Lecture 2: Structure & Function of Molecules #1: Water
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
9/5/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What percentage of cells is made up of water?
~70% to 95%
In what physical states does water exist?
Liquid, solid (ice), and gas (vapor)
Why is liquid water essential for life?
It enables biochemical reactions and supports cellular structures like membranes
What type of molecule is water in terms of polarity?
Polar molecule (due to polar covalent bonds)
Which atom in water is more electronegative, oxygen or hydrogen
Oxygen
What causes the polarity in water molecules?
Unequal sharing of electrons - oxygen attracts electrons more strongly than hydrogen
What is a hydrogen bond?
A weak attraction between the slightly positive hydrogen atom of one water molecule and the slightly negative oxygen atom of another
What is cohesion?
The tendency of water molecules to stick to each other via hydrogen bonding
What is adhesion?
Water’s ability to stick to other substances with charges or polar groups
How do cohesion and adhesion help plants?
They allow water to be transported upward through plant tissues, even over 100 meters in tall trees
What property of water enables insects like water striders to walk on water?
Surface tension, caused by cohesion between water molecules at the surface
Why does ice float on water?
Ice is less dense than liquid water due to the formation of a stable hydrogen bonded lattice
Why is it important that ice floats?
It insulates water below, preventing oceans and lakes from freezing solid and allowing life to survive underneath
What happens when ice forms inside cells?
Ice crystals can damage cells by acting like tiny knives, destroying cell structures and killing the cell
What makes water an excellent solvent?
Its polarity allows it to dissolve charged and polar substances by forming hydration shells around them
What happens when NaCl dissolves in water?
Na+ ions are attracted to the O- end of water molecules
Cl- ions are attracted to the H+ end of water molecules
Why is water’s ability to dissolve substances essential for life?
It enables biochemical reactions and the formation of cellular structures like membranes
What does hydrophilic mean?
“Water-loving” - substances that interact well with water due to their polarity charge
What does hydrophobic mean?
“Water-fearing” - substances that do not interact well with water, usually non-polar molecules
Why are hydrocarbons hydrophobic?
Because carbon and hydrogen share electrons equally, resulting in non-polar bonds
Give an example of a hydrophobic substance
Fats and oils
What types of atoms in organic molecules make them hydrophilic?
Oxygen and nitrogen, due to their strong attraction for electrons and ability to form polar bonds
Give an example of a hydrophilic organic molecules
Sugars (e.g. glucose)
Draw a set of water molecules showing their polar nature and the hydrogen bonds between them
Image
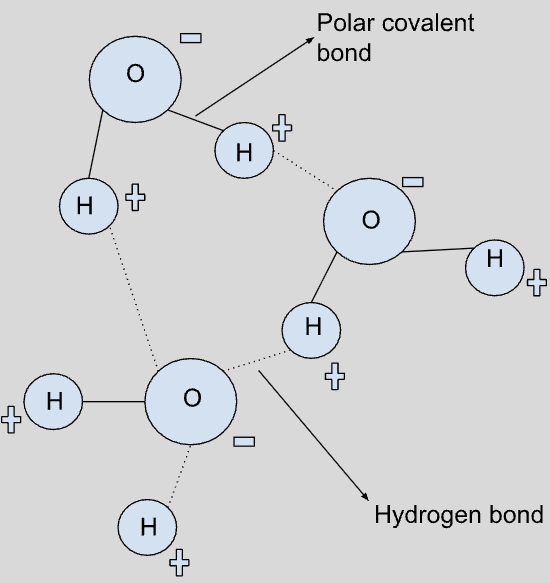
Explain how the features of water molecules lead to the properties of cohesion and adhesion
Water molecules consist of a positive hydrogen bond and a negative oxygen bond. Since opposite charges attract each other, the negatively charged oxygen is attracted to the positively charged hydrogen, therefore forcing molecules to “stick” together. This sticking of water molecules is known as cohesion.
Due to the slightly negatively charged oxygen atom, water can also “stick” to other positively charge molecules. This sticking of water molecules to molecules other than itself is known as adhesion
Explain how they physical and chemical properties of water lead to it being a good biological solvent and define how water interacts with a hydrophilic and hydrophobic compound
Water is a good biological solvent because its polarity (positive and negative ends) allows it to form hydrogen bonds with and surround other polar and ionic substances. Positive binds to negative and dissolves. Negative binds to positive and dissolves.
Water interacts with a hydrophilic compound by forming strong attractions like hydrogen bonds (polar molecules). These favorable interactions allow hydrophilic molecules to dissolve in water. Water interacts with a hydrophobic compound by repelling it. This is because water molecules can’t form hydrogen bonds with non-polar hydrophobic molecules
Define polar covalent bond
Type of chemical bond where electrons are shared unevenly between two atoms due to a difference in their electronegativity
Unequal sharing results in dipole (positive and negative charge)
Ex.) O-H bonds in water molecule
Define hydrogen bond
A weak electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom, which is covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom, and another nearby electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons
Define cohesion
Water molecules stay close to each other by hydrogen bonding (water molecules stick together)
Define adhesion
The process where molecules of different substances attract and stick together (water can stick to other molecules than itself)
Define organic chemistry
The study of carbon-containing compounds focusing on their structure, properties, composition, and reactions