APAH Byzantine, Early christian, Islamic Art & architecture
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ap art history
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Early Christian/Antiquity Time Period
200-550 AD
Byzantine Art Time period
500-1453 AD
Islamic Time period
630 AD-Present
5 Pillars of Islamic Faith
Faith - no god but Allah, Muhammad is his messenger; Prayer - (salat) 5 times daily; Charity - (Zakat) purification or growth; Fasting - during the month of Ramadan; Pilgrimage - (Hajj) traveling to Mecca.
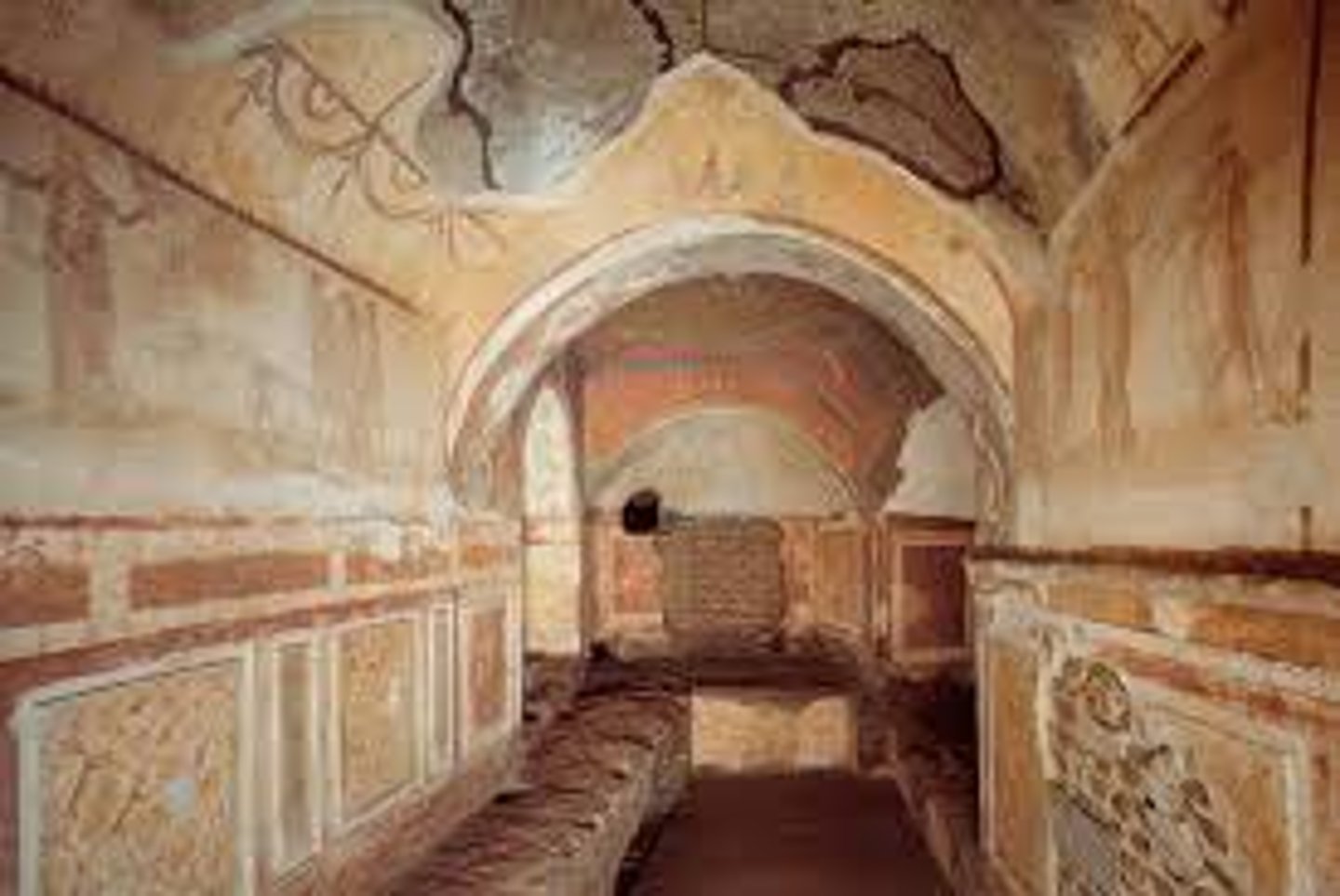
Catacomb of Priscilla
Early Christian burial site in Rome, notable for its frescoes and architecture.

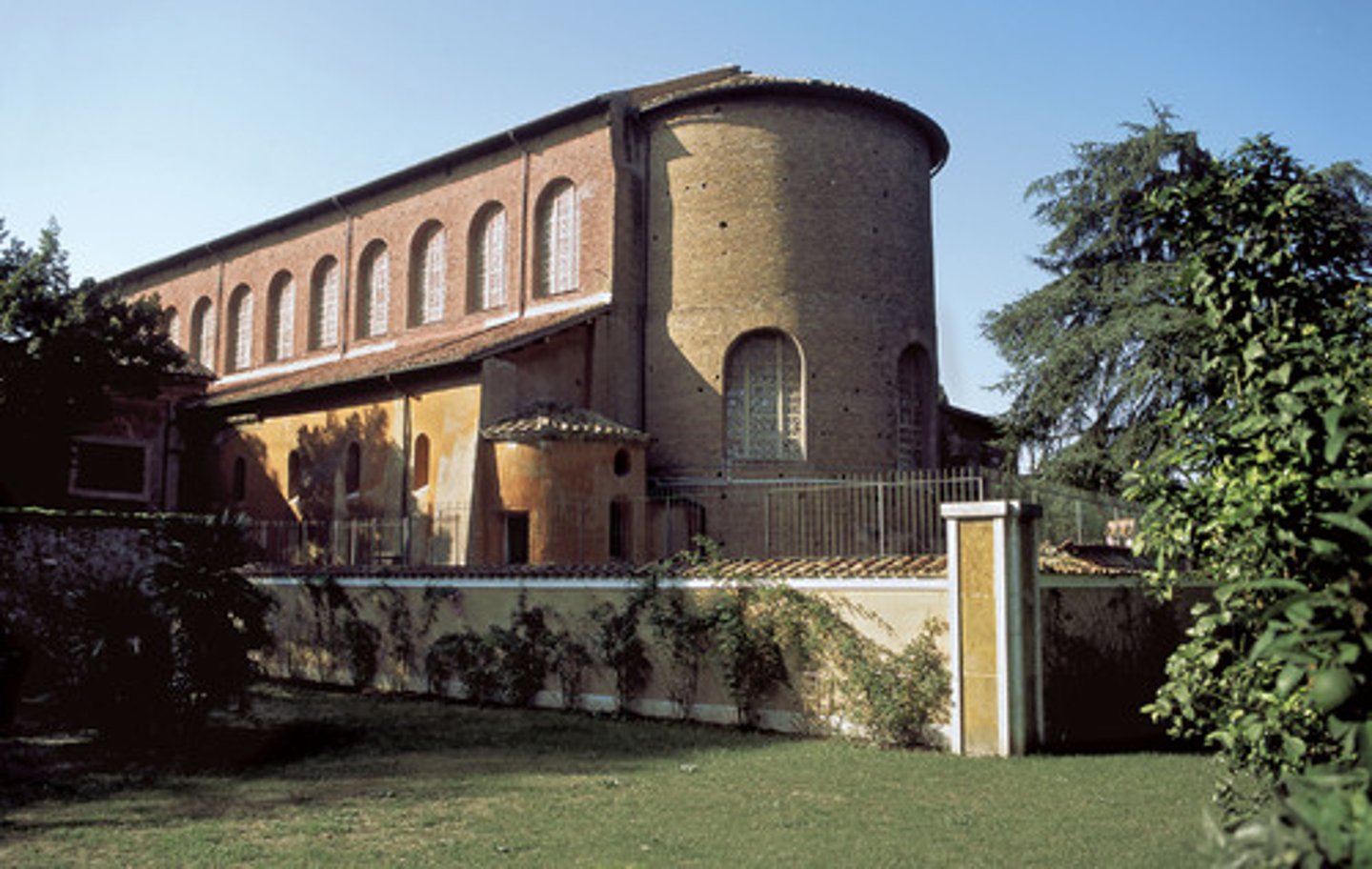
Santa Sabina
Early Christian basilica in Rome, notable for its simple, vast interior and use of early Christian architecture.

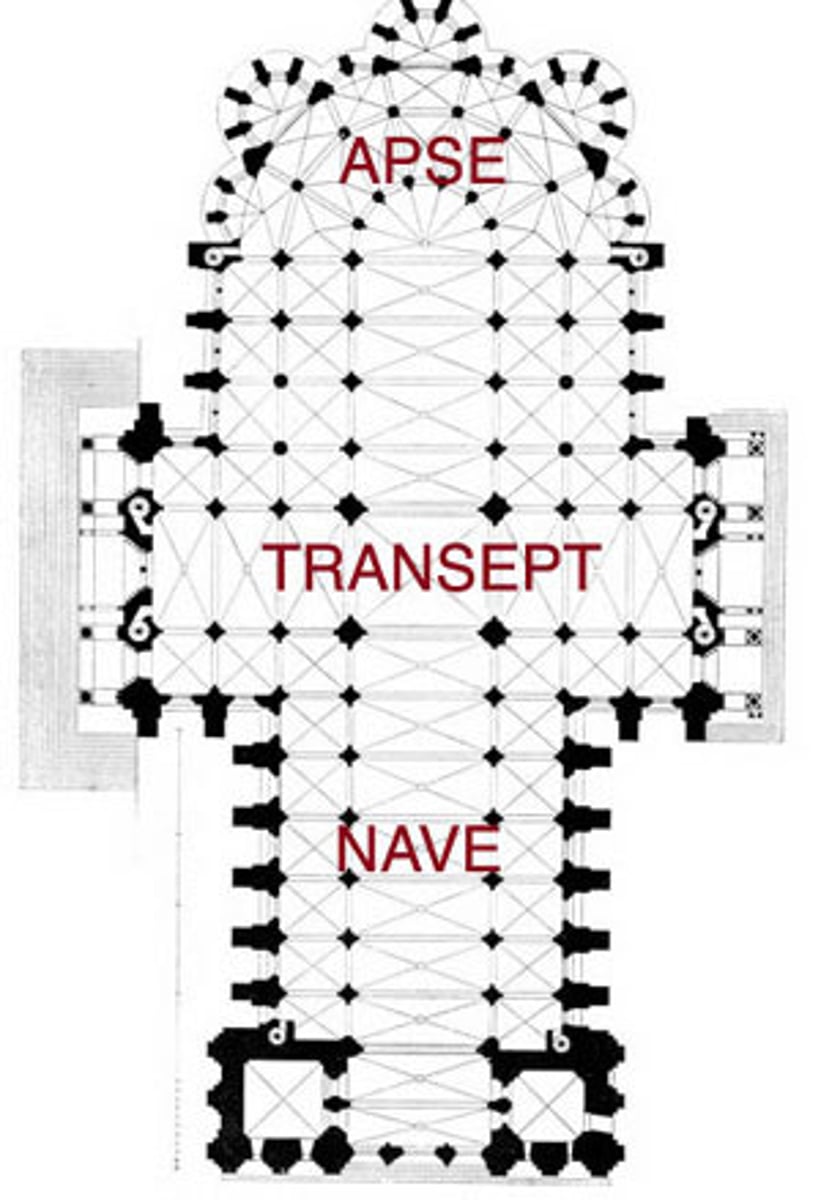
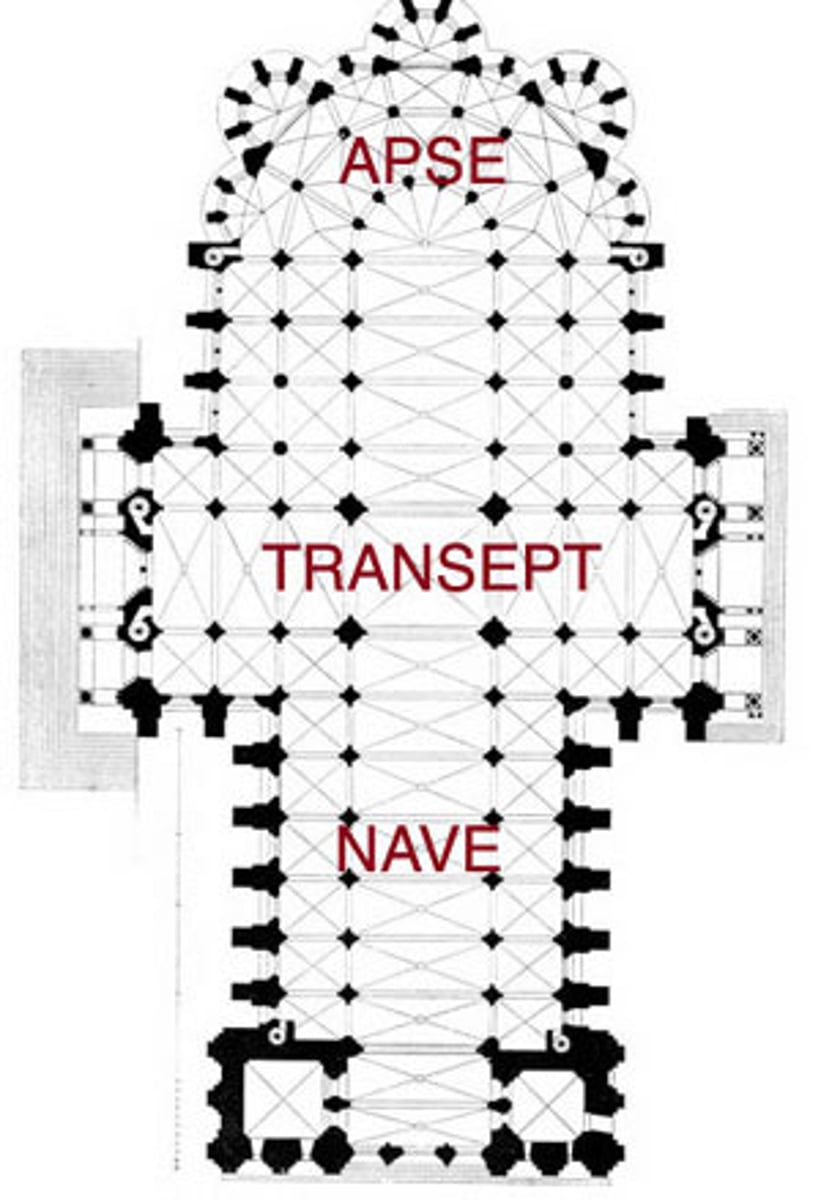
Apse
A semicircular or polygonal architectural feature, often found at the end of a Christian church, housing the altar.
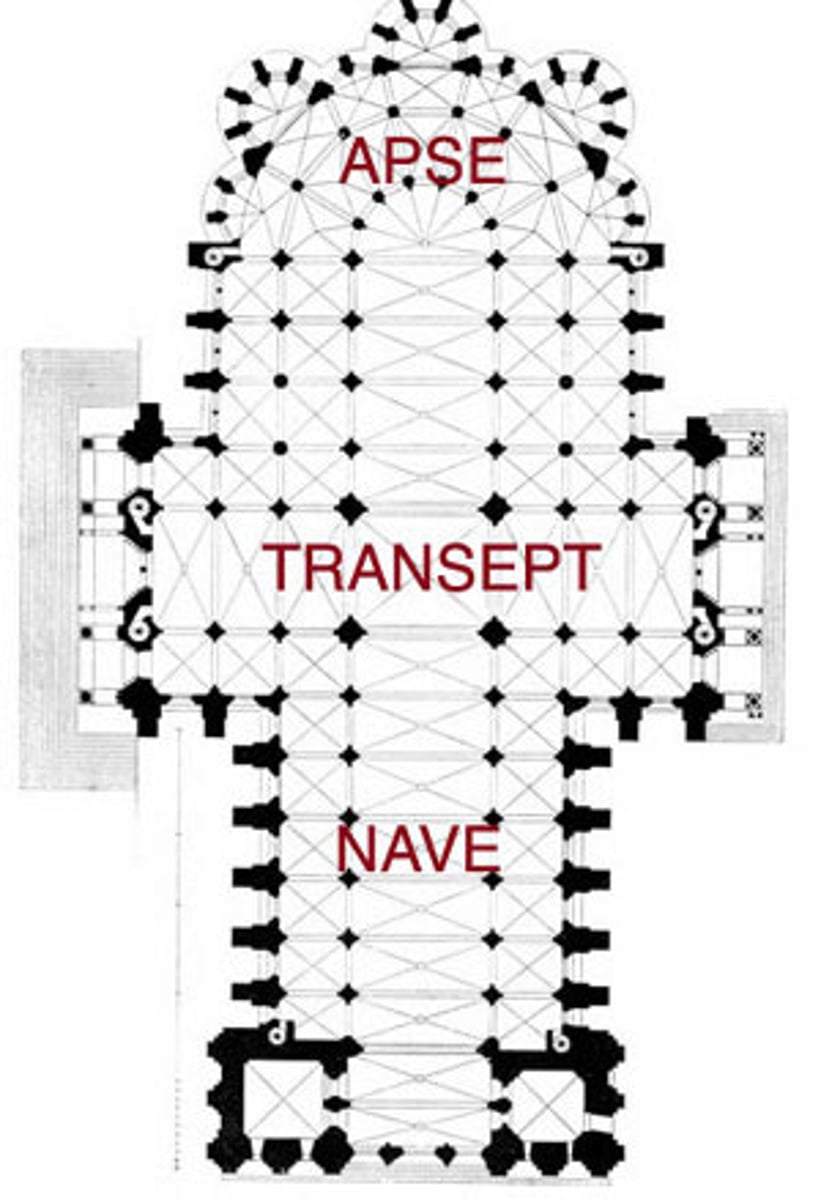
Atrium
A large open space in front of or within a building, often seen in Roman and early Christian church architecture.
Axial Plan
A layout for buildings, particularly churches, where the central axis leads directly to the altar or main focal point.
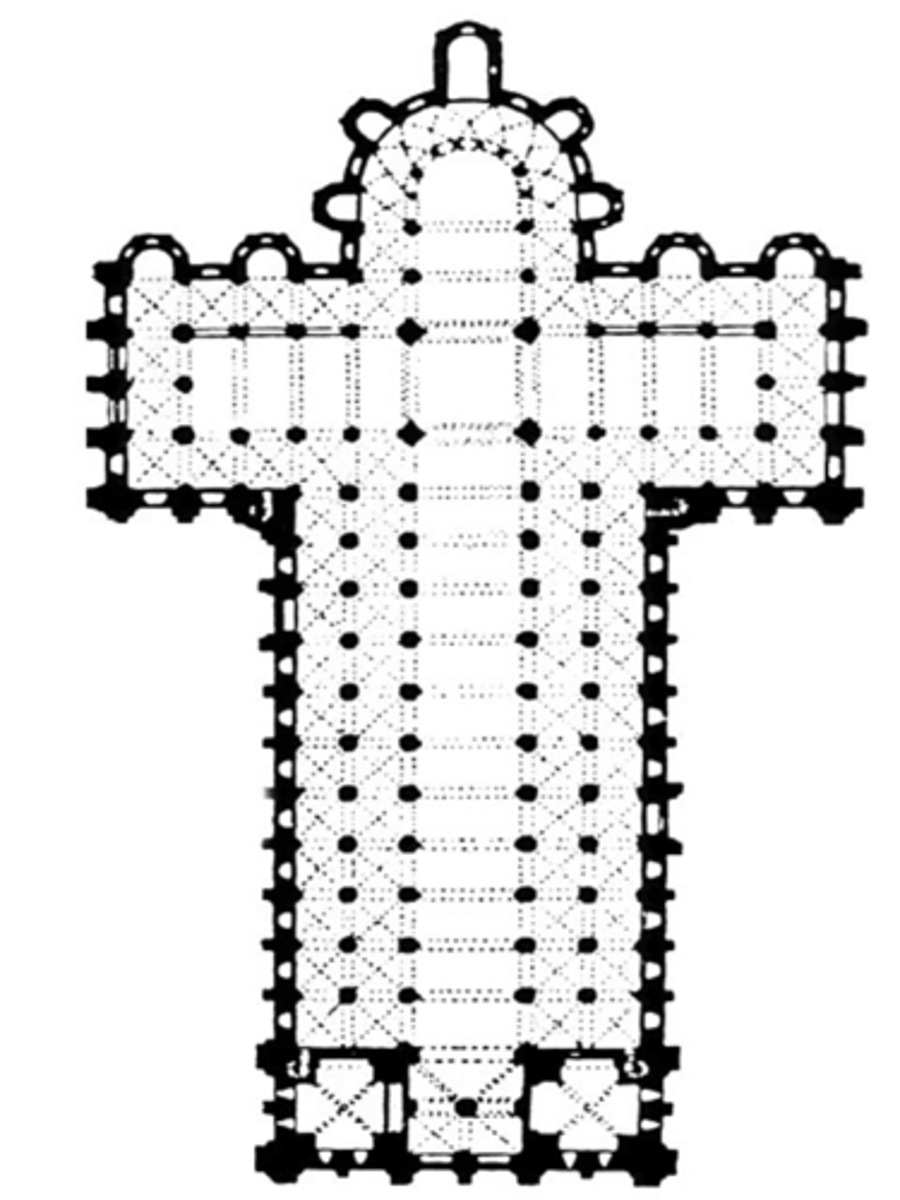
Catacomb
Underground burial sites used by early Christians, often featuring wall paintings and frescoes.
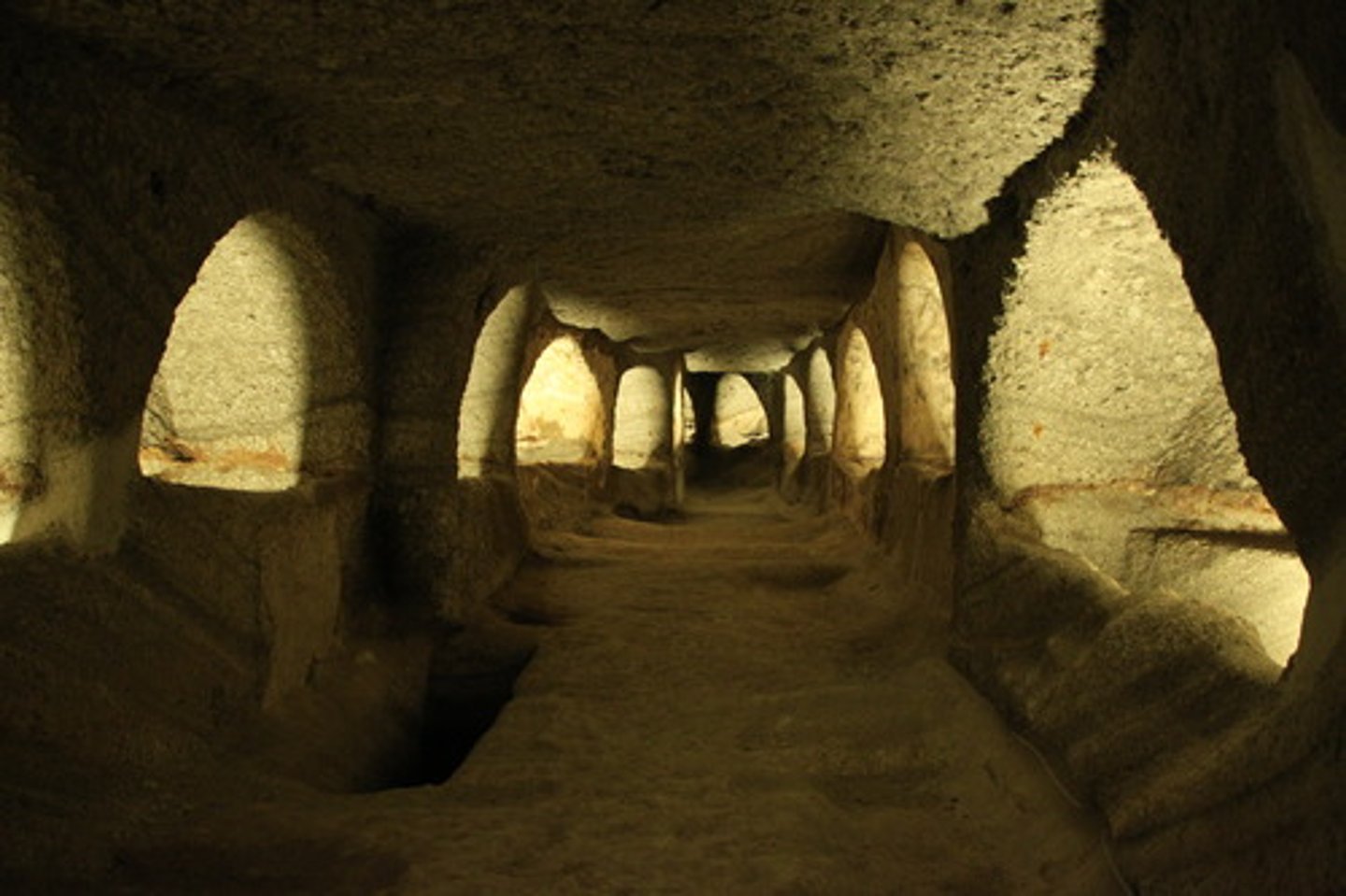

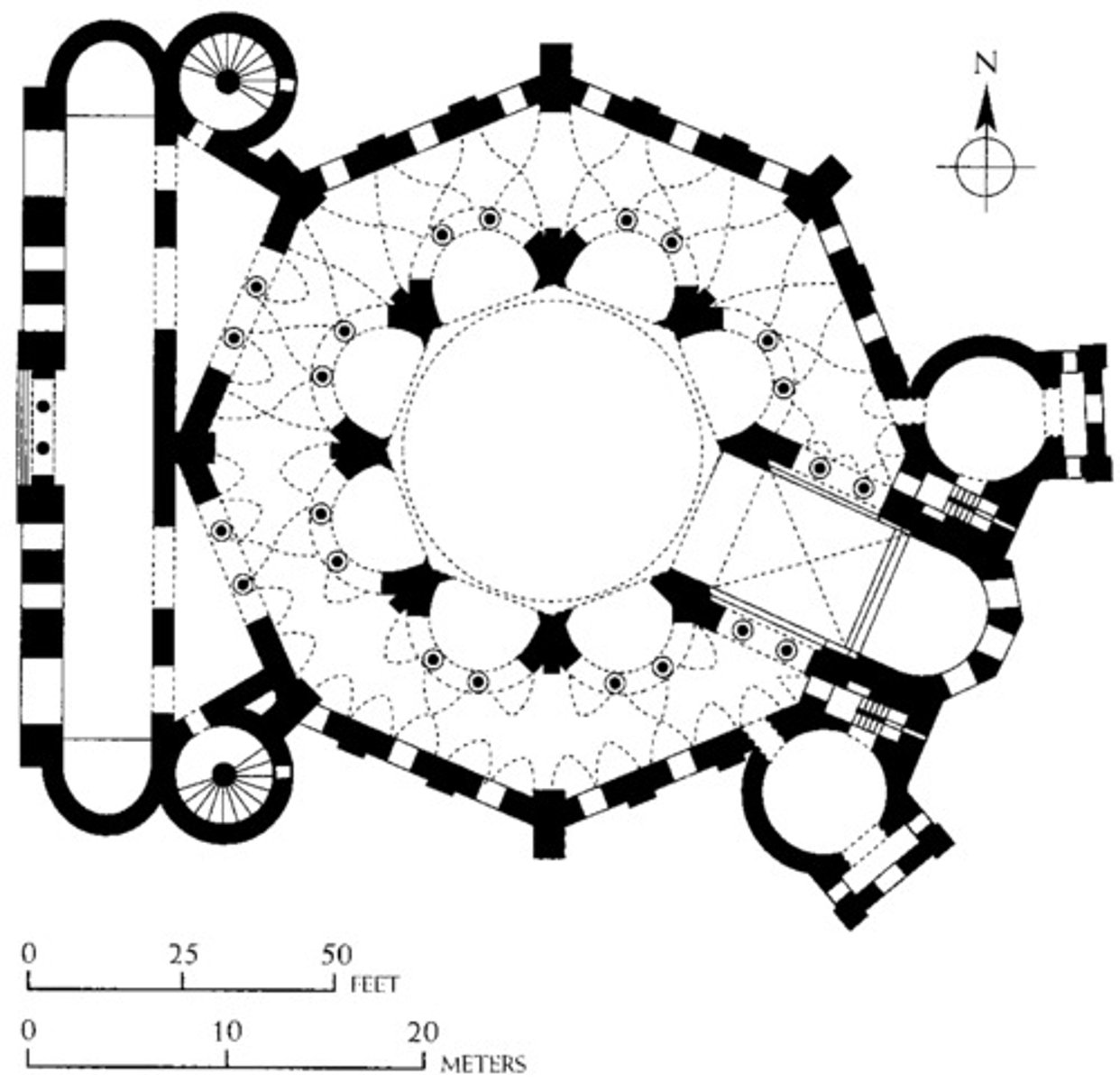
Central Plan
A layout where the structure is designed around a central point, commonly used in churches and shrines.
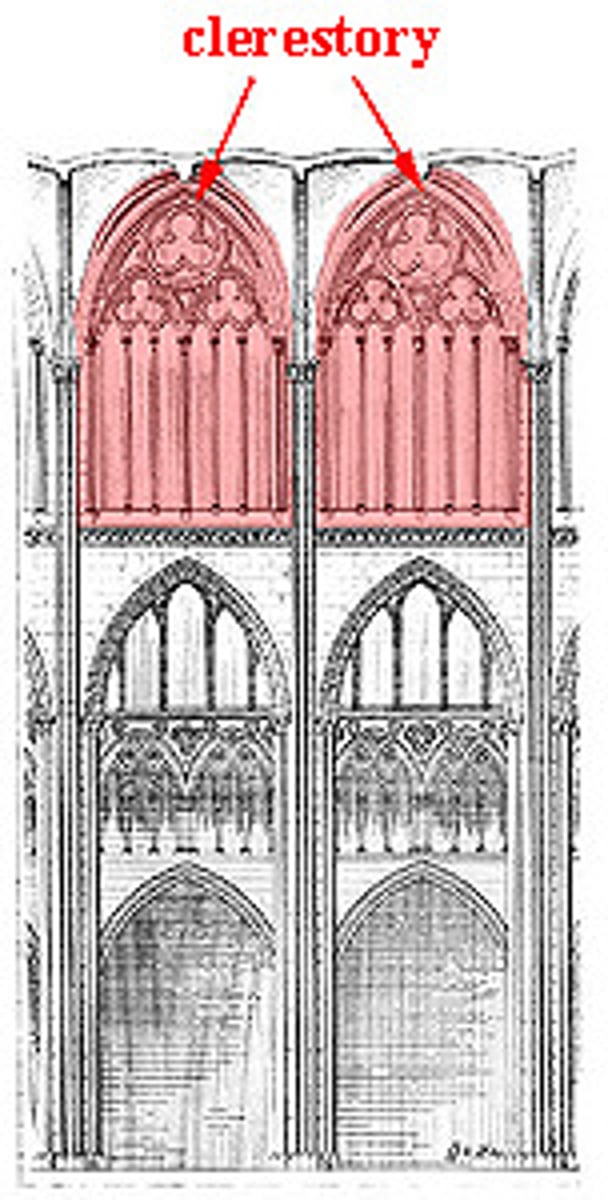
Clerestory
Upper part of a church or hall that contains windows, allowing light into the interior.
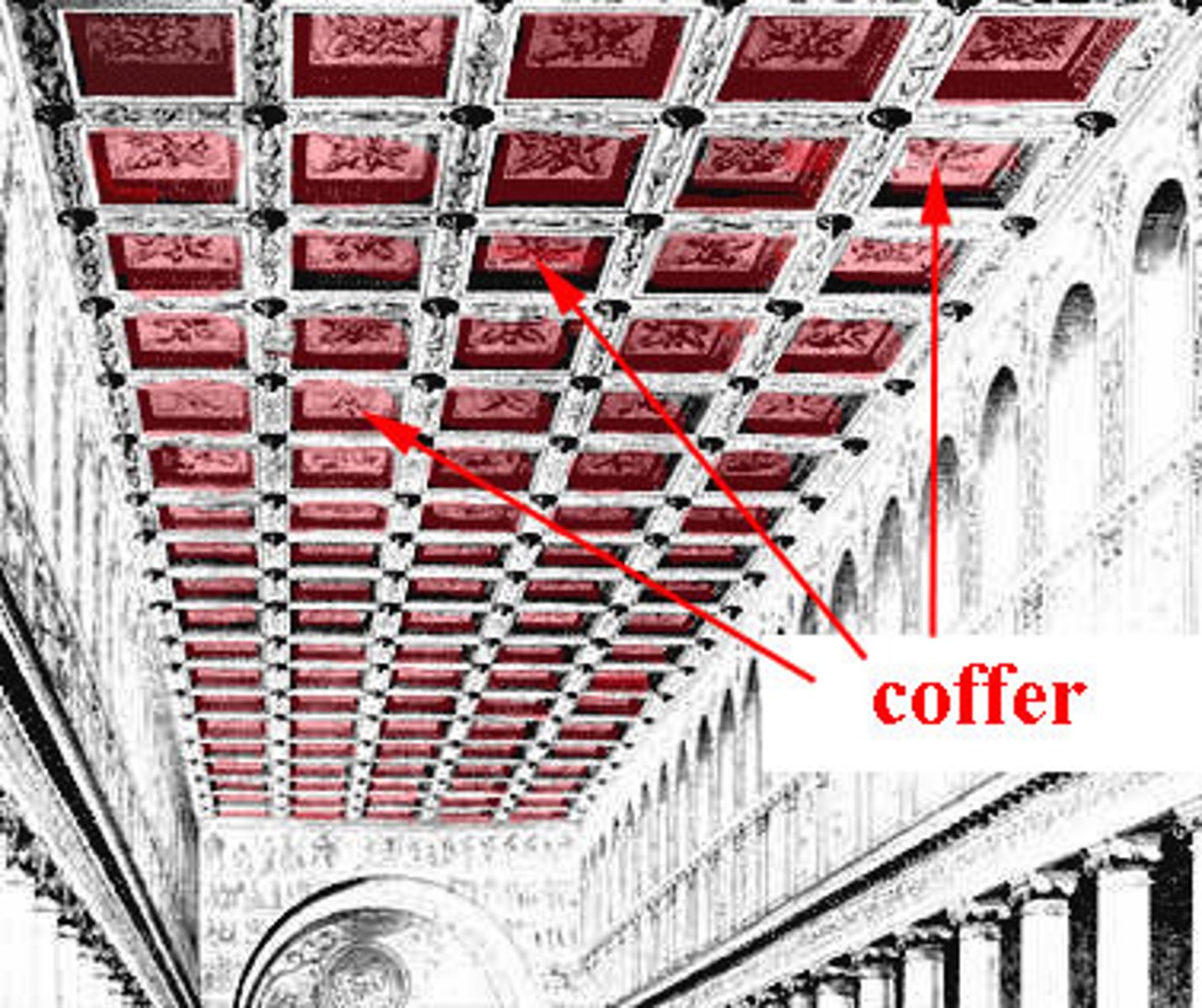
Coffer
A recessed panel in a ceiling or dome, often used for decorative or structural purposes.
Cubicula
Small, private rooms or burial chambers in catacombs.
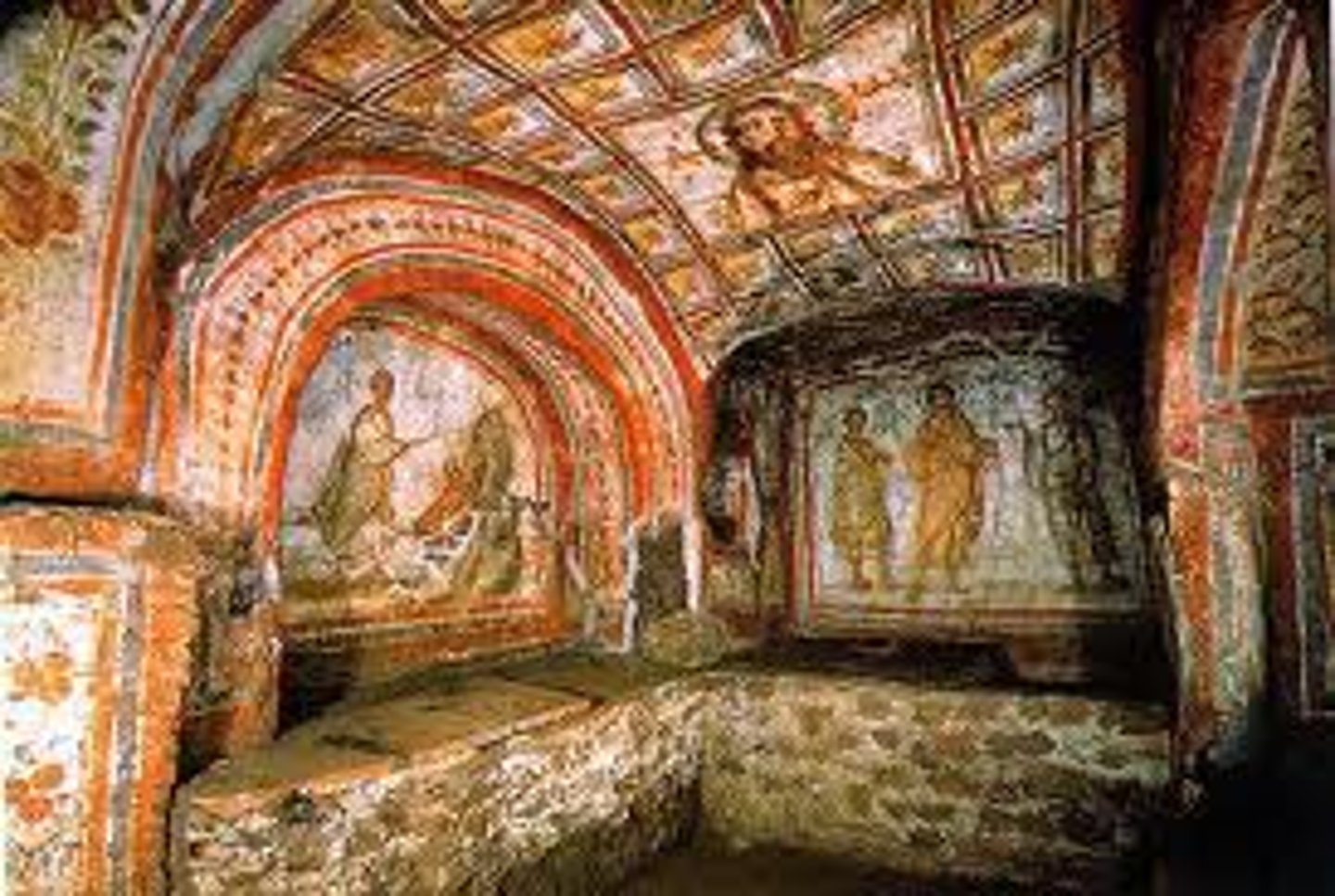

Gospels
The first four books of the New Testament in the Bible—Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John—accounting for the life and teachings of Jesus Christ.
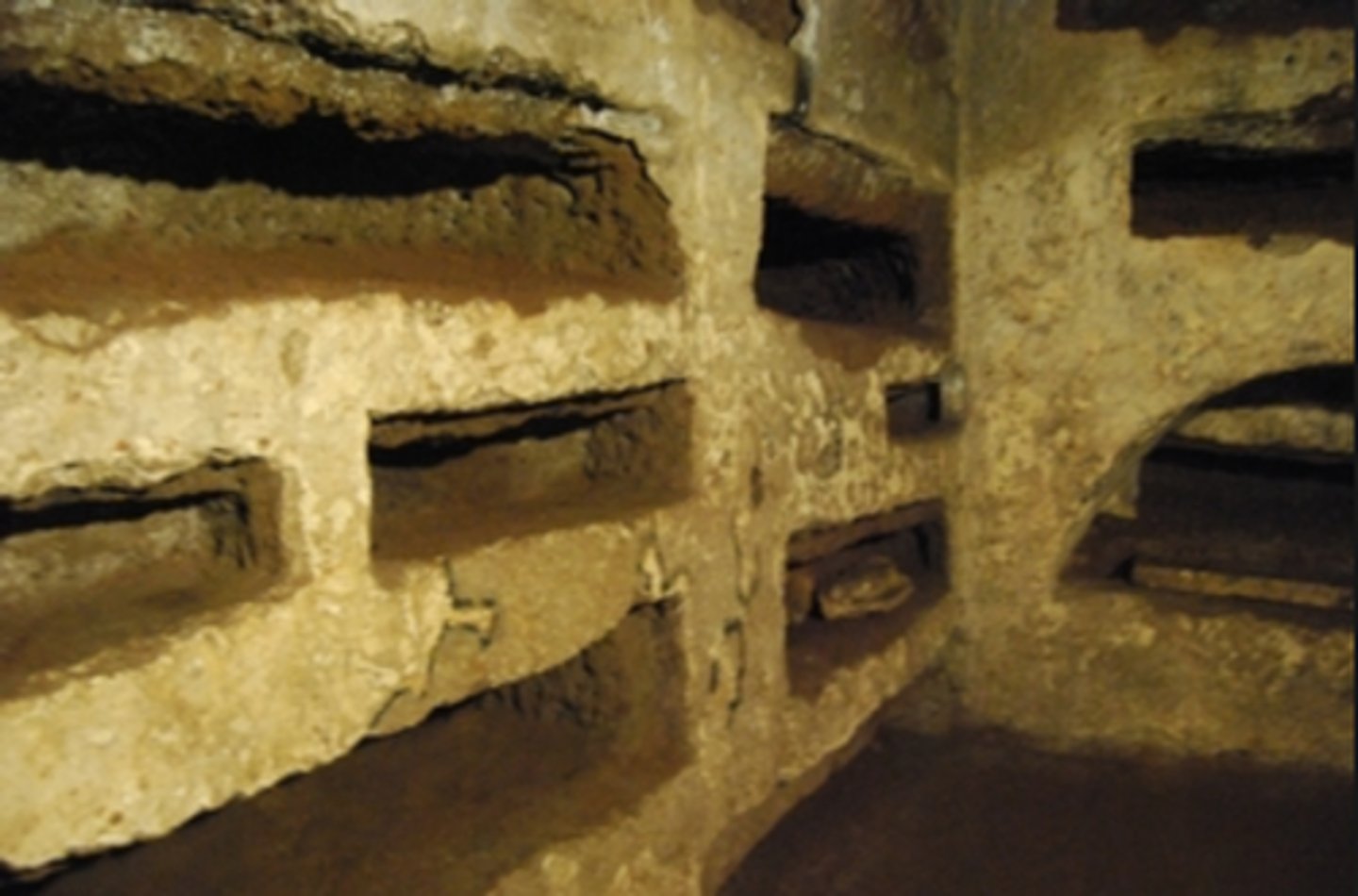
Loculi
Horizontal niches in the walls of catacombs, used for placing the deceased.

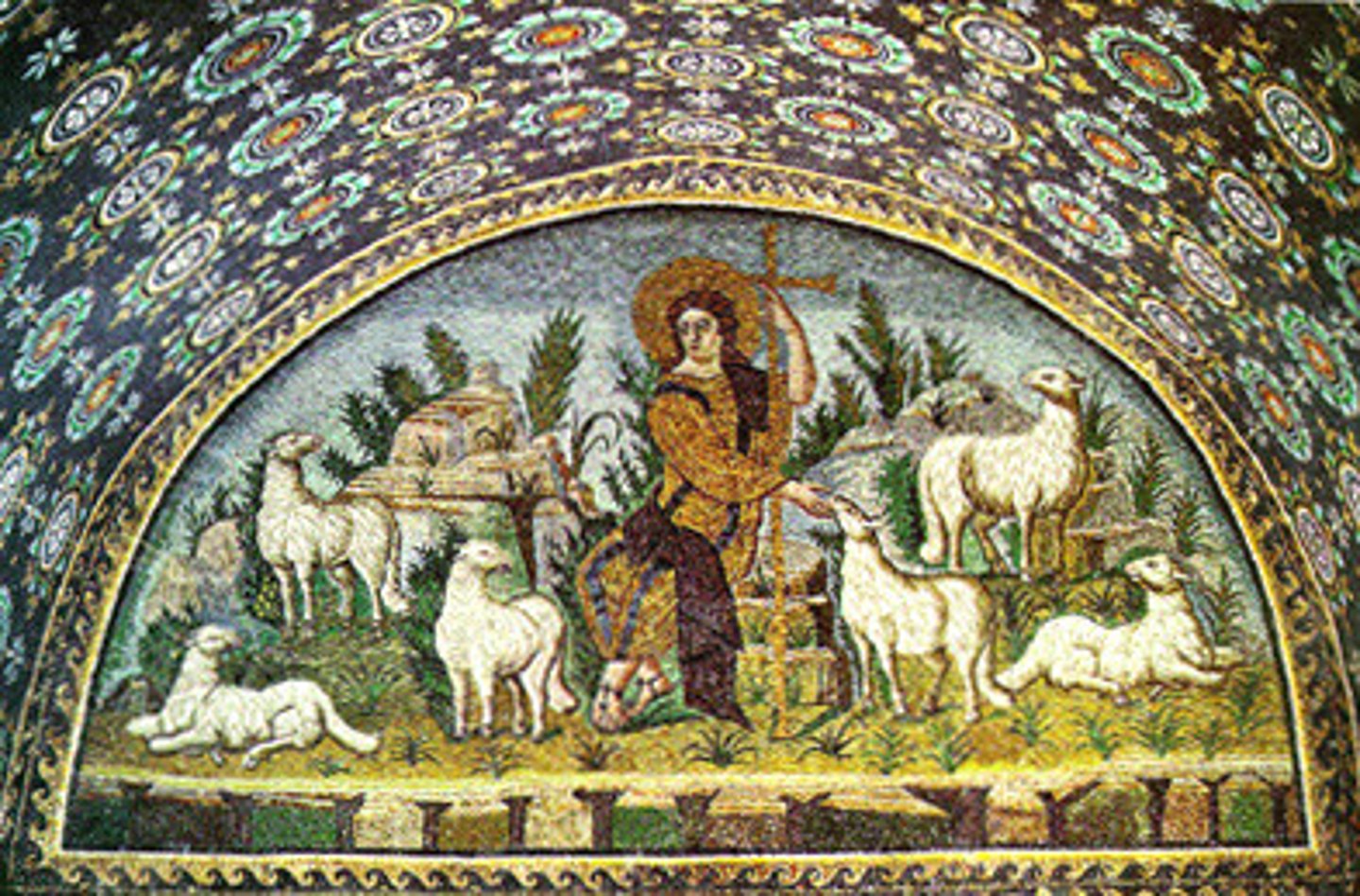
Lunette
A crescent-shaped space, often found above a door or window, frequently decorated with frescoes or mosaics.

Narthex
The entrance or lobby area of a church, located at the front of the building.
Nave
The central hall of a church, typically extending from the entrance to the altar.
Orant Figure
A figure with arms raised in prayer, commonly seen in early Christian art.
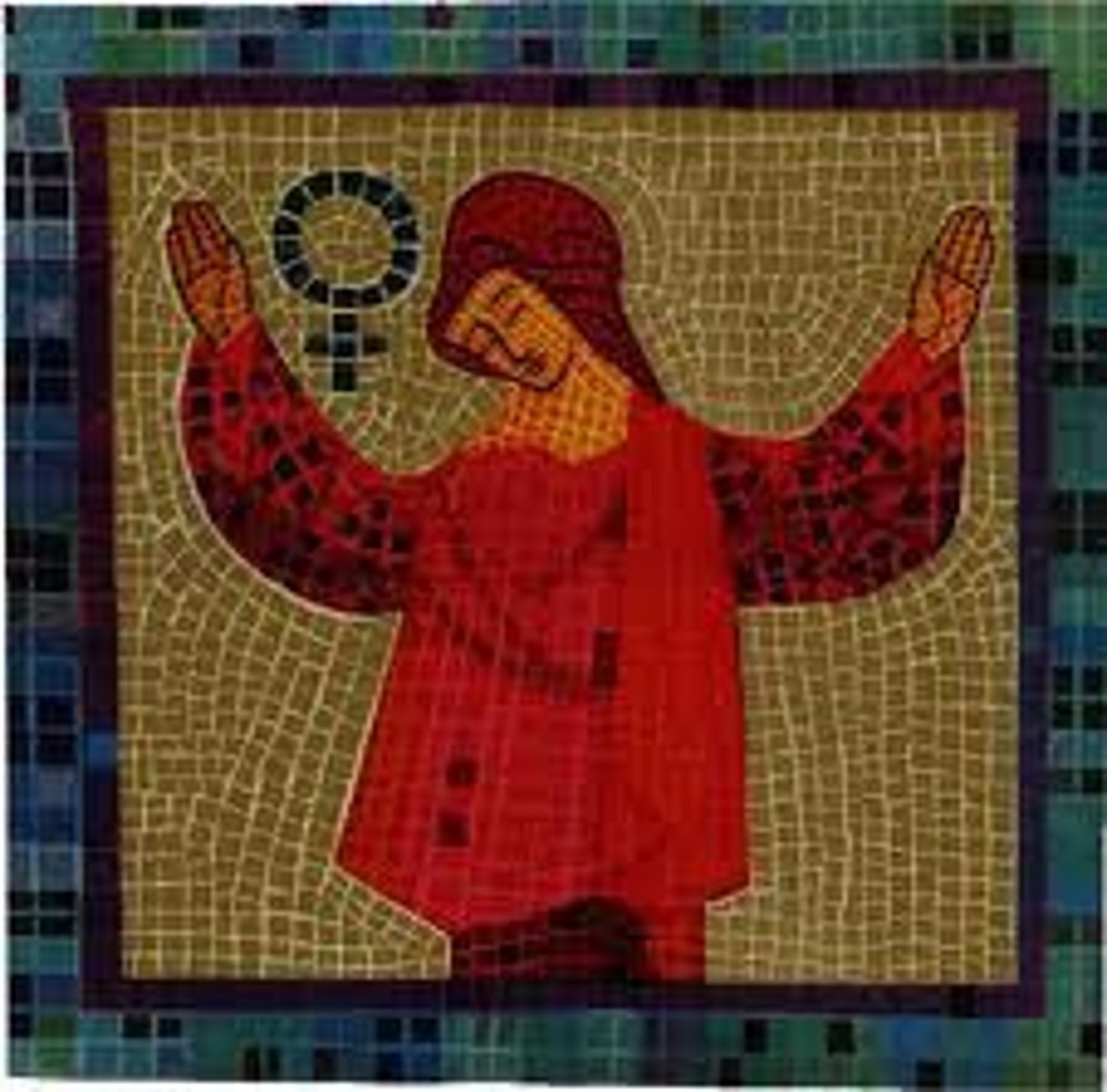

Spolia
The reuse of older building materials, sculptures, or architectural elements in new structures, often as a symbol of power or continuity.
Transept
The arms of a cruciform church that intersect the nave, creating a cross-shaped floor plan.
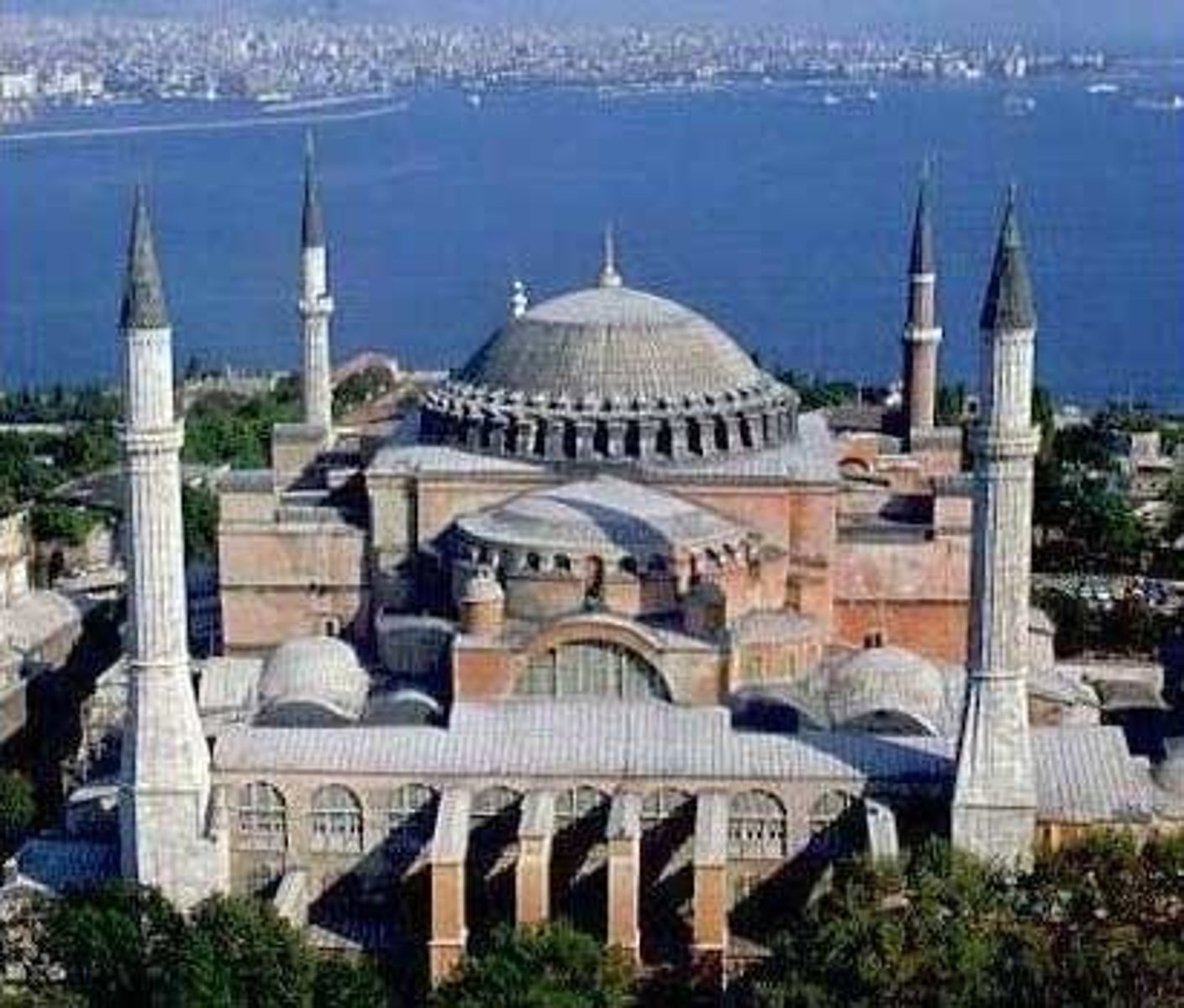
Hagia Sophia (Building & Ground Plan)
A monumental Byzantine church in Istanbul, originally constructed as a Christian cathedral, later converted to a mosque, and now a museum. Known for its vast dome and innovative engineering.

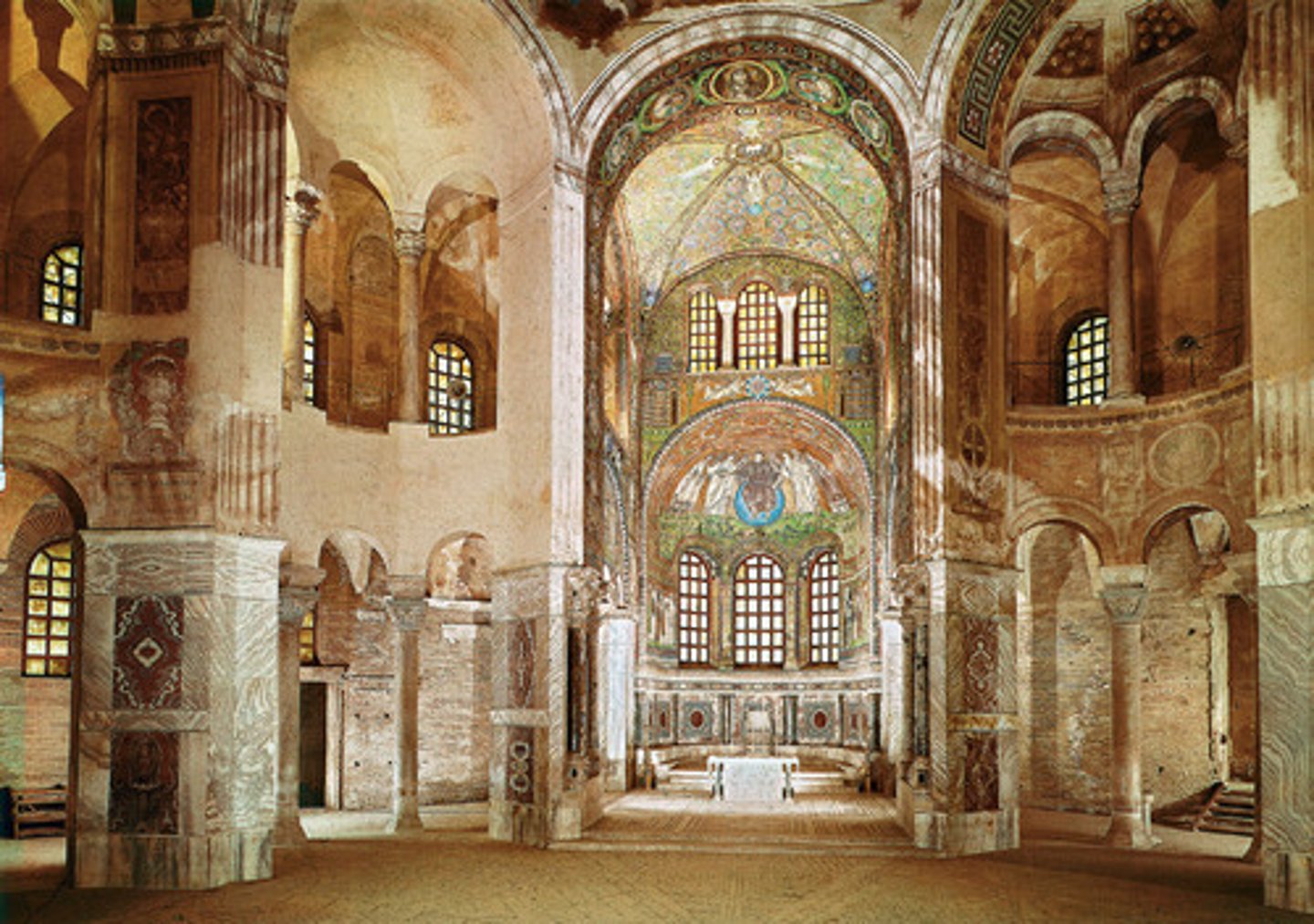
San Vitale (Church & Ground Plan)
A central-plan church in Ravenna, Italy, renowned for its mosaics and unique octagonal shape.

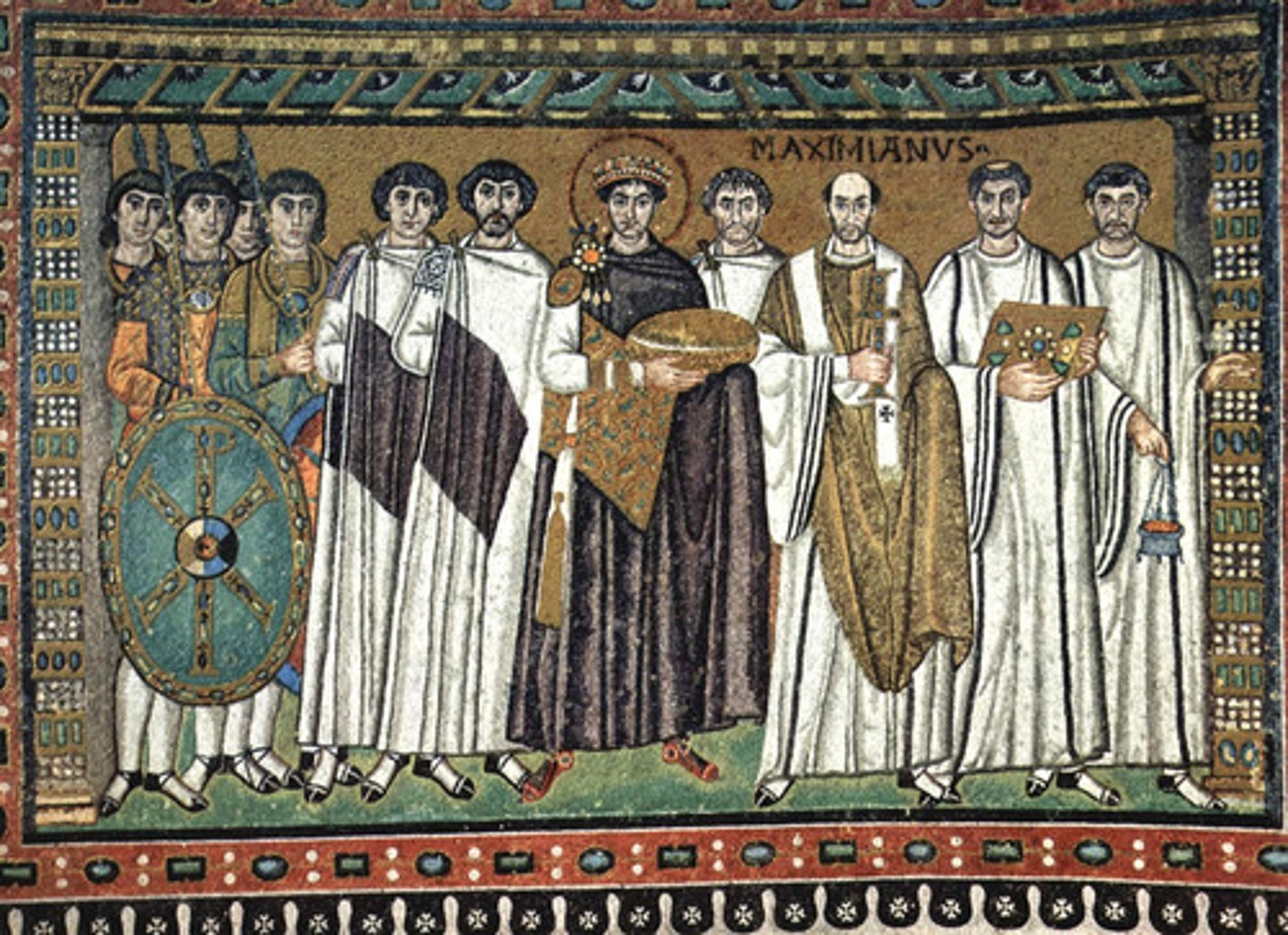
Justinian and Attendants
A famous mosaic in San Vitale depicting the Byzantine emperor Justinian, his attendants, and clergy, symbolizing imperial and religious authority.

Theodora and Attendants
A mosaic in San Vitale depicting Empress Theodora with her attendants, showing her influence and power within the Byzantine court.
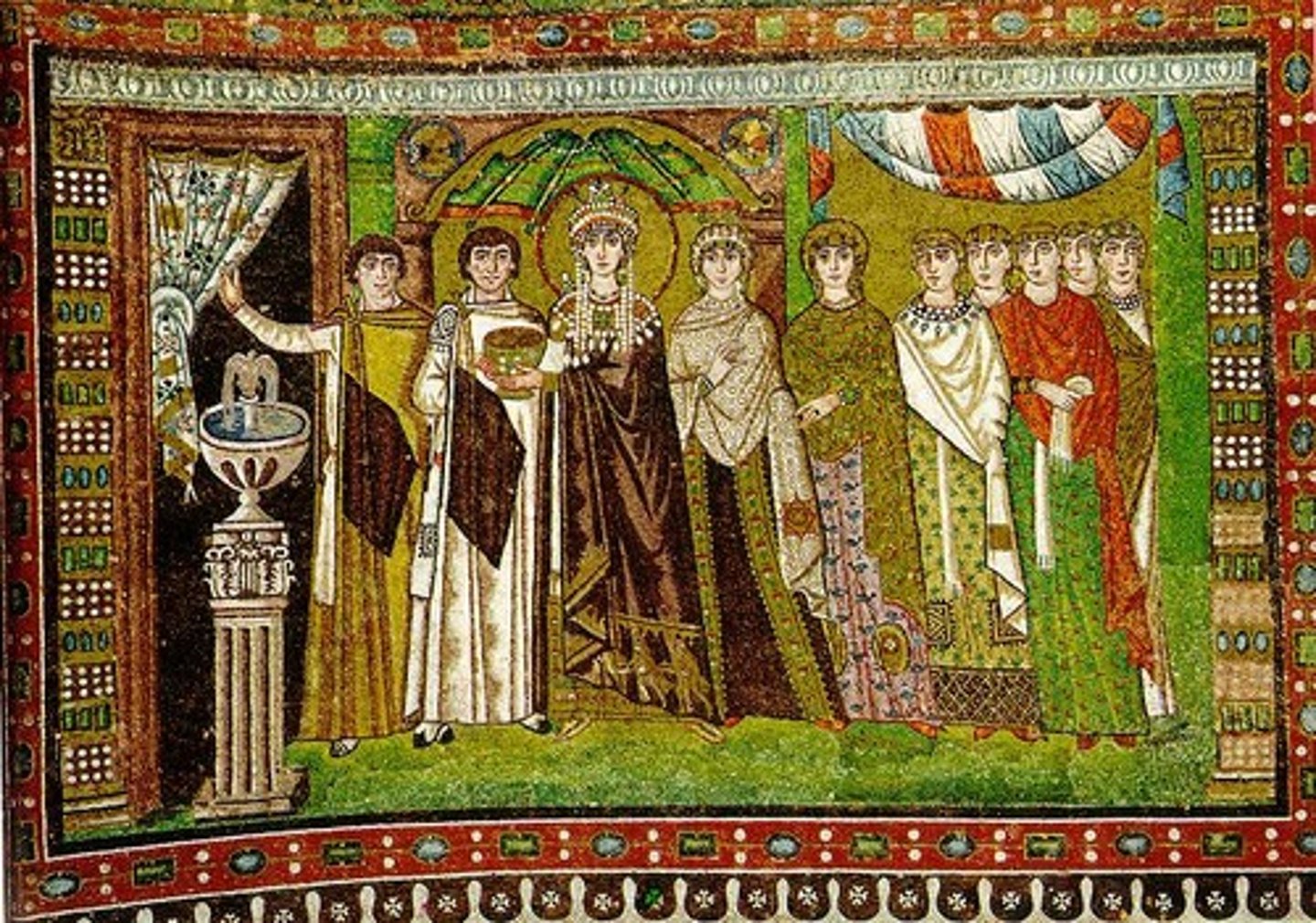

Virgin (Theotokos) and Child between Saints Theodore and George
A Byzantine icon depicting the Virgin Mary and Child flanked by two saints, emphasizing the veneration of Mary (Theotokos) in Christian iconography.
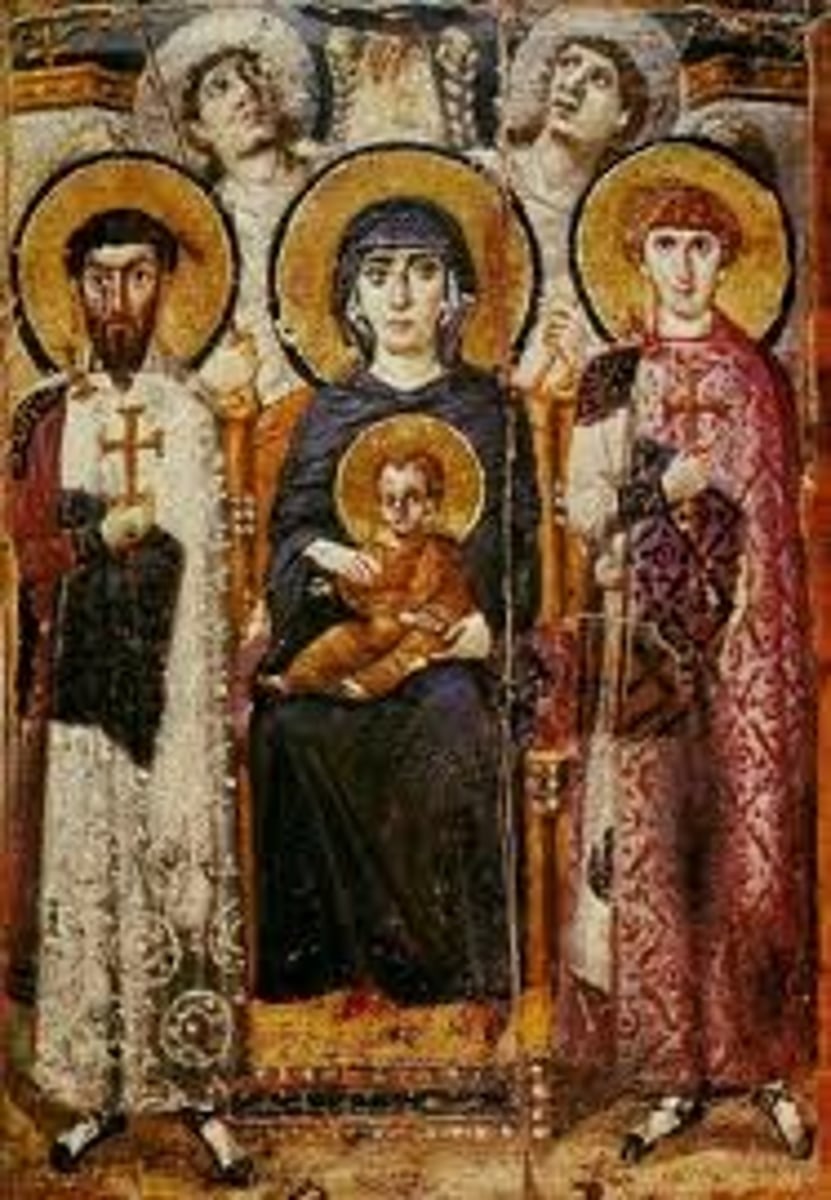

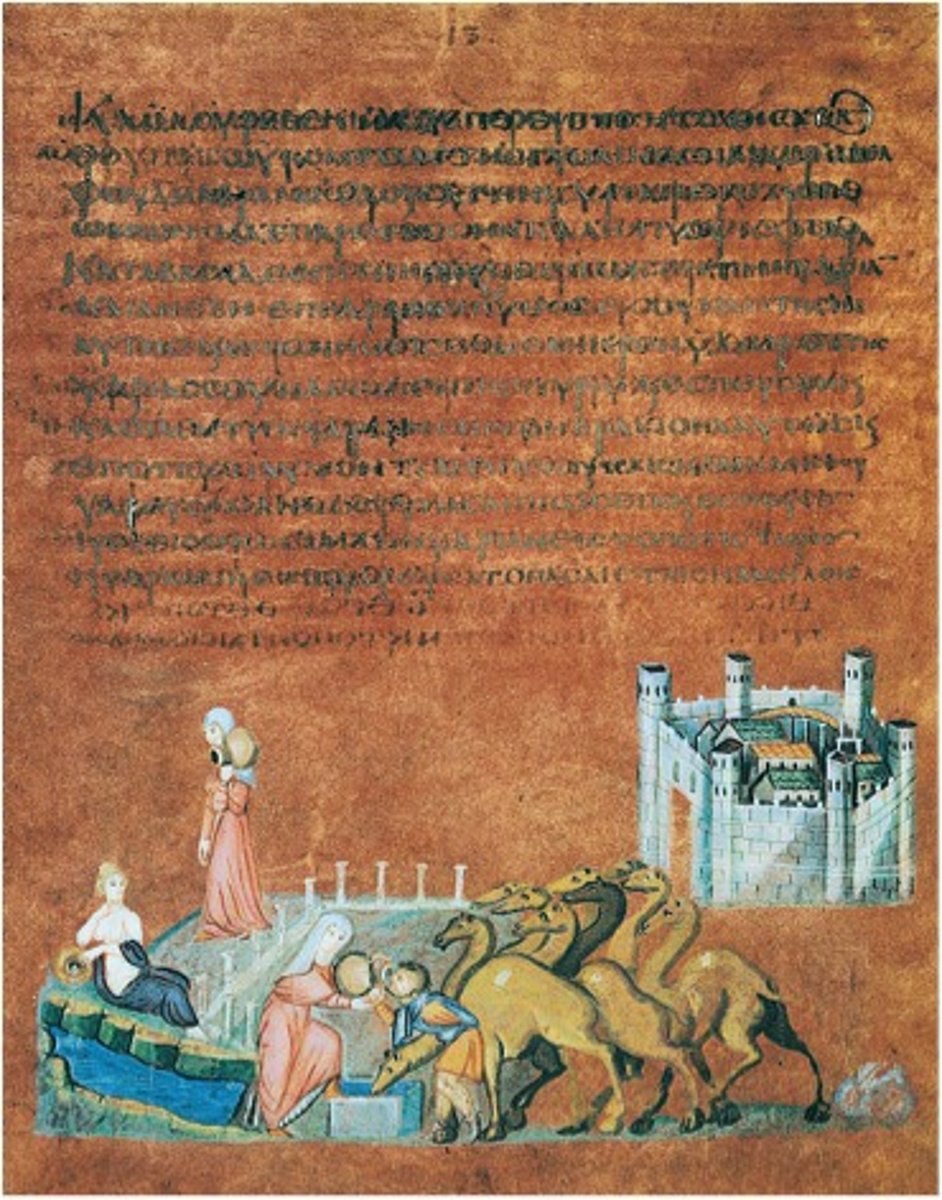
Rebecca and Eliezer at the Well from the Vienna Genesis
A scene from the illuminated manuscript known as the Vienna Genesis, depicting the Biblical story of Rebecca and Eliezer.
Jacob Wrestling the Angel
A narrative scene from the Bible, often depicted in Early Christian and Byzantine art, illustrating the struggle between Jacob and an angel.

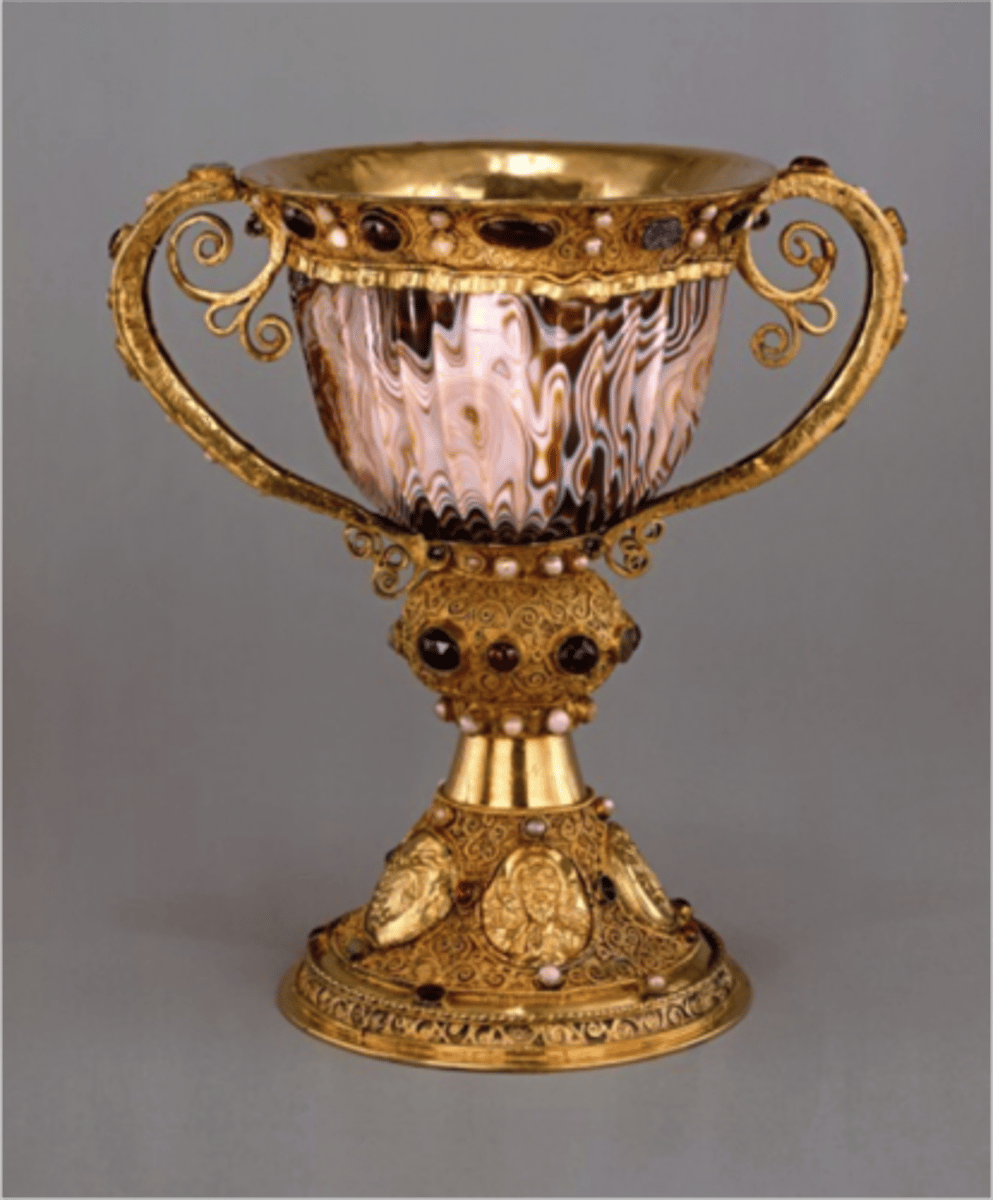
Chalice
A large cup used in Christian liturgical ceremonies to hold wine, representing the blood of Christ during the Eucharist.

Codex
An early form of a book, made of bound pages, used in place of scrolls in ancient times.

Eucharist
A Christian sacrament commemorates the Last Supper, where bread and wine are consecrated and consumed as the body and blood of Christ.
Icon
A religious image or painting, particularly in the Eastern Orthodox Church, often depicting saints or Christ.
Iconoclasm
The deliberate destruction or rejection of religious images or icons, often associated with the Byzantine Iconoclast Controversy.
Mosaic
Artwork created by arranging small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials to form a picture or design.
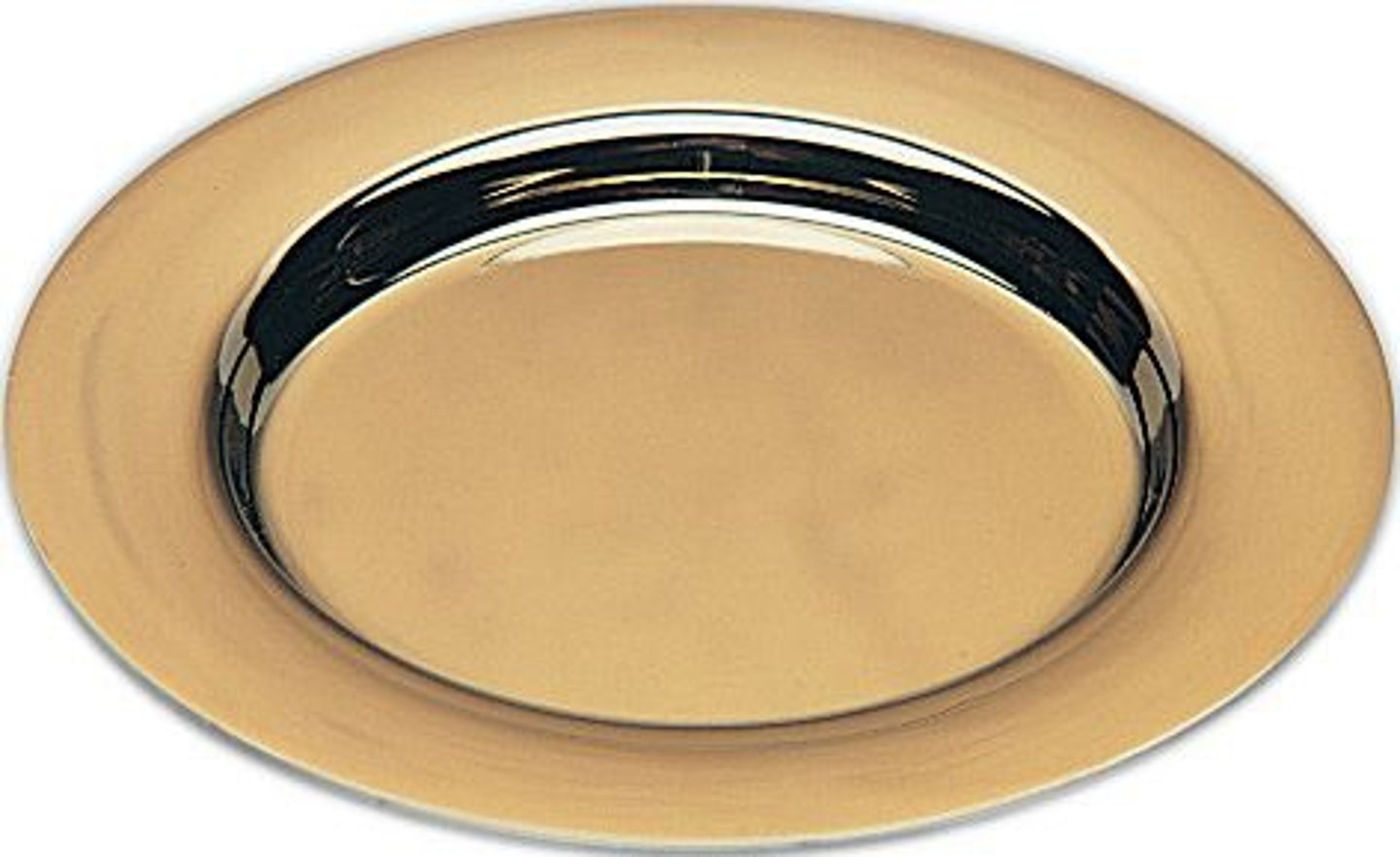
Paten
A flat, shallow dish used in Christian liturgy to hold the Eucharistic bread.

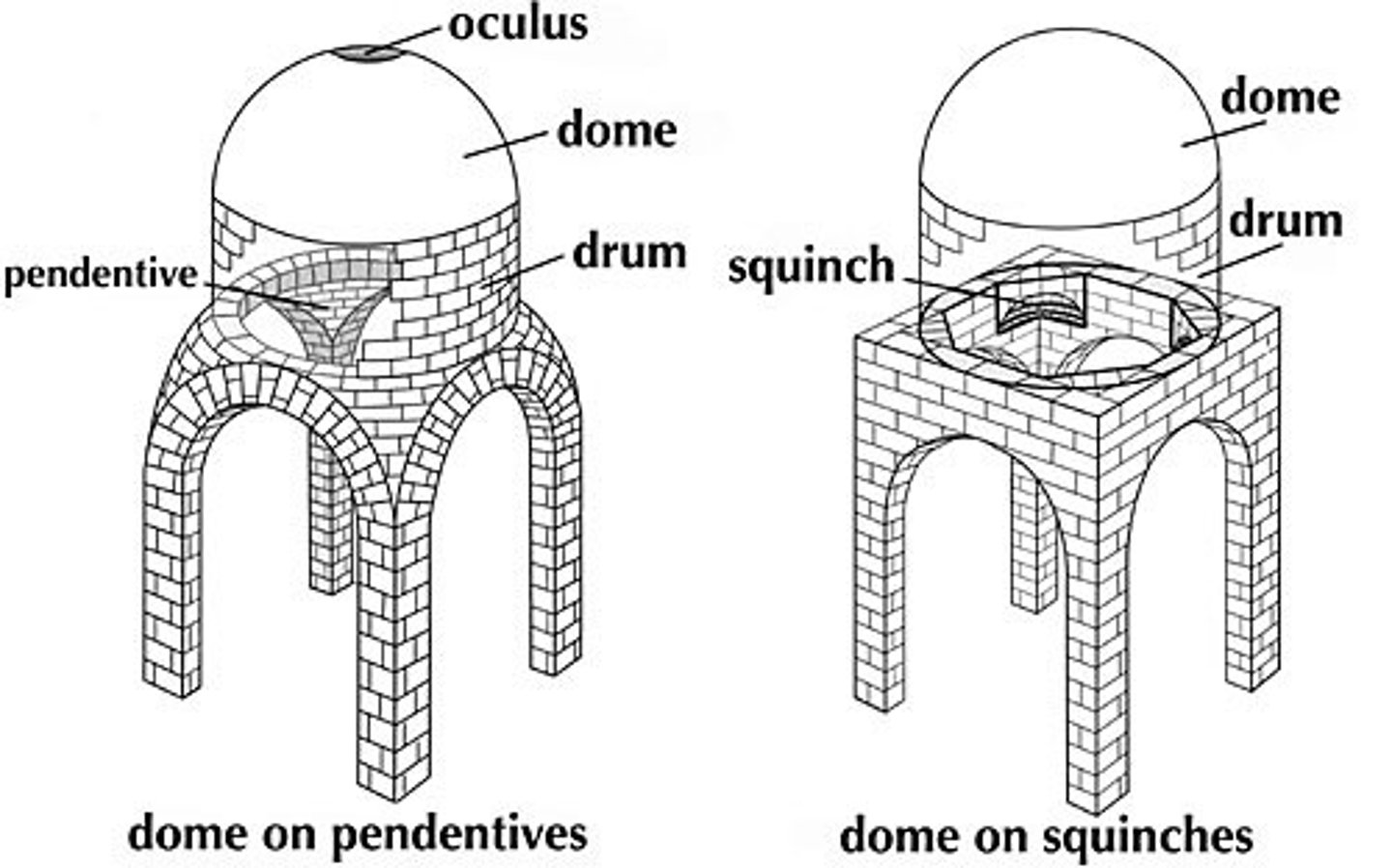
Pendentive
A spherical triangle of masonry that supports a dome, transitioning from the square base to the circular base of the dome.
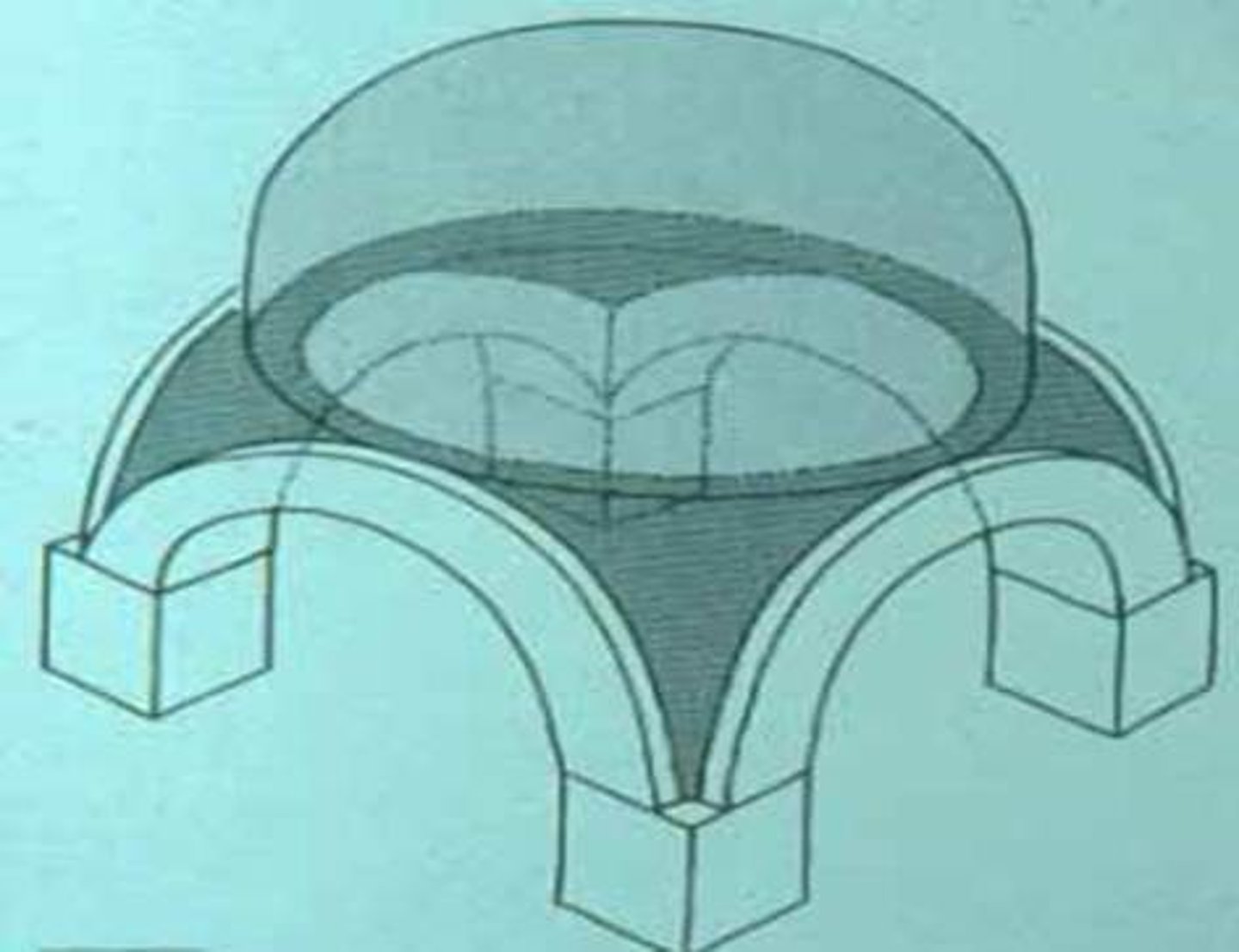
Squinch
A construction feature used to support a dome, usually through the use of pendentives or arches.
Theotokos
A title for the Virgin Mary, meaning 'God-bearer' or 'Mother of God' in Greek.
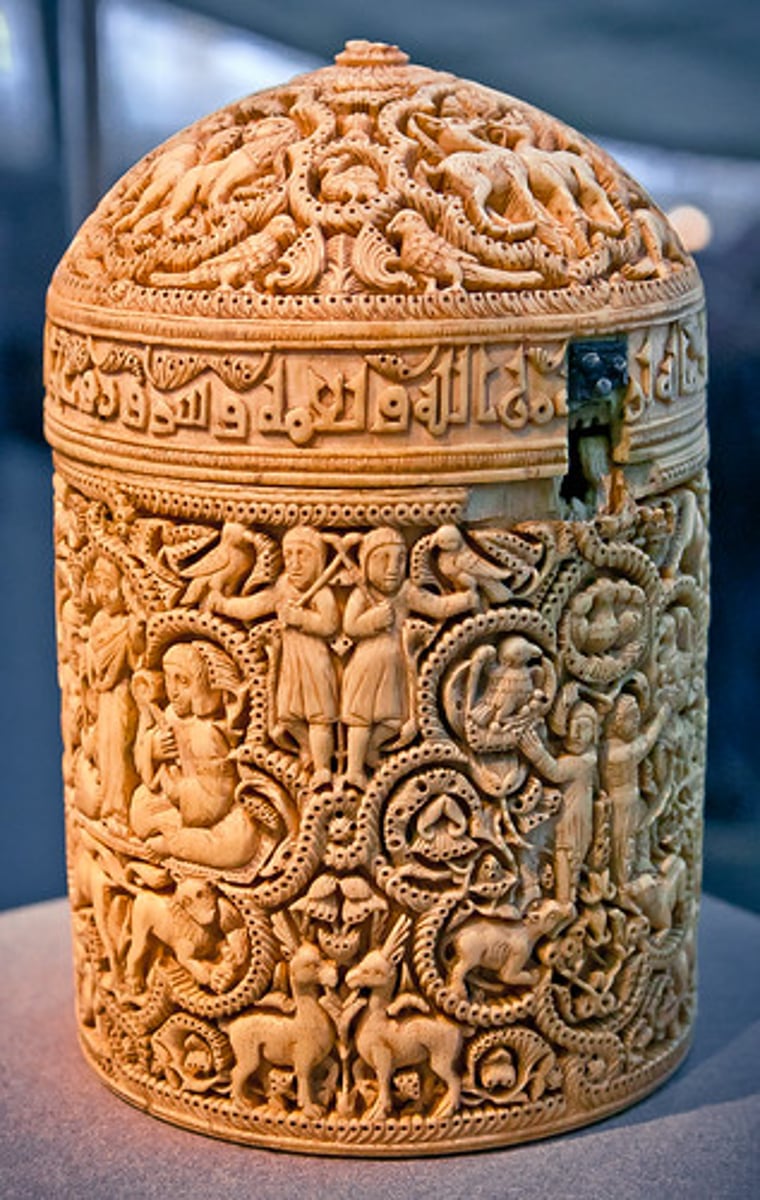
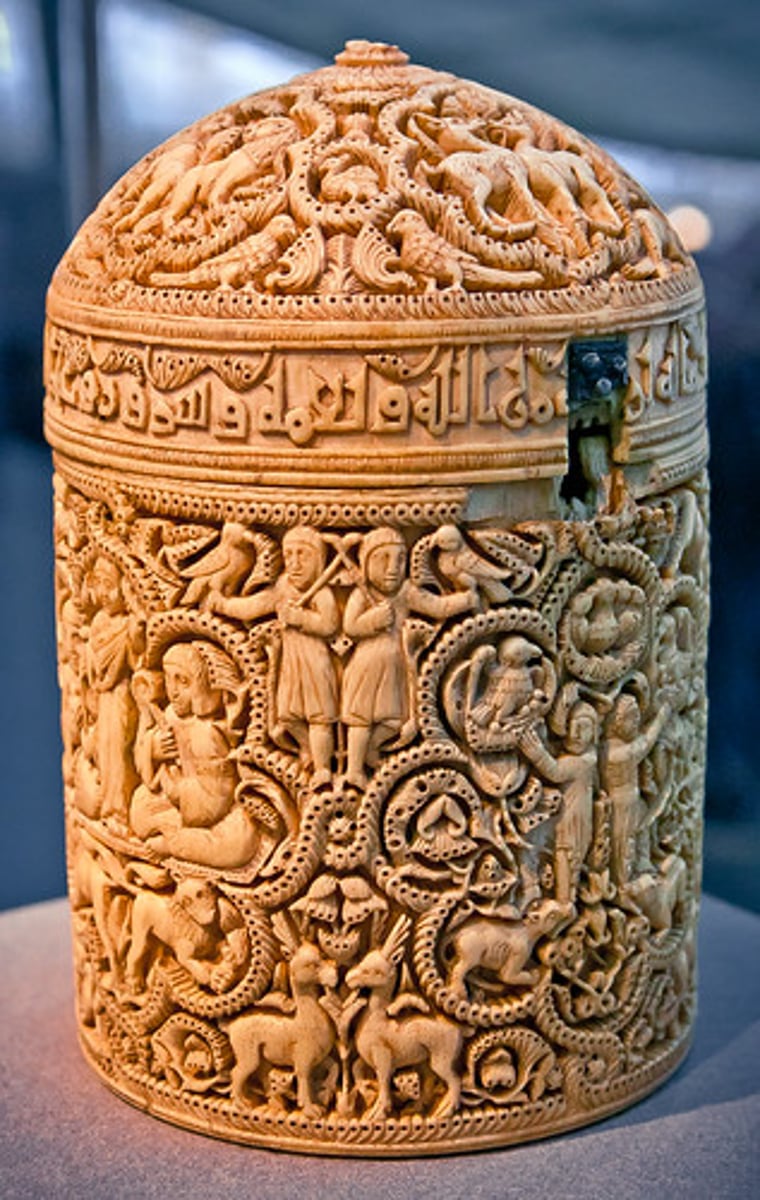
Pyxis of al-Mughira Muhammad ibn al-Zain
A cylindrical container from the Islamic world, decorated with intricate designs, including depictions of the caliph's life.

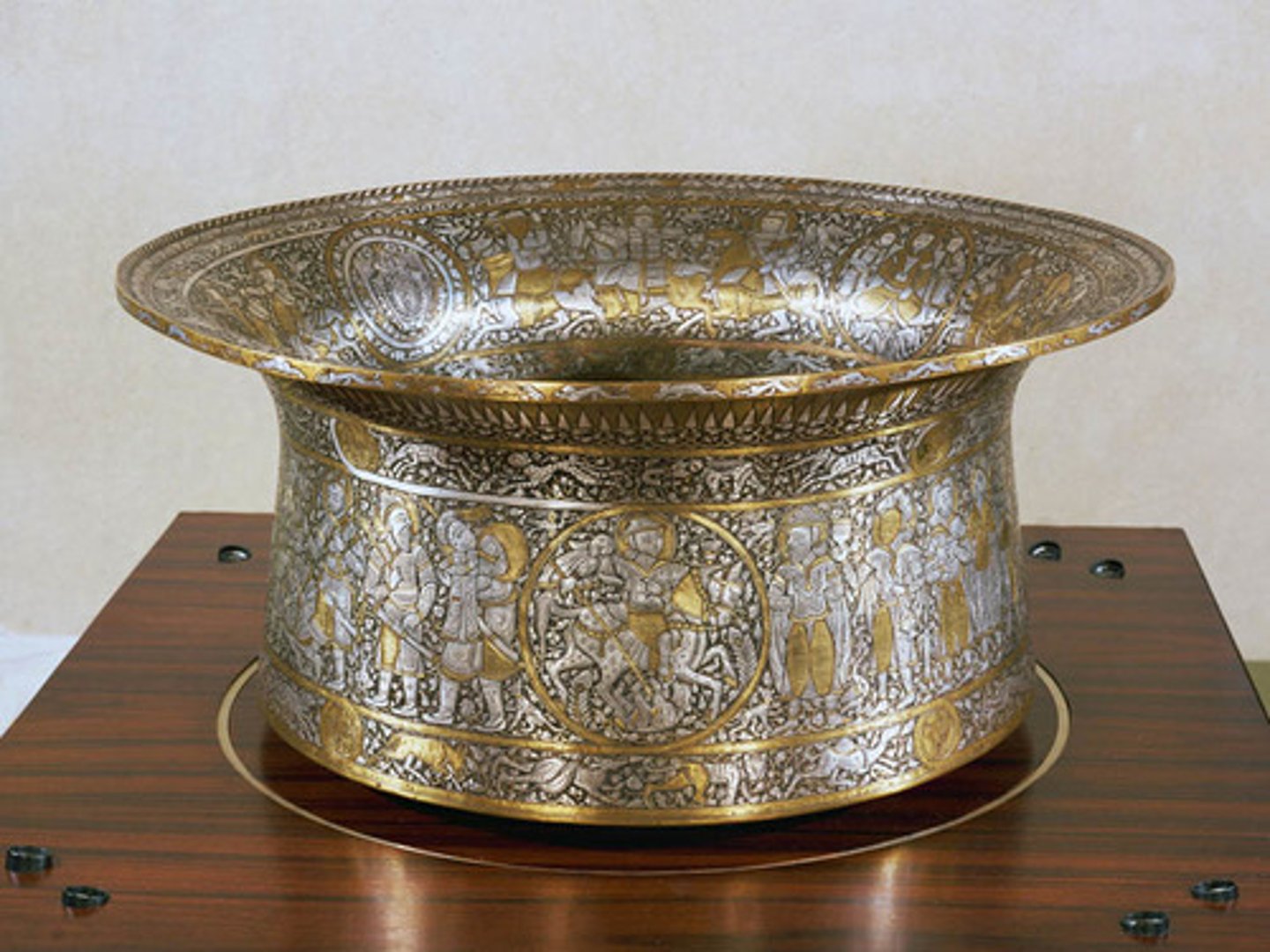
Basin or Baptiistère de St. Louis
An Islamic brass basin with intricate designs, often associated with the Mamluks, and used for ceremonial purposes/ Later used as a christening basin for Louis XIV(one of the Louis)

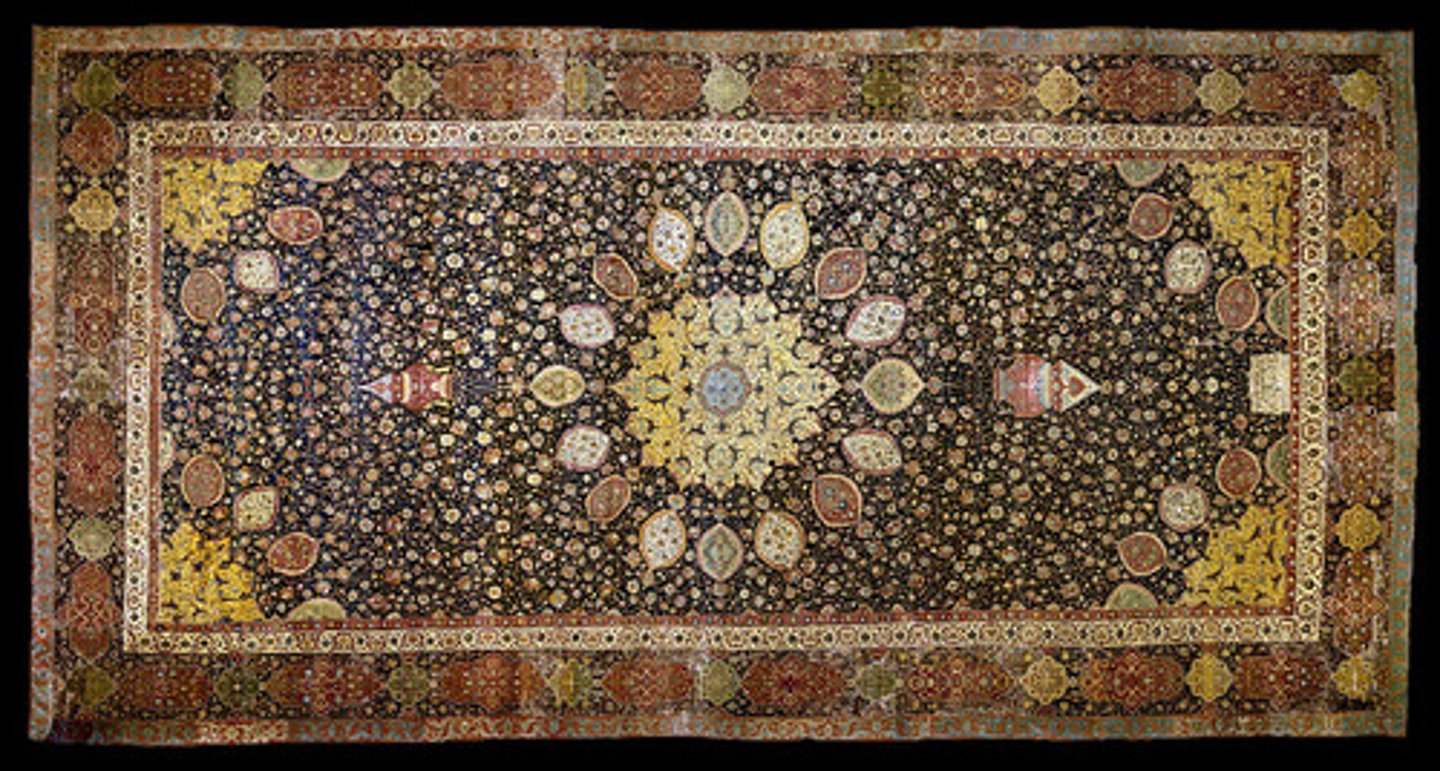
The Ardabil Carpet
A famous Persian carpet, one of the finest examples of Islamic art, produced in the 16th century.

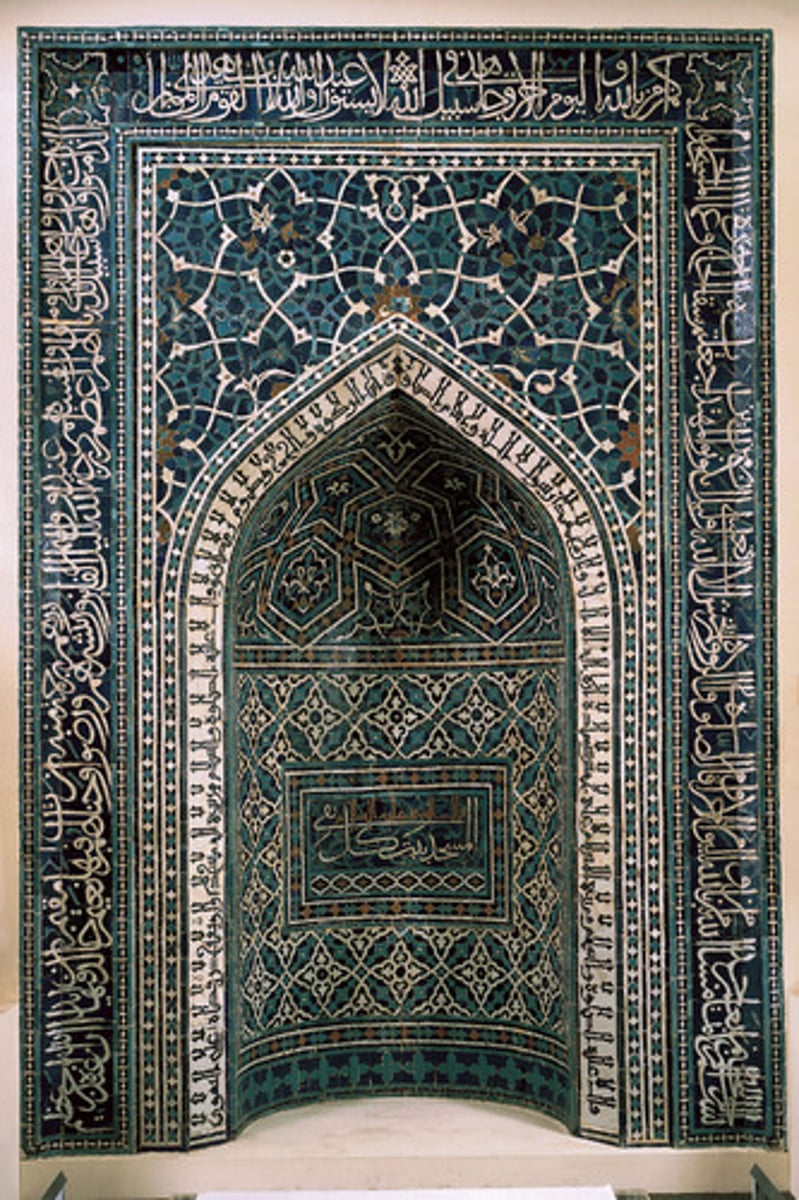
A Mihrab
A niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the direction of Mecca, toward which Muslims face during prayer.

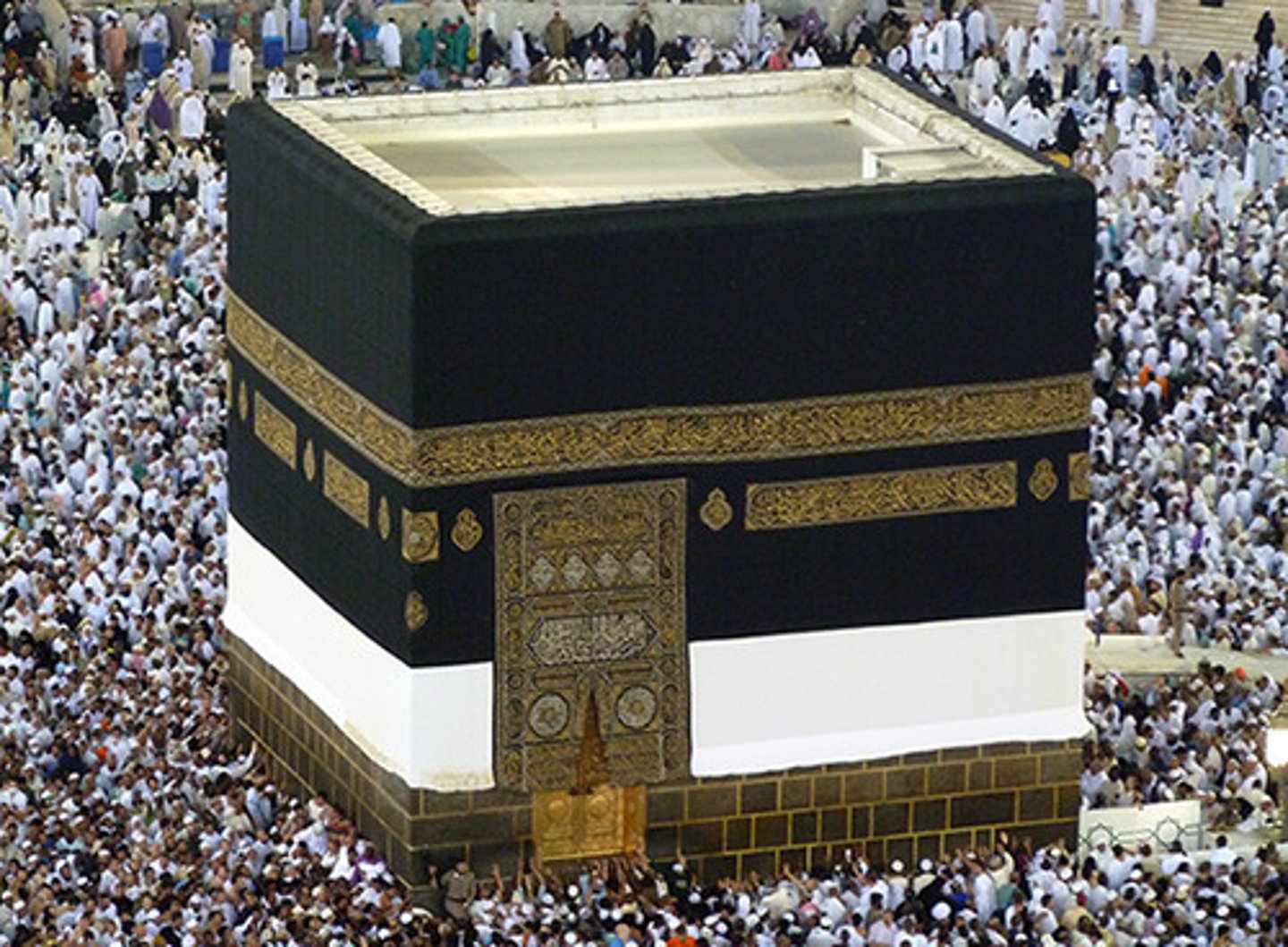
The Kaaba
The sacred structure located in the center of the Great Mosque in Mecca, Saudi Arabia, considered the holiest site in Islam.

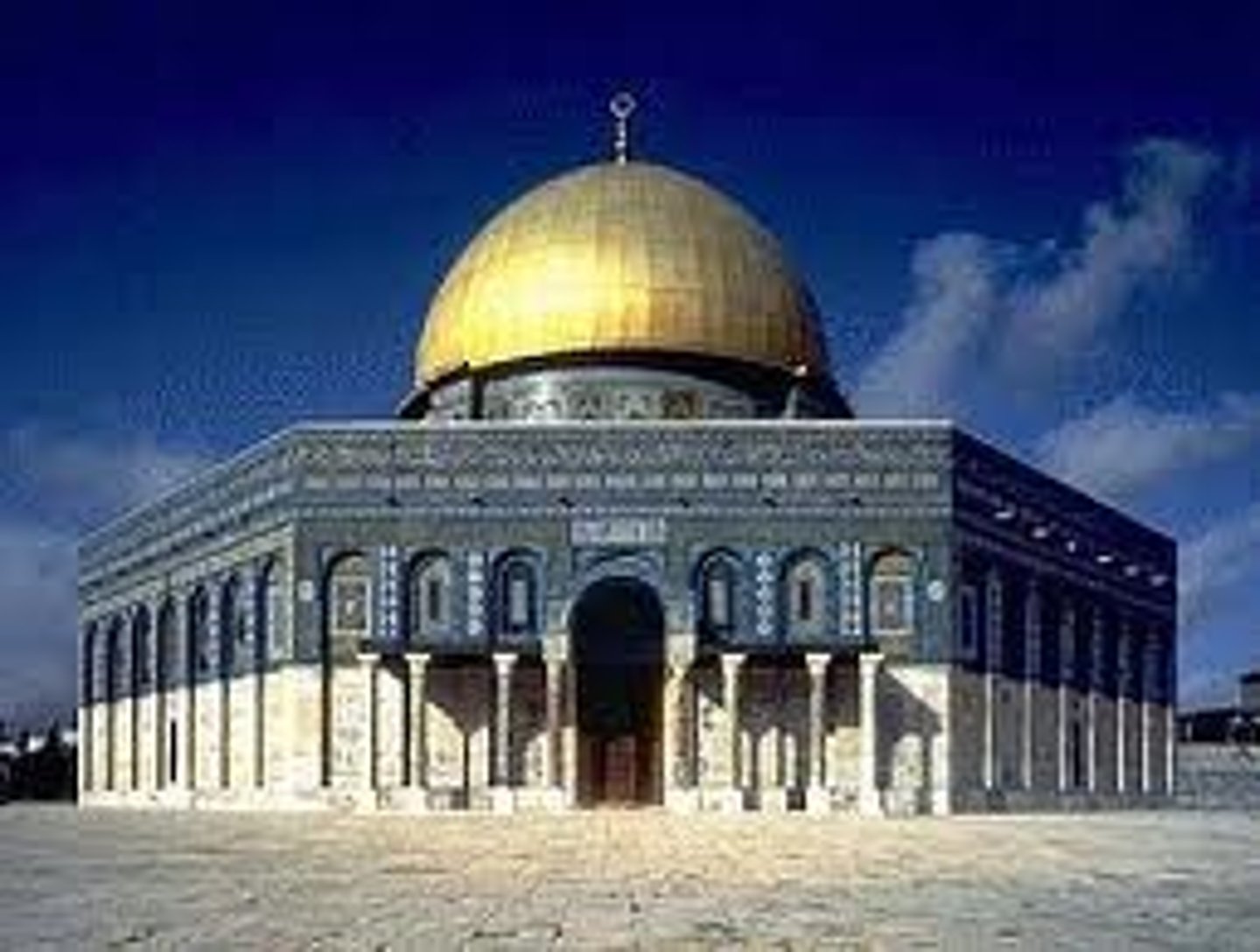
Dome of the Rock
An Islamic shrine in Jerusalem, built over the rock where it is believed the Prophet Muhammad ascended to heaven.

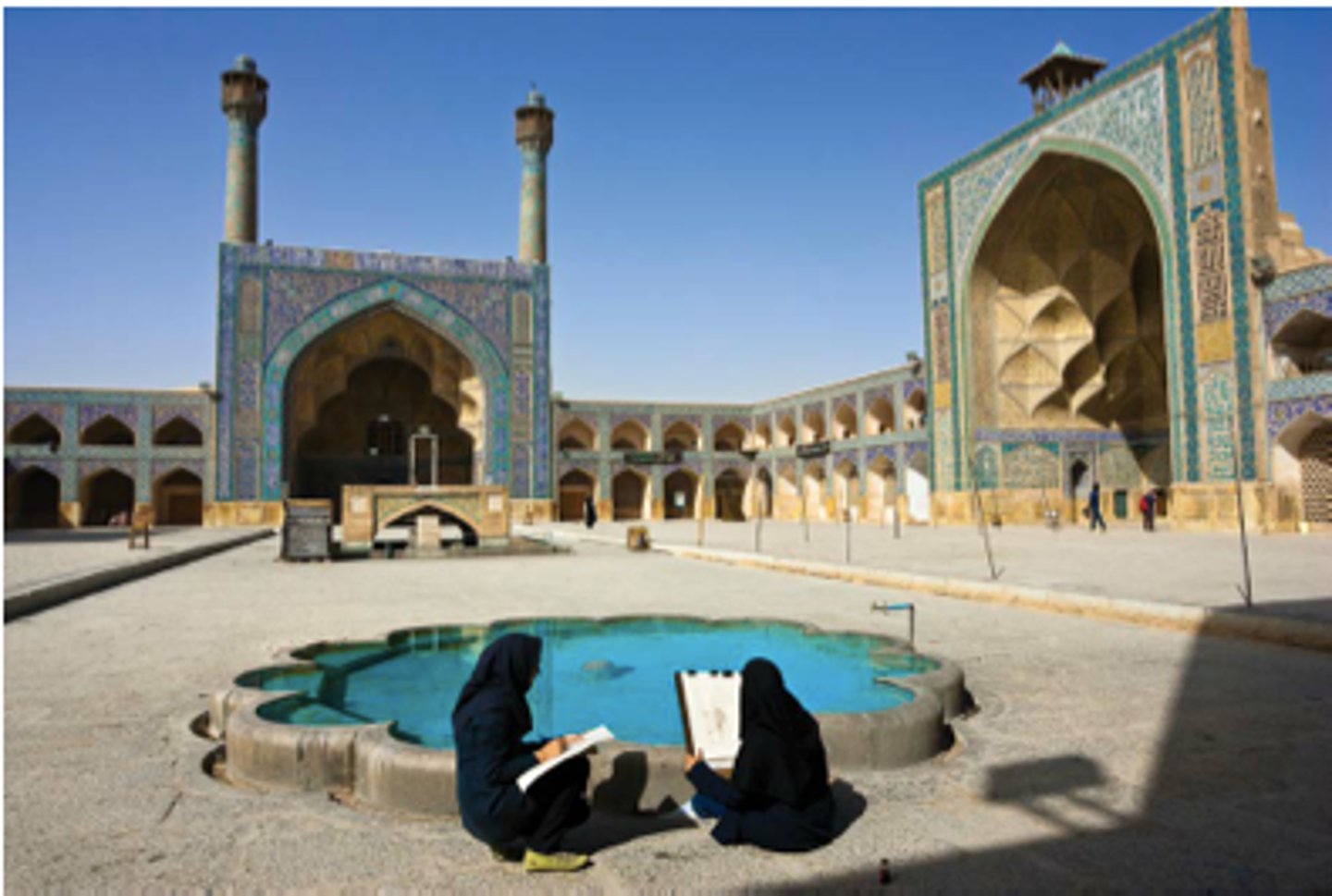
Great Mosque in Isfahan, Iran
A large and influential mosque known for its grand scale, iwans, and use of intricate tilework.

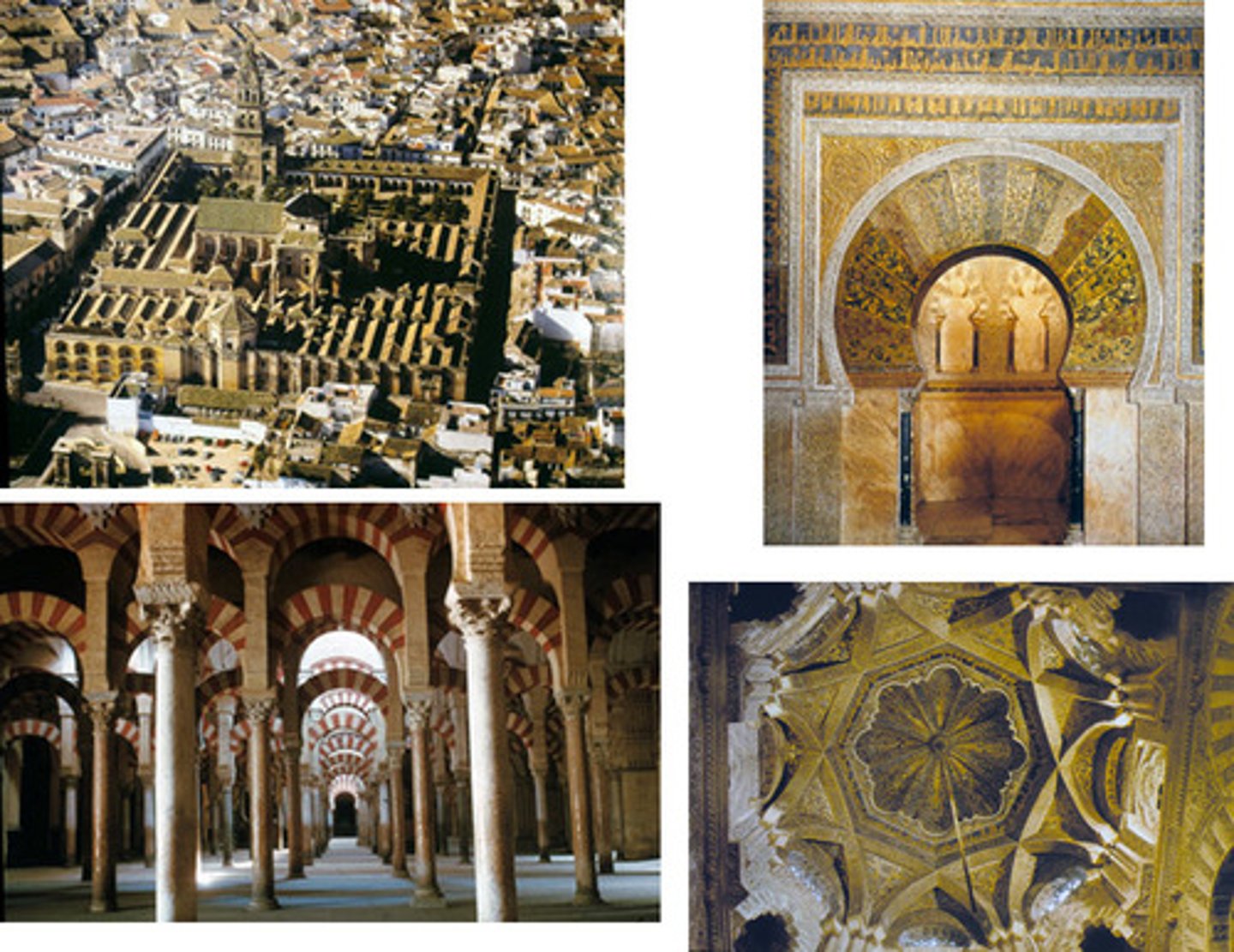
Great Mosque in Córdoba, Spain
A mosque in Spain renowned for its horseshoe arches and expansive hypostyle hall, later converted into a cathedral.

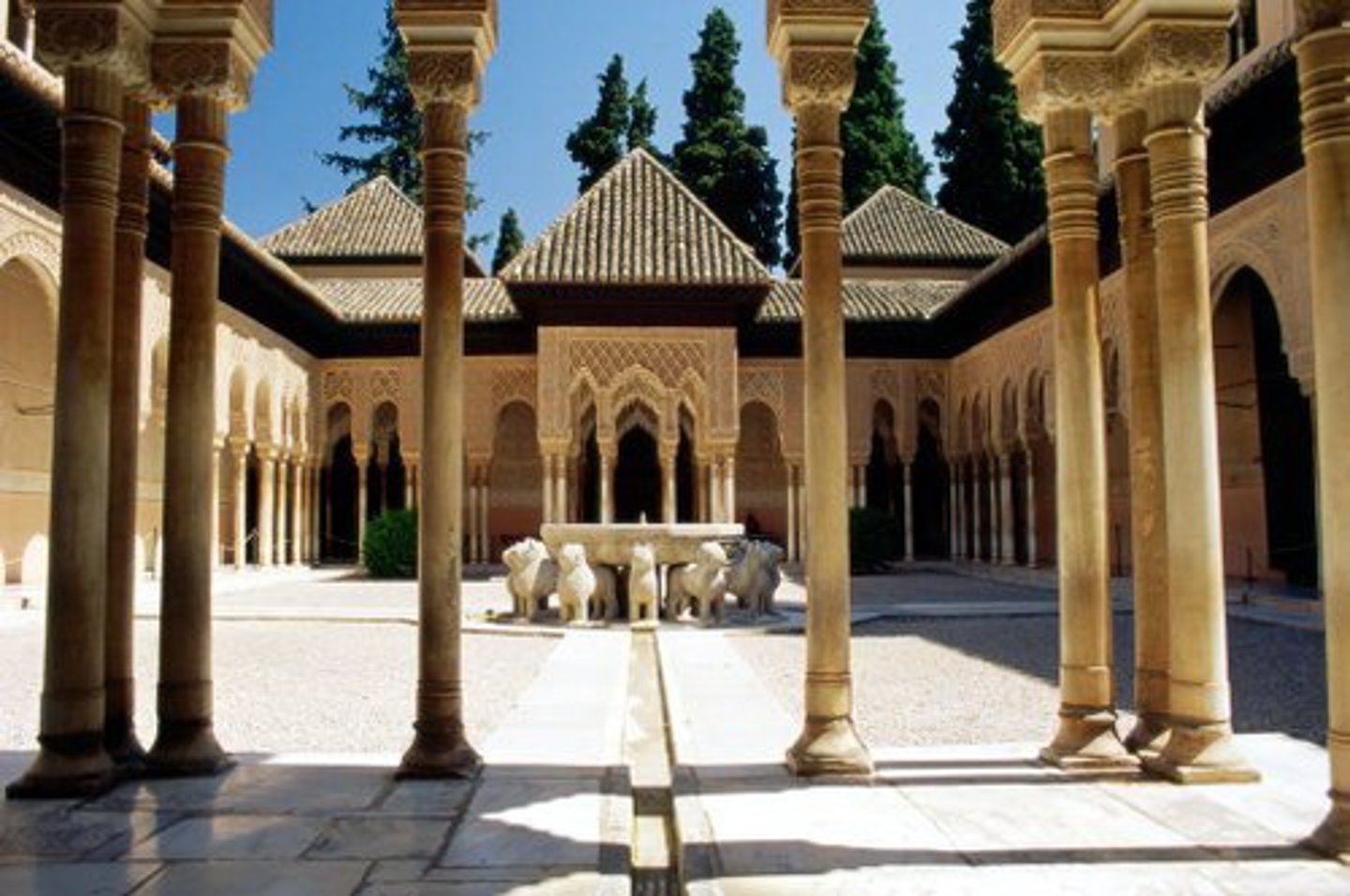
Alhambra (Court of the Lions & Hall of the Sisters)
A famous Islamic palace and fortress in Spain, known for its elaborate Islamic architecture, courtyards, and intricate tilework.

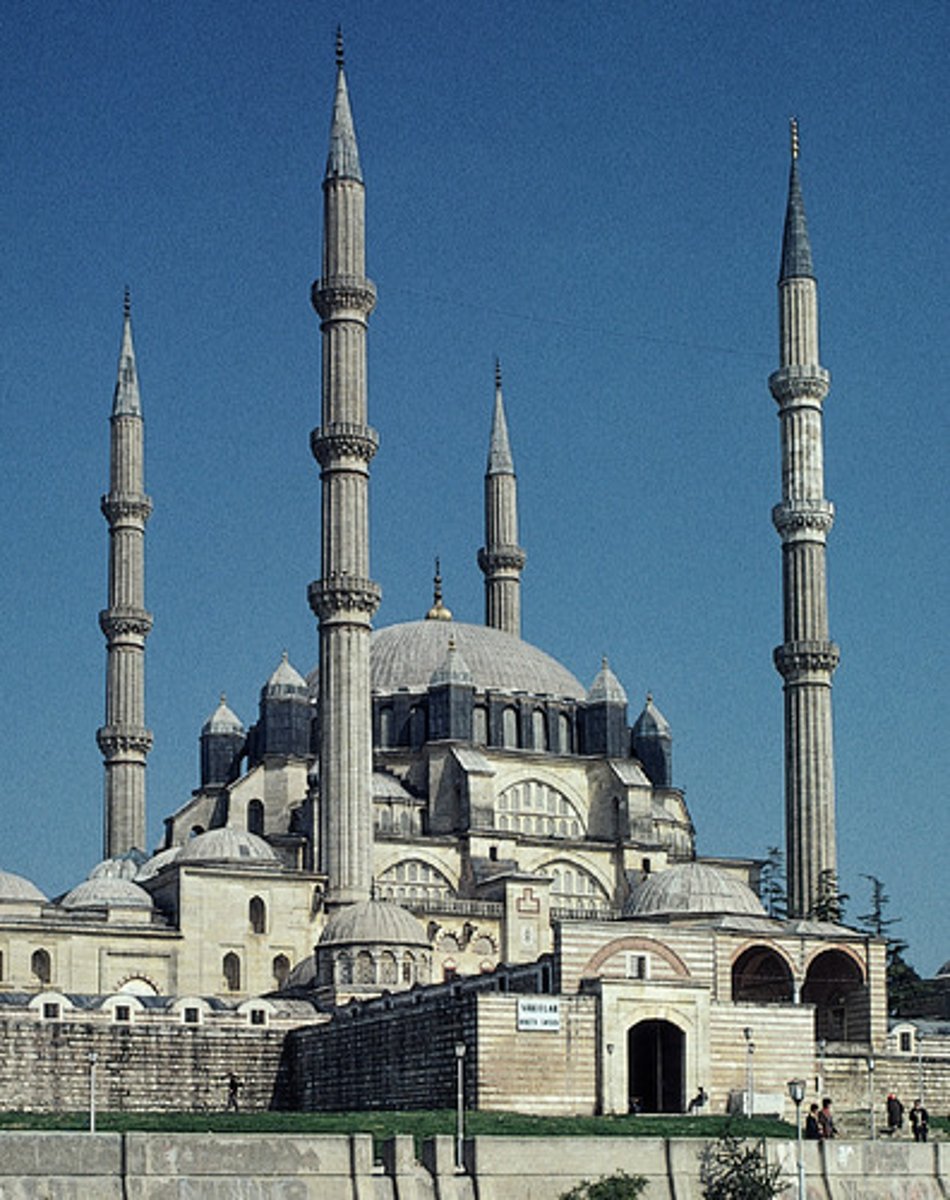
Sinan Mosque of Selim II in Edirne, Turkey
An Ottoman mosque designed by the architect Sinan, notable for its large dome and architectural innovation.

Taj Mahal
A white marble mausoleum in India, built by Mughal Emperor Shah Jahan in memory of his wife, known for its symmetry and intricate decoration.

Arabesque
A decorative style featuring intricate, flowing patterns, often involving floral, geometric, or abstract designs.

Calligraphy
The art of beautiful handwriting, particularly in Islamic culture where it was used as a highly esteemed art form.

Horror Vacui
The fear of empty space, leading to a densely packed decorative style, commonly seen in Islamic art and early Christian art.

Hajj
The annual pilgrimage to Mecca that every Muslim is required to undertake at least once in their lifetime, if able.
Iwan
A vaulted hall or space in Islamic architecture, often with three sides and an open side, seen in mosques and palaces.

Kufic
A script used in early Islamic calligraphy, characterized by angular, geometric letterforms.

Mihrab
A niche in a mosque that indicates the qibla, the direction of Mecca, where Muslims pray.

Minaret
A tall tower, typically part of a mosque, from which the call to prayer is announced.

Mosque
A place of worship for Muslims, typically with a central prayer hall, a mihrab, and a minaret.

Muqarna
A decorative architectural feature used in Islamic buildings, often appearing as a series of small, vaulted niches that form a honeycomb-like pattern.

Pyxis
A small, cylindrical container used in the Islamic world, often for holding perfumes or cosmetics.

Qibla
The direction of Mecca, towards which Muslims face during prayer.
Qur'an
The holy book of Islam, believed to be the word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad.