Blood smear practical
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What part of the blood smear are we interested in?
We want to look at the monolayer when evaluating cell morphology and counting different types of WBC's
What can be do at x10?
§Scan feathered edge, identify monolayer, estimate RBC and WBC density
What can be do at x40?
§Platelets, RBC morphology, WBC differential and morphology
how do you make a blood smear
Use a capillary tube to transfer a few drops of blood to a glass slide near the frosted label end
Use a spreader slide held at around 45 degrees to pull back towards the blood drop
As the spreader slide meets the drop, blood will travel along the angled edge and just before it reaches the sides, push the spreader slide forward in a smooth continuous motion maintaining the angle
You should end up with a “bullet” outline
Air-dry (staining wet smears creates “water artefact” – refractile circles in red blood cells)
what is the feathered edge, monolayer and body
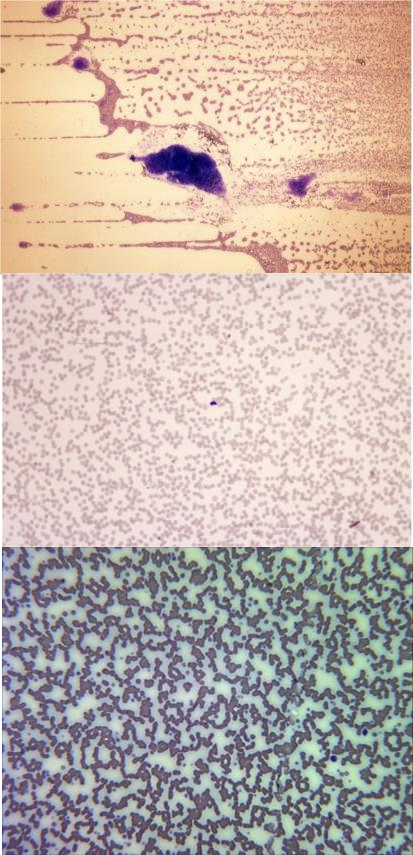
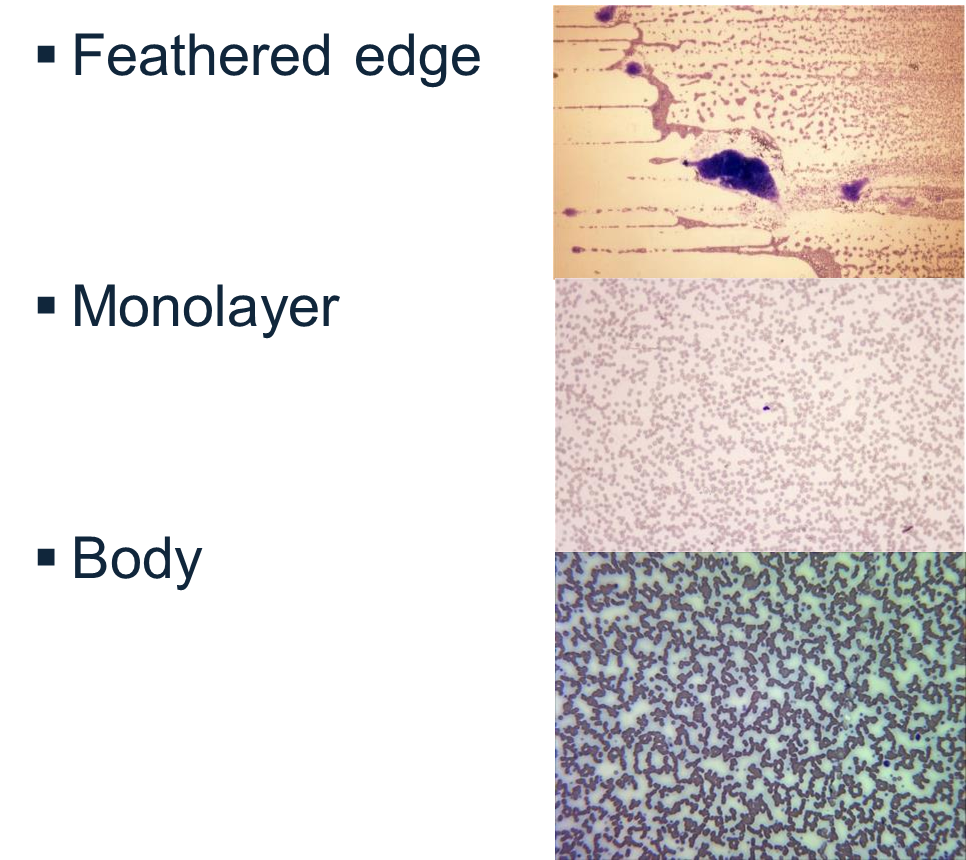
dog
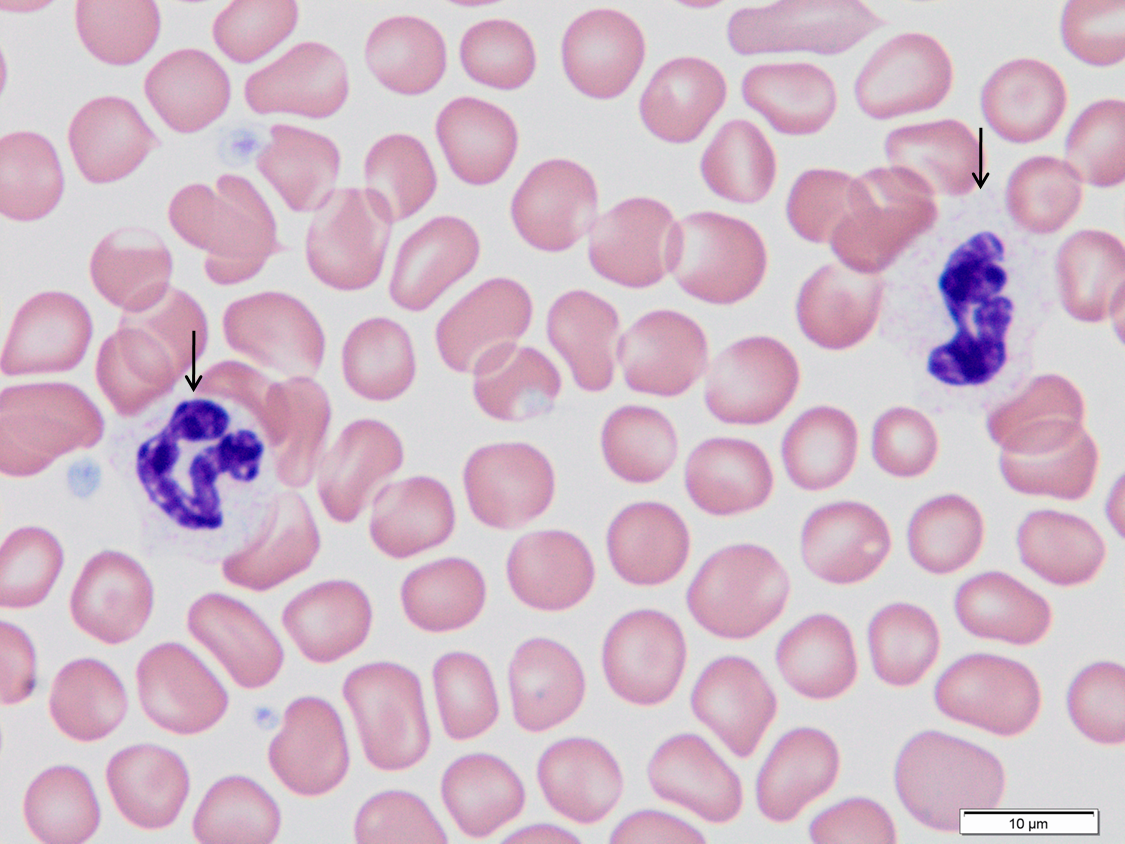
Segmented neutrophils.
Note irregular shape and irregular, non-parallel sides to the nucleus. Neutrophils may have very faint ‘neutral’ staining granules that vary in prominence.
dog
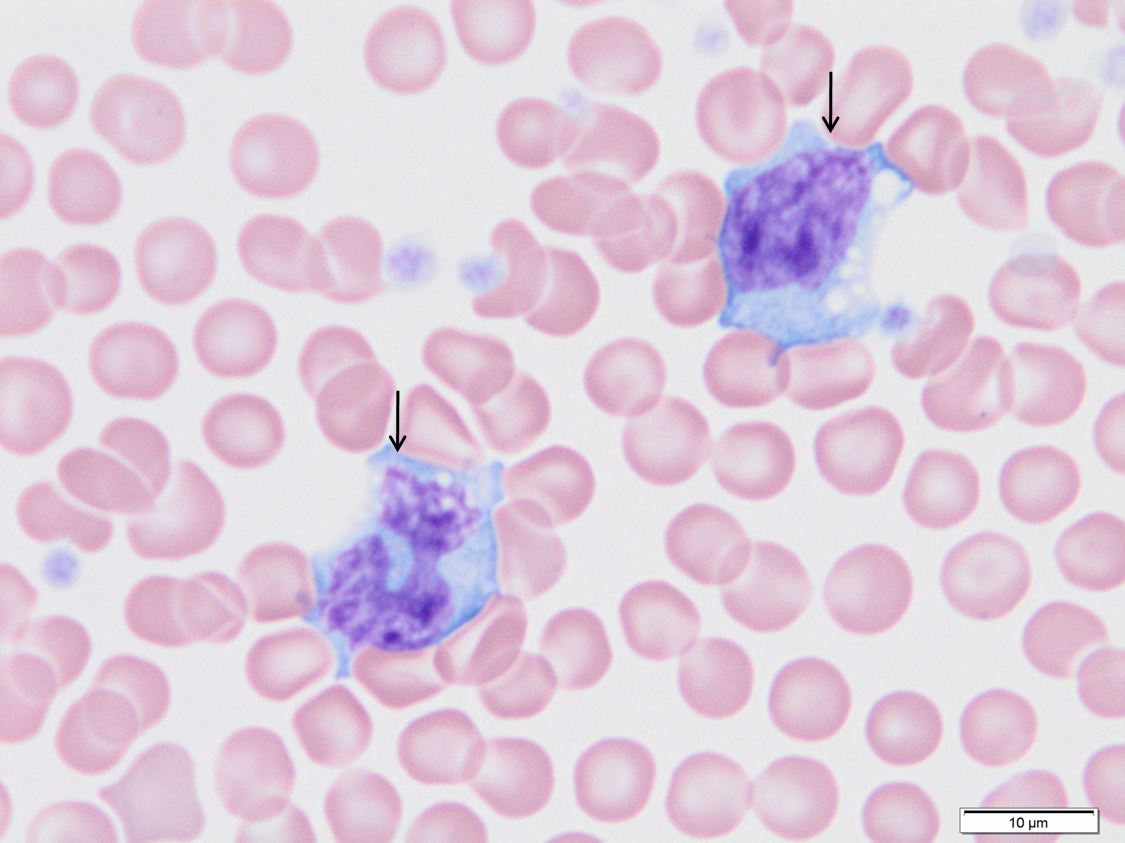
Monocytes.
Monocytes create confusion because of highly irregular nuclear shape, often being confused with neutrophils. Monocytes will have larger diameter than adjacent neutrophils and monocyte cytoplasm is darker blue-gray. The cytoplasm may have vacuoles.
dog
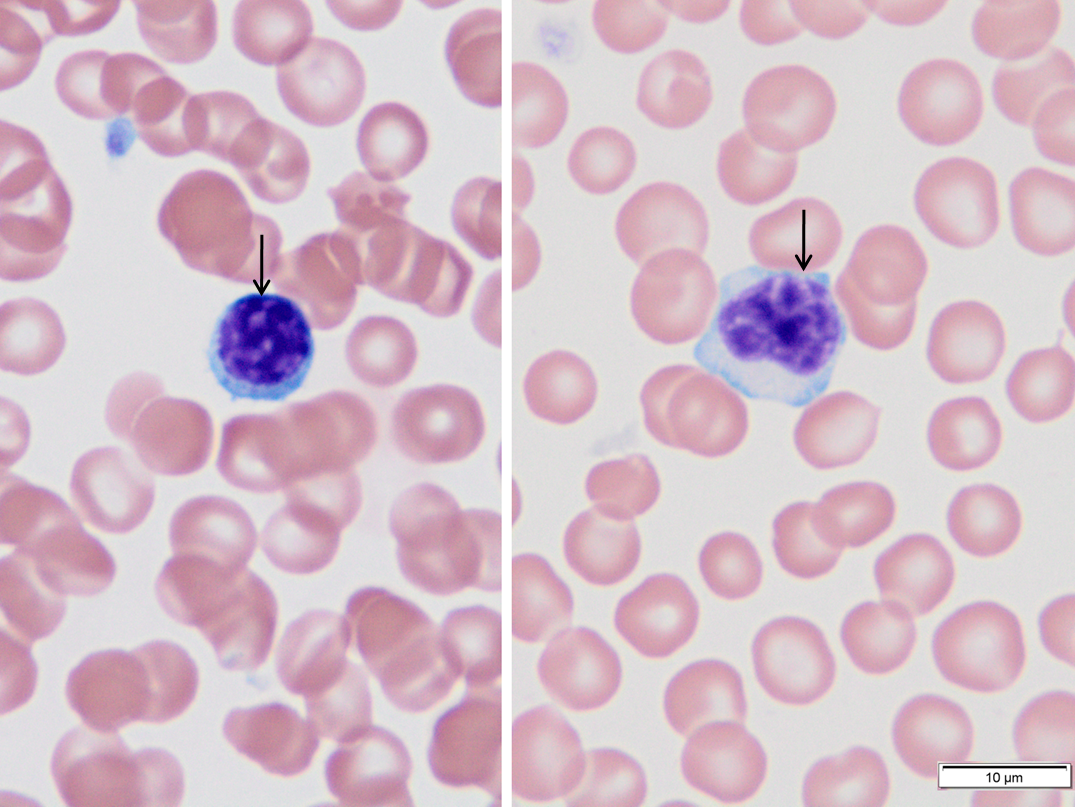
Lymphocytes.
Small resting lymphocytes in the circulation usually have a round nucleus, with little to no cytoplasm – similar to the cell on the left. Variants may have increased cytoplasm – similar to the cell on the right. Nuclear shape can have an indentation, but in all cases small lymphocytes will have chromatin condensed into the clumpy pattern shown
cat
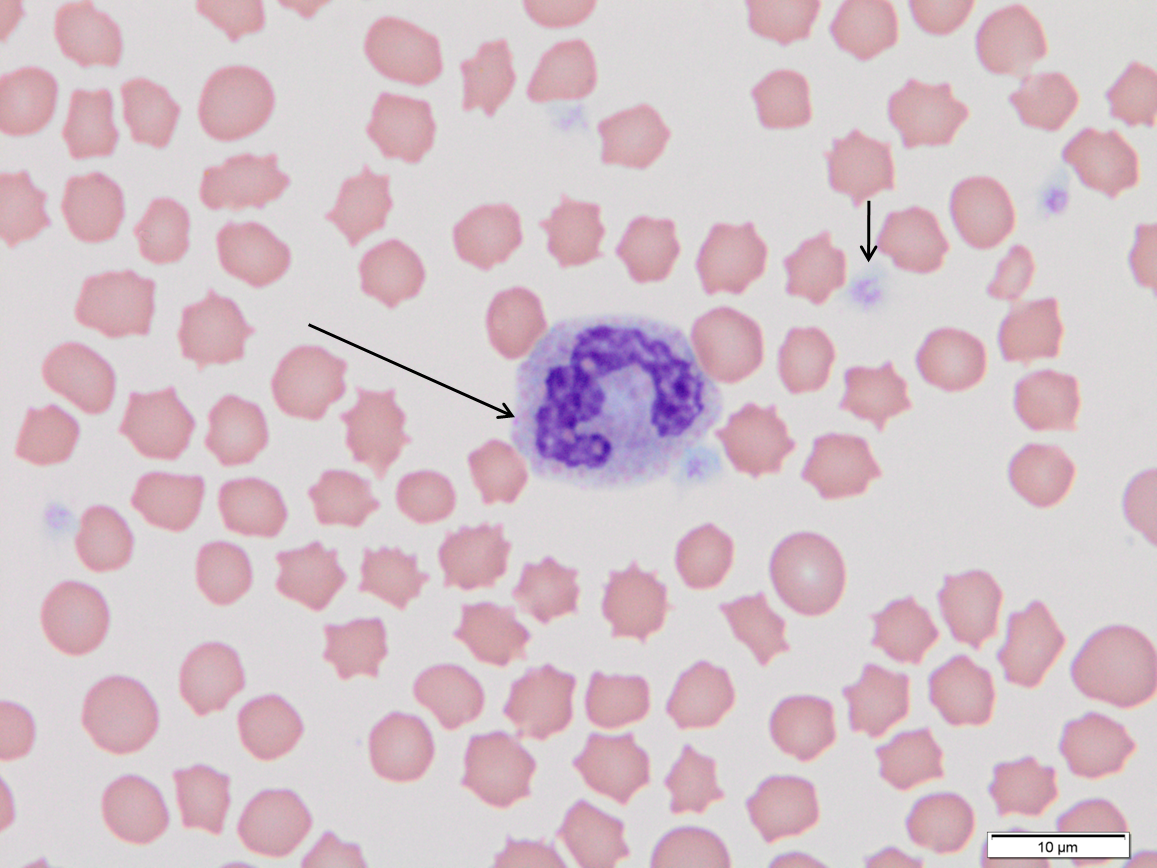
Long arrow. Feline basophil. The cytoplasm is typically consists of a pavement stone arrangement of faintly staining granules.
Short arrow. Platelet. Several are in the field of view.
dog
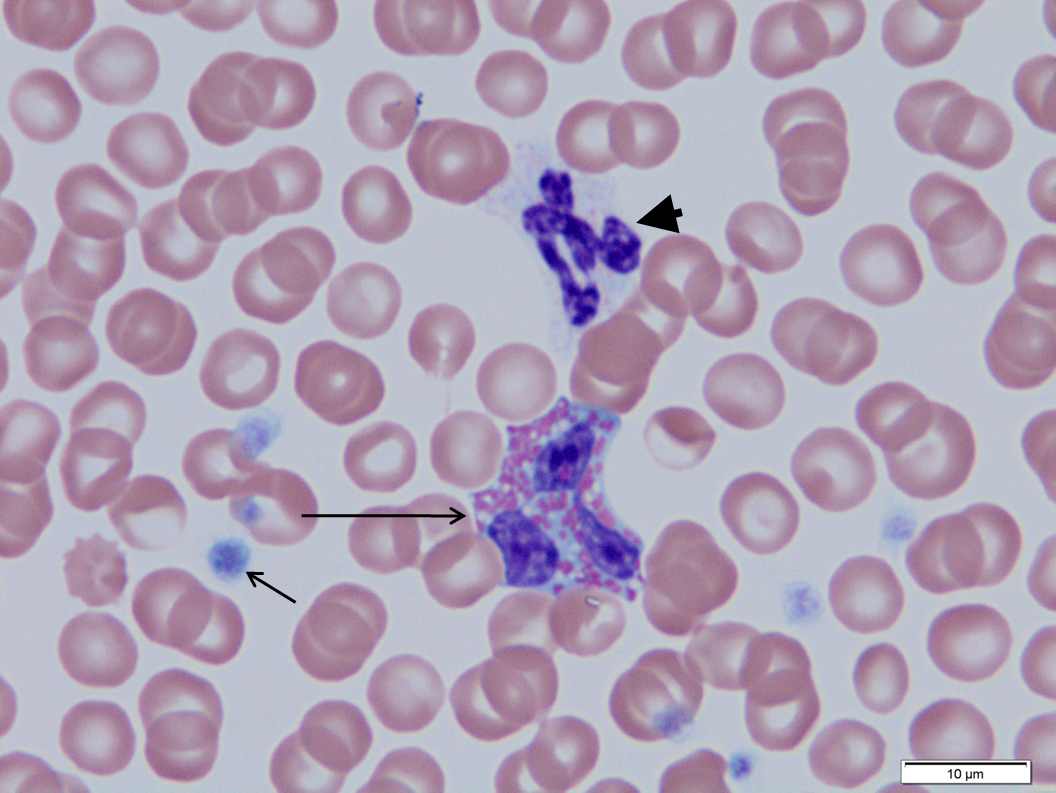
Long arrow.
Eosinophil, note large eosinophilic granules
Short arrow.
Platelet
Arrowhead.
Segmented neutrophil, note very faint neutrophilic granules
dog
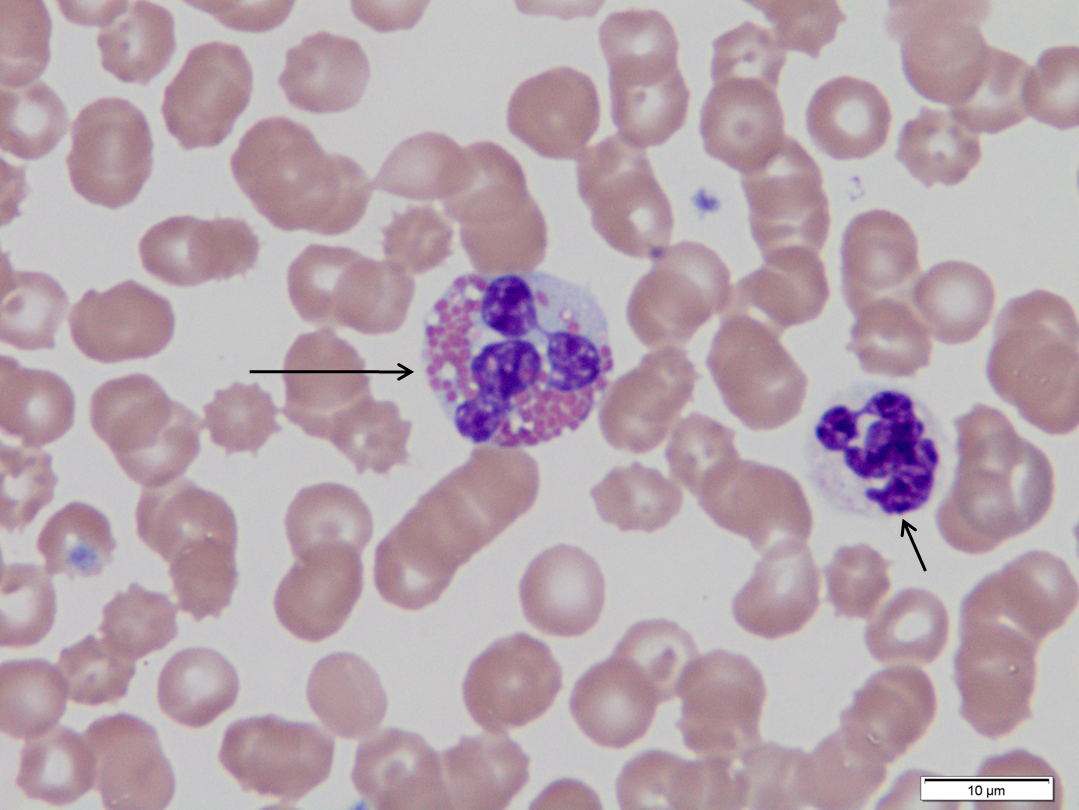
Long arrow.
Eosinophil, note large eosinophilic granules. There are a few cytoplasmic vacuoles; these are washed out granules.
Short arrow.
Segmented neutrophil.
cat
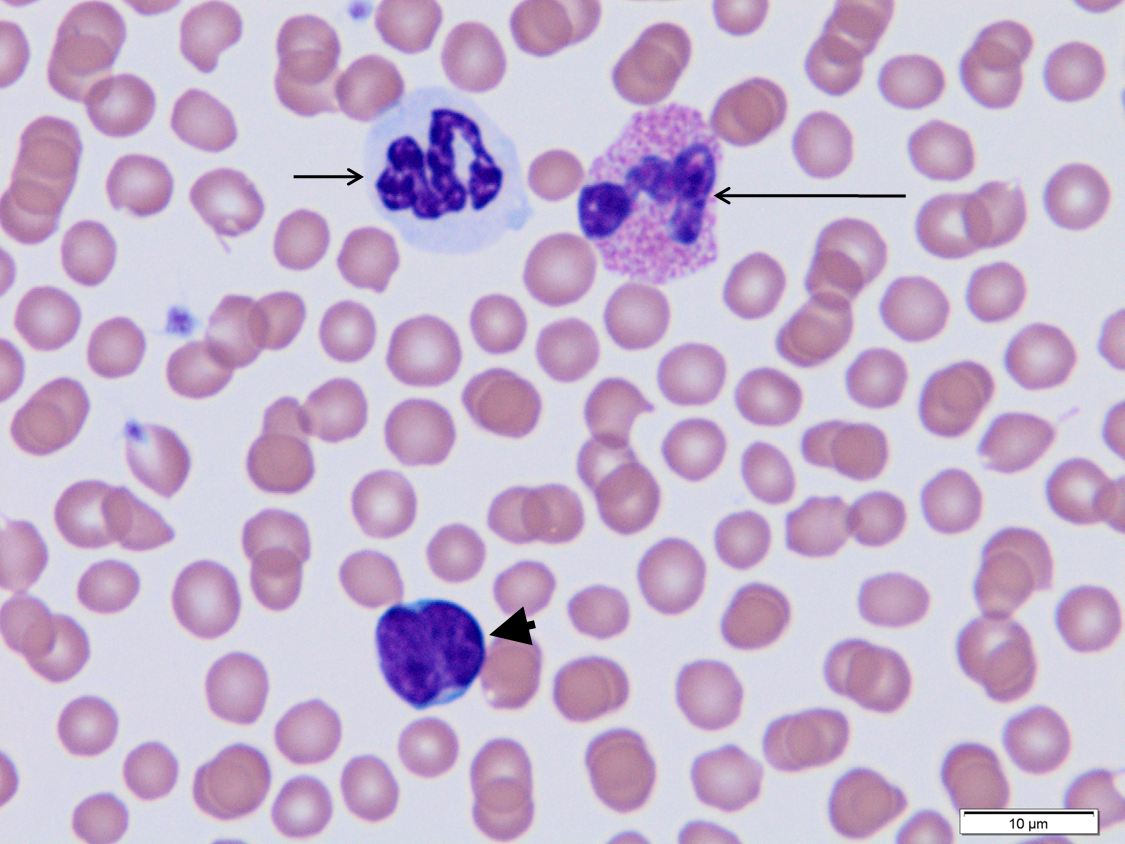
Long arrow.
Feline eosinophil. The cytoplasm packed with short rod shaped granules.
Short arrow.
Segmented neutrophil.
Arrowhead
Lymphocyte.
dog
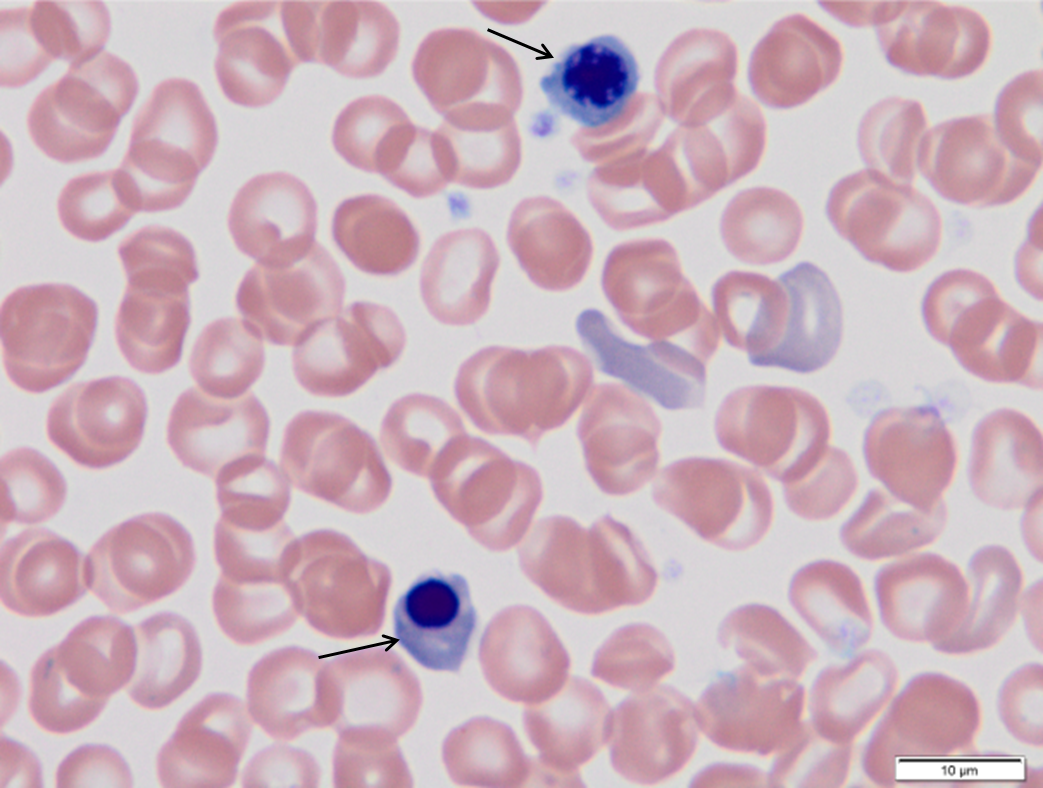
Arrows
Nucleated red blood cells (NRBC)
Note nuclear condensation leading to pyknosis.
Associated polychromatophilic erythrocytes are indicated by arrowheads.