AP Psychology MIDTERM
1/146
Earn XP
Description and Tags
have you been paying attention in class? no? well ur fucked. Come get unfucked with us.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
147 Terms
Central Nervous System
Nerves found in your Brain and Spiral Cord Only
Peripheral Nervous System
Nerves that travel to and from your spinal cord
Autonomic nervous system
(communicates with internal organs and glands, part of peripheral nervous system)
Somatic nervous system
(communicates with sense organs and voluntary muscles, part of peripheral nervous system)
Sympathetic
(arousing)
Parasympathetic
(calming)
Sensory (afferent)
(sensory input) “arriving at the brain”
Motor “efferent”
(motor output) “exiting the brain”
Sensory (Afferent) Neurons
Take information from the senses to the brain
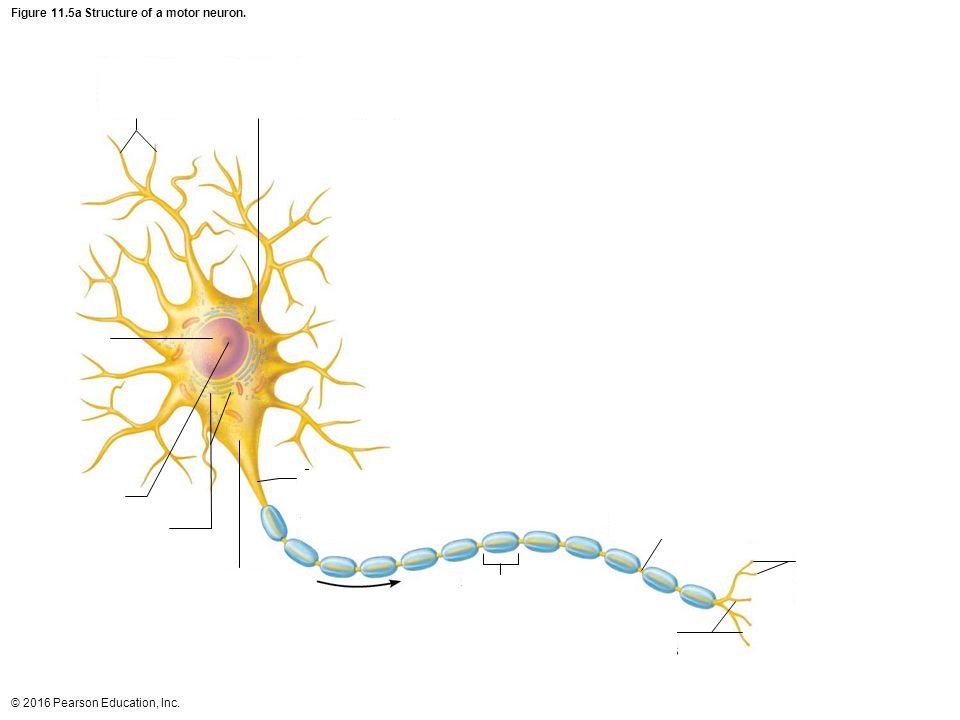
Motor (Efferent) Neurons
Take information from brain to the rest of the body
Interneurons
Take messages from Sensory Neurons to other parts of the brain or to Motor Neurons
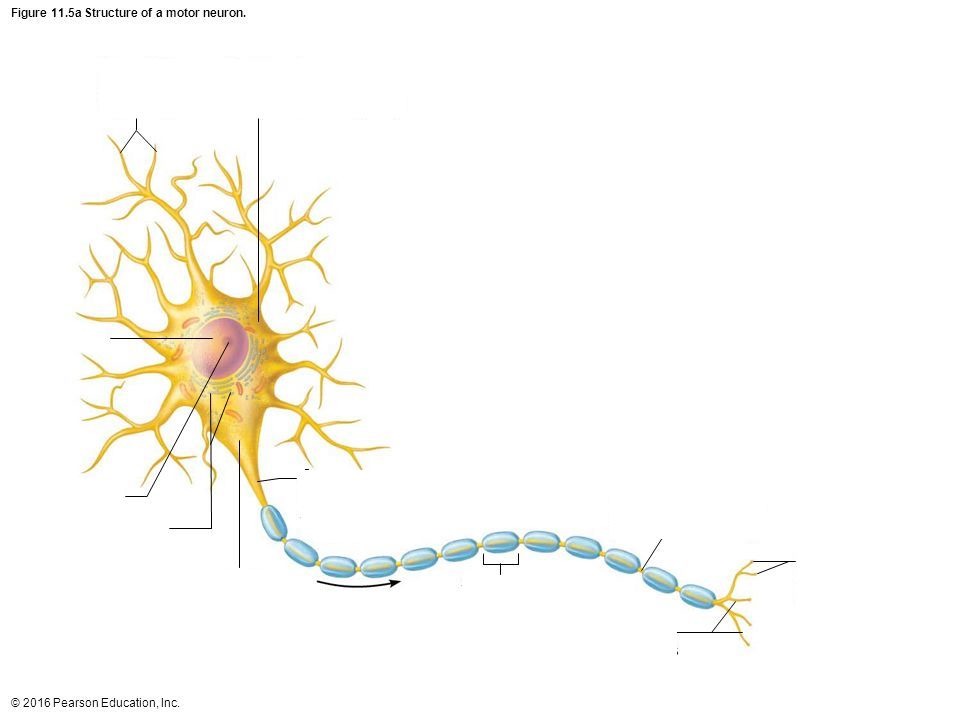
Axon
portion of a nerve cell (neuron) that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body
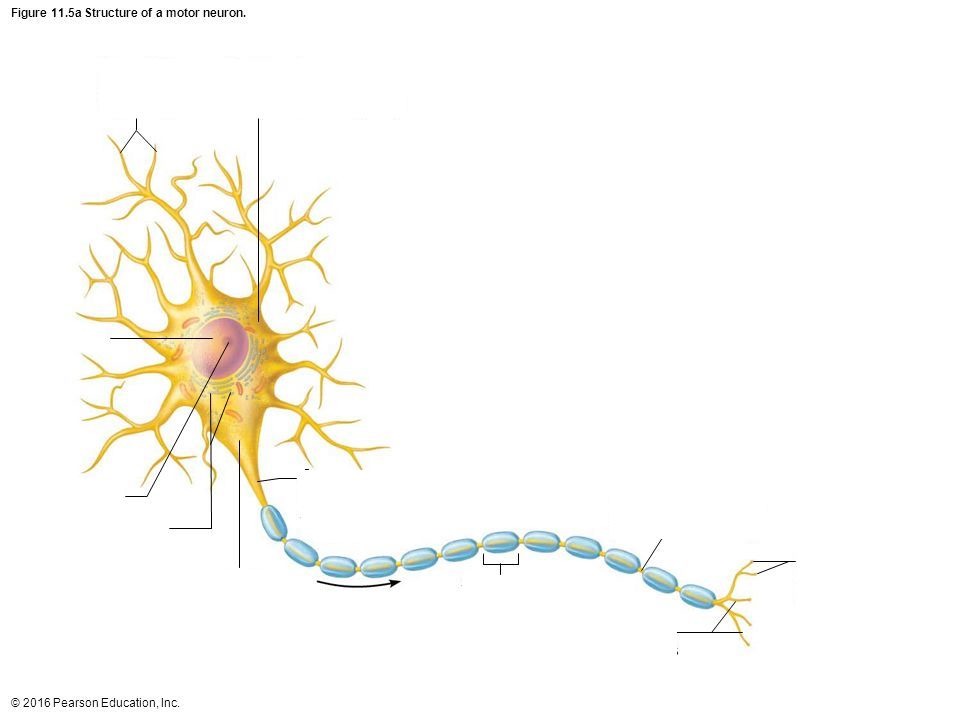
Soma
Cell Body
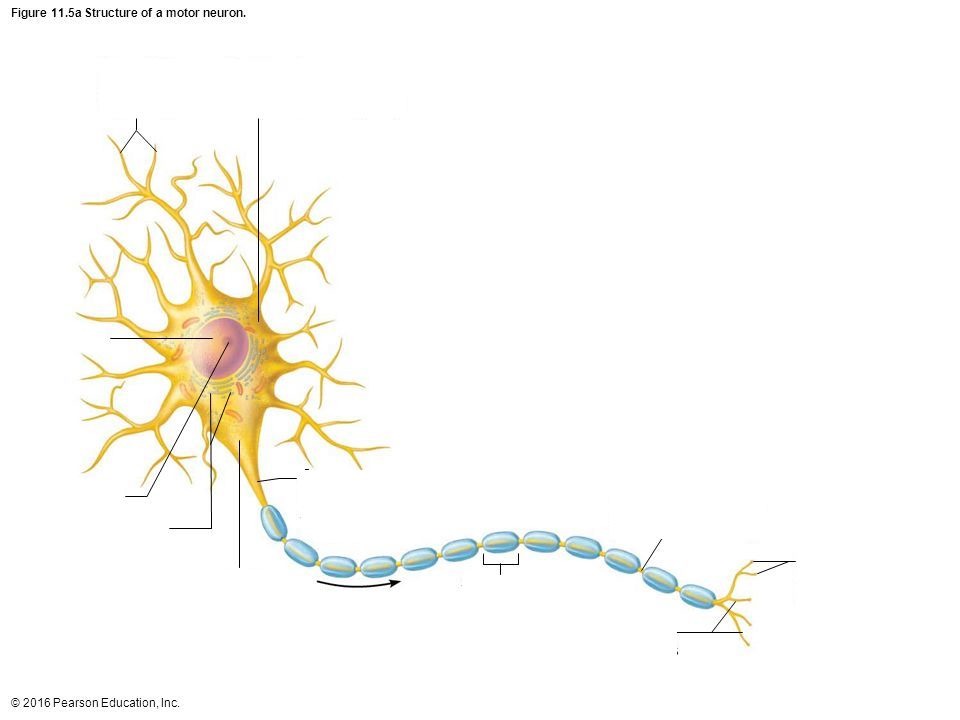
Terminal Branch
a part of a motor nerve fiber, a branch of an artery, or a branch of the brachial plexus
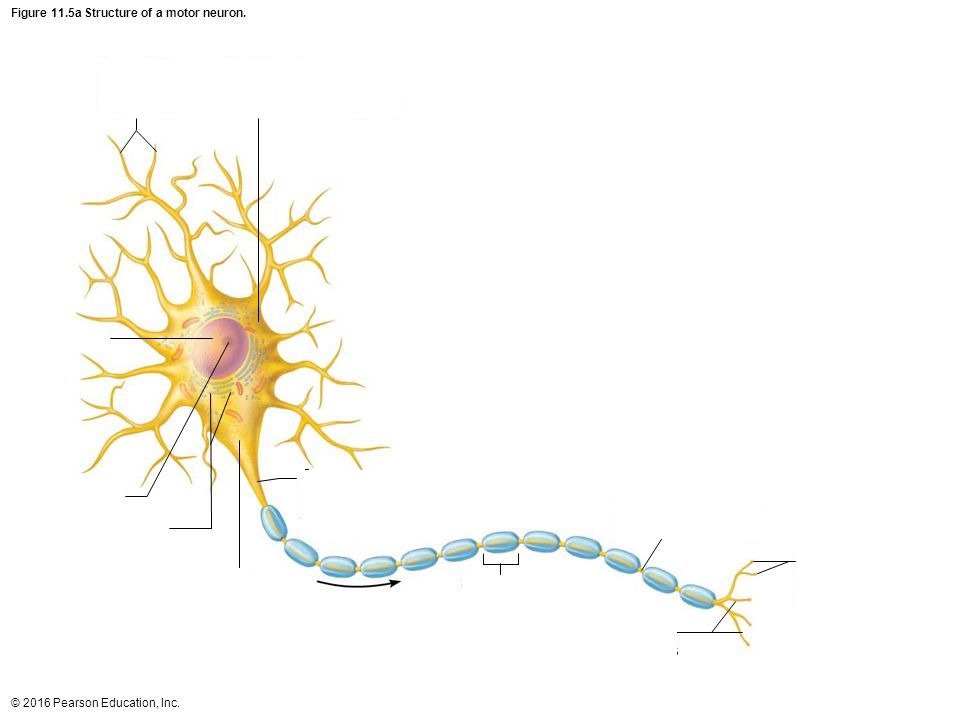
Nucleus
the positively charged central core of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons and containing nearly all its mass.
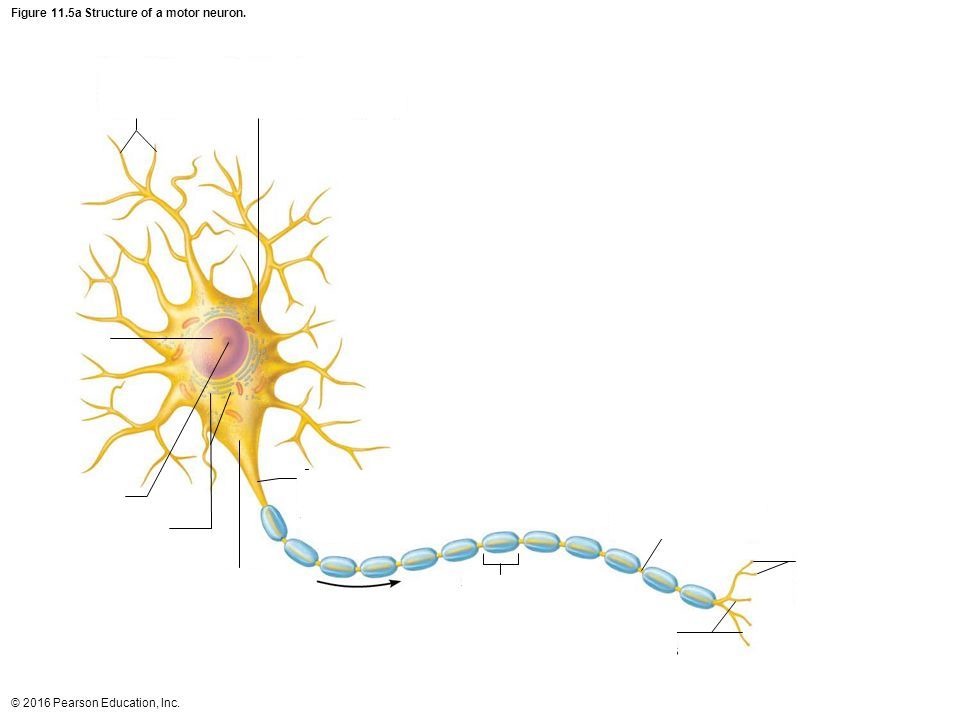
Axon Hillock
a cone-shaped region of a neuron that connects the axon to the cell body
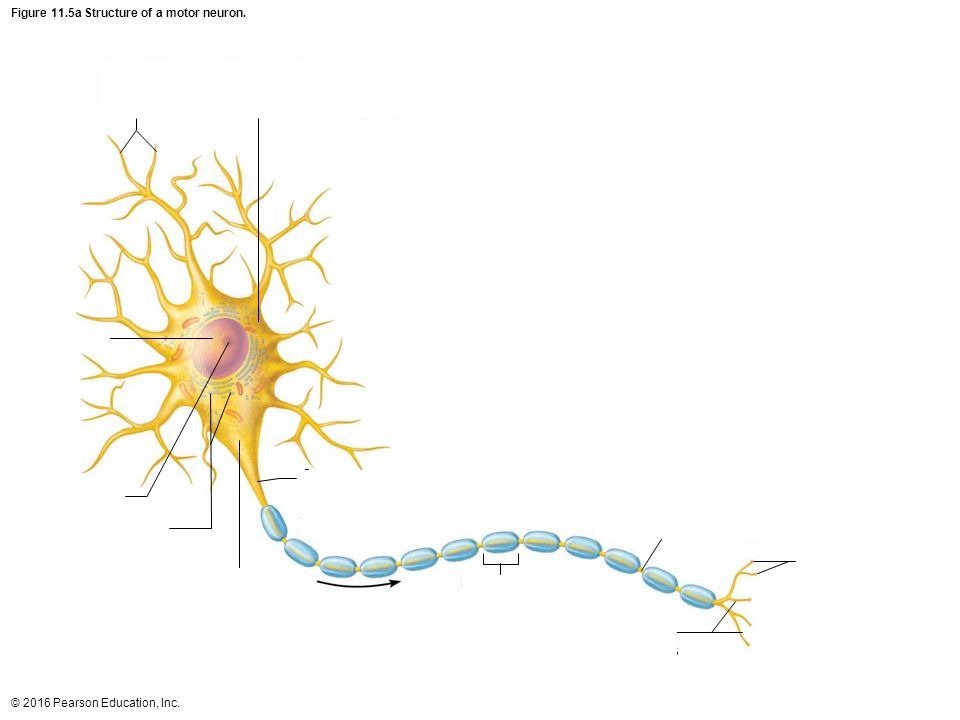
Dendrite
the receiving or input portions of a neuron.
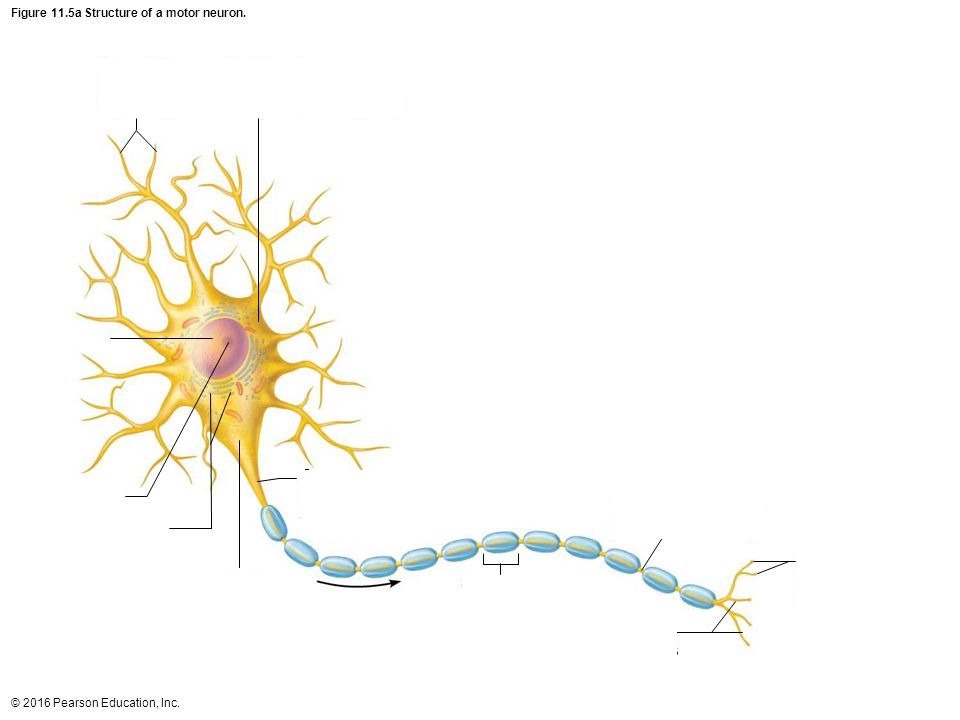
Myelin Sheath/Schwann Cell
a fatty, insulating layer that surrounds nerve cells, or neurons, in the brain and spinal cord
N/N and S/S are magnet forces, that?
repel
N/S and S/N are magnet forces, that?
attract
Action Potential (AP)
electrical message (carries a negative charge)
Polarized
Carries a Negative charge
the charge of the outside of the axon (extracellular) is ?
positive
the charge of the inside (intracellular) is ?
Negative
Resting Potential
Nothing is happening in the neuron. It is Negative.
Threshold
The level that a depolarization must reach for an action potential to occur.
Depolarization
Neuron becomes positive
Repolarization
Neuron becomes negative again
Hyperpolarization
The neuron is flooded with too much negativity.
What happens when the action potential doesnt fire ?
disorders and diseases (MS, Fragile X, etc)
Nerve Synapse
the space between neurons
Neurotransmitter
chemical messengers inside the body that carry messages between neurons
Excitatory: “Excited”, Agonistic, Agonist
increase the likelihood of the neuron firing the action potential
Inhibitory: “Hinder, Restrain” , Antagonistic, Antagonist
Decrease the likelihood of the neuron firing the action potential
Modultory
Affect a large number of neurons and neurotransmitters at the same time. They are slower-acting. Re-uptake is also slower.
epinephrine and norepinephrine are examples of ?
excitatory neurotransmitters
serotonin and GABA are examples of ?
inhibitory neurotransmitters
acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, histamine, and cannabinoids are examples of
modultory neurotransmitters
adrenaline (fight or flight) / epinephrine
surplus: insomnia, anxiety, allergic reactions
deficit: depression
noradrenaline (concentration) / norepinephrine
surplus: anxiety
deficit: depression
dopamine (pleasure)
surplus: schizophrenia
deficit: parkinsons
serotonin (mood)
surplus: autism
deficit: depression
GABA (calming)
surplus: sleep and eating disorders
deficit: anxiety
acetylcholine (learning)
surplus: severe muscle spasms
deficit: alzheimer’s
glutamate (memory)
surplus: seizures, anxiety
deficit: fatigue, poor memory
endorphins (euphoria)
surplus: artificial highs, inadequate warnings of pain
deficit: pain
addiction
involves other changes to brain circuitry and is distinguished by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite negative consequences
dependence
the body physically relies on a drug
tolerance
the need to take higher doses of a substance to get the same effect and often accompanies dependence
psychoactive drugs
substances that, when taken in or administered into one’s system, affect mental processes (depressants, stimulants, hallucinogens, hypnotics)
Depressants (Antagonists)
drugs that reduce neural activity (alcohol, barbiturates, opiates)
alcohol
depressant. slows motor skills, judgement, and memory, and increases aggressiveness while reducing self awareness
barbiturates
slow the activity of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgement
opiates
slows neural and neurotransmitter activity, blocks transporter sites, temporarily lessening pain and anxiety
Stimulants (Agonist)
agonistic drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions (caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, ecstasy, amphetamines, methamphetamines)
caffeine and nicotine
increase heart rate and other autonomic functions
cocaine
induces immediate euphoria followed by a crash.
ecstasy
stimulant and mild hallucinogen. provides a euphoric high and can damage serotonin producing neurons.
Hallucinogens (Agonist)
Psychedelic (mind-manifesting) drugs that distort perceptions
Evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input.
LSD
powerful hallucinogenic drug that is also known as acid.
THC
the major active ingredient in marijuana that triggers a variety of effects, including mild hallucinations
Psilocybin Mushrooms
alter reality
Hypnotic (Antagonist)
slow down the activity of the brain
EEG
detects brain waves. for general information about the brain
CAT or CT
sophisticated x-ray. provides detailed 3-D images.
MRI
3-D pictures of structures not function. uses magnet tech, no radiation. measures density and location
PET
measures chemical usage by the body to determine brain function using different dyes that make structures “light up”
signs of stroke
Face - is it drooping ? Arms - Can you raise both ? Speech - is it slurred or jumbled? Time - to call 911 right away!
Neocortex
Rational or Thinking Brain
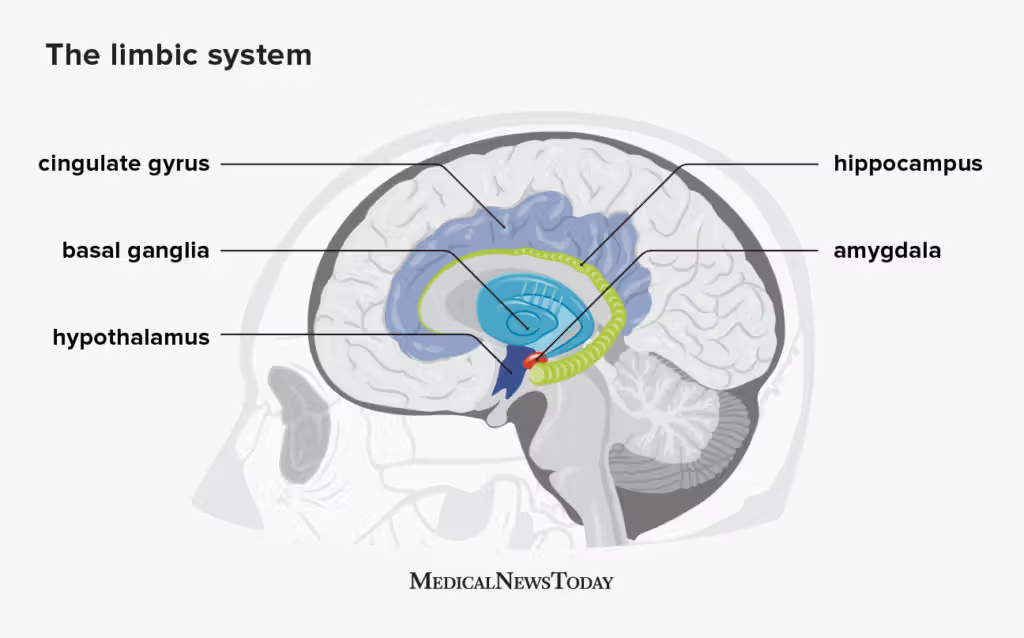
Limbic Brain
Emotional or Feeling Brain
Reptilian Brain
Instinctual or Dinosaur Brain
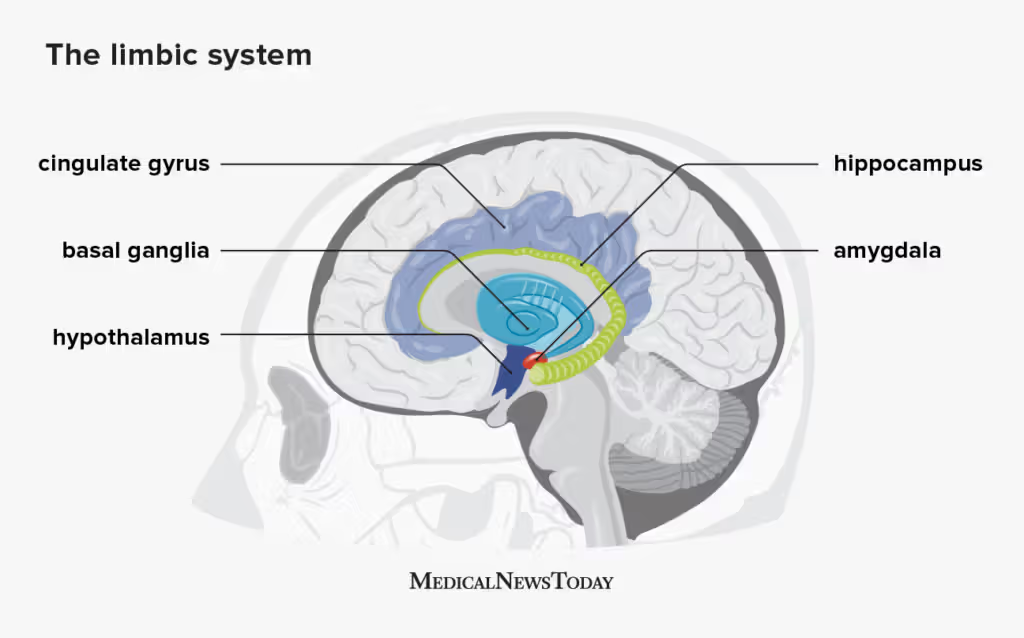
Basil Ganglia
controls our innate and automatic self-preserving behavior patterns, which ensures survival
Split Brain
callosal syndrome is a type of disconnection syndrome when the corpus callosum connecting the two hemispheres of the brain is severed to some degree.
Globulus Pallides
Conscious movement. Connects to cerebellum for balance.
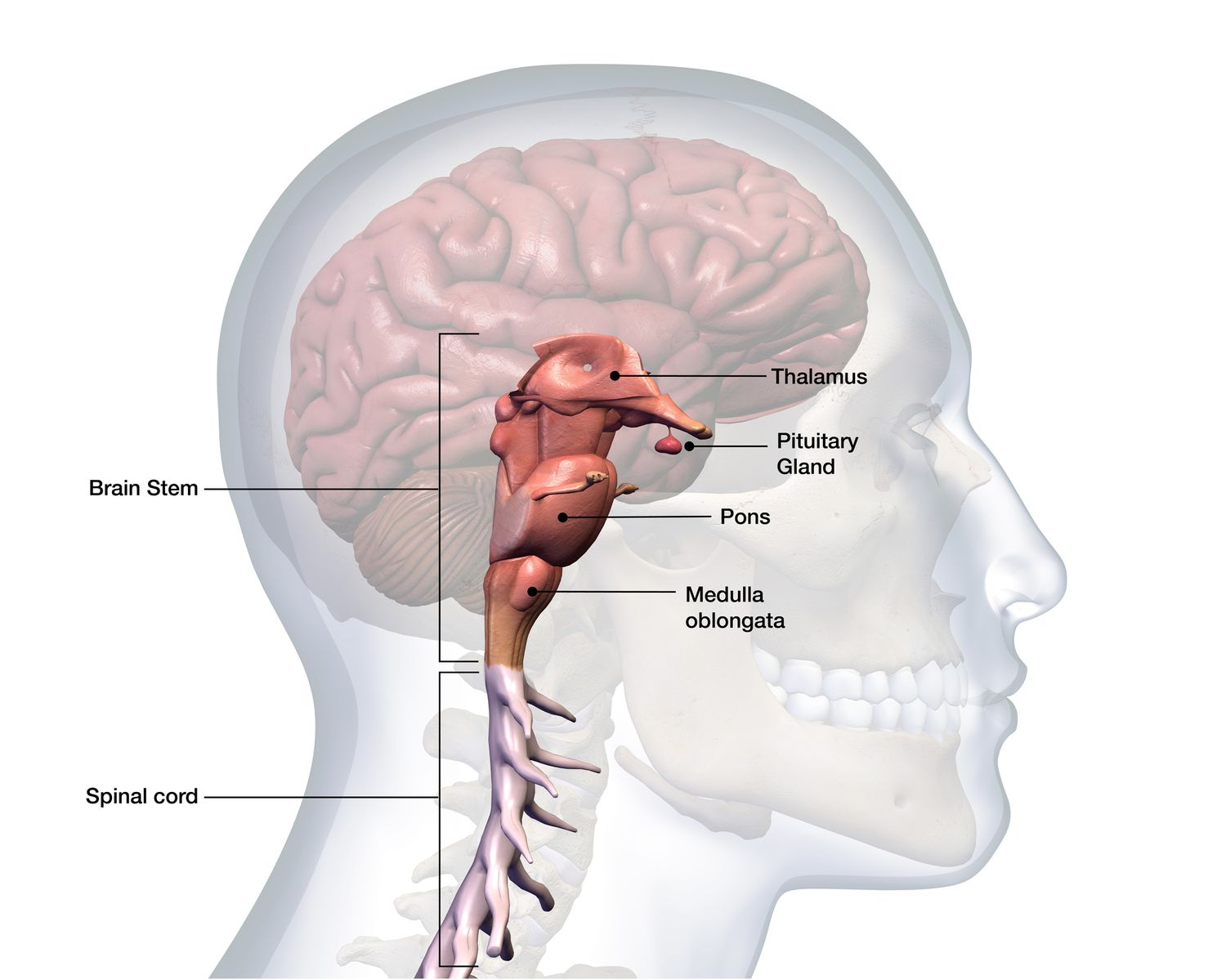
Brain Stem
Heart beat, breathing, alertness and sleep patterns
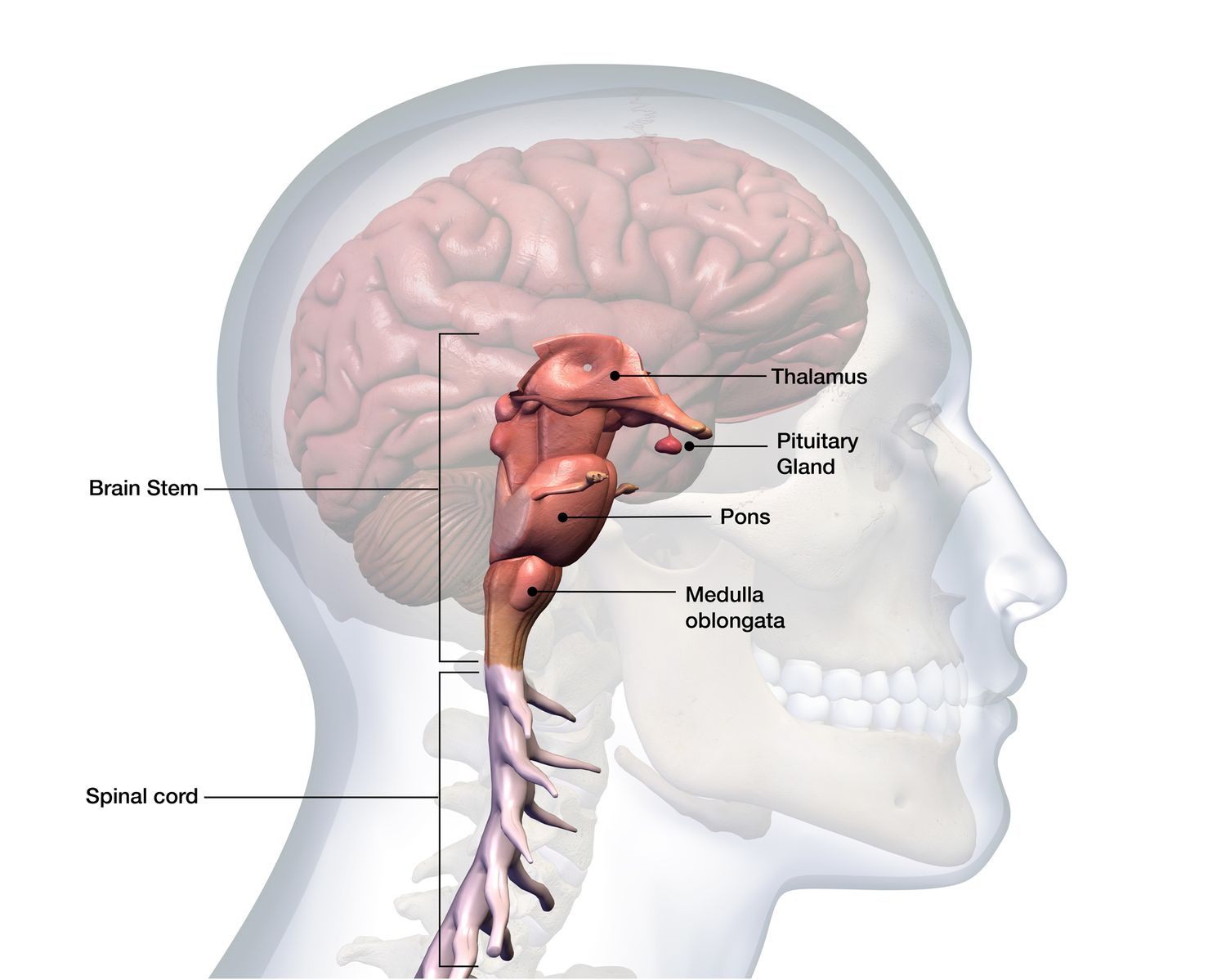
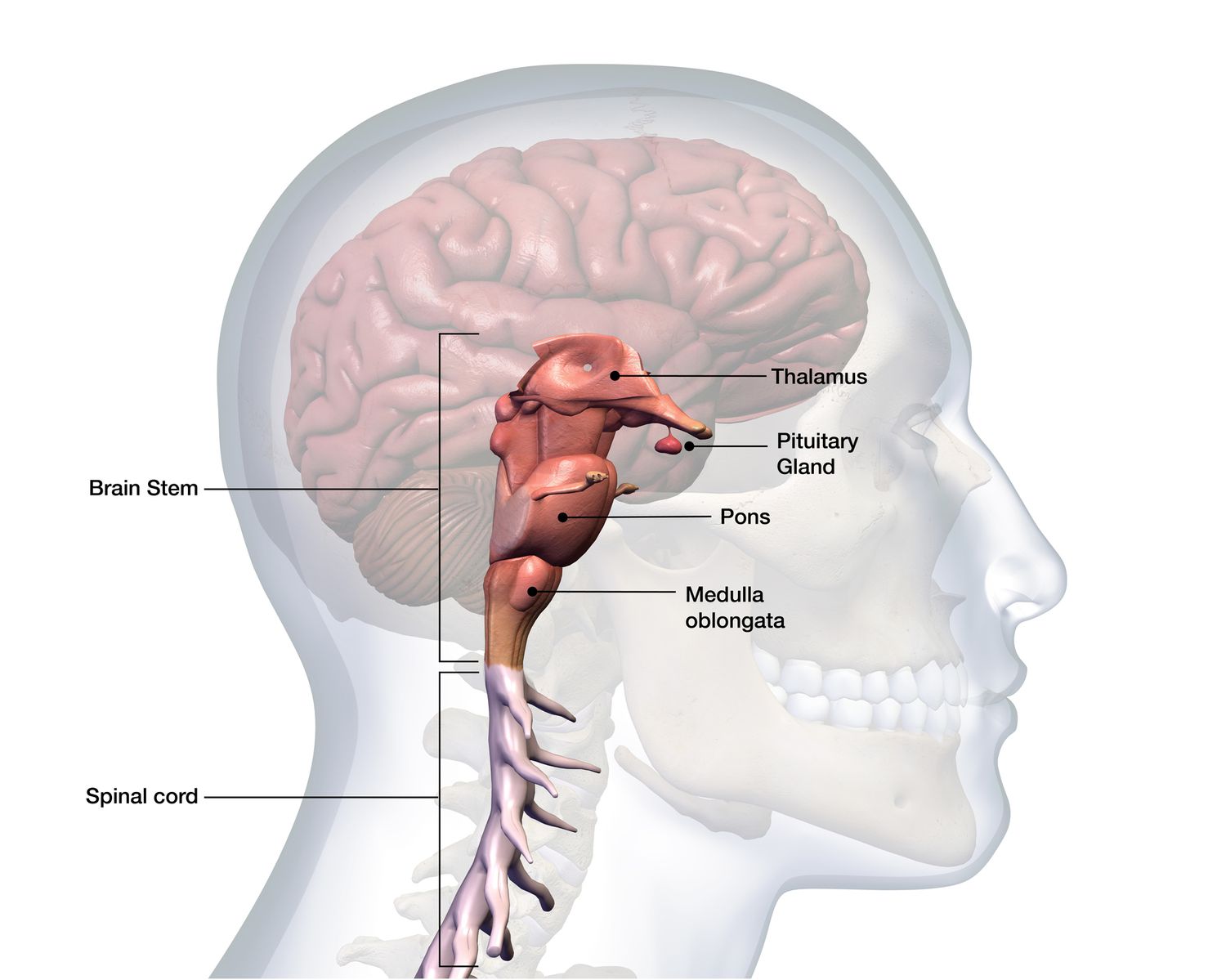
Thalamus
Brain’s relay station (relays info from sensory organs to cerebral cortex)
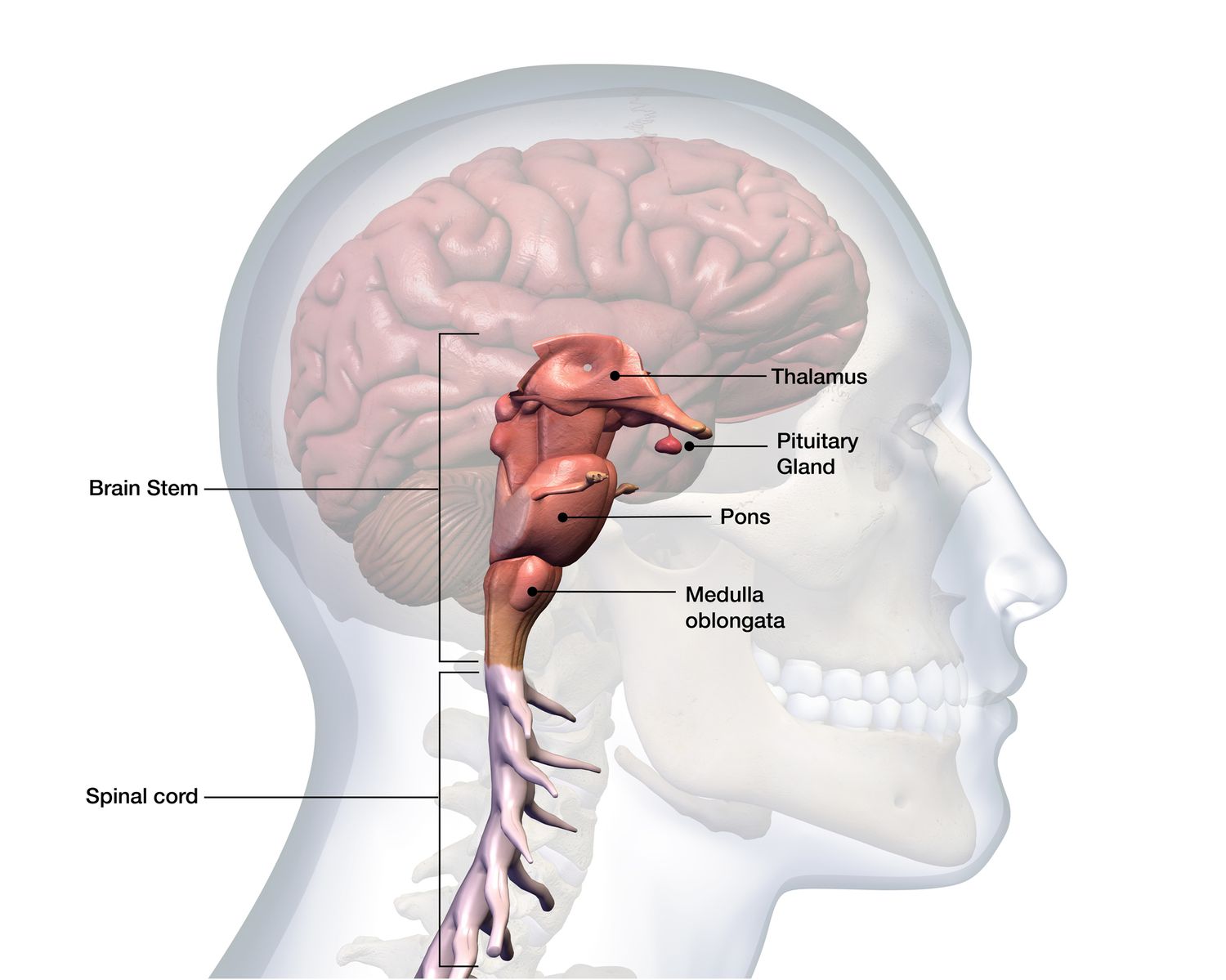
Pons
Sleep/wake cycle, arousal and breathing.
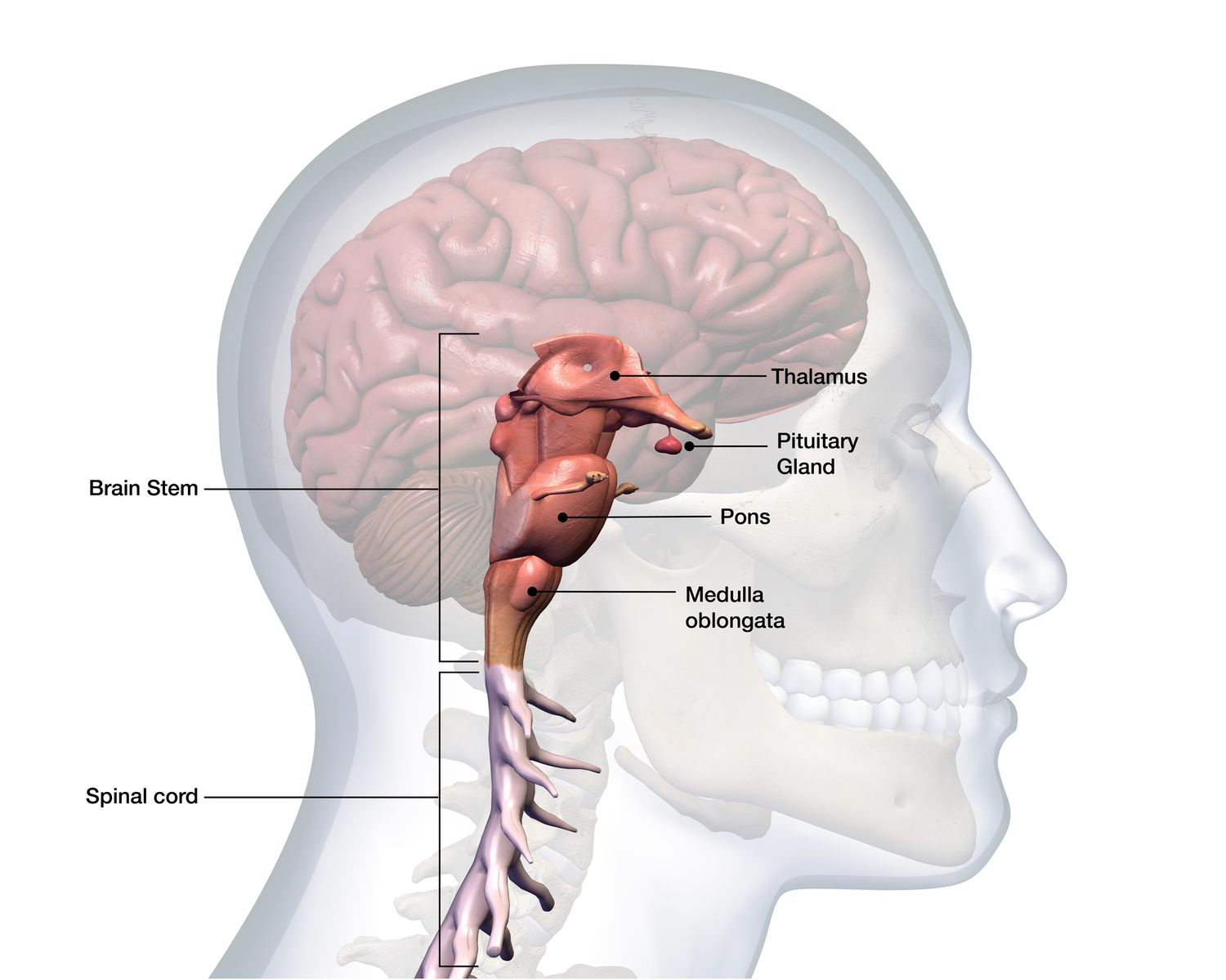
Medulla Oblongata
Heartbeat, respiration, swallowing, digestion.
Optic Nerve
Conduit for vision
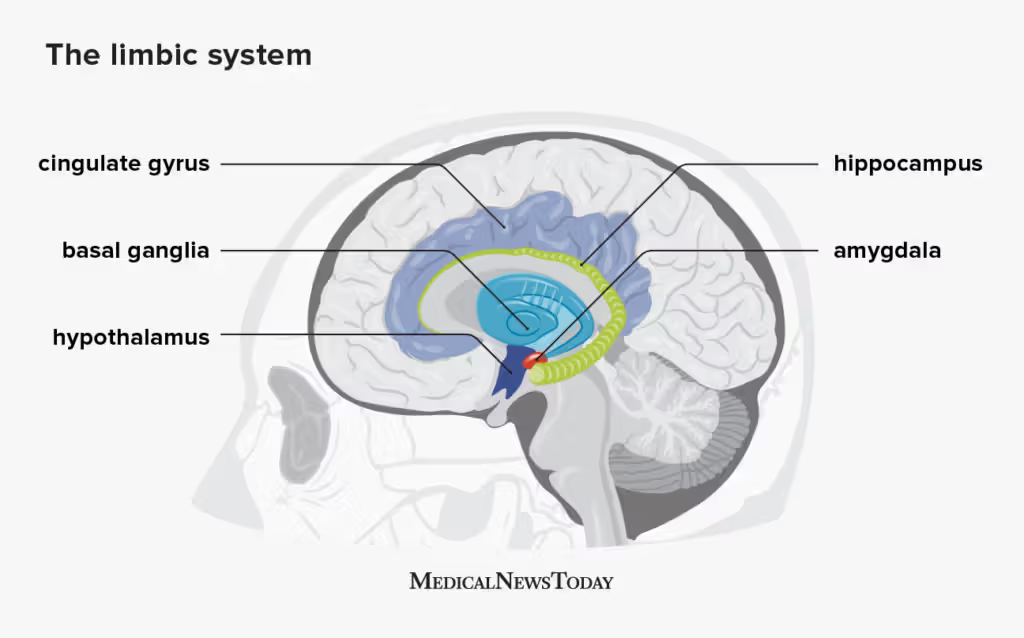
Amygdala
influences our motivation, emotional control, fear response, and interpretations of nonverbal expressions.
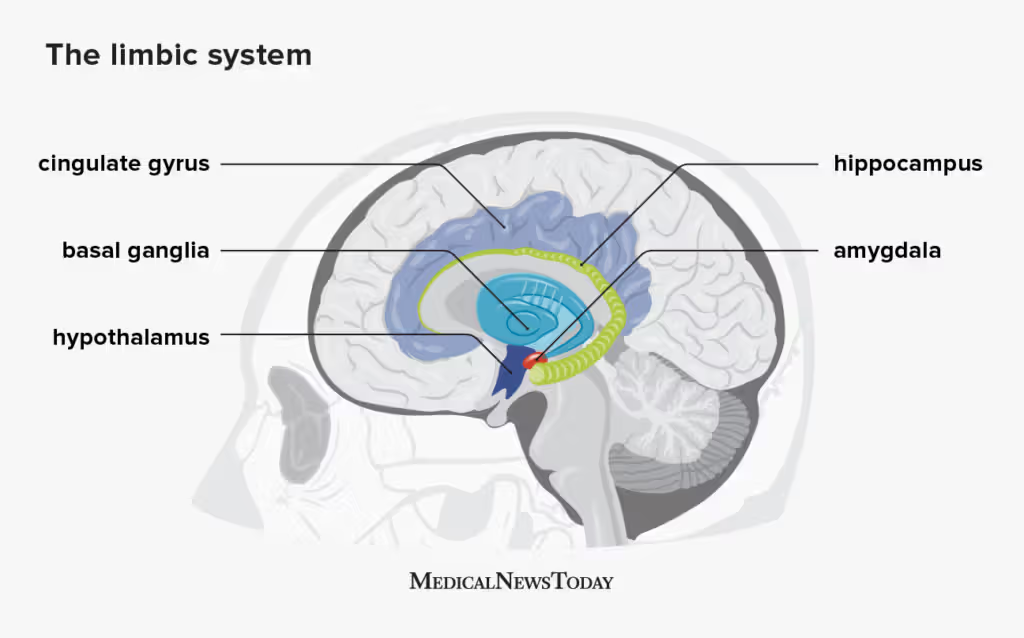
cingulate cortex/gyrus
Primary cortical component of the limbic system, involved in emotional and cognitive processing
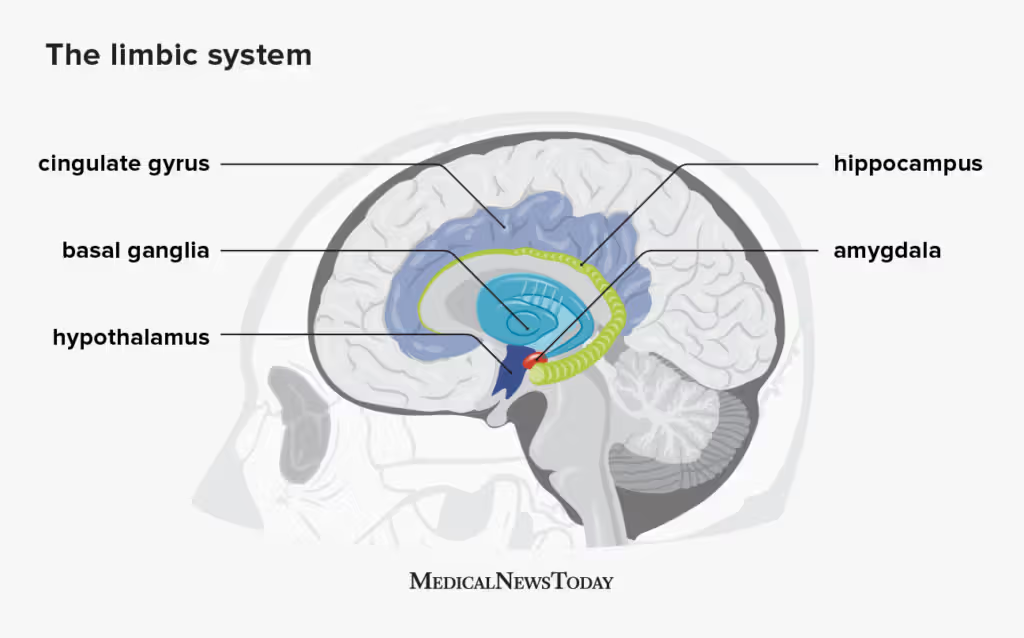
Hypothalamus
Part of the forebrain that regulates the amount of fear, thirst, sexual drive, and aggression we feel.
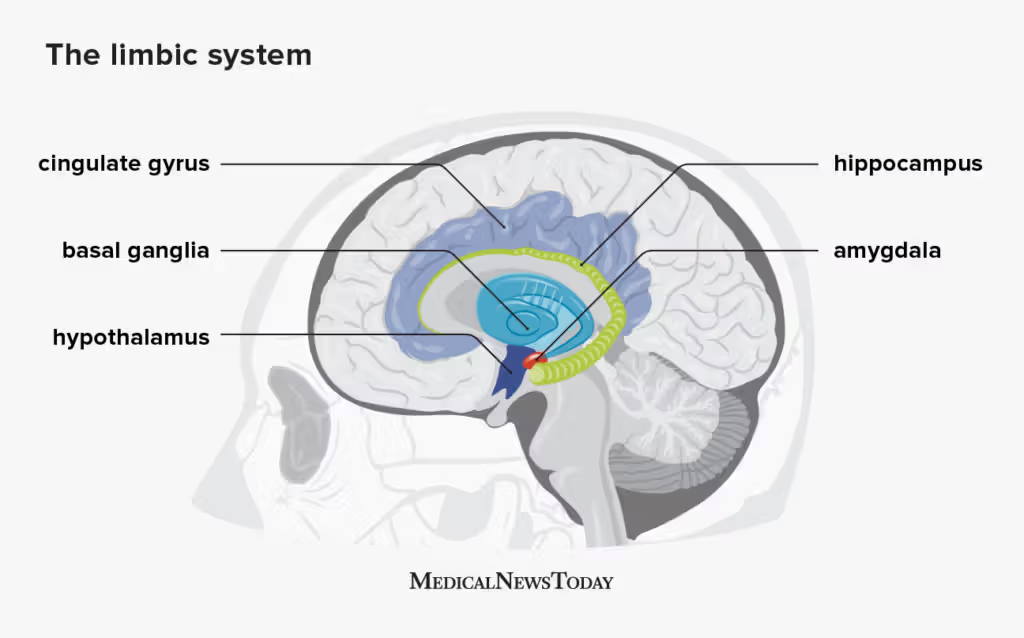
Hippocampus
Plays a role in our learning, memory, and ability to compare sensory information to expectations
Broca’s area
located in the left hemisphere. Associated with speech production and articulation.
Wernicke's area
Located in the posterior, superior (back, top) temporal lobe. Critical language area responsible for understanding and comprehension that connects to Broca's area via a neural pathway.
speech aphasia
the inability to speak coherently, understand spoken or signed language, follow directions, recognize objects by name
left hemisphere
linear thinking mode (writing, language, scientific skills, math, lists, logic and analytical reasoning). and right hand control
right hemisphere
holistic thinking mode (art, music, spatial skills, intuition, emotional expression and left hand control).
cerebellum
a brain structure located at the back of the skull that is responsible for coordination, balance, and fine motor skills.
encoding
getting info in
storage
retaining info
retrieval
getting info out
Gustatory Memory
refers to the recall of taste-related information, allowing individuals to remember flavors and food experiences. (taste)
Iconic Memory
the brief visual memory that lasts for a very short duration, typically under a second, allowing individuals to retain a snapshot of visual information. (sight)
Haptic Memory
refers to the recall of tactile information, enabling individuals to remember sensations related to touch and texture. (touch)
Olfactory Memory
refers to the recall of scent-related information, allowing individuals to remember smells and olfactory experiences. (smell)
Echoic Memory
the brief auditory memory that lasts for a few seconds, enabling individuals to retain sounds and auditory information. (hearing)
long-term potentiation
the more a memory is utilized, the more potential strength that neuron has
Visual encoding
requires the use of an image or a spatial relationship to remember something