Drug Delivery Final Exam
1/125
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
126 Terms
A particular drug can crystallize in different shapes, depending on how the molecules within the crystal are arranged. Drugs that can exist in more than one crystalline shape are called __________ .
A. Polymorphs
B. Amorphous
C. Unstructured
D. Unformed
A. Polymorphs
Hydrophobic interactions are ___________ forces that arise from the inability of nonpolar molecules to interact with water, and are thus driven together by the hydrophobic effect, which is important for a protein's tertiary structure as well as for the formation of lipid bilayers and micelles.
A. Attractive
B. Van der Waals
C. Repulsive
D, Repugnant
A. Attractive
Which forces include dipole-dipole, dipole-induced dipole, and induced dipole-induced dipole? These are relatively weak forces compared to covalent forces, but they are very important in pharmacy, being significant for solubility, complexation, and other types of physical bonding.
A. van der Waals Forces
B. H-bonding Forces
C. Hydrophobic Forces
D. Intermolecular Repulsive Forces
A. van der Waals Forces
Clearance is a primary pharmacokinetic parameter used as a measure of drug _____________ .
A. Absorption
B. Distribution
C. Metabolism
D. Elimination
D. Elimination
Drug targets are generally ____________ that are located in tissues and fluids throughout the body. Some of these targets can be accessed without drug absorption into the bloodstream. For most drug products, however, the targets are in tissues and cells that are accessed from the bloodstream.
A. Macromolecules
B. Micromolecules
C. Nanomolecules
D. Metabolites
A. Macromolecules
Dissolution is well modeled by the _______________ relationship, which describes the relationship between the rate of dissolution and such properties as solute particle surface area (a function of particle size), the thickness of a stagnant solvent layer surrounding the drug particle, the concentration gradient between that in the stagnant layer and that in the bulk solvent, and the solvent viscosity.
A. Noyes-Whitney
B. VanKel
C. Hixson-Crowell Cube-Root
D. Distek
A. Noyes-Whitney
For certain drug products that are administered to sensitive areas, such as parenterals and ophthalmics, it is important to consider their relative osmolarity to body fluids to avoid untoward consequences, such as cell and tissue _________ and patient discomfort.
A. Damage
B. Proliferation
C. Liberation
D. Hydration
A. Damage
Two important categories of solutions relevant to pharmacy practice are solutions of electrolytes, such as sodium chloride, and nonelectrolytes, such as dextrose. Drugs that are weak acids or weak bases, are refered to as _____ _________.
A. Nonelectrolyte Solutions
B. Weak Electrolytes
C. Strong Electrolytes
D. Anion Solutions
B. Weak Electrolytes
Salts of weak acids and weak bases are completely ionized in water and are very soluble. What are two ways to increase the solubility of a weak acid drug in aqueous solution?
A. Increase pH
B. Increase alcohol content
C. Decrease pH
D. Increase water content
A. Increase pH
B. Increase alcohol content
In an aqueous solution, electrolytes exhibit important properties that differentiate them from nonelectrolytes. Which of the following is a property?
A. Electrolytes tend to show slow chemical reactions compared with nonelectrolyte solutions
B. Electrolytes can conduct an electrical current
C. Electrolytes do not exhibit anomalous colligative properties compared with nonelectrolytes
D. Electrolytes can be classified into four groups, depending on their ability to ionize in an aqueous solution.
B. Electrolytes can conduct an electrical current
According to the pH-partition hypothesis, the absorption of a weak electrolyte is determined mainly by the extent to which the drug exists in its _____________ form at the site of absorption.
A. Unionized
B. Ionized
C. Precipitation
D. Amorphous
A. Unionized
Pharmacokinetics mathematically relates the ADME processes to parameters that are used to calculate and adjust dosing regimens for patients. Which of the following is the process of drug being broken down into a less toxic form? ( Hint: During this step the drug is prepared for removal from the body)
A. Absorption
B. Distribution
C. Excretion
D. Metabolism
D. Metabolism
Which of the following states of matter can be defined as something that occupies a definite volume and takes the shape of the container required to hold it? (Hint: this state of matter is denser than gases and possess less kinetic energy than gases)
A. Liquids
B. Vapor
C. Air
D. Solids
A. Liquids
If the drug is an aqueous suspension, the suspended crystals must dissolve in the body fluid to result in drug absorption. If the drug is in a compressed tablet, the drug crystals are released and must dissolve, during and after a process of tablet disintegration, which functions to fully expose the drug crystals to the gastrointestinal fluids for dissolution. The above examples best describe which of the following pharmacokinetic processes?
A. Liberation
B. Distribution
C. Excretion
D. Metabolism
A. Liberation
Once a drug is in the bloodstream, it will distribute fairly rapidly throughout the body. Distribution is generally fastest to well-perfused organs. Which of the following is a well-perfused organ? Select all that apply.
A. Liver
B. Brain
C. Muscle
D. Fat
A. Liver
B. Brain
An intravenous drug is administered directly into the systemic circulation and has a bioavailability of _____ %.
A. 0
B. 10
C. 50 or half-life
D. 100
D. 100
If liberation of the tablet takes the longest time, which of the following is the rate limiting step in drug absorption from a tablet dosage form?
A. Tablet disintegration
B. Dissolution of the solid drug particles in gastrointestinal fluids
C. Gastric emptying into the small intestine
D. Absorption into the systemic circulation
A. Tablet disintegration
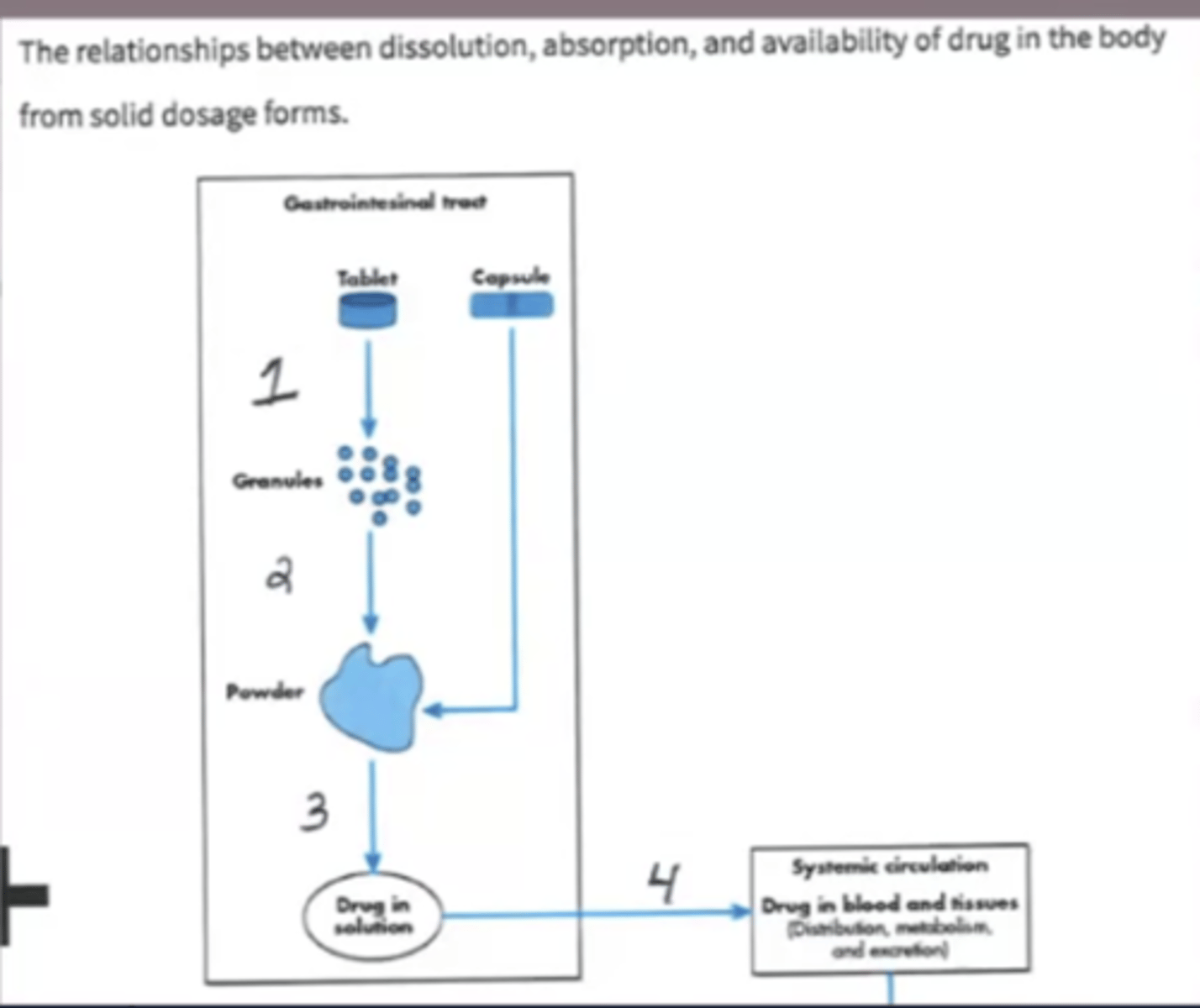
Using the attached diagram that depicts the dissolution of a solid dosage form, identify what process is labeled at #3.
A. Absorption
B. Dissolution
C. Disintegration
D. Freezing Point Depression
B. Dissolution
Aqueous solution systems can be classified by thermodynamics. Which of the following can be described as a solution for which there is no change in the physical properties of the components other than dilution when they are mixed. No heat is given off or taken in, and the volume does not shrink or expand.
A. Ideal
B. Real
C. Exothermic
D. Endothermic
A. Ideal
A salt is formed by an acid-base reaction involving either a proton donation or a proton acceptance. When a salt is added to water, the solution can be neutral, acidic, or basic, depending on the salt. Which of the following terms is the interaction of the ions of the salts with the ions of water?
A. Anhydrous
B. Hydrolysis
C. Cation
D. Anion
B. Hydrolysis
Which of the following can be defined as a chemically and physically homogeneous mixture of two or more substances?
A. Solution
B. Binary Solution
C. Emulsion
D. Suspension
A. Solution
There are two types of stability that need to be considered for stability in the solid state: chemical and physical. Chemical stability can result from a number of different chemical reactions depending on the molecule, conditions, and other components of the dosage form. Which of the following reactions is an example of this phenomenon? Select ALL that apply.
A. Cyclization
B. Hydrolysis
C. Oxidation
D. Combustion
A. Cyclization
B. Hydrolysis
C. Oxidation
Surface tension is another physical property of liquids. The surface tension of liquids decreases with an increase in temperature. Therefore, the relationship between surface tension of liquids and temperature is nearly _____________ .
A. Linear
B. Non-linear
C. Perpendicular
D. Peripheral
A. Linear
The temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure describes which of the following? Hint: Vapor pressure and this variable are inversely related.
A. Boiling Point
B. Freezing Point
C. Buffer Capacity
D. Hydrogen Bonding
A. Boiling Point
Which of the following statements is true about the liquid state of matter? Select ALL that apply.
A. A liquid occupies a definite volume and takes the shape of the container required to hold it.
B. Liquids are less compressible than gases and more compressible than solids
C. Liquids flow very readily, and the flow is not influenced by friction
D. Liquids do not exhibit surface tension
A. A liquid occupies a definite volume and takes the shape of the container required to hold it.
B. Liquids are less compressible than gases and more compressible than solids
One of the applications of gases in pharmaceutical sciences is in the interpretation of blood gases in patients. Which of the following is an "important" blood gas ? Select ALL that apply.
A. Oxygen
B. Carbon Dioxide
C. Hydrogen
D. Sodium Chloride
A. Oxygen
B. Carbon Dioxide
Using the attached diagram that depicts the dissolution of a solid dosage form, identify what process is labeled at #1.
A. Disintegration
B. Deaggregation
C. Dissolution
D. Absorption
A. Disintegration
The two types of attractive forces are called cohesive forces and adhesive forces. Which of the following terms describes the forces that originate from molecular internal vibrations in nonpolar molecules to produce attraction that arises because of synchronized fluctuating dipoles in neighboring atoms?
A. London Forces
B. Debye Forces
C. Dipole-Dipole Forces
D. Keesom Forces
A. London Forces
Which of the following statements are true? Select ALL that apply.
A. The liver is the major excretory organ
B. The kidneys are the major excretory organ
C. First pass metabolism can limit bioavailability
B. The kidneys are the major excretory organ
C. First pass metabolism can limit bioavailability
Which of the following statements are true pertaining to factors that affect the fate of the drug in the body? Select ALL that apply.
A. Most drugs are weak acids or bases
B. Some solubility in lipids and water is essential
C. Protein binding is a irreversible process D. Only bound drug can transfer from the blood to interstitial fluid
A. Most drugs are weak acids or bases
B. Some solubility in lipids and water is essential
If the bioavailability factor for a drug in a dosage form is 0.65, how many mg of a drug would be available for absorption from a 126-mg tablet of the drug? Report to the tenths place. NO UNITS
A. 81.9
B. 63.4
C. 87.2
D. 43.6
A. 81.9
Which of the following is the primary absorption site and purpose of a drug given as an IV infusion ?
A. None, formulated to give a systemic effect
B. None, for local action in the CNS
C. Dura mater, local effect
D. Stratum Corneum, systemic effect
A. None, formulated to give a systemic effect
Which of the following is the primary absorption site of a drug given as a topical formulation?
A. Blood Capillaries
B. Stratum Corneum
C. Sinusoidal Capillaries
D. Lymphatic Capillaries
B. Stratum Corneum
Depending on the pH of the environment in which organic weak electrolytes are present, they can exist in either an ionized form or an unionized form. This degree of ionization can affect the absorption, transport, and excretion of drugs. What are ionization constants used to measure?
A. The strength of acids and bases
B. The potential of the drug to leave the formulation
C. The state of the drug at a neutral pH
D. The rate of absorption
A. The strength of acids and bases
Which of the following are true about ophthalmics? Select all that apply.
A. Isotonic
B. Free of particulates
C. Active for viscosity
D. Not sterile
A. Isotonic
B. Free of particulates
Pharmaceutical solutions are mostly solids dissolved in a liquid, which is usually water or water combined with other liquids. Which of the following is an example of this type of solution?
A. Air
B. Fog
C. Gold-silver mixture, mixture of alums
D. Aqueous sodium chloride solution
D. Aqueous sodium chloride solution
Which of the following is an example of a dosage form that can be formulated as en epidural injection?
A. Aqueous Solution
B. Aqueous Suspension
C. Tablet
D. Cream
E. Semisolid Mixture
A. Aqueous Solution
If a drug is given via the buccal route, what is the site of administration?
A. Between cheek and gums
B. Bone Marrow
C. Mouth
D. Under the tongue
A. Between cheek and gums
Weakly ___________ drugs tend to dissolve better in the stomach, where more of the drug will be ionized.
A. Acidic
B. Basic
C. Soluble
D. Organic
B. Basic
__________________ can be defined as the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation.
A. Mole Fraction
B. Bioavailability
C. Liberation
D. Absorption
B. Bioavailability
In which type of dispersion, homogenous or heterogenous, is the dispersed phase physically distinguishable from the medium in which it is dispersed?
a. Homogenous dispersion
b. True solution
c. Heterogenous dispersion
d. None
c. Heterogenous dispersion
Which of the following is an example of solid in liquid dispersion?
a. Cream
b. Suppositories
c. Suspension
d. Gels
c. Suspension
A physician has two injection vials, A and B, which are unlabeled. One is saline, and the other albumin-containing solution. They look very similar. A pharmacist is consulted to identify vials A and B.The pharmacist shines light through the two vials. Solution A does not scatter light when light passes through. Solution B scatters light when light passes through.Which of the following statements is true regarding vials A and B?
a. Vial B is a saline solution
b. Vial A is an albumin solution and Vial B is a saline solution
c. Vial A is saline solution and Vial B is albumin solution
d. Vial A contains colloidal particles
c. Vial A is saline solution and Vial B is albumin solution
Which of the following is an example of liquid in solid dispersion?
a. Solid foams
b. Suppositories
c. Gels
d. Liquid spray
c. Gels
Which of the following is an example of a solid in solid emulsion?
a. Cream
b. Suppositories
c. Gels
d. Pediatric suspension
b. Suppositories
Creams and lotions are examples of a(n)
a. Foam
b. Emulsion
c. Suspension
d. Aerosol
b. Emulsion
Creams tend to separate from the dispersion medium by rising.
a. True
b. False
a. True
The light scattering properties of colloidal systems is called
a. Brownian effect
b. Tyndall effect
c. Rising
d. Sedimentation
b. Tyndall effect
Insulin and albumin are examples of
a. Hydrophobic colloids
b. Hydrophillic colloids
c. None
b. Hydrophillic colloids
Ibuprofen suspension is an example of
a. Colloidal dispersions
b. Coarse dispersion
c. None
b. Coarse dispersion
According to Stoke's equation, an increase in the crystal particle size of a coarse suspension ___________ the sedimentation rate of the suspension:
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Contains constant
a. Increases
A bottle of milk is an example of
a. None
b. Coarse dispersion
c. Colloidal dispersion
d. Molecular dispersion
c. Colloidal dispersion
If the length of the bar, L, is 5 cm and the mass required to break a soap film is 0.50 g, what is the surface tension of the soap solution? Recall that the downward force equals the mass multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity. With g=9.81 m/s^2= 981 cm/s^2 1 dyne/cm= 1 g/s^2
a. 40 dynes/cm
b. 25 dynes/cm
c. 49 dynes/cm
d. 35 dynes/cm
c. 49 dynes/cm
According to Stoke's equation, an increased viscosity of a coarse suspension ___________ the sedimentation rate of the suspension:
a. Increases
b. Contains constant
c. Decreases
c. Decreases
What are the two phases in contact for emulsion, creams, and lotions?
a. Solid and liquid
b. Liquid and gel
c. Liquid and liquid
d. Gels and solid
c. Liquid and liquid
A liquid-solid interface is found in a(n)
a. Emulsion
b. Suspension
c. Aerosol
d. Powder particle in contact
b. Suspension
What is an anti-foaming agent's Hydrophilic Lipophilic Balance (HLB) range?
a. 13-15
b. 2-3
c. 3-6
d. 7-9
b. 2-3
When water-loving groups in a surfactant are predominant, the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance is
a. High
b. Low
c. Balanced
a. High
When oil-loving groups in a surfactant are predominant, the hydrophilic-lipophilic balance is
a. High
b. Balanced
c. Low
c. Low
The properties of the molecules forming the suspension interface are sufficiently different from those in the bulk of each phase.
a. True
b. False
a. True
What is the HLB of Polysorbate 80, NF, (Tween 80), for which S=50 and A=200?
a. 5
b. 10
c. 15
d. 20
c. 15
How much B=Span 80 (HLB=4.3) and A=Tween 80 (HLB=15) do we need for a requires HLB of 10?
a. 47% and 53%
b. 62% and 38%
c. 35% and 65%
d. 73% and 27%
a. 47% and 53%
Which of the following is not a component of creams or lotions?
a. Water
b. Oil
c. Surfactant
d. Interfacial tension enhancers
d. Interfacial tension enhancers
What is the essential first step in a solid dosage form dissolution process?
a. Disintegration
b. Wetting
c. Absorption
d. Diffusion
b. Wetting
Viscosity is the study of the resistance to flow of (_____________________)
a. Liquids
b. Solids
c. None
a. Liquids
What is the definition of the term "η" is the Newton equation of flow?
a. Viscosity
b. Fluidity
c. Diffusion
d. Rate of shear
a. Viscosity
What is the definition of the term "Φ" is the Newton equation of flow?
a. Viscosity
b. Fluidity
c. Diffusion
d. Rate of shear
b. Fluidity
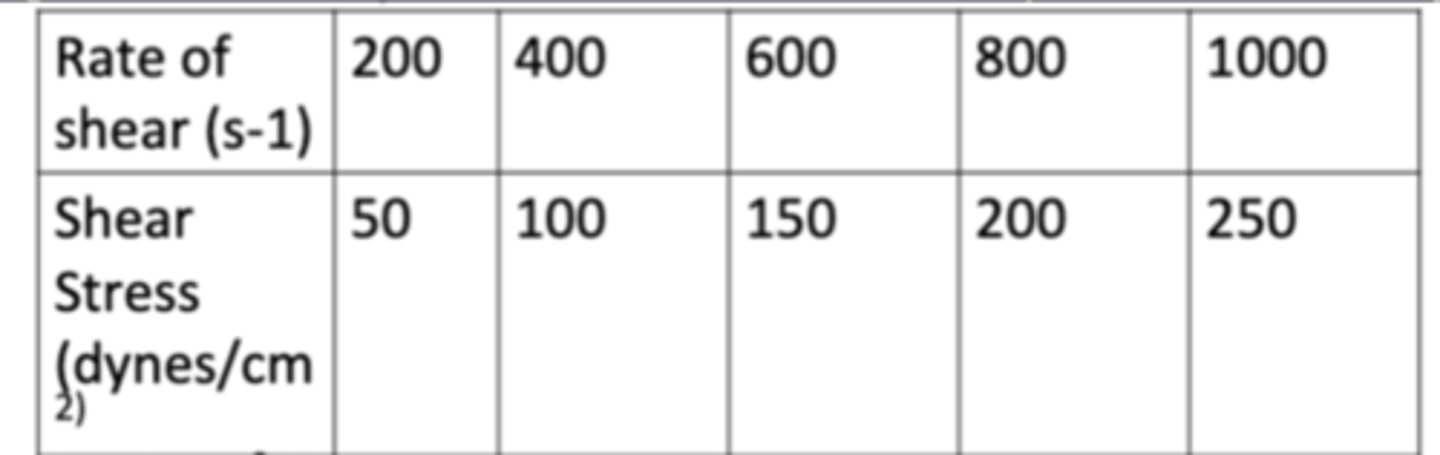
The following data show the rate of shear as a function of shear stress for a Newtonian fluid at 25C (77F). Determine the fluidity of the fluid.
a. 1 cm^2/dynes
b. 4 cm^2/dynes
c. 8 cm^2/dynes
d. 10 cm^2/dynes
b. 4 cm^2/dynes
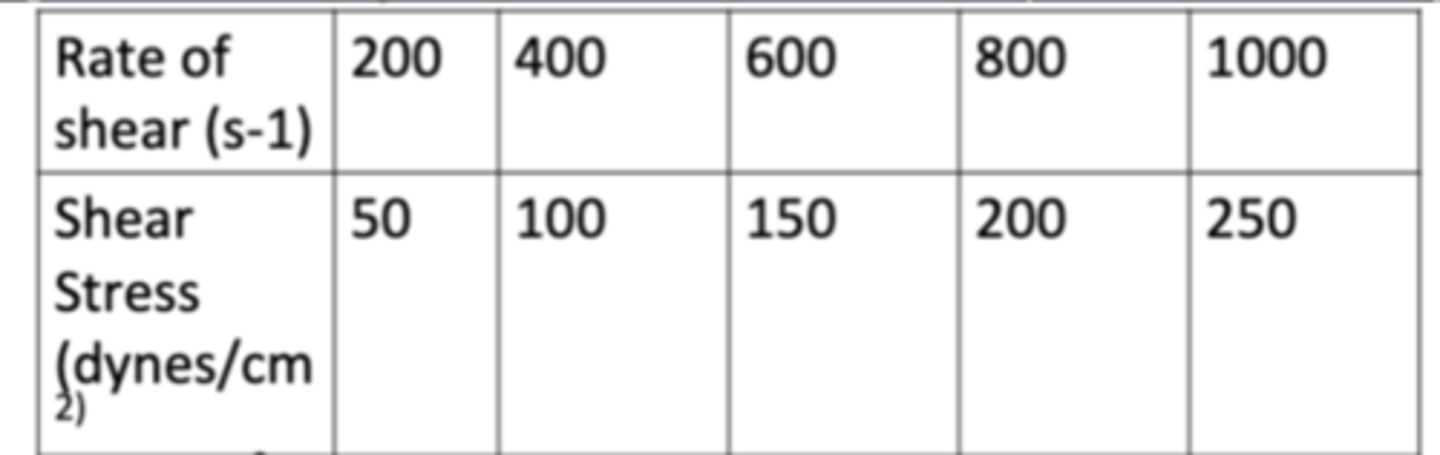
The following data show the rate of shear as a function of shear stress for a Newtonian fluid at 25C (77F). Determine the viscosity of the fluid in cps.
a. 15 cps
b. 10 cps
c. 25 cps
d. 10 cps
c. 25 cps
The viscosity of Newtonian fluids ____________ with increasing temperature.
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Remains constant
d. None
b. Decreases
A pharmacist prepares a micelle by adding an amphiphilic molecule in water. Then the measured size of the micelle at the critical micelle concentration was 80 nanometers. The pharmacist concludes that he has successfully prepared a (_______________).
a. Coarse dispersion
b. Colloidal dispersion
c. True solution
d. None
b. Colloidal dispersion
An aqueous solution of insulin and albumin are examples of (_______________).
a. Hydrophillic colloids
b. Hydrophobic colloids
c. Lipophobic colloids
d. None
a. Hydrophillic colloids
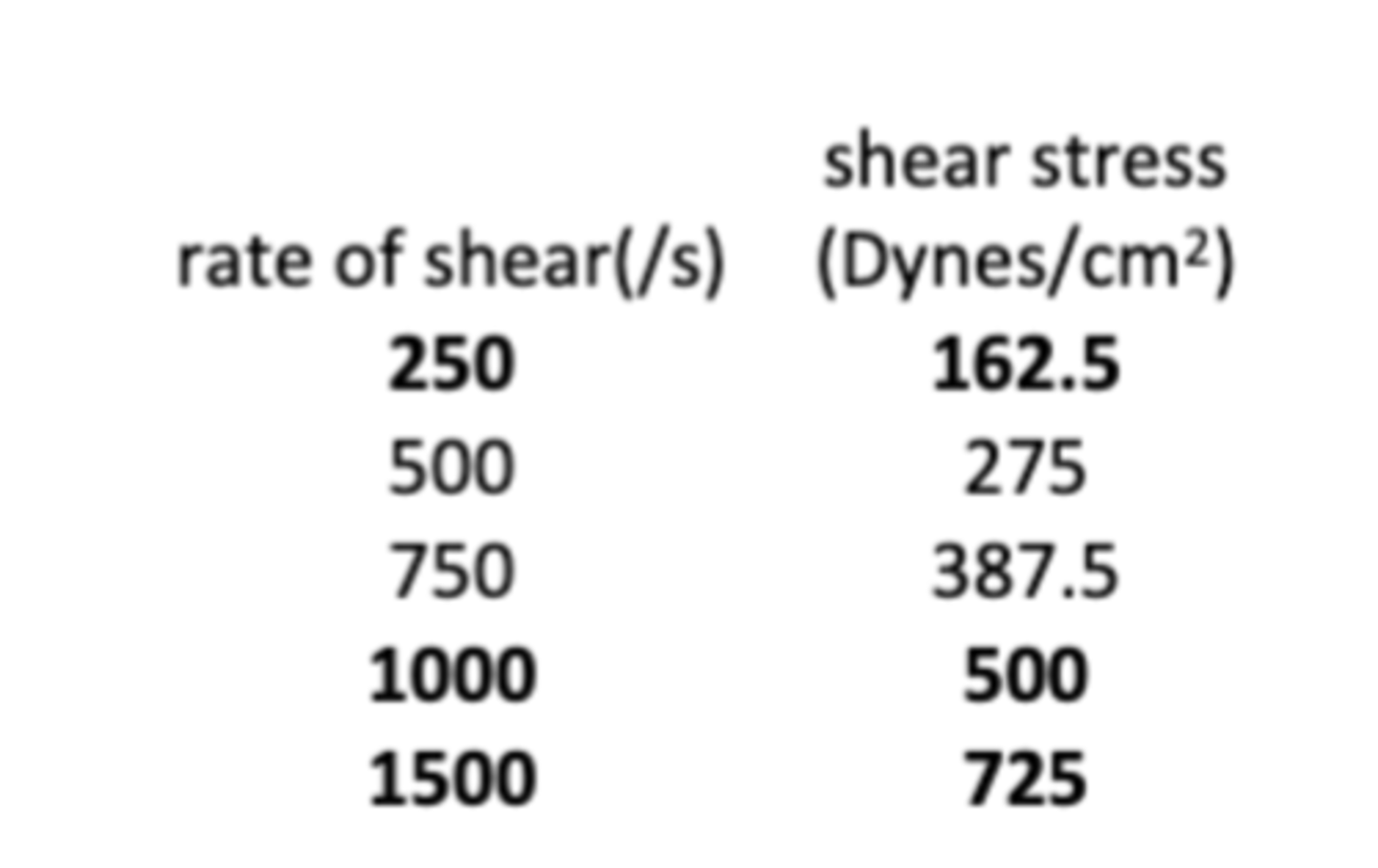
The following data show the relationship between the shear and shear stress rate for a topical formulation that exhibits plastic rheology. What is the yield value of the formulation?
a. 20 dynes/cm2
b. 50 dynes/cm2
c. 75 dynes/cm2
d. 100 dynes/cm2
b. 50 dynes/cm2
What is the viscosity of a Newtonian fluid if the activation energy is 4.25 x 10^3 cal/mole, the gas constant R=1.987 and A = 1.21 x 10^-3 cps and the temperature = 25C?
a. 1.58 cps
b. 2.54 cps
c. 2.34 cps
d. 1.24 cps
a. 1.58 cps
The following data shows the relationship between the rate of shear and shear stress for a topical formulation that exhibits plastic rheology. What is the plastic viscosity of the formulation?
a. 35 cps
b. 40 cps
c. 45 cps
d. 50 cps
c. 45 cps
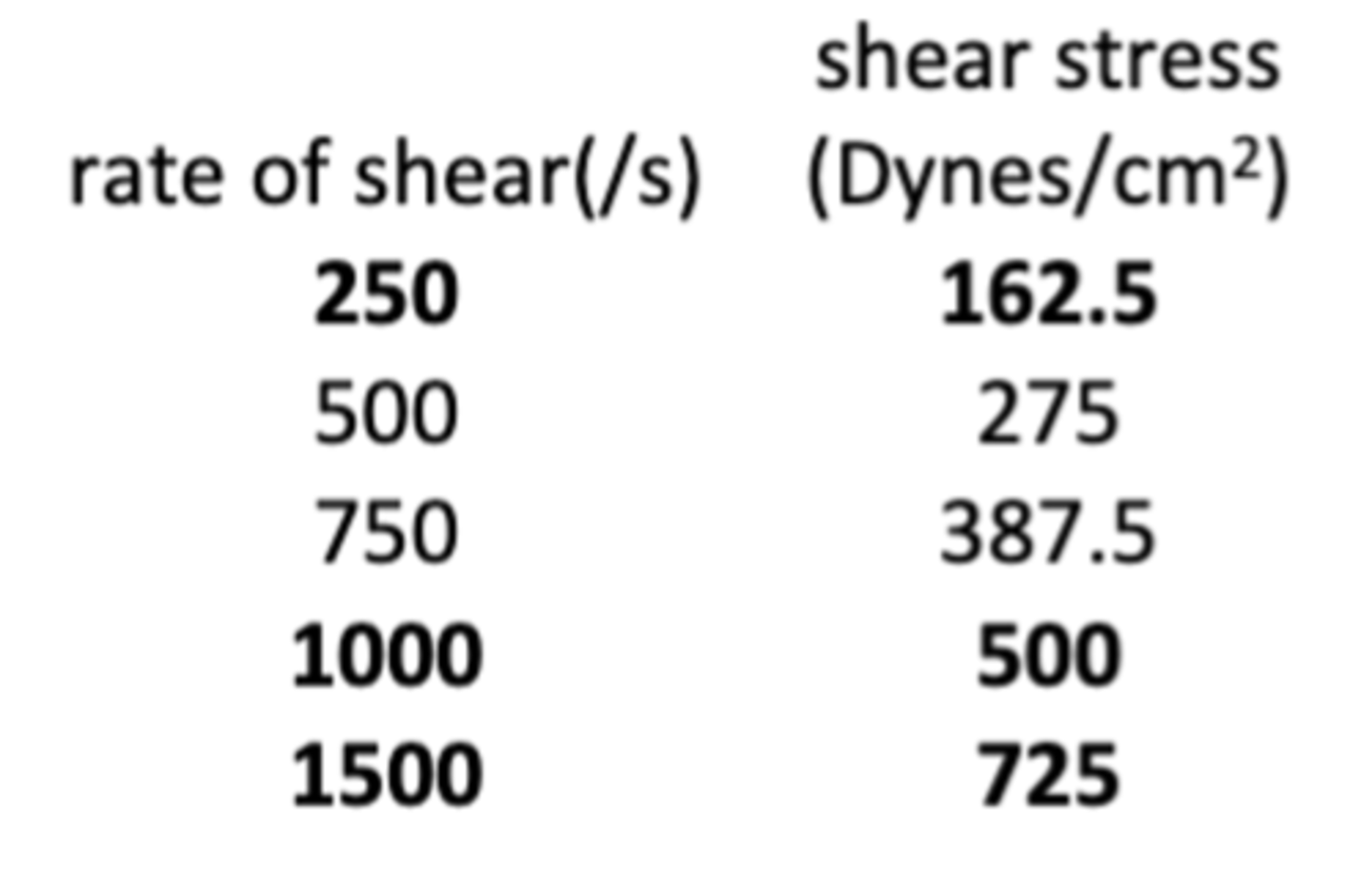
The following graph depicts the viscosity of different rheology system vs the shear rate. Which of the following curve is a dilatant or shear thickening system?
a. Curve A
b. Curve B
c. Curve C
c. Curve C
A nicotine transdermal patch (Habitrol) is designed with a cross-sectional area of 10.5 cm^2 and has a membrane thickness of 0.075 cm. The lag time of diffusion of nicotine was calculated to be 12.5 min. The concentration of nicotine inside the patch is 3.0 x 10^-5 g/cm^3. The diffusion coefficient of nicotine from this patch is 1.025 x 10^-6 cm^2/sec
A. True
B. False
B. False
Mineral oil was dispersed as globules in an oil-water emulsion to form a total surface area of globules of 10^8c m^2. If the presence of emulsifying agent results in an interfacial tension between oil and the water phase of 5 erg/cm^2, what is the total surface free energy of the system in calories, in SI units?
a. 50.2 joule
b. 40.6 joule
c. 78.3 joule
d. 38.8 joule
a. 50.2 joule
The HLB of polyoxyethylene sorbitan monolaurate(Tween 20), for which S = 45.5 and A = 276, is
a. 15.8
b. 19.2
c. 16.7
d. 20.1
c. 16.7
Calculate the HLB value of polyoxyethylene 20 sorbitanmonolaurate (Tween 20) which has a MW = 1226? The hydrophilic portion of this molecule consists of sorbitan (MW=164=> P) and 20 moles of ethylene oxide (MW= 880=>E).
a. 18
b. 17.03
c. 20.4
d. 15
b. 17.03
How much Span 80 (HLB = 4.3) and Tween
80 (HLB = 15) do we need for a required HLB of 12 for a stable prescription (Rx).
A) 72% Tween 80 and 28% Span 80
B) 28% Tween 80 and 72% Span 80
C) 25% Tween 80 and 75% Span 80
D) 75% Tween 80 and 25% Span 80
A) 72% Tween 80 and 28% Span 80
Calculate the rate of shear applied by a patient in rubbing a 200-μm-thick film of ointment on the skin surface at a rate of 10 cm/s.
a. 300 /s
b. 400 /s
c. 500 /s
d. 600 /s
c. 500 /s
Use an Ostwald viscometer at 20 ºC the time for the flow of water through the apparatus is 297.3 seconds. When the instrument was calibrated with carbon disulfide (density 1.2632 g/mL), the time of flow was 85.1 sec. The density and the viscosity of water at 20ºC are 0.9982 g/mL and 1.002 cp, respectively. What is the viscosity of carbon disulfide at 20 ºC?
a. 0.454 cps
b. 0.363 cps
c. 0.545 cps
d. 0.672 cps
b. 0.363 cps
The time for water to flow through an Ostwald pipette at 20ºC was 297.3 sec. The density of water at 20 ºC is 0.9982g/mL and the density of a sample of olive oil is 0.910g/mL. The viscosity of water at 20 C is 1.002 cp and the viscosity of the sample of olive oil is 84.0 cps. How long will it take for the olive oil to flow through the Ostwald pipette at 20 ºC?
a. 455.65 minutes
b. 312.72 minutes
c. 537.84 minutes
d. 404.92 minutes
a. 455.65 minutes
Fluocinolone acetonide is a topical corticosteroid drug with anti-inflammatory properties. The release of fluocinolone acetonide from a patch with a cross-sectional area of 12.5 cm^2 and a membrane thickness of 75 μm was investigated. The lag time of diffusion of fluocinolone acetonide was calculated to be 8.45 min. The concentration of fluocinolone acetonide inside the patch is 4.5 x 10^-5 g/cm^3. and a partition coefficent (K) is 2.43 (Select all that apply)
A. The permeability coefficient is 6 x 10^-6 cm/s
B. The permeability coefficient is 1.85 x 10^-6 cm/s
C. The total amount of fluocinolone acetonide in micrograms released from the patch in 24h is 290 μg
D. The diffusion coefficient is 1.85 x 10^-6 cm/s
E. The permeability coefficient is 6 x 10^-6 s/cm
A. The permeability coefficient is 6 x 10^-6 cm/s
C. The total amount of fluocinolone acetonide in micrograms released from the patch in 24h is 290 μg
Mechanisms of mass transport include active, passive, and facilitated processes:
A. True
B. False
A. True
Passive diffusion is the most common way drugs cross biological and synthetic membranes. It is well modeled by Fick's law of diffusion, which contains important parameters for estimating the speed of movement (the flux) of a substance down its concentration gradient:
A. True
B. False
True
All of the following statements about plasma protein binding of a drug are true except?
A. Displacement of a drug from plasma protein binding sites results in a transient increased volume of distribution (VD)
B. Displacement of a drug from plasma protein binding sites makes more free drug available for glomerular filtration.
C. Albumin is the major protein involved in the protein binding of drugs
D. Drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins generally have a greater volume of distribution compared with drugs that are highly bound to tissue proteins
D. Drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins generally have a greater volume of distribution compared with drugs that are highly bound to tissue proteins
Drug displacement is when a highly protein-bound drug is displaced from binding by a second drug or agent.
A. True
B. False
A. True
Drugs that are highly bound to tissue proteins have a:
A. low volume of distribution
B. high volume of distribution
C. No volume of distribution
A. low volume of distribution
Which of the following statements are true about drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins? (Select all that apply)
A. They have a low fraction of free drug (fu = unbound or free drug fraction) in the plasma water.
B. Plasma protein-bound drug does not diffuse easily and is therefore less extensively distributed to tissues.
C. They have a high fraction of free drug (fu = unbound or free drug fraction) in the plasma water.
D. Highly plasma protein-bound drugs diffuse easily and is therefore more extensively distributed to tissues
A. They have a low fraction of free drug (fu = unbound or free drug fraction) in the plasma water.
B. Plasma protein-bound drug does not diffuse easily and is therefore less extensively distributed to tissues.
Which of the parameters are affected by the protein binding of drugs in the body? Select all that apply.
A. Drug distribution
B. Drug excretion
C. Drug metabolism
D. Drug metabolism but not distribution
A. Drug distribution
B. Drug excretion
C. Drug metabolism
Which of the following may bind to drugs if albumin sites become saturated?
A. Lipoprotein
B. Immunoglobulin
C. alpha-1-acid glycoprotein
D. lidocaine
A. Lipoprotein
alpha-1-acid glycoprotein binds with which type of drugs:
A. Weak acidic drugs
B. Weak basic drugs
C. Strong acidic drugs
D. Strong basic drugs
B. Weak basic drugs
Albumin binds to which of the following types of drugs:
A. Weak acidic drugs
B. Weak basic drugs
C. Strong acidic drugs
D. Strong basic drugs
A. Weak acidic drugs
Factor(s) influencing drug and protein binding are: (Select all that apply)
A. Affinity between drug and plasma protein
B. Competition of drugs at the plasma protein binding site
C. The pathophysiologic condition of the patient (hepatic or renal impairment may drastically affect protein binding)
D. None
A. Affinity between drug and plasma protein
B. Competition of drugs at the plasma protein binding site
C. The pathophysiologic condition of the patient (hepatic or renal impairment may drastically affect protein binding)
For a drug that has an affinity for plasma protein, only free drug will diffuse freely between the plasma and extracellular water:
A. True
B. False
A. True
Protein-bound drug is a large complex that will cross the capillary wall:
A. True
B. False
B. False
Protein-bound drug is pharmacologically active:
A. True
B. False
B. False
The drug molecules that do not bind to plasma protein are pharmacologically active:
A. True
B. False
A. True