APES Unit 7
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/275
Earn XP
Last updated 5:20 PM on 3/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
276 Terms
1
New cards
The elements and minerals that were present when the planet formed are all we have today (t/f)
True
2
New cards
Core
* The innermost zone of Earth’s interior
* composed mostly of iron and nickel
* includes a liquid outer layer and a solid inner layer
* composed mostly of iron and nickel
* includes a liquid outer layer and a solid inner layer
3
New cards
Mantle
* above core
* containing magma (molten rock)
* containing magma (molten rock)
4
New cards
Asthenosphere
* the layer of Earth located in the outer part of the mantle
* composed of semi-molten rock
* composed of semi-molten rock
5
New cards
Lithosphere
* the outermost layer of Earth
* include mantle and crust
* made up of several large and numerous smaller plates → overlie the convection cells within the asthenosphere
* include mantle and crust
* made up of several large and numerous smaller plates → overlie the convection cells within the asthenosphere
6
New cards
Crust
* the chemically distinct outermost layer of the lithosphere
* a thin layer of soil on top allows life to exist
* crust + overlying soil → provide most chemical elements that make up life
* a thin layer of soil on top allows life to exist
* crust + overlying soil → provide most chemical elements that make up life
7
New cards
Earth layers overlap
Ex. the lowest part of the lithosphere is the uppermost portion of the mantle
8
New cards
Hot spots
a place where molten material from Earth’s mantle reaches the lithosphere
9
New cards
High temp of Earth’s outer core and mantle is the result of
radioactive decay of isotopes of elements, which release heat
10
New cards
Plate tectonics
the theory that the lithosphere of Earth is divided into plates, most of which are in constant motion
11
New cards
Tectonic cycle
the sum of the processes that build up and break down the lithosphere
12
New cards
Crust of oceanic plates: rich in ___
iron
13
New cards
Crust of continental plates: rich in ___
silicon dioxide (less dense than iron)
14
New cards
new vs old lithosphere
New lithosphere is added at spreading zones; older lithosphere is recycled into the mantle at subduction zones
15
New cards
Oceanic and continental plates movements are driven by
convection cells (driven by heat from the core) in Earth’s mantle
16
New cards
Seafloor spreading
convection in the mantle → seafloor spreading
* the formation of new areas of oceanic crust, which occurs through the upwelling of magma at midocean ridges and its subsequent outward movement on either side
* create new lithosphere
* bring important elements to surface
* the formation of new areas of oceanic crust, which occurs through the upwelling of magma at midocean ridges and its subsequent outward movement on either side
* create new lithosphere
* bring important elements to surface
17
New cards
subduction
the process of one crustal plate passing under another
18
New cards
consequences of plate movement
Plates move → continent drift → climate change & geographic barriers formed or removed → species evolved and adapted or went extinct
19
New cards
Volcanoes formed at/in
* hotspots
* seafloor spreading
* subduction
* divergence
* seafloor spreading
* subduction
* divergence
20
New cards
Divergent plate boundary
* An area beneath the ocean where tectonic plates move away from each other
* seafloor spreading
* seafloor spreading
21
New cards
Convergent plate boundary
* An area where plates move toward one another and collide
* The plates generate lot pressure as they push against one another
* The plates generate lot pressure as they push against one another
22
New cards
Transform fault boundary
* An area where tectonic plates move sideways past each other
23
New cards
Fault
a fracture in rock caused by a movement of Earth’s crust
24
New cards
Seismic activity
the frequency and intensity of earthquakes experienced over time
25
New cards
fault zone (aka areas of high seismic activity)
* a large expanse of rock where a fault has occurred
* form in the brittle upper lithosphere where two plates meet or slide past one another
* form in the brittle upper lithosphere where two plates meet or slide past one another
26
New cards
Two continental plates meet & both plate margins lifted →
mid-continental mountain range
27
New cards
Earthquake
* the sudden movement of Earth’s crust caused by a release of potential energy along a geologic fault and usually causing a vibration or trembling at Earth’s surface
* occur when the rocks of the lithosphere rupture unexpectedly along a fault
* occur when the rocks of the lithosphere rupture unexpectedly along a fault
28
New cards
Epicenter
the exact point on the surface of Earth directly above the location where rock ruptures during an earthquake
29
New cards
Ring of Fire
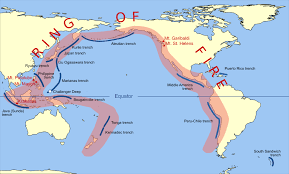
30
New cards
Richter scale
a scale that measures the largest ground movement occurs during an earthquake (logarithmic)
31
New cards
Impacts of moderate earthquakes (5.0-5.9)
collapsed structures, fires, contaminated water supplies, ruptured dams, deaths
32
New cards
Tsunami
a series of waves in the ocean caused by seismic activity or an undersea volcano
33
New cards
impacts of volcanoes
deaths, habitat destruction and alteration, air pollution, etc
34
New cards
Rock cycle
the geologic cycle governing the constant formation, alteration, and destruction of rock material that results from tectonics, weathering, and erosion, among other processes
35
New cards
Slowest of all of Earth’s cycles
Rock cycle
36
New cards
Rocks form when ___
magma from Earth’s interior reaches the surface, cools, and hardens
37
New cards
3 ways rocks at surface can be formed: Directly from molten magma →
igneous rocks
38
New cards
3 ways rocks at surface can be formed: by compression of sediments →
sedimentary rocks
39
New cards
3 way rocks at surface can be formed: By exposure of rocks and other Earth minerals to high temps and pressures →
metamorphic rocks
40
New cards
intrusive igneous rocks
form when magma rises up and cools in a place underground
41
New cards
extrusive igneous rock
form when magma cools above the surface of Earth
Cools rapidly → no large mineral individual crystals → fine-grained, smooth types of rock
Cools rapidly → no large mineral individual crystals → fine-grained, smooth types of rock
42
New cards
Formation of igneous rock brings surface ___
rare elements and metals
43
New cards
Fractures
a crack that occurs in rock as it cools
44
New cards
what rocks are fossils found?
sedimentary rocks
45
New cards
what rocks are important building materials?
metamorphic rocks
46
New cards
Which layer of Earth is composed primarily of iron and nickel?
the core
47
New cards
the Hawaiian Islands were formed at ___
hot spot
48
New cards
weathering
occurs when rock is exposed to air, water, certain chemical compounds, or biological agents such as plant roots, lichens, and burrowing animals
49
New cards
Physical weathering
* the mechanical breakdown of rocks and minerals
* can be caused by water, wind, or variation in temp, biological agents, burrowing animals
* expose more surface area and makes rock more vulnerable to further degradation
* increase the rate of chemical weathering
* can be caused by water, wind, or variation in temp, biological agents, burrowing animals
* expose more surface area and makes rock more vulnerable to further degradation
* increase the rate of chemical weathering
50
New cards
Chemical weathering
* release essential nutrients from rocks
* breakdown of rocks and minerals by chemical reactions, the dissolving of chemical elements from rocks, or both
* occurs most rapidly on primary minerals
* breakdown of rocks and minerals by chemical reactions, the dissolving of chemical elements from rocks, or both
* occurs most rapidly on primary minerals
51
New cards
example of chemical weathering
water that contains carbonic acid wears away limestone, sometimes forming cave systems
52
New cards
Chemical weathering sometimes are result of human activities
acid precipitation
* Acid rain falls on soil → promotes chemical weathering of certain minerals in the soil → leaching of soil
* Acid rain falls on soil → promotes chemical weathering of certain minerals in the soil → leaching of soil
53
New cards
weathering can reduce atmospheric CO2 concentrations (t/f)
true
54
New cards
Erosion
the physical removal of rock fragments from a landscape or ecosystem
55
New cards
what can create/accelerate erosion problems
poor land use practices
* deforestation
* overgrazing
* unmanaged construction activity
* road building
* deforestation
* overgrazing
* unmanaged construction activity
* road building
56
New cards
soil functions
* medium for plant growth
* breaks down organic material and recycles nutrients
* habitat for organisms
* filter water
* breaks down organic material and recycles nutrients
* habitat for organisms
* filter water
57
New cards
soil formation
result of physical and chemical weathering of rocks and gradual accumulation of detritus from the biosphere
58
New cards
5 factors simultaneously determine the properties of soil
parent material, climate, topography, organisms, time
59
New cards
parent material
the underlying rock material from which the inorganic components of a soil are derived
60
New cards
topography
the surface slope and arrangement of a landscape
61
New cards
how do plants speed chemical weathering
Plants remove nutrients from soil & excrete organic acids that speed chemical weathering
62
New cards
overuse land for agriculture, forestry, and other activities →
soil degradation
63
New cards
compaction of soil by machines, humans, and livestock →
alter properties and reduce ability to retain moisture, increase erosion
64
New cards
intensive agricultural use and irrigation →
deplete soil nutrients
65
New cards
horizon
a horizontal layer in a soil defined by distinctive physical features such as texture and color
* vary depending on climate, vegetation, parent material
* vary depending on climate, vegetation, parent material
66
New cards
soil horizon orders
O, A, E, B, C
67
New cards
O horizon
* composed of organic detritus in various stages of decomposition
* most pronounced in forest soils and some grasslands
* most pronounced in forest soils and some grasslands
68
New cards
Humus
the most fully decomposed organic matter in the lowest section of the O horizon
69
New cards
A horizon (aka topsoil)
a zone of organic material and minerals that have been mixed together
70
New cards
E horizon
a zone of leaching, or eluviation, found in some acidic soils under the O horizon, or less often, the A horizon
71
New cards
B horizon
composed primarily of mineral material with very little organic matter, including humus
72
New cards
C horizon
* the least-weathered soil horizon
* similar to the parent material
* similar to the parent material
73
New cards
texture: soil consist of a mixture of ___
clay, silt, sand
74
New cards
soil texture particles big to small:
sand > silt > clay
75
New cards
the permeability of soil depends on it ___
texture
76
New cards
best agricultural soil:
mixture of sand and clay that would be characterized as loam (40% sand, 40% silt, 20% clay)
77
New cards
what particles contribute to most chemical properties of soil?
clay particles
78
New cards
cation exchange capacity (CEC)
the ability of a particular soil to absorb and release cations (positively charged mineral ions)
79
New cards
soils with high CECs
provide essential cations to plants → desirable for agriculture
80
New cards
soil acids
detrimental to plant nutrition (bad)
81
New cards
soil bases
promote plant growth
essential for plant nutrition (except sodium)
essential for plant nutrition (except sodium)
82
New cards
Base saturation
the proportion of soil bases to soil acids, expressed as a percentage
83
New cards
soil with high CECs and high base saturation → support ___ productivity
high
84
New cards
crustal abundance
the average concentration of an element in Earth’s crust
85
New cards
most abundant elements in the crust
oxygen, silicon, aluminum, iron
86
New cards
ores
concentrated accumulation of minerals from which economically valuable materials can be extracted (ex. salt and sand)
87
New cards
how do ores form
* form when magma contact with water
* form after the deposition of igneous rock
* formed by intense chemical weathering in tropical regions (ex. bauxite)
* form after the deposition of igneous rock
* formed by intense chemical weathering in tropical regions (ex. bauxite)
88
New cards
metal
an element with properties that allow it to conduct electricity and heat energy, and to perform other important functions
89
New cards
reserve
the known quantity of a resource that can be economically recovered
90
New cards
Surface mining includes:
strip mining, open-pit mining, mountaintop removal, placer mining
91
New cards
strip mining
* the removal of strips of soil and rock to expose ore
* often the case for deposits of sedimentary materials (coal, sand)
* often the case for deposits of sedimentary materials (coal, sand)
92
New cards
mine tailing
unwanted waste material created during mining including mineral and other residues that are left behind after the desired metal or ore is removed
93
New cards
open-pit mining
create a large visible pit or hole in the ground
ex. copper mines
ex. copper mines
94
New cards
one of the largest open-pit mines in the world
Kennecott Bingham Canyon mine
95
New cards
mountaintop removal
entire top of a mountain is removed with explosives
96
New cards
subsurface mining is safer than mountaintop removal (t/f)
false
97
New cards
placer mining
the process of looking for minerals, metals, and precious stones in river sediments
* use river water to separate heavier items from lighter items
* use river water to separate heavier items from lighter items
98
New cards
subsurface mining
* used when the desired resource is more than 100m below the Earth surface
* ex. coal, diamonds, gold
* ex. coal, diamonds, gold
99
New cards
mining impacts: road construction →
soil erosion, waterway damage, habitat fragmentation
100
New cards
mining impacts: mine tailings →
rainfall leads to contamination of water and land with acids and metals