Bio 12 systems and regulations
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/92
Last updated 4:05 AM on 5/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
Four Main Components of Digestion
1. ingestion
2. digestion
3. absorption
4. egestion
2. digestion
3. absorption
4. egestion
2
New cards
Ingestion
the taking in of nutrience. it involves saliva, teeth, and the esophagus.
3
New cards
Saliva (Ingestion)
produced in the salivary glands. lubricates food so it can be swallowed. dissolves food particles and makes it possible to taste what's been eaten. contains amylase.
4
New cards
Amylase in Saliva
an enzyme that breaks down complex carbohydrates
5
New cards
Teeth (Ingestion)
important structures for physical digestion. allow for cutting, tearing, grinding, and crushing of food. enamel is a calcium compound that covers the tooth. the hardest substance in the body. analogy: a blender can be like this.
6
New cards
Esophagus (Ingestion)
the passageway by which food travels from the mouth to the stomach. the food stretches the walls of the esophagus, causing peristalsis.
7
New cards
Peristalsis
a rhythmic wave-like contraction of the smooth muscle that moves food along the esophagus.
8
New cards
Digestion
the break down of complex molecules into smaller components by enzymes. occurs in the stomach and small intestines.
9
New cards
Stomach (Digestion)
the site of food storage and initial protein digestion. the movement of food into and out of the stomach is controlled by the sphincters. one sphincter is at the top and one is at the bottom. the top one is called the cardiac sphincter and the lower one is called the pyloric sphincter.
10
New cards
Sphincters in the Stomach
constrict muscles that surround a tube-like structure and act like draw strings on a bag.
11
New cards
Cells Lining the Stomach \______________________
secrete digestive fluids
12
New cards
Digestive Fluids in the Stomach
hydrochloric acid, pepsin, and mucus
13
New cards
Hydrochloric Acid in the Stomach
kills harmful organisms (mainly bacteria) that enter with the food
14
New cards
Pepsin in the Stomach
a protein digesting enzyme. breaks long amino acid chains into smaller ones.
15
New cards
Mucus in the Stomach
protects the stomach from hydrochloric acid and pepsin. stomach fluid has a pH of two (strong enough to dissolve rug fibres). mucus forms a lining on the inside of the stomach. when a section of this lining breaks down, an ulcer will develop.
16
New cards
Small Intestine (Digestion)
is the site in which most digestion occurs. up to seven meters in length. the pancreas releases five substances into the small intestine: bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻), trypsinogen and erepsin, amylase, and lipase. the small intestine releases an enzyme called disaccharidase which completes the digestion of carbohydrates. bile is released into the small intestines to break down large fat globules into smaller droplets. the increase in surface area allows lipase to break down the fat.
17
New cards
Bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) in the Small Intestine
released to neutralize the hydrochloric acid from the stomach
18
New cards
Trypsinogen and Erepsin in the Small Intestine
enzymes that break down proteins
19
New cards
Amylase in the Small Intestine
an enzyme that continues the digestion of carbohydrates that was started in the mouth
20
New cards
Lipase in the Small Intestine
an enzyme that breaks down fat
21
New cards
Disaccharidase in the Small Intestine
breaks down disaccharides into monosaccharides, completes the digestion of carbohydrates.
22
New cards
Bile in the Small Intestine
produced in the liver and stored in the gall bladder. released into the small intestines to break down large fat globules into smaller droplets. it gives feces the characteristic brown colour.
23
New cards
Absorption
the transport of digestive nutrients to the tissues of the body. occurs in the small and large intestine.
24
New cards
Small Intestine (Absorption)
is the site in which most of the absorption occurs. the large amount of absorption is due to villi. digested food goes to the capillaries in your villi then that goes to all the parts of your body.
25
New cards
Villi in the Small Intestine
small, finger-like projections that extend into the small intestine which increase the surface area for absorption. the cells that line each villus have micro villi.
26
New cards
Micro Villi
fine, thread-like extensions of the membrane that further increase the surface area for absorption.
27
New cards
Large Intestine (Absorption)
it stores waste long enough for water to be absorbed. it also absorbs some vitamins.
28
New cards
Egestion
the removal of waste food material from the body. the solid waste passes through the rectum and exits the body through the anus.
29
New cards
Digestive System Diagram
\+mouth at the oral cavity
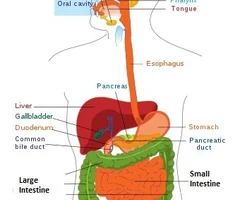
30
New cards
Functions of Blood
its main function is to carry oxygen to cells in the body. it also brings nutrients to cells in the body. it's important to the body's immune system, permitting the transport of immune cells throughout the body. it takes waste away from cells and distributes heat throughout the body.
31
New cards
Why Blood Carries Oxygen to Cells
we need oxygen because it helps us break down glucose and release energy in cellular respiration. oxygen is the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
32
New cards
Amount of Blood in the Body and Percent Composition of Different Components of Blood
the average person has 5 litres of blood inside them. 55% of it is plasma, 45% is red blood cells, and less than 1% is white blood cells.
33
New cards
Four Components of Blood
plasma, erythrocytes (red blood cells), leukocytes (white blood cells), and platelets
34
New cards
Plasma
this is the fluid portion of the blood. it contains water, glucose, vitamins, minerals, and waste products.
35
New cards
Erythrocytes (Red Blood Cells)
cells that contain hemoglobin and carry oxygen. hemoglobin molecules allow these cells to carry large amounts of oxygen. these cells don't have a nucleus and as a result, they are produced in the bone marrow.
36
New cards
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
contain a nucleus and are produced in the bone marrow. important part of the immune system. some of these cells destroy invading microbes by phagocytosis - they engulf the microbe and release enzymes that digest it. other ones of these cells function in allowing the body to recognize and fend off specific microbes.
37
New cards
Platelets
fragments of a large cell in the bone marrow. they move through the smooth blood vessels and rupture if they strike a sharp edge. when they rupture, they initiate blood clotting.
38
New cards
Types of Blood Vessels
arteries, capillaries, and veins
39
New cards
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart. have thick walls composed of different layers to withstand great pressure. blood from the arteries passes into smaller arteries called arterioles.
40
New cards
Aneurysm
when the wall of the artery weakens and a bulge develops. this bulge can rupture and as a result, less blood gets to the area beyond the rupture and the cells die. in the brain, it leads to a stroke.
41
New cards
Vasodilation
the widening of blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to tissues. (ex. blushing)
42
New cards
Blushing
the arterioles of the face dilate in order to release the excess heat that you produce when you are nervous. example of vasodilation.
43
New cards
Vasoconstriction
the narrowing of blood vessels, allowing less blood to go to tissues. (ex. fainting)
44
New cards
Fainting
you become pale because the arterioles of your skin constrict so that more blood is available for your brain. example of vasoconstriction.
45
New cards
Capillaries
tiny blood vessels with a wall only a single cell thick. the site of fluid and gas exchange. connects arteries and veins. no cell is further than two cells away from a capillary. bruising is a result of capillaries rupturing and blood rushing into the spaces between tissues.
46
New cards
Veins
carry blood back to the heart. capillaries merge and become venules, which merge into veins. pressure in the veins is much lower than in the arteries. when our muscles contract, they push on our veins causing blood to flow. one way valves prevent blood from flowing back.
47
New cards
Blood Flow in the Heart
deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava. when the atria contract, the blood enters the right ventricle. when the ventricles contract, the blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs, through the pulmonary arteries. the oxygenated blood returns to the heart through the pulmonary veins, which are blood vessels that enter the left atrium. when the atria contract again, the blood enters the left ventricle (more muscular). when the ventricles contract again, the blood is pumped through the aorta to the rest of the body.
48
New cards
Two Types of Valves in the Heart
atrioventricular (AV) valves and semilunar valves
49
New cards
Atrioventricular (AV) Valves
prevents the blood from flowing from the ventricles back to the atria.
50
New cards
Semilunar Valves
prevents blood that has entered the arterius from flowing back into the ventricles.
51
New cards
Heart Sounds
lub-dub heart sounds are caused by the closing of heart valves.
52
New cards
Lubb
these sounds occur when the blood is pumped from the ventricles in the arteries, causing the atrioventricular valves to shut
53
New cards
Dubb
when the ventricles relay, they increase the volume. this increase in volume causes the blood in the artery to want to re-enter the ventricles. the semilunar valves close, producing these sounds.
54
New cards
Blood Pressure
the force of blood on the walls of the arteries. it involves two measurements: systolic and diastolic. it depends on cardiac output and arteriolar resistance. the main reason for constant high blood pressure is hypertension.
55
New cards
Systolic Blood Pressure
a measure of the pressure during heart contraction. the normal pressure for a young adult is 120mmHg.
56
New cards
Diastolic Blood Pressure
a measure of the pressure when the heart is relaxed (between beats). normal pressure for a young adult is 80mmHg.
57
New cards
Cardiac Output
an increase in the amount of blood the heart pumps increases blood pressure. (ex. stress)
58
New cards
Arteriolar Resistance
if arteries constrict (decrease in size), blood pressure increases.
59
New cards
Hypertension
main reason for constant high blood pressure. caused by an increased resistance to blood flow. (ex. cholesterol)
60
New cards
Cholesterol
it can form a plaque that may block blood vessels.
61
New cards
Heart Diagram
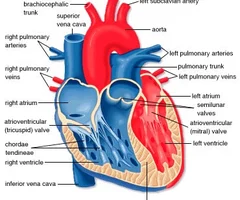
62
New cards
Importance of the Respiratory System
oxygen is essential to the survival of humans. it is required for the breakdown of glucose, which provides energy for the cells.
63
New cards
Respiration
all the processes involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between cells and the body. it includes breathing, gas exchange, and cellular respiration.
64
New cards
Steps to Breathing
1. air enters the respiratory system through the nose or the mouth
2. the air enters a channel in the mouth called the pharynx
3. air passes by the epiglottis
4. air from the pharynx enters the larynx (voice box) located at the upper end of the trachea (windpipe)
5. inhaled air moves from the trachea into two bronchi
6. air moves into smaller airways called bronchioles
7. air moves from the bronchioles into tiny sacs called alveoli
2. the air enters a channel in the mouth called the pharynx
3. air passes by the epiglottis
4. air from the pharynx enters the larynx (voice box) located at the upper end of the trachea (windpipe)
5. inhaled air moves from the trachea into two bronchi
6. air moves into smaller airways called bronchioles
7. air moves from the bronchioles into tiny sacs called alveoli
65
New cards
Epiglottis
a flap-like structure that covers the opening to the trachea when food is being swallowed, causes food to enter the esophagus and not the trachea.
66
New cards
Bronchi
the passage from the trachea to either the left or right lung
67
New cards
Bronchioles
the smallest passageway of the respiratory tract
68
New cards
Alveoli
sacs of the lung in which the exchange of gasses between the air and the blood occurs. composed of a single layer of cells and are surrounded by capillaries.
69
New cards
Alveolus
singular alveolar sac
70
New cards
Alveolar Sac
a group of alveolus
71
New cards
Movement of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
they move from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration. therefore, oxygen moves from the air inside the lung into the blood. carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the air inside the lung.
72
New cards
Ways Our Respiratory System is Protected From Foreign Particles
hair, mucus, and cilia. mostly a combination of the second two.
73
New cards
Hair Protecting Our Respiratory System
located in the nasal passage. function as a filter.
74
New cards
Mucus Protecting Our Respiratory System
probably the biggest source of protection. found in the nose and trachea. traps debris and keeps the cells lining the respiratory system moist.
75
New cards
Cilia Protecting Our Respiratory System
tiny hair-like protein structures found in the trachea. sweep the foreign debris in the mucus up the trachea to the pharynx.
76
New cards
Breathing Movements
the movement of gasses into and out of the lungs is determined by the difference in pressure between the atmosphere and the chest. gases move from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. pressure in the chest is controlled by the diaphragm and the intercostal muscles.
77
New cards
Diaphragm
a dome-shaped sheet of muscle below the lungs
78
New cards
Intercostal Muscles
muscles between the ribs which cause the ribs to move
79
New cards
Inspiration (Inhalation)
the diaphragm contracts and becomes flat, pulling downward. the intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribcage up and outwards. the chest volume increases, causing a decrease of pressure in the lungs. air moves into the lungs.
80
New cards
Expiration (Exhalation)
the diaphragm relaxes and becomes dome-shaped, pushing upwards. the intercostal muscles relax, causing the ribcage to fall. the chest volume decreases, causing an increase of pressure in the lungs. air moves out of the lungs.
81
New cards
Respiratory System Diagram
mouth is oral cavity and tongue is below
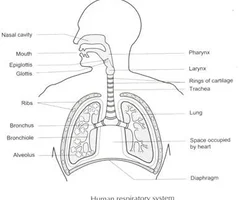
82
New cards
Bronchioles Diagram
smooth muscle on where bronchiole is labelled and bronchiole underneath on beige part. blood vessel coming off of it as well.
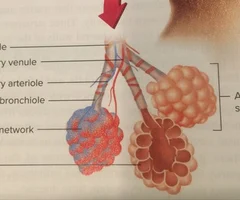
83
New cards
Two Main Parts of the Urinary System
the kidneys and the bladder
84
New cards
Kidneys
filter out waste from the blood. we have two. they are bean-shaped and are located on each side of our backbone. the stuff that they take out of our blood makes up our urine. each of them are made up of 2.4 million tiny units called nephrons.
85
New cards
Nephrons
a special tube system that does the actual filtering of the blood. most of the waste in the blood is small molecules. unfortunately, some of the things we need in our blood (water, salt, and sugar) also get pushed through the walls of the glomerulus. the purpose of the nephron is to get the good stuff back into the blood and get rid of the waste.
86
New cards
Steps to Filtering Blood
1. blood enters the glomerulus
2. the small molecules in the blood get pushed through the thin walls of the glomerulus and into the bowman's capsule. nephron ensures the good molecules are kept and gets rid of the waste.
3. the solution of small molecules goes to the loop of henle. here, water diffuses out into the capillaries surrounding the loop. salt also diffuses out and into the capillaries.
4. the solution goes to the distal tubule. here, more water and salt are removed.
5. the solution, made mostly of urine, now flows down the collecting duct and into the bladder.
2. the small molecules in the blood get pushed through the thin walls of the glomerulus and into the bowman's capsule. nephron ensures the good molecules are kept and gets rid of the waste.
3. the solution of small molecules goes to the loop of henle. here, water diffuses out into the capillaries surrounding the loop. salt also diffuses out and into the capillaries.
4. the solution goes to the distal tubule. here, more water and salt are removed.
5. the solution, made mostly of urine, now flows down the collecting duct and into the bladder.
87
New cards
Glomerulus
a bunch of capillaries bunched together
88
New cards
Alcohol, Caffeine, and Salt Affecting the Urinary System
they cause us to reabsorb less water. therefore, more water enters our bladder and we urinate more. this causes us to become dehydrated.
89
New cards
Bladder
it can hold 200-400mL of urine. when we urinate, we send a message to the sphincter muscle around the opening of our bladder to relax. children can't learn to control their sphincter muscles until they're two years old.
90
New cards
Nephron Diagram
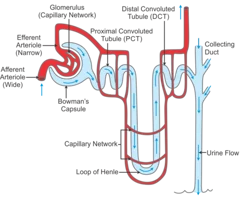
91
New cards
Measuring Blood Pressure
put cuff above their elbow and stethoscope on their elbow. pump the cuff to 180mmHg (above the systolic blood pressure). let some air out slowly and listen. wherever the gauge is when you first hear a sound is the systolic blood pressure (the maximum pressure of the artery). keep releasing pressure slowly until there is no more sound. the gauge at that point tells you the diastolic blood pressure. write it as systolic/diastolic.
92
New cards
Path of a Water Molecule from the Mouth to the Bladder
mouth -\> pharynx -\> esophagus -\> cardiac sphincter -\> stomach -\> pyloric sphincter -\> small intestine -\> large intestine (where absorption occurs) -\> capillaries -\> arterioles -\> arteries -\> aorta -\> renal artery. in the kidney (nephron): arteriole -\> glomerulus (bunch of capillaries) -\> bowman's capsule -\> loop of henle -\> distal tubule -\> collecting duct -\> ureter -\> bladder
93
New cards
Path of Carbon Dioxide from the Toe to the Mouth
capillary up the leg -\> merges into venules -\> merges into veins -\> inferior vena cava -\> right atrium -\> AV valve -\> right ventricle -\> semilunar valve -\> pulmonary arteries -\> arterioles -\> capillaries -\> alveolus in the lungs -\> carbon dioxide is released -\> bronchioles -\> bronchi -\> trachea -\> larynx - epiglottis - pharynx -\> oral cavity