25
New cards
Hindsight Bias
“I knew that” Phenomenon.
26
New cards
Overconfidence
Thinking you know more than you do.
27
New cards
Confirmation Bias
Searching for data that only confirms your POV and ignoring the rest.
28
New cards
Scientific Method
1. Theory
2. Hypotheses (Testable prediction)
3. Replication (Copy or reproduce)
4. Operational Definitions (Clearly defined variable used to properly replicate an experiment)
29
New cards
Case study
One or a few subjects in great depth (Pro: Easy to conduct on small group, Con: Tough to generalize)
30
New cards
Survey
Little bits of info from many people (Pro: info from many people, Con: surface level info)
31
New cards
Population vs. Sample
A small percentage of the population
32
New cards
Random Sampling
Everyone in the group has an equal chance of being chosen (More accurate in estimating whole population)
33
New cards
False Consensus Effect
We hang around people who agree with us/ share our beliefs, so we overestimate how many people agree with us.
34
New cards
Naturalistic Observation
Stalking
35
New cards
Correlations (Positive, Negative, illusory)
(Pos: as x increases, y increases)
(Neg: as x increases, y decreases)(Inverse)
(ill: No actual correlation
(Neg: as x increases, y decreases)(Inverse)
(ill: No actual correlation
36
New cards
Experimentation
How you establish causation. (Pro: Provides evidence, Con: Prone to human error.
37
New cards
Experimental Condition vs. Control Condition
Exp:Receives the possible “cause” (the “test” group).
Con: Doesn’t get the possible “cause” (baseline group).
Con: Doesn’t get the possible “cause” (baseline group).
38
New cards
Placebo and Double Blind Procedure
Placebo: Blank or empty factor
\
Double Blind: The Scientists and participants don’t know who is in which condition.
\
No group is biased one way or another.
\
Double Blind: The Scientists and participants don’t know who is in which condition.
\
No group is biased one way or another.
39
New cards
Independent and Dependent Variables
Independent: The manipulated factor
Dependent: The studied factor
Dependent: The studied factor
40
New cards
Measures of Central Tendency
Mean: Average
Median: Middle number
Mode: Most common result
Median: Middle number
Mode: Most common result
41
New cards
Standard Deviation
Picture
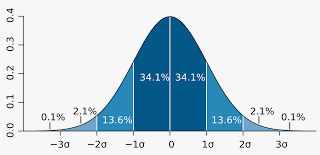
42
New cards
Statistical Significance
Difference is enough to mean something
43
New cards
Ethics
Moral principles that govern a person’s behavior or the conducting of an activity
44
New cards
Ethics in Psych
1. Informed consent: Subjects agree to participate
2. Protection from harm of subjects
3. Ability to stop/leave the study
4. Confidentiality
\
45
New cards
Neuron
Dendrite: Receiving fiber
Axon: Transmitting fiber
Soma: Cell body, triggers action
Terminal Branches: allows messages to be sent in different directions
Terminal Buttons: hold synaptic vesicles which hold neurotransmitters
Myelin Sheath: cover on the axon to accelerate speed of neural impulses
Synapse: Space in between neurons
Axon: Transmitting fiber
Soma: Cell body, triggers action
Terminal Branches: allows messages to be sent in different directions
Terminal Buttons: hold synaptic vesicles which hold neurotransmitters
Myelin Sheath: cover on the axon to accelerate speed of neural impulses
Synapse: Space in between neurons
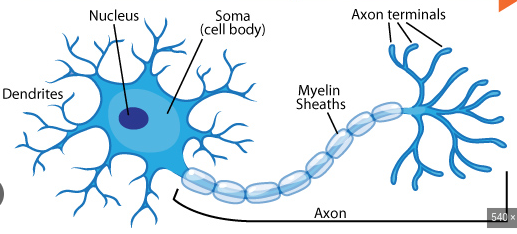
46
New cards
Action Potential and Refractory Period
AP: Firing of a neuron
RP: Time it takes for a neuron to reset
RP: Time it takes for a neuron to reset
47
New cards
Reuptake
The process by which neurotransmitter molecules that have been released at a synapse are reabsorbed by the presynaptic neuron that released them
48
New cards
Neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine(ACH): Muscle contraction and general brain activity
Dopamine: Learning, emotion, attention, movement, and pleasure
Endorphins: Natural Opiates
Serotonin
Dopamine: Learning, emotion, attention, movement, and pleasure
Endorphins: Natural Opiates
Serotonin
49
New cards
Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
CNS: Brain and Spinal Cord
PNS: Links the CNS w/ everything else
PNS: Links the CNS w/ everything else
50
New cards
Somatic/Skeletal Nervous System
Controls voluntary movements
51
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
Controls “automatic” bodily functions
52
New cards
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems
SNS: Fight or flight
PsNS: Returns us to homeostasis
PsNS: Returns us to homeostasis
53
New cards
Sensory, Motor, and Interneurons
S: Receive external stimuli and send to CNS
M: Carry info from CNS to body to carry out actions
I: Processing neuron in the CNS
M: Carry info from CNS to body to carry out actions
I: Processing neuron in the CNS
54
New cards
Neural Networks
Clusters of neurons working together
55
New cards
Endocrine System
Glands and Hormones
Adrenal Gland: Release epinephrine (adrenaline)
Pituitary Gland: “Master Gland” (puberty, hormone release, controlled by thalamus)
Adrenal Gland: Release epinephrine (adrenaline)
Pituitary Gland: “Master Gland” (puberty, hormone release, controlled by thalamus)
56
New cards
Hormones
Chemical messengers that are released in the bloodstream
57
New cards
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
Brain wave recording (levels of electrical activity traced)
58
New cards
PET Scan
Radioactive glucose used to create picture
59
New cards
CAT Scan
X-rays of the brain
60
New cards
1\.MRI
2\.fMRI
2\.fMRI
1. Magnets used to make the clearest picture of the brain
2. Multiple MRI’s strung together to make a video
61
New cards
Brainstem
Base of the spine that controls the left-right crossover with many parts:
Medula: “Primal” involuntary actions (breathing, heart rate)
Pons: Bladder control, coordinates movement, and sleep paralysis
Reticular Formation: Wakefulness (injured causes coma)
Medula: “Primal” involuntary actions (breathing, heart rate)
Pons: Bladder control, coordinates movement, and sleep paralysis
Reticular Formation: Wakefulness (injured causes coma)
62
New cards
Thalamus
Egg-shaped structure at the top of brainstem that acts as a sensory switchboard that receives and sorts incoming and outgoing information (except smell)
63
New cards
Cerebellum
Lower back of the brain (behind brainstem) coordinates voluntary movement and balance
64
New cards
Limbic System
Core system of memory, emotions, and motivation
Amygdala: Almond shaped on the ends of the Hippocampus, it deals with aggression and fear
Hypothalamus: (Below Thalamus) Monitors/controls hormones (is the autonomic nervous system)
Hippocampus: Deals with memory (processes into long-term)
Amygdala: Almond shaped on the ends of the Hippocampus, it deals with aggression and fear
Hypothalamus: (Below Thalamus) Monitors/controls hormones (is the autonomic nervous system)
Hippocampus: Deals with memory (processes into long-term)
65
New cards
Cerebral Cortex/Cerebrum
The surface level of the Brain that contain billion of neuron and glial cells
66
New cards
Glial Cells
Vital (Glue) cells that help with neural communication
67
New cards
Frontal Lobes/Prefrontal Cortex
Large chunk of association areas, it’s responsible for judging, planning, and decision making (“woah tiger” part of the brain)
\
\
68
New cards
Parietal Lobes
Areas at sides of head concerned with sensory reception and correlation
69
New cards
Occipital Lobes
Rearmost part of brain concerned with vision
70
New cards
Temporal Lobes
Parts of brain under temple concerned with hearing
71
New cards
Motor Cortex
In back of the frontal lobe that stretches ear to ear, it has a section designated to each body part (parts are in the opposite side of the body part they’re designated towards)
72
New cards
Association Areas
Majority of the frontal cortex, it’s not designated for one purpose, it’s the part of the brain that thinks
73
New cards
Language Aspects of the Brain
Aphasia: Impaired use of language
Broca’s Area: (Left frontal lobe) Formation of words
Wernicke’s Area: Comprehension (Written and spoken language)
Angular Gyrus: Processing written words into auditory code (rear left parietal lobe)
Broca’s Area: (Left frontal lobe) Formation of words
Wernicke’s Area: Comprehension (Written and spoken language)
Angular Gyrus: Processing written words into auditory code (rear left parietal lobe)
74
New cards
Right and Left Hemispheres of the Brain
Left: Deals with right side of body, so deals with the right field of vision (is more active than right side so is easier to study)
Right: Left side of body and left field of vision (Less active, but still crucial)
Right: Left side of body and left field of vision (Less active, but still crucial)
75
New cards
Corpus Callosum
Band of fibers that connect the two brain hemispheres allowing them to communicate
(Injury to this area can cause epilepsy)
(Injury to this area can cause epilepsy)
76
New cards
Brain Plasticity and Neurogenesis
BP: The brain has the ability to reorganize/rewire to some extent
Ngen: Brain does, at a very slow rate, produce new brain cells that can help out
Ngen: Brain does, at a very slow rate, produce new brain cells that can help out
77
New cards
Sensation
Detecting stimuli and encoding neural signals (feeling/sensing it)
78
New cards
Transduction
Stimuli/energy must be converted into neural messages so the brain can understand it
79
New cards
Perception
Organizing and processing sensations (how we understand them)
80
New cards
Bottom-up vs. Top-down Processing
BU: Sensory info to the brain and then processed (new sensations)
TD: Preconceived notions in the brain begin processing
TD: Preconceived notions in the brain begin processing
81
New cards
Selective Attention
At any one time we focus conscious awareness on select stimuli, generally at the expense of other stimuli
(Cocktail Party Effect)
(Cocktail Party Effect)
82
New cards
Absolute Threshold
Minimum stimulation needed for detection about 50% of the time
83
New cards
Signal Detection Theory
Detection depends on the individual as well as the stimulus
84
New cards
Subliminal Messages
Messages that are below the threshold
85
New cards
Difference thresholds (JND)
Minimum difference needed to detect the difference between two stimuli about 50% of the time
86
New cards
Weber’s Law
JND= Proportion of the stimulus (a ratio 1/10 = 10/100)
87
New cards
Sensory Adaptation
Decreasing sensitivity to a constant stimulus
88
New cards
Properties of light waves
1. What are light waves?
2. Wavelength?
3. Amplitude?
1. What are light waves?
2. Wavelength?
3. Amplitude?
1. Pulses of electromagnetic energy/waves
2. Determines the hue (color we experience)
3. Height of the wave (high amplitude = more energy = brighter light/colors)
89
New cards
Accommodation (of the lens)
Changing curvature of focus (lack of accommodation can lead to vision problems)
90
New cards
Parts of the eye
Cornea: Outer covering, protection for the eyeball
Pupil: Opening of the eyeball (the black part)
Iris: Colored muscle in the eye, controls the pupil (how much light enters the eye)
Lens: Focuses light rays onto the retina
Retina: Surface lining of back of the eyeball (light sensitive “screen” where lens focuses light) (receives images upside down)
Optic Nerve: Axons of ganglion cells (one million per)
Blindspot/Optic Disc: Where the optic nerve leaves the eye
Fovea: Area of central focus on the retina (only cones)
Pupil: Opening of the eyeball (the black part)
Iris: Colored muscle in the eye, controls the pupil (how much light enters the eye)
Lens: Focuses light rays onto the retina
Retina: Surface lining of back of the eyeball (light sensitive “screen” where lens focuses light) (receives images upside down)
Optic Nerve: Axons of ganglion cells (one million per)
Blindspot/Optic Disc: Where the optic nerve leaves the eye
Fovea: Area of central focus on the retina (only cones)
91
New cards
Rods and Cones
1. Transduce light energy
Rods: Black and white, outlines of objects (share bipolar cells)
Cones: Color, detail (may have their own bipolar cells)
2. Rods and Cones then activate Bipolar Cells
3. Bipolar cells activate Ganglion Cells
92
New cards
Feature Detection
Some cells in the visual cortex of the brain respond to specific visual features
93
New cards
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory
Primary colors are: red, green, and blue
(Colorblind= dichromatic/monochromatic)
(Men are more often colorblind than women)
(Colorblind= dichromatic/monochromatic)
(Men are more often colorblind than women)
94
New cards
Opponent Process Theory
Thalamus cells responsible for seeing one of two color (Teeter-Totter of color vision)
Afterimages: See the “opponent” color after looking at a color long enough
Afterimages: See the “opponent” color after looking at a color long enough
95
New cards
Properties of sound waves
1. What are sound waves?
2. Decibels?
3. Amplitude?
4. Frequency/Wavelength?
1. What are sound waves?
2. Decibels?
3. Amplitude?
4. Frequency/Wavelength?
1. Molecules of air bumping each other (ripples)
2. Measure of sound energy
3. Loudness
4. Pitch (long waves = low frequency)
96
New cards
Outer Ear
\
What you can see:
Auditory Canal: Passageway into the ear
Eardrum/Tympanic Membrane: Membrane that vibrates
What you can see:
Auditory Canal: Passageway into the ear
Eardrum/Tympanic Membrane: Membrane that vibrates
97
New cards
Middle Ear
Transmits sound from eardrum to inner ear
Pinston/Ossicles: Consists of 3 delicate bones
**H**ammer, **A**nvil, **S**tirrup (I **HAS** a piston)
Pinston/Ossicles: Consists of 3 delicate bones
**H**ammer, **A**nvil, **S**tirrup (I **HAS** a piston)
98
New cards
Inner Ear
Cochlea: Snail shaped tube with fluid that vibrates
Oval Window: Cochlea’s membrane
1. Stirrup vibrates the oval window
2. Oval window vibrates the fluid in the Cochlea
Basilar Membrane: Runs through the middle of the Cochlea
Hair Cells: Line the Basilar Membrane (bend and transduce sound) (The louder the sound = more hairs bend, and bend further)
Auditory Nerve: Carries info from Cochlea into brain
\
Oval Window: Cochlea’s membrane
1. Stirrup vibrates the oval window
2. Oval window vibrates the fluid in the Cochlea
Basilar Membrane: Runs through the middle of the Cochlea
Hair Cells: Line the Basilar Membrane (bend and transduce sound) (The louder the sound = more hairs bend, and bend further)
Auditory Nerve: Carries info from Cochlea into brain
\
99
New cards
Place Theory, Frequency Theory, and the Volley Principle
PT: Different pitch= activity at different places along the basilar membrane (Only explains medium to high pitches)
FT: Basilar membrane vibrates with the same speed as a sound wave (Only explains low to medium pitch)
VP: Combines Place and Frequency Theories
FT: Basilar membrane vibrates with the same speed as a sound wave (Only explains low to medium pitch)
VP: Combines Place and Frequency Theories
100
New cards
Conduction Deafness and Sensorineural/Nerve Deafness
CD: Damage to the outer or middle ear caused by physical damage such as a pebble to the ear (Can be helped via hearing aids which amplify sounds)
SD: Damage to the Cochlea/Hair Cells caused by age and/or prolonged exposure to loud sound (unable to be completely fixed)
SD: Damage to the Cochlea/Hair Cells caused by age and/or prolonged exposure to loud sound (unable to be completely fixed)