animal repro anatomy
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Ovary
Female
Contains thousands of growing follicles
each follicle contains ovum (egg)
Received rich supply of blood vessels & nerves
Follicles
Female
Grows in response to hormones called GONADOTROPINS
either dies (atretic) or ovulate and release egg
Each one contains an ovum (egg)
Corpus Luteum (Corpora Lutea)
Female (on ovary)
AKA CL
forms from tissue left over after a follicle has ovulated
Produces several pregnancy hormones
Produces Progesterone primarily
Corpus Albicans (corpora albicanria)
Female (on ovary)
AKA CA
scar tissue left behind after CL dies or regresses
Avascular, non-functional tissue
Oviduct
Female
Funnel shaped organ
Has specialized end near ovary called fimbria that picks up ovulated eggs
Anterior: ampulla
Posterior: isthmus
Fertilization & early embryonic development takes place in oviduct for most animals
Uterus
Female
Maintains pregnancy
Releases hormones that regresses luteal tissue
Glandular inner lining surrounded by 2 layers of muscle
Longitudinal & circular layers
Cervix
Female
Thick, muscular organ
Isolates uterus fro, external environment during pregnancy
Site for semen deposition in some animals
Vagina
Female
Part of birth canal
Protect uterus from bacteria
Site of semen deposition in most animals
Vulva
Female
External genitalia of vagina
Involved w/ recognition of receptivity & producing pheromones
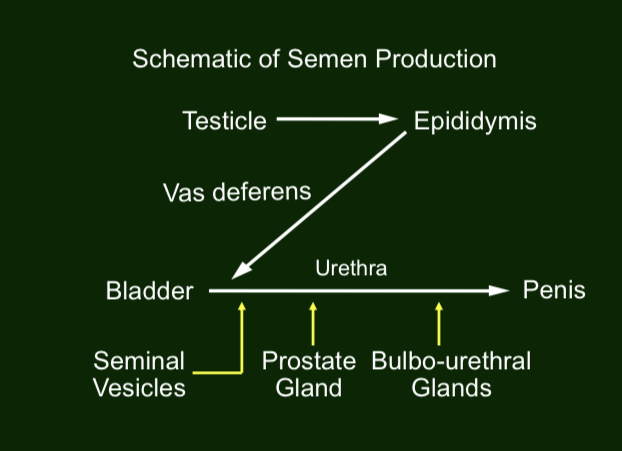
Testicles
Male
Series of seminiferous tubules
Produces spermatozoa
Produces hormones (testosterone, androgens, etc)
Epididymis
Male
Continuation of tubules in testicle
Specialized for maturation & storage of spermatozoa
Immature sperm enter epididymis
& During passage thru epidemics they become mature
Vas deferens
Male
Muscular tube w/ small diameter
Passage for spermatozoa from epididymis to urethra during ejaculation
Secondary sex glands
Male
Seminal vesicles, prostate, & bulbourethral glands
Produce & secrete most liquid portion of semen
Composition of each is specialized
Penis
Male
Deposit semen to female repro tract
Central canal is urethra
Urethra is common exit for repro & urinary systems
Sheath
Male
Pouch where penis remains when not in use
Sometimes invoked w/ pheromone production
Semen
Male
“Suspension” (sperm cells in seminal fluid)
1. Concentrated sperm leaves epididymis
2. Then travels thru vas deferens to urethra
3. Secondary sex glands secrete fluids into urethra that mix w/ sperm (seminal vesicles = largest amount