Plasma membrane
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MCAT
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
triacylglycerol and fatty acids:
where are they found?
Act as?
found in lower levels in the membrane act as phospholipid precursors
Function of glycerophospholipids
replace one fatty acid with a phosphate group which is often linked to other hydrophilic groups
cholesterol function in plasma membrane
lots of it in the membrane and it contributes to membrane fluidity and stability
waxes function in membrane
small ampunts if at all more common in plants function in water proofing and defince
transmembrane proteins vs embedded proteins vs membrane-associated proteins
transmembrane proteins:1 or more hydrophobic domains(usually receptors/channels)
embedded proteins: part of catalytic complex or involved in cell communication
membrane-associated proteins: may act as recognition molecules or enzymes
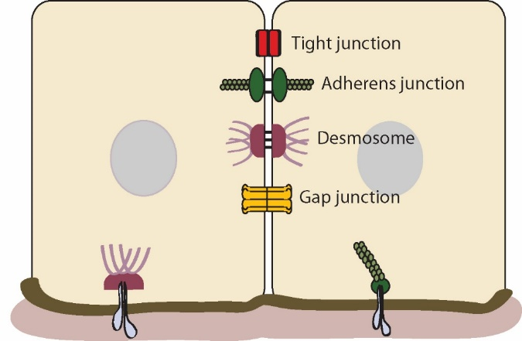
Gap junctions vs Tight junctions vs desmosomes and hemidesmosomes
Gap junctions: rapid exchange of ions and other small molecules between adjacent cells
Tight junctions: prevent paracellular transport not intercellular transport
desmosomes and hemidesmosomes anchor ⚓️ layers of epithelial tissues together

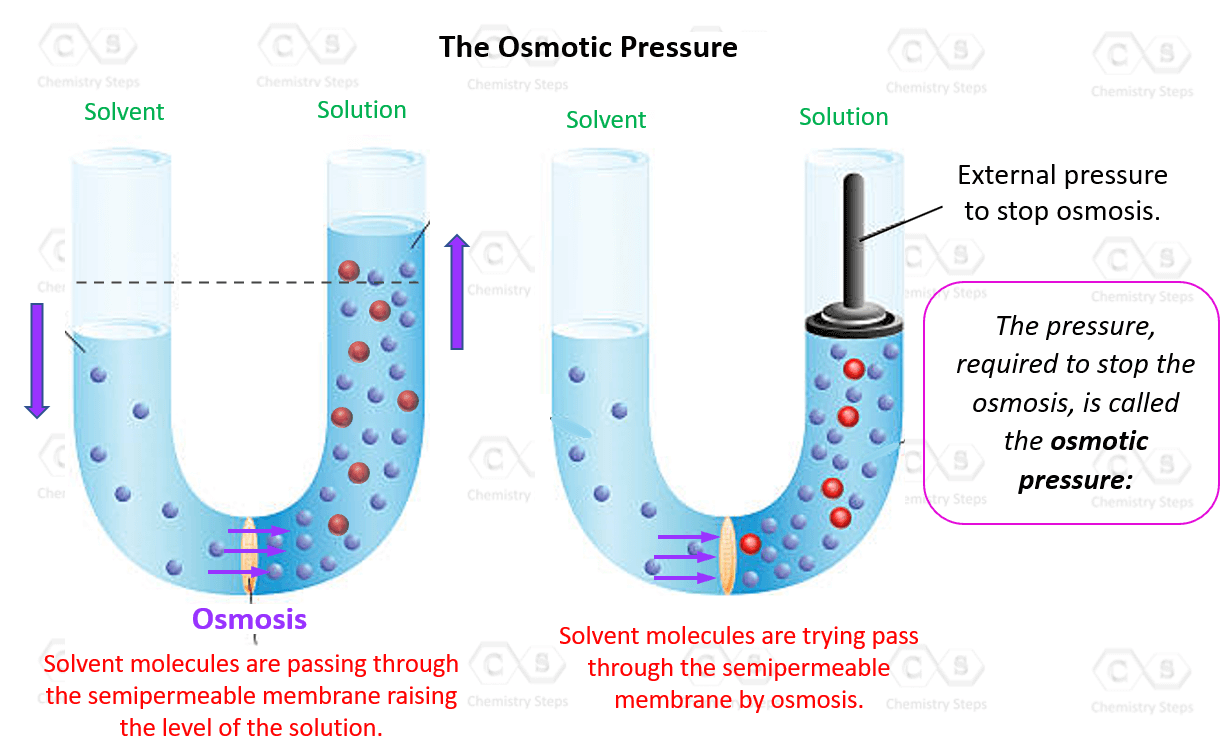
osmosis pressure
Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop the net flow of solvent (like water) across a semipermeable membrane from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated one, aiming to equalize solute concentrations
passive vs active (primary and coupled \)
Passive transport: higher concentration to lower (simple diffusion doesn’t require transporter, osmosis is water fusion across selective membrane and facilitated diffusion require transporter)
Active primary requires ATP secondary or coupled is when the the movement of two substances across a cell membrane simultaneously, where the energy from one substance moving down its concentration gradient powers the other substance's movement, often against its own gradient
Na+/ K+ATPase ration of ions in vs out
main function is to maintain low concentration of sodium (Na+) ions and high concentration of (K+) ions in the cellby pumping 3 sodium out for every 2 potacium in this maintains negtive charge in the cell
trans phospholipid does not contribute to membrane fluidity because…
trans increases melting point and decreases membrane fluidity