Upper Respiratory Passageways - Comparative Anatomy and Structural/Functional Considerations
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
M.9,W.1,L.2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
describe respiratory epithelium
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells
how does the respiratory nasal passageway modify and regulate the volume of inspired air?
rich blood supply warms the air
Glandular secretions/mucus moisten the air
mucus and cilia cleanse the air
blood vessel congestion or constriction regulates airflow
what does the olfactory nasal pathway do?
runs alongside resp. pathway
responsible for detecting smells
which respiratory passages are NOT lined by respiratory epithelium?
ethmoidal and middle conchae
Vomeronasal gland
describe a mucus sheet (what produces it and functions)
produced by goblet cells and submucosal glands
moistens air
traps particulate matter
describe the cilia in respiratory epithelium
motile; beats at same time
wafts mucus and trapped particulate towards pharynx where it is swallowed or expectorated
describe the submucosa of respiratory epithelium
highly vascular
warms incoming air
erectile tissue like
congestion - disrupts airflow
vasoconstriction - allows increased airflow during exercise
what passages have an olfactory epithelium?
ethmoidal conchae (and middle concha)
vomeronasal organ
list the contents that make up the olfactory epithelium
Olfactory receptor cells
Bowmans glands
Supporting cells
Basal cells
describe olfactory receptor cells and how they work
bipolar neurons - apical pole carries non-motile cilia with specific odorant binding receptors
unite to form an olfactory nerve which passes through the cribriform plate to terminate in olfactory bulb
what do Bowmans glands do?
secretion solubilizes incoming odorants and washes away excess
what do the supporting cells of olfactory epithelium do?
provide metabolic and physical support to olfactory cells
what do the basal cells of olfactory epithelium do?
stem cells - can differentiate and replace olfactory receptor cells
how many olfactory receptors in the nose: dogs vs humans?
300 million - dogs
600 million - humans
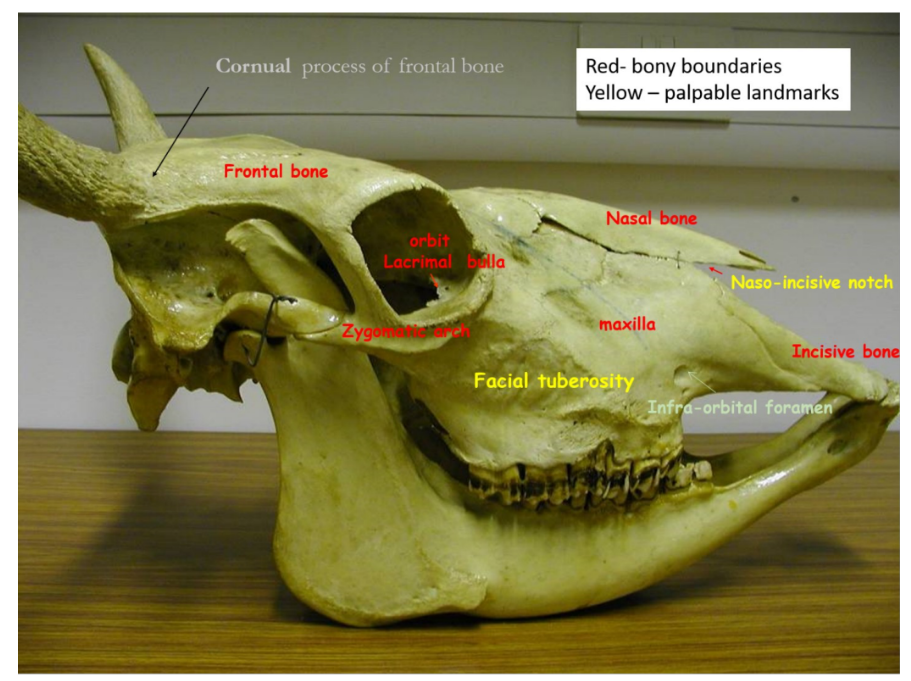
list the bony boundaries of the adult bovine skull?
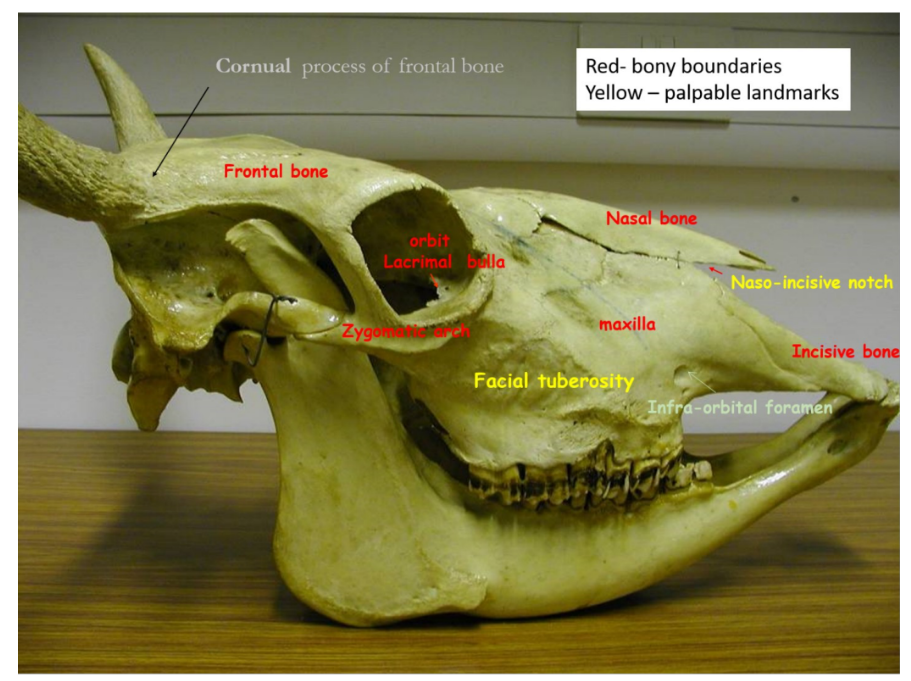
what are the palpable landmarks of an adult bovine skull?
facial tuberosity
Naso-incisive notch
Infra-orbital foramen