
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Heterogenous process of getting older
Longevity is linked with
diet quality and physical activity
Theories of aging: Hayflick’s limited cell replication
human cells have a pre-programed limited ability to divide and after which they go through cellular senescence
Theories of aging: Molecular Clock
reduction of telomeres, shortening the chromsome each division
Theories of aging: Free radical and Oxidative stress theory
accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damages cells and membranes
Humans have the antioxidant capacity to combat these free radical species which declines with age
despite the theory we all…
age and experience a physiological decline in the major systems of our body
5 physiological changes when old
gastrointestinal
endocrine
musculoskeletal
cardiovascular
nervous system
Gastrointestinal changes
decline in…
mastication → ability to mechanical breakdown
dental health → ability to chew food
xerostomia → reduce in saliva
stomach acid and digestive enzymes in the pancreas
peristalsis → random constriction and relaxation of muscles in the intestines, decreasing rate at which foods go through the body
Endocrine changes
reduce in estrogen → bone loss
reduce in testosterone → muscle loss
decrease in vitamin D production
dysregulation of ghrelin, insulin and leptin
involved in regulating appetite and satiety cues
ghrelin → hunger hormone
insulin → cant digest sugar
leptin → satiety hormone
cardiovascular / musculoskeletal changes
Thickening of the chamber walls of the left ventricle
decrease cardiac output
Reduction in blood volume
reduction in bone and muscle mass → lower basal metabolic rate
Nervous system changes
decay of nerve cells(atrophy) → signaling capacity
decline in olfactory signaling receptors → taste and smell
reduction in appetite → no enjoyment in eating food
food safety → cant tell if it went bad
decline in cognitive function
dementia
alzheimer’s disease
reduced ability to self-feed
TEE declines by ____ there for ____ declines too
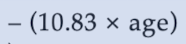
age, EER
Calculating EER using the DRI chart
subtract calories to account for the decline in TEE from DRI charts.
males → subtract 10kcal/day
females → subtract 7kcal/day
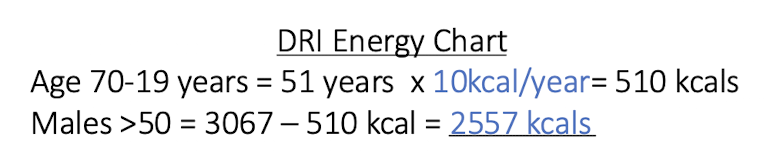
Water function
maintenance of body temperature, vascular volume, transport medium for nutrient and removal of waste
makes up 60% of our body weight
adequate intake of water
male → 15 cup eq or 3.7L
female → 11 cup eq or 2.7L
water: aging considerations
deficiency in thirst and fluid regulation → forgets they are thirsty
could result in dehydration and hyper-natreimia (too much sodium in blood)
aging population lack b12 becuase…
stomach acid declines
intrinsic factor doesn’t release
cant digest protein
no b12 absorbed
vitamin b12
obtained from animal source
vitamin b12 deficiency
pernicious anemia → deficiency in cellular division
solution for Vitamin b12 deficiency
b12 injection directly to the blood stream
→ DO NOT advise an elder to eat more animal product to supplement b12 since without intrinsic factor, no matter how much you eat, you will not absorb b12.
what is important consideration in advising elders ?
Delivering the Nutrient requirements while being sensitive to the physiological changes happening with age
maintaining of autonomy, independence, and social integrity
Challenges following the neurological changes
failure to feel hungry or thirsty
dementia → reduced ability to be self-fed via memory lost
decline in the olfactory receptors → no taste or smell = no appetite
solution for the neurological changes
food timer → alarms as reminder to eat and drink
eating in a social environment → meals with family and peers
select foods with high nutrient density → make every bite matter
ex. peanut butter, eggs, salmon
nutrition supplements → high energy drinks & caloric enhancement powders added to beverages
Challenges: Gastrointestinal changes → Difficulty swallowing
Xerostomia → decline in saliva making it painful to eat certain food like whole fruits or insoluble fibers
Dysphagia → difficulty swallowing as it slips out of forming food bolus
risk for chocking and aspiration → food/liquid entering lungs
social concern → anxiety when eating food as it dribbles out the moth
Solutions: Challenges: Gastrointestinal changes → Difficulty swallowing
Provide a diet specific to Dysphagia to improve oral consumption
level 3: soft solid foods that are easily cut and mashed
steamed sweet potatoes, strawberries, bananas, steamed cauliflower
level 2: chopped softened foods that are mashed
mashed sweet potatoes, cottage cheese, peanut butter w soft bread
level 1: completely pureed to a pudding like consistency. No chewing required
pudding, apple sauce, pureed meats and vegetables
beverages are THICKENED → promote bolus formation and enhance swallowing of liquids
** liquids are harder to swallow as it just slips out of their mouth
level 1 Dysphagia Diet

molded into food shapes → maintain independence and social integrity
thickening agents are added to increase the viscosity of the liquid without changing the property of the food → starches or agar
3 different consistencies
nectar → mild
honey → moderate
pudding → substantial
Challenges: Challenges: Gastrointestinal changes → reduction in digestive capacity
decrease in stomach acid and enzymes
can’t digest food therefore no nutrient absorbed
Solution: Challenges: Gastrointestinal changes → reduction in digestive capacity
elemental diet → provide foods that have pre-hydrolyzed lipid, carbs, and protein in liquid form
UNBEARABLE TASTE
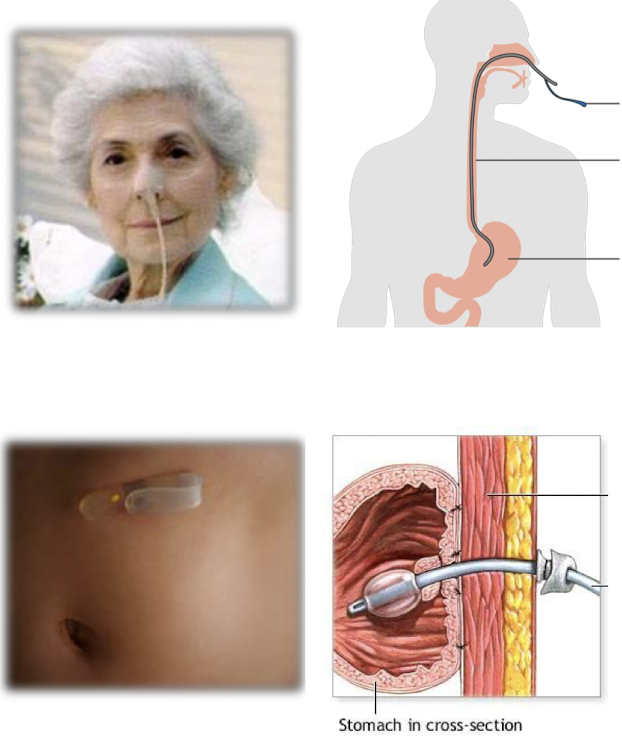
2 Ways to overcome elemental diet’s unbearable taste
Nasogastric tube (NG) → tube through nose
Gastric Tube (G-tube) → tube that is surgically placed through the gastric wall
→ both methods bypass tongue so they don’t have to taste the pre-hydrolyzed
Challenges: Endocrine Changes → loss of lean muscle and bone density
Sarcopenia → muscle wasting as a natural result of aging
Osteoporosis → severe decrease in bone mineral density, creating a porous bone that is fragile and susceptible to breaks
Kyphosis → significant curvature of the spine
Solution: Endocrine Changes → loss of lean muscle and bone density
promote dietary adequacy of
high-quality protein → muscle loss
calcium → bone holes
vitamin D
use it or lose it → work the muscles
Food insecurity in aging population
7 million americans aged 60 and above are moderate to high food insecurity
cause → financial, accessibility, cognitive function, health status
pension
a fund in which u make regular payments during working days then get distributed as routine payments once one retires
personal savings
personal saving for retirement
social security
today’s working force pay social security taxes for the elders to get monthly
Medicare
healthcare service for 65 yrs or older.
part B → covers medical expenses and prescribed drugs and Medical Nutrition services
Medicare: Medical Nutrition services
→ nutrition / life style assessment and management, nutritional therapy,
may cover medical nutrition therapy (MNT)
definitely covers individuals with diabetes or kidney disease
MNT can only be conducted by registered dietitian and a referral by a physician
Older American Act: nutrition services program
federal initiative to provide comprehensive support nutrition services to senior citizens aged 60 and older
provide at least one meal per day with the consultation of a registered dietitian
meal must adhere to the dietary guidelines and each meal must provide a third of the DRIs
sanitary handling of foods
Goals of Older American Act: nutrition services program
reduce hunger and food insecurity
promote the socialization of older adults
promote the health and well-being of older individuals by assisting to access nutrition services
Congregate Nutrition Programs
promotes socialization and maintenance of independence,
meal service in a group setting → senior community center / adult daycare
transportation provided
nutrition education programs offered quarterly by a registered dietitian
Home delivered nutrition programs
meals on wheels → fresh, frozen, dried, or canned