The Muscular System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Last updated 2:08 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Organs of the muscular system include:
Approximately 650 skeletal muscles, the heart, and organs containing smooth muscle like the stomach, bladder, blood vessels, etc.
2
New cards
What are the functions of the muscular system?
Producing movement by contracting (shortening) and relaxing (elongating), maintaining posture, stabilizing joints, and generating heat
3
New cards
What are the three types of muscles tissues?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth
4
New cards
Skeletal and smooth are elongated and are called
Fibers
5
New cards
Nonstriated; involuntary
Smooth Muscle
6
New cards
Spindle-shaped with a single nucleus.
Smooth Muscle
7
New cards
Contraction is slow and sustained.
Smooth Muscle
8
New cards
Striated; Involuntary
Cardiac Muscle
9
New cards
Found only in the heart.
Cardiac Muscle
10
New cards
Branching cells joined by special junctions called intercalated discs.
Cardiac Muscle
11
New cards
Contract slowly and in close coordination.
Cardiac Muscle
12
New cards
Striated; Voluntary
Skeletal Muscle
13
New cards
Contract rapidly and with great force, but tire easily and must rest after short periods of activity.
Skeletal Muscle
14
New cards
Muscle fibers are bundled together to form a fascicle which is wrapped by the epimysium.
Skeletal Muscle
15
New cards
Epimysia blend into strong tendons, which attach muscles indirectly to bones, cartilages, or connective tissue coverings.
Skeletal Muscle
16
New cards
Functions of skeletal muscle:
Maintains posture, stabilizes joints, and generates heat
17
New cards
The 5 Golden Rules: 1st Rule
All skeletal muscles cross at least one joint
18
New cards
The 5 Golden Rules: 2nd Rule
The bulk of a skeletal muscle lies proximal to the joint crossed
19
New cards
The 5 Golden Rules: 3rd Rule
All skeletal muscles must have at least two attachments: the origin, and the insertion
20
New cards
The 5 Golden Rules: 4th Rule
Skeletal muscles can only pull; they never push
21
New cards
The 5 Golden Rules: 5th Rule
During a contraction, a skeletal muscle insertion moves toward the origin
22
New cards
Point attached to the immovable or less movable bone
Origin
23
New cards
Point attached to the movable bone
Insertion
24
New cards
Large muscles consist of thousands of single _______ that are contractile units.
Muscle fibers (muscle cells)
25
New cards
Muscle fibers are bound together by a connective tissue called __________.
Endomysium
26
New cards
**__________** wrap around a bundle of muscle fibers.
Perimysium
27
New cards
A bundle of muscle fibers is called a ________.
Fascicle
28
New cards
Many fascicles are bound together by the _________.
Epimysium
29
New cards
Epimysia blend into _______ which connect to bones, cartilages and other connective tissue coverings.
Tendons
30
New cards
**______** covers the epimysium to cover the entire muscle and runs into the tendon.
Fascia
31
New cards
The specialized plasma membrane of muscle cells.
Sarcolemma
32
New cards
Long organelles filling the cytoplasm of muscle cells.
Myofibrils
33
New cards
Contains only thin filaments called ______.
Actin
34
New cards
A darker midline interruption of the light I band.
Z disc
35
New cards
Contains entire length of thick filaments called ________.
Myosin
36
New cards
Lighter central area of the dark A band.
H zone
37
New cards
The center of the H zone
M line
38
New cards
Smallest unit of a muscle fiber that contracts
Sarcomere
39
New cards
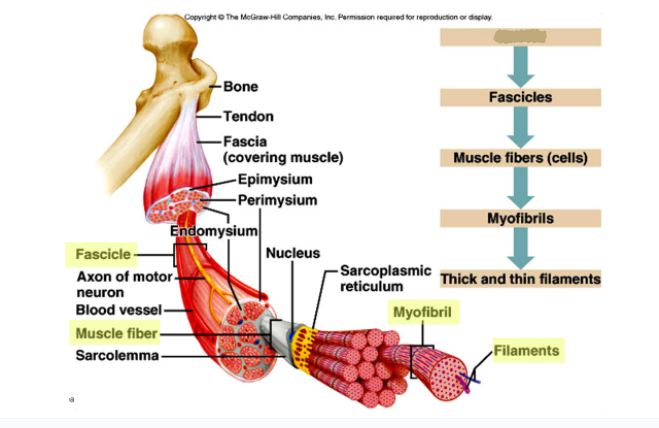
What goes here?
Muscle
40
New cards
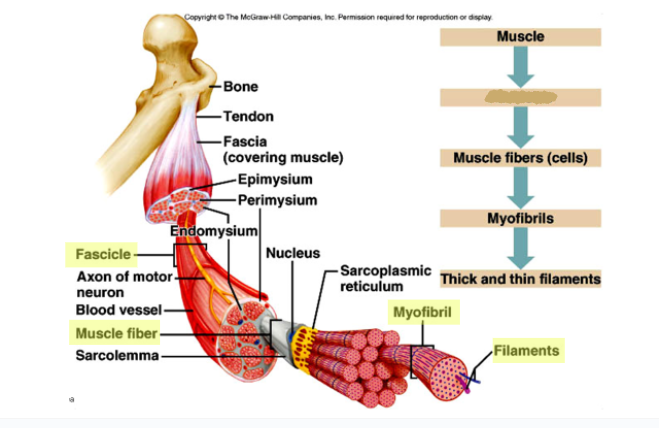
What goes here?
Fascicles
41
New cards
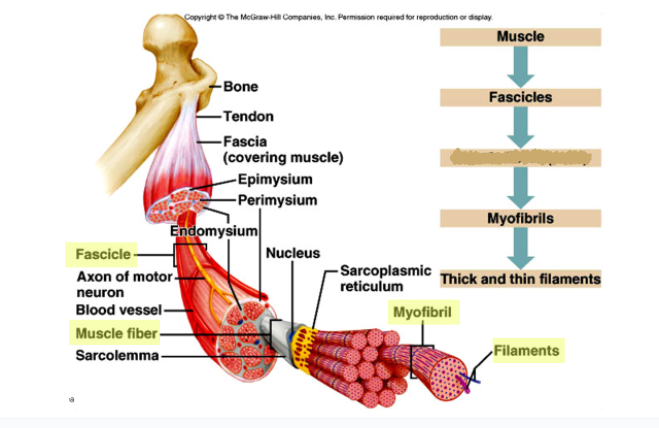
What goes here?
Muscle Fibers (Cells)
42
New cards
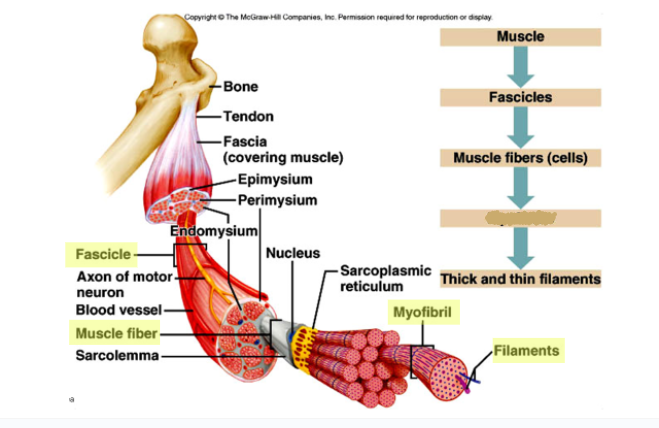
What goes here?
Myofibrils
43
New cards
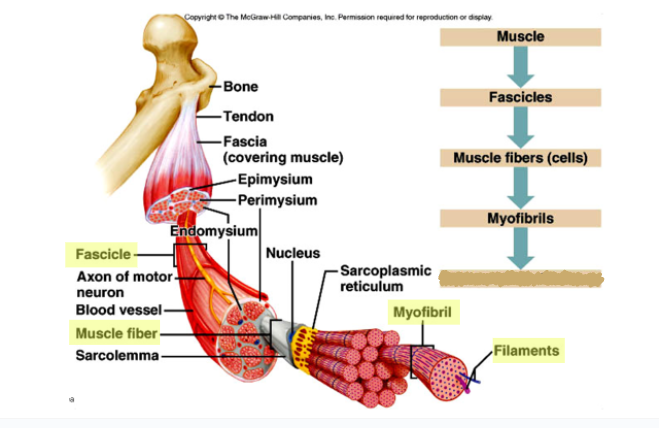
What goes here?
Thick and Thin Filaments
44
New cards
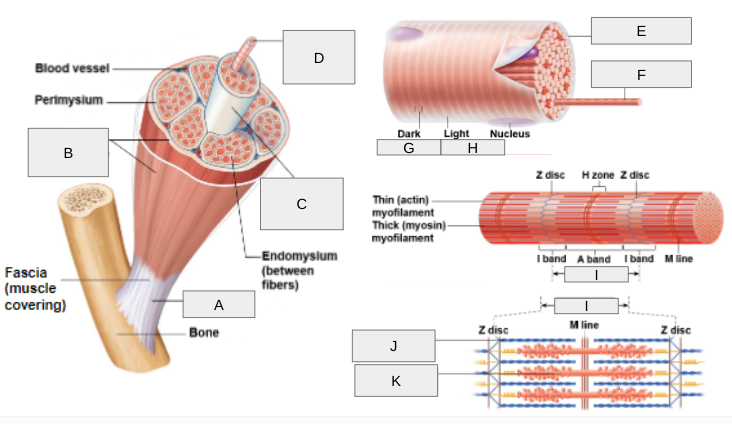
What is A?
Tendon
45
New cards
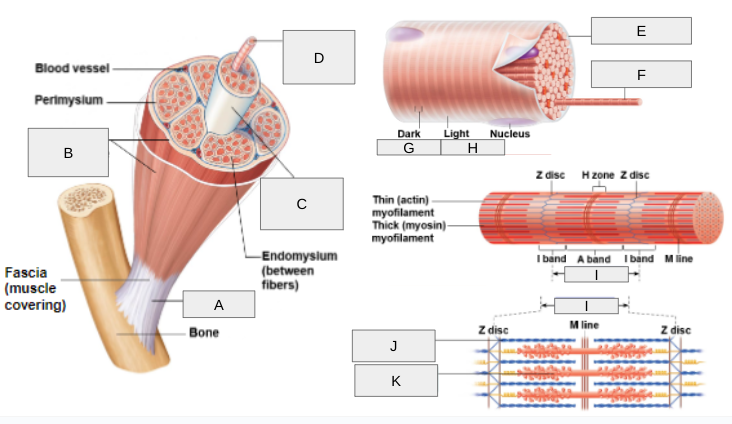
What is B?
Epimysium
46
New cards
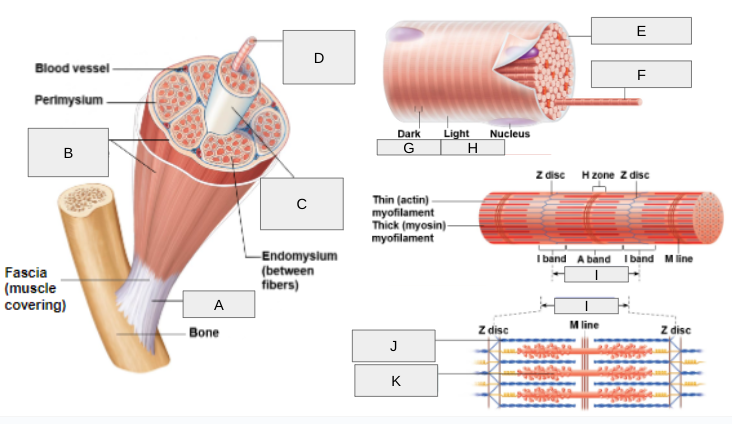
What is C?
Fascicle
47
New cards
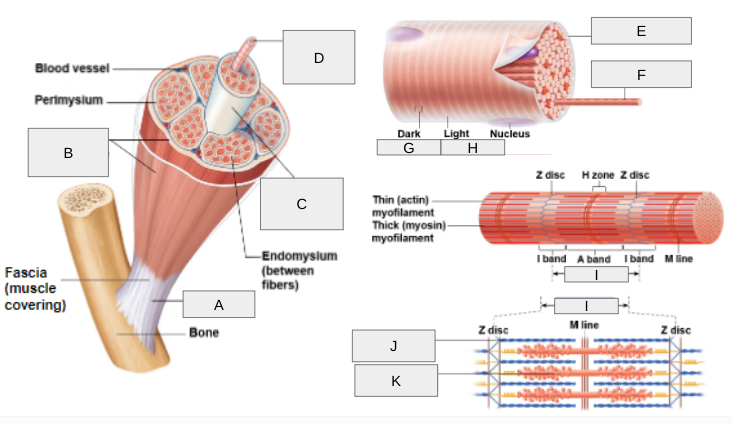
What is D?
Muscle Fiber
48
New cards
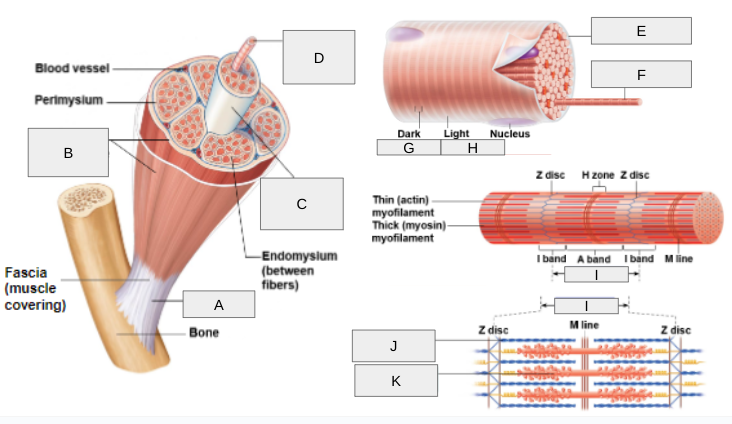
What is E?
Sarcolemma
49
New cards
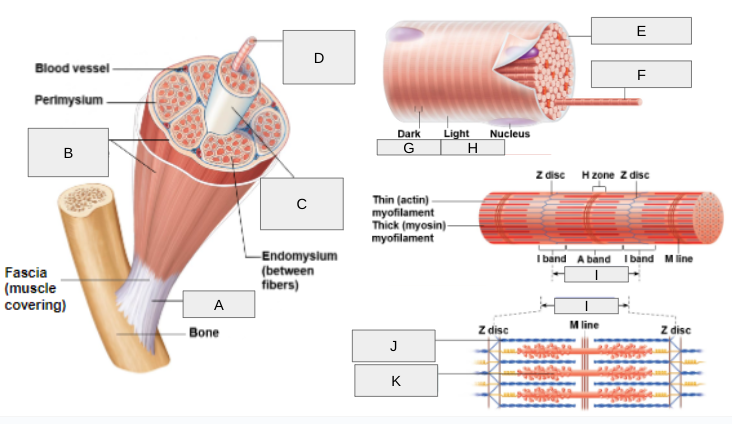
What is F?
Myofibril
50
New cards
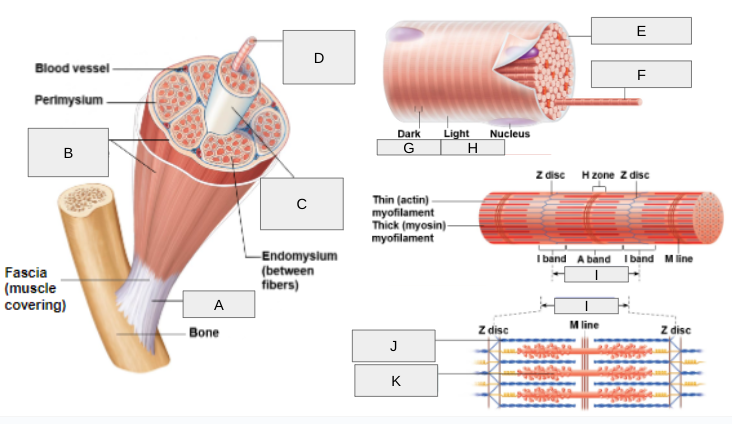
What is G?
(A) Band
51
New cards
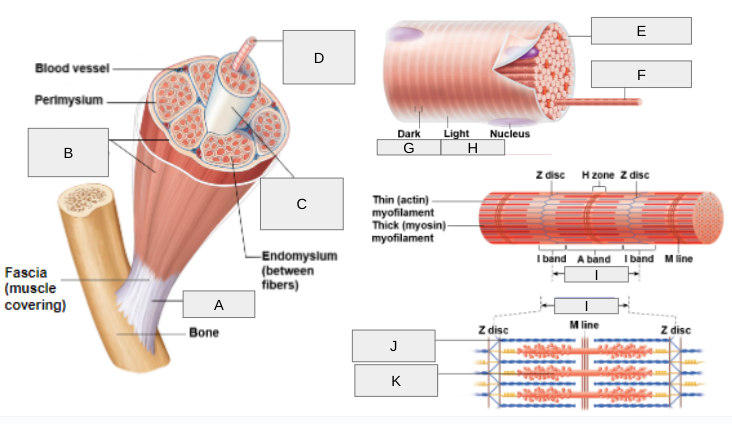
What is H?
(I) Band
52
New cards
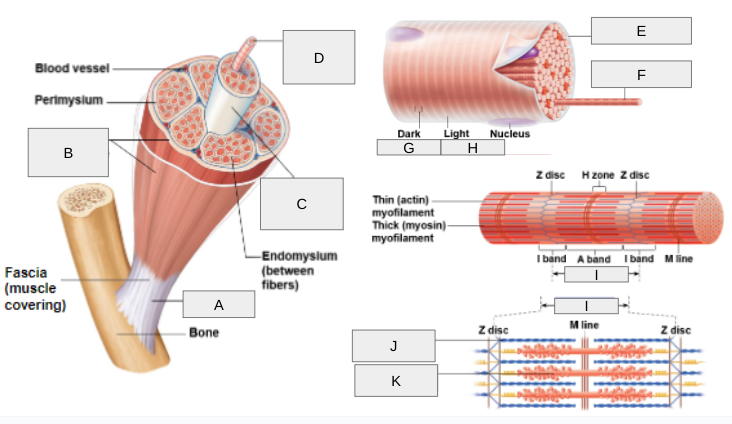
What is I?
Sarcomere
53
New cards
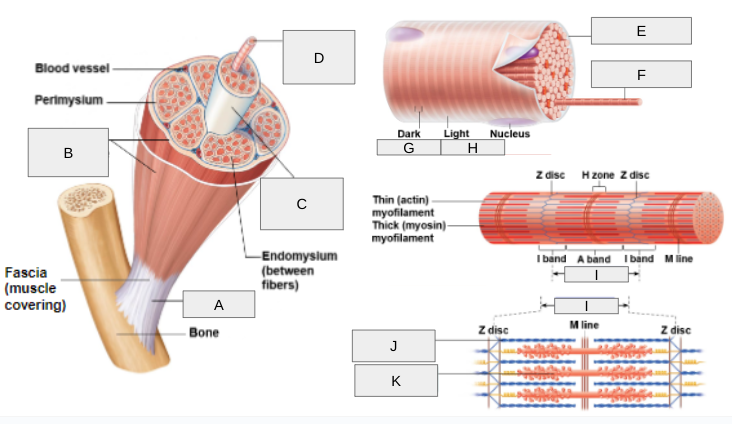
What is J?
Thin (actin) myofilament
54
New cards
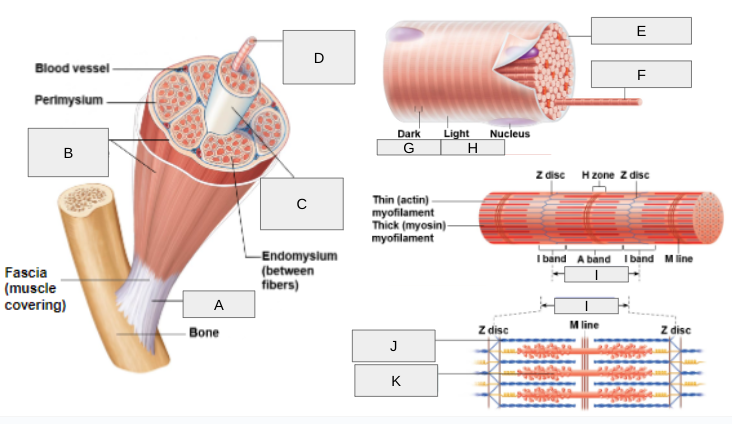
What is K?
Thick (myosin) myofilament
55
New cards
Ability to receive and respond to a stimulus.
Irritability
56
New cards
Ability to shorten when adequate stimulus is received.
Contractility
57
New cards
Ability of muscle cells to be stretched.
Extensibility
58
New cards
Ability of muscle cells to recoil and resume resting length after being stretched.
Elasticity
59
New cards
Muscles shorten and contract as the actin and myosin interact through a crossbridge formation
Sliding Filament Theory
60
New cards
Myosin heads attach to binding sites on the thin filaments forming a ___________.
Cross bridge
61
New cards
When a muscle is relaxed, regulatory proteins called ______ __and__ _______ cover part of the actin that myosin needs to bind to, preventing it from forming a cross bridge.
Troponin, tropomyosin
62
New cards
________are needed to bind to these regulatory proteins and change their shape and position on the actin. This Ca²⁺ is released from the _______.
Calcium ions, sarcoplasmic reticulum
63
New cards
In order for the myosin heads to release, energy from ______________ is needed.
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
64
New cards
Without ATP, the myosin cannot release the actin so the muscle stays contracted
Rigor Mortis
65
New cards
One motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle cells it stimulates.
Motor Unit
66
New cards
Long, thread-like extensions of the neuron that reach the muscle cell and branch into axon terminals.
Axons
67
New cards
Branches of axons that form junctions with the sarcolemma of a muscle cell to form neuromuscular junctions.
Axon Terminals
68
New cards
Junctions between the nerve and muscle, specifically the motor neuron and sarcolemma, that contain vesicles filled with a chemical referred to as a neurotransmitter.
Neuromuscular Junctions
69
New cards
Chemical released by nerve upon arrival of nerve impulse in the axon terminal.
Neurotransmitter
70
New cards
The neurotransmitter that stimulates skeletal muscle.
Acetylcholine
71
New cards
Although the nerve endings and the sarcolemma are very close, they never touch. This gap between them is filled with tissue fluid and is called the ___________.
Synaptic Cleft
72
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Direction of muscle fibers
Rectus Femoris, Transversus Abdominis
73
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Relative size of the muscle
Gluteus Maximus, Gluteus Medius
74
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Location of the muscle
Temporalis, Frontalis
75
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Number of origins
Triceps Brachii, Biceps Brachii
76
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Location of the muscle’s origin and insertion
Sternocleidomastoid, Brachioradialis
77
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Shape of the muscle
Trapezius, Deltoid
78
New cards
Naming Skeletal Muscles: Action of the muscle
Flexor Carpals Ulnaris, Adductor Muscle
79
New cards
Movement that decreases the angle of the joint and brings two bones closer together; typical of a hinge joint
Flexion
80
New cards
Movement that increases the angle or distance between two bones or parts of the body; the opposite of flexion; typical of straightening elbow or knee
Extension
81
New cards
Extensions beyond 180°
Hyperextension
82
New cards
Movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis; common of ball-and-socket joints; example is moving the atlas around the axis (shaking your head “no”)
Rotation
83
New cards
Movement of a limb away from the midline or median plane of the body
Abduction
84
New cards
Movement of a limb towards the body midline; opposite of abduction
Adduction
85
New cards
A combination of flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction; common of ball-and-socket joints; proximal end of bone is stationary, and distal end moves in a circle
Circumduction
86
New cards
Lifting the foot so that the superior surface approaches the shin (towards the dorsum)
Dorsiflexion
87
New cards
Depressing the foot (pointing the toes); “planting” the foot toward the sole
Plantar Flexion
88
New cards
Turning sole of the foot medially
Inversion
89
New cards
Turning the sole of the foot laterally
Eversion
90
New cards
Forearm rotates laterally so palm faces anteriorly; radius and ulna are parallel
Supination
91
New cards
Forearm rotates medially so palm faces posteriorly; radius and ulna cross each other like an X
Pronation
92
New cards
Moving the thumb to touch the tips of the fingers on the same hand
Opposition
93
New cards
Muscle that has major responsibility for causing a particular movement
Primer Mover
94
New cards
Muscles that oppose or reverse a movement
Antagonist
95
New cards
Help prime movers by producing the same movement or reducing undesirable movements
Synergist
96
New cards
Myofilaments are able to slide past each other during contractions, shortening the muscle and movement occurs.
Isotonic Contractions
97
New cards
tension in the muscle increases due to myosin “spinning their wheels”; myosin is trying to slide, but the muscle is pitted against some immovable object ending in the muscle being unable to shorten or produce movement.
Isometric Contractions
98
New cards
Continuous partial contractions of muscle fibers as a result of a staggered series of nerve impulses being delivered to different muscle cells.
Muscle Tone
99
New cards
If the nerve supply is damaged, the muscle is no longer stimulated in this manner and loses tone, becomes paralyzed, and begins to _______: waste away.
Atrophy
100
New cards
Result in stronger, more flexible muscles with greater resistance to fatigue thanks to an increase in the number of blood vessels; improves digestion and coordination
Aerobic (Endurance) Exercises