Gross Anatomy Module 5: Muscle And Fascia In The Upper Extremities
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
(Upper limb fascia:) Fascia of pectoral region
•Pectoral fascia
•Axillary fascia
•Clavipectoral fascia

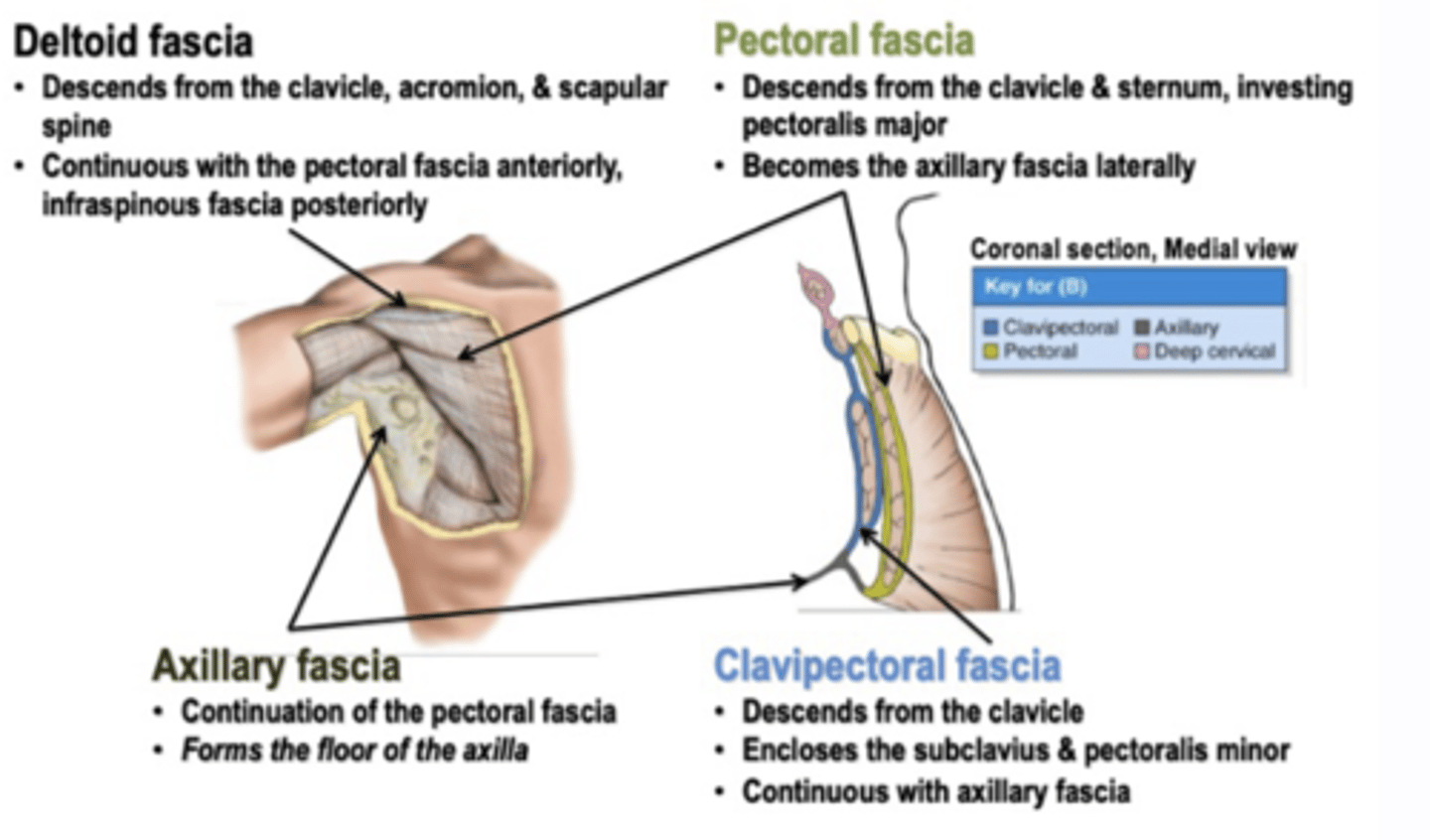
(Fascia of pectoral region:) Pectoral fascia
invests pectoralis major muscle and is continuous inferiorly with the fascia of the anterior abdominal wall
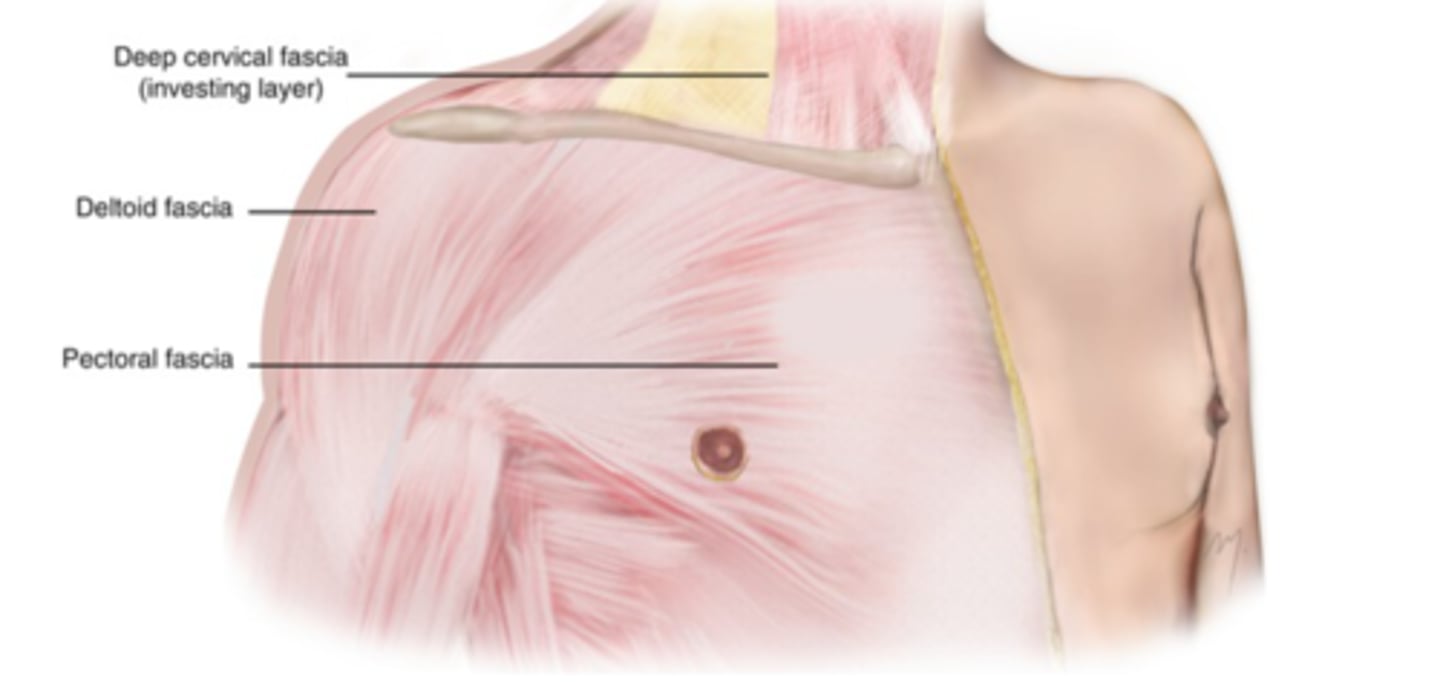
(Fascia of pectoral region:) Axillary fascia
forms the floor of the axilla and is continuous with the pectoral fascia. Clinical relevance: holds anesthetics for brachial plexus blocks
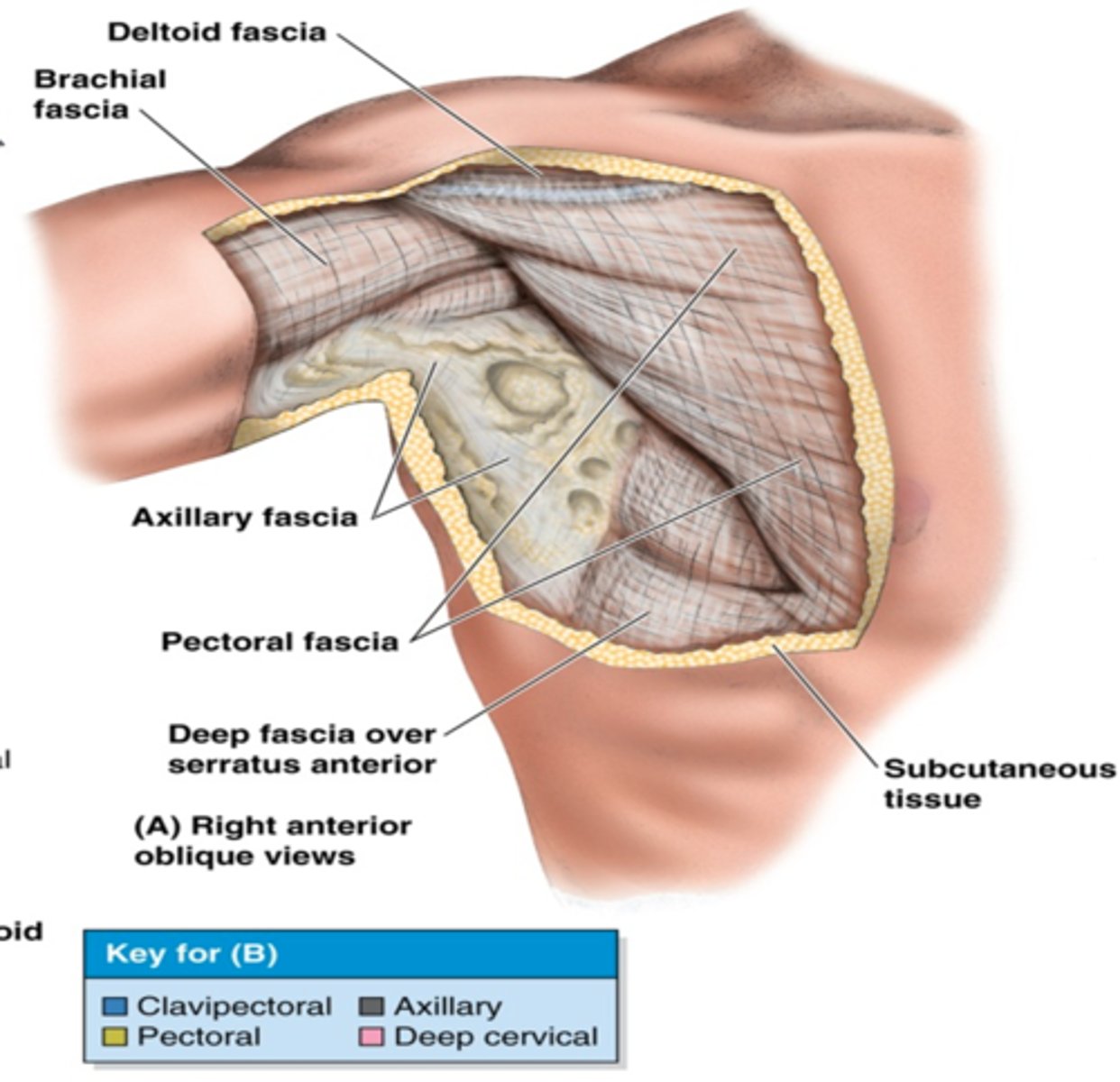
(Fascia of pectoral region:) Clavipectoral fascia
deep to pectoral fascia, invests the pectoralis minor muscle and is continuous inferiorly with the axillary fascia
(Upper Limb Fascia:) Fascia of the shoulder region
•Deltoid fascia
•Supraspinous and infraspinous fascias
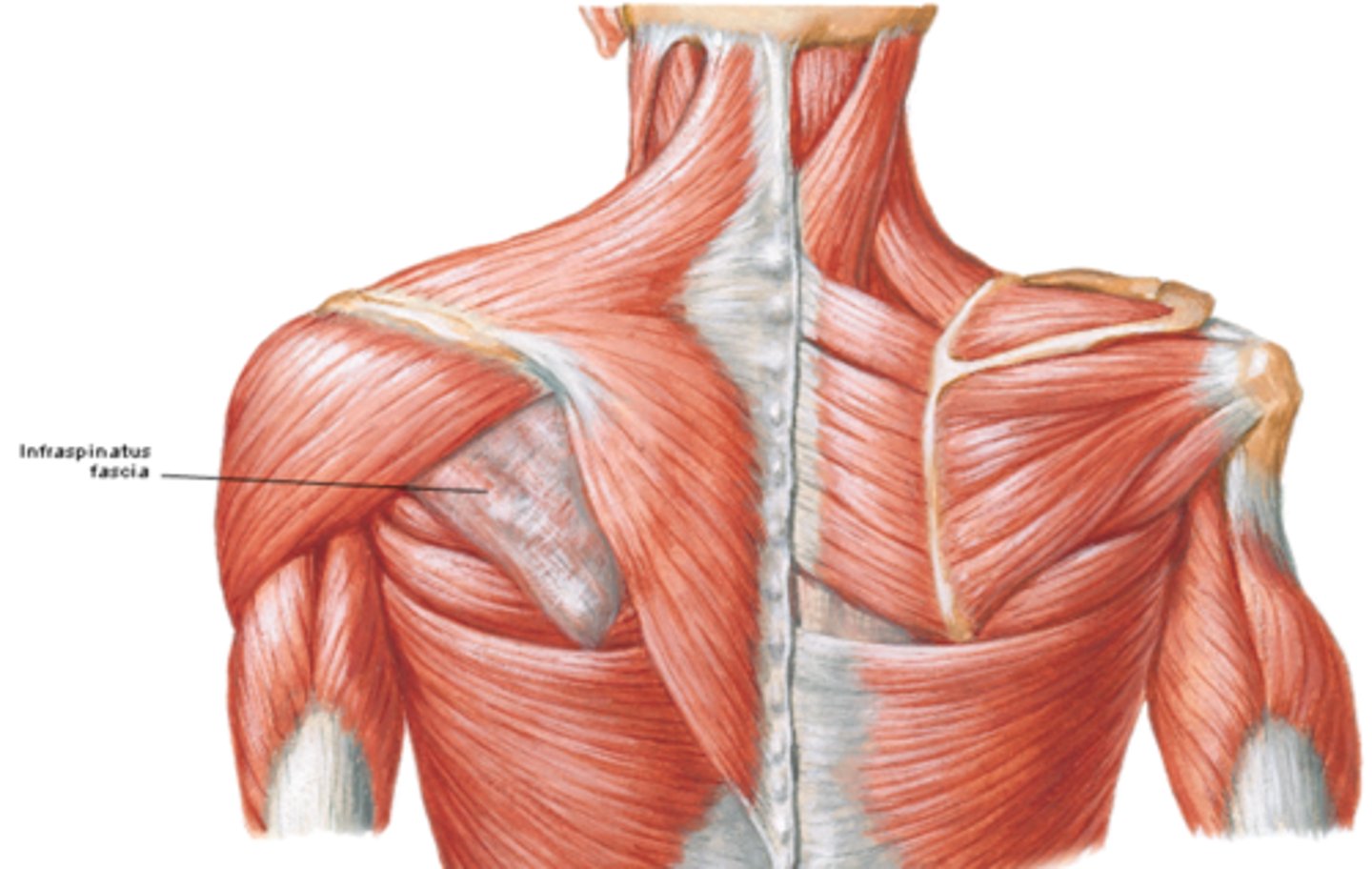
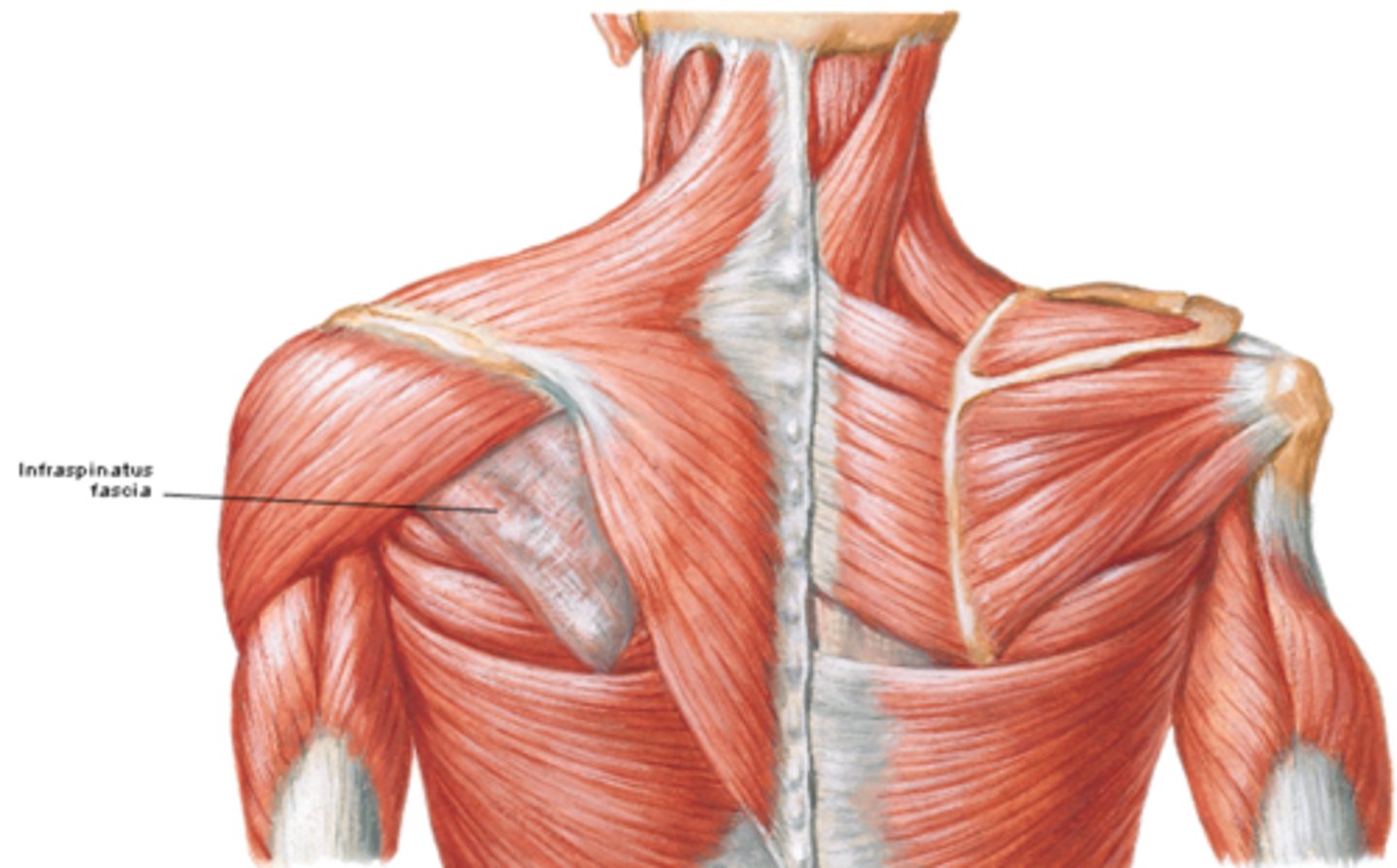
(Fascia of the shoulder region:) Deltoid fascia:
covers the deltoid muscle and is continuous anteriorly with the pectoral fascia and posteriorly with the infraspinous fascia
(Fascia of the shoulder region:) Supraspinous and infraspinous fascias:
overlies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, respectively; and attaches to the scapula
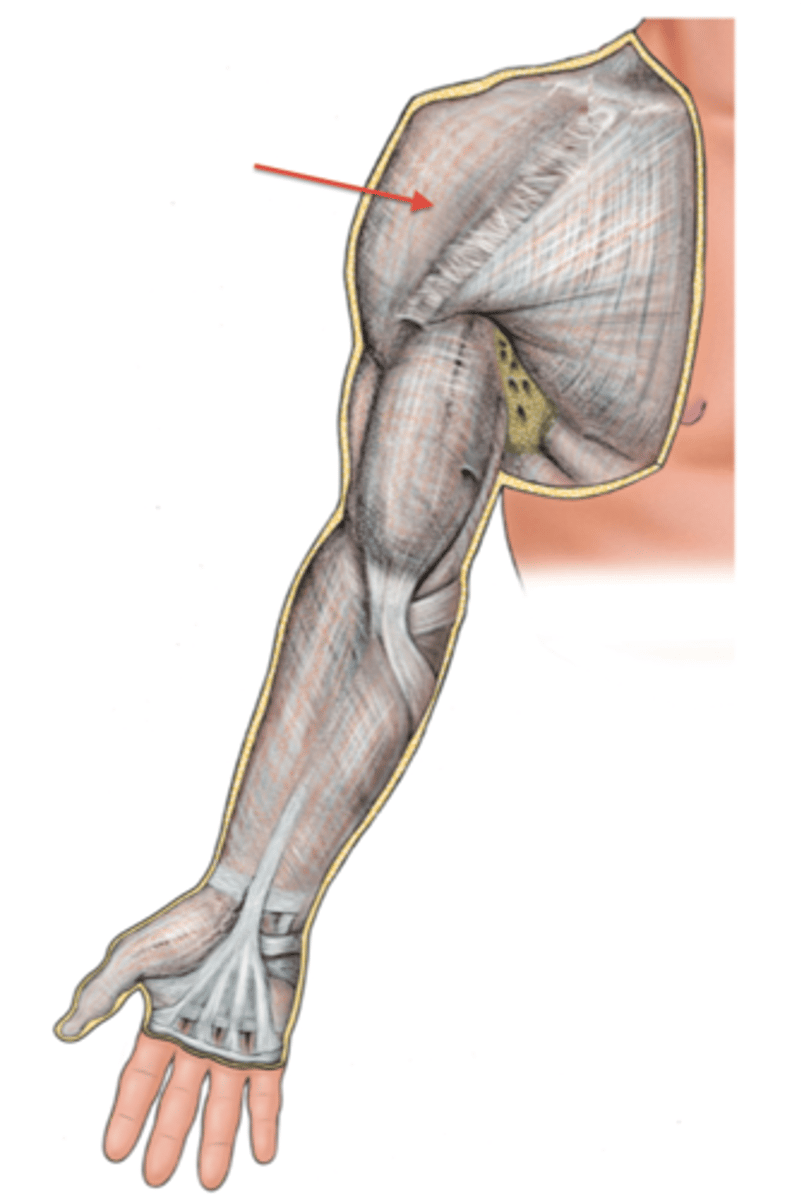
(Upper limb fascia) Fascia of arm region
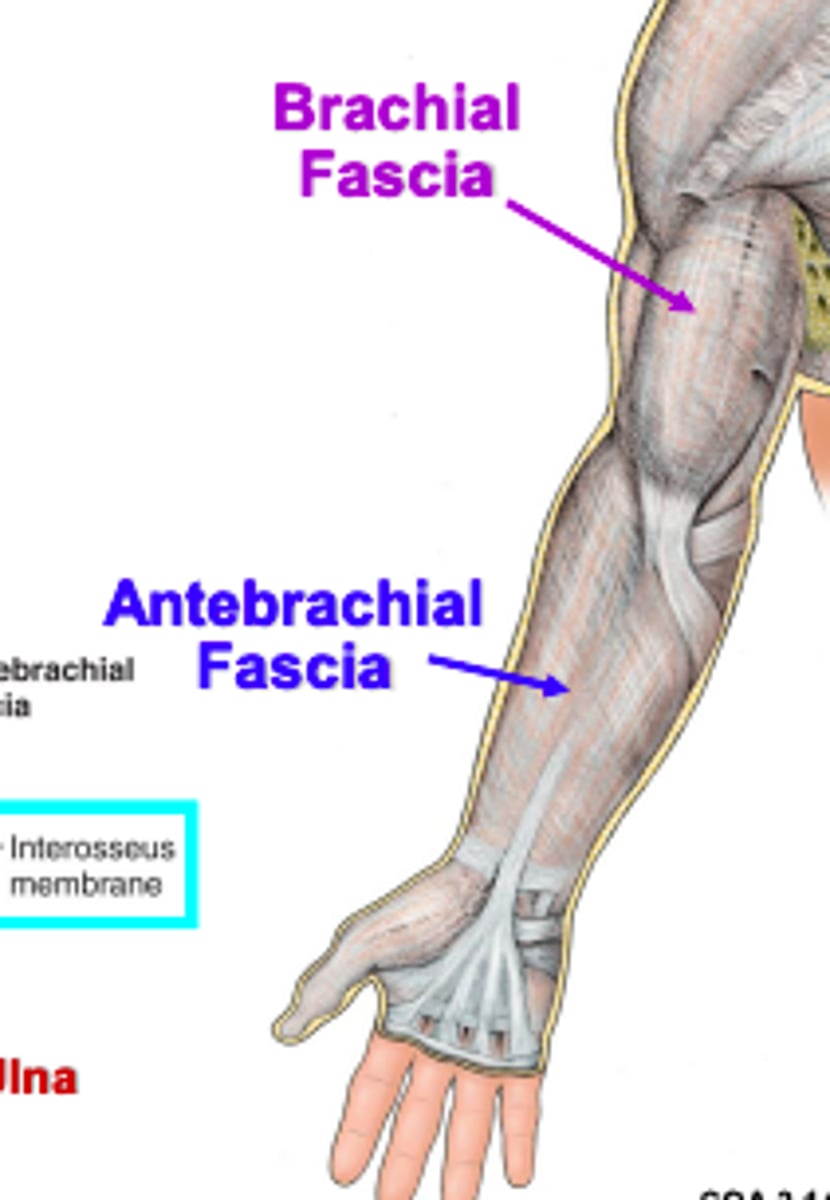
Brachial fascia
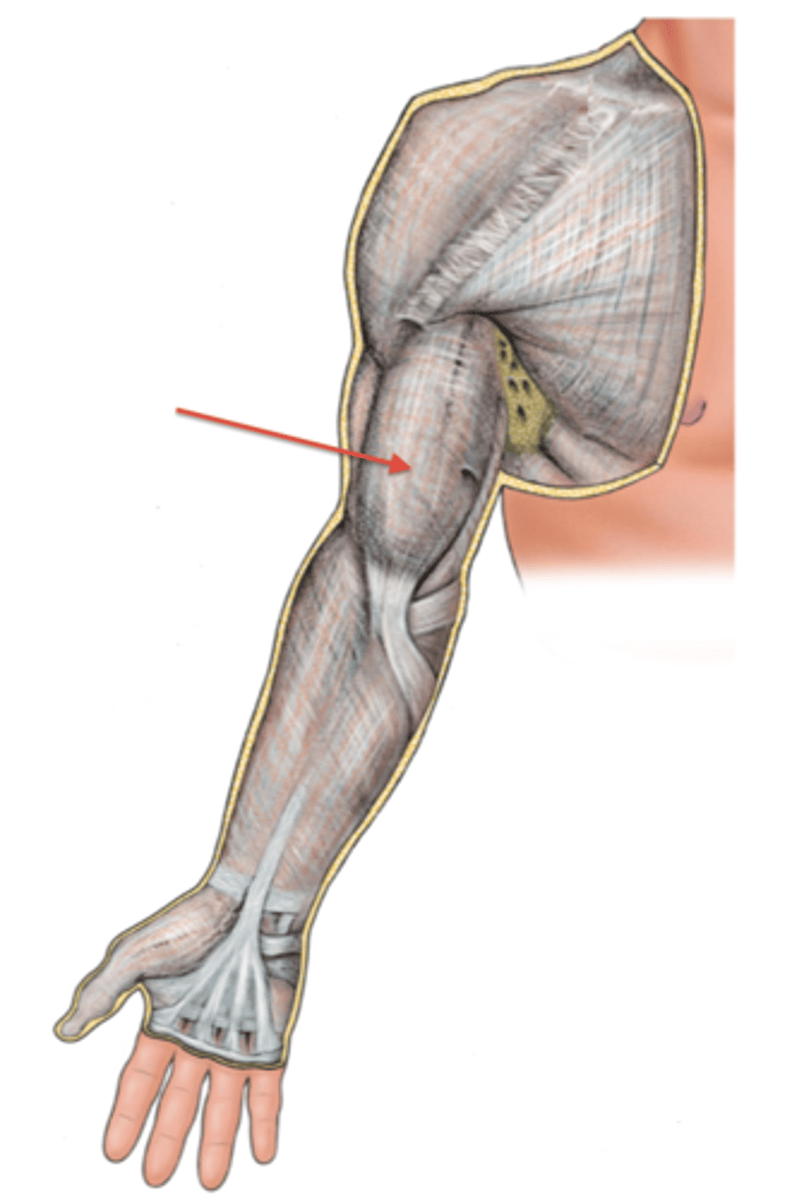
(Fascia of arm region:) Brachial fascia
sheath of deep fascia that encloses the arm like a sleeve deep to skin and superficial fascia. It is continuous superiorly with the deltoid, pectoral, axillary, and infraspinous fascias, and inferiorly with the antebrachial fascia (at the level of the elbow)
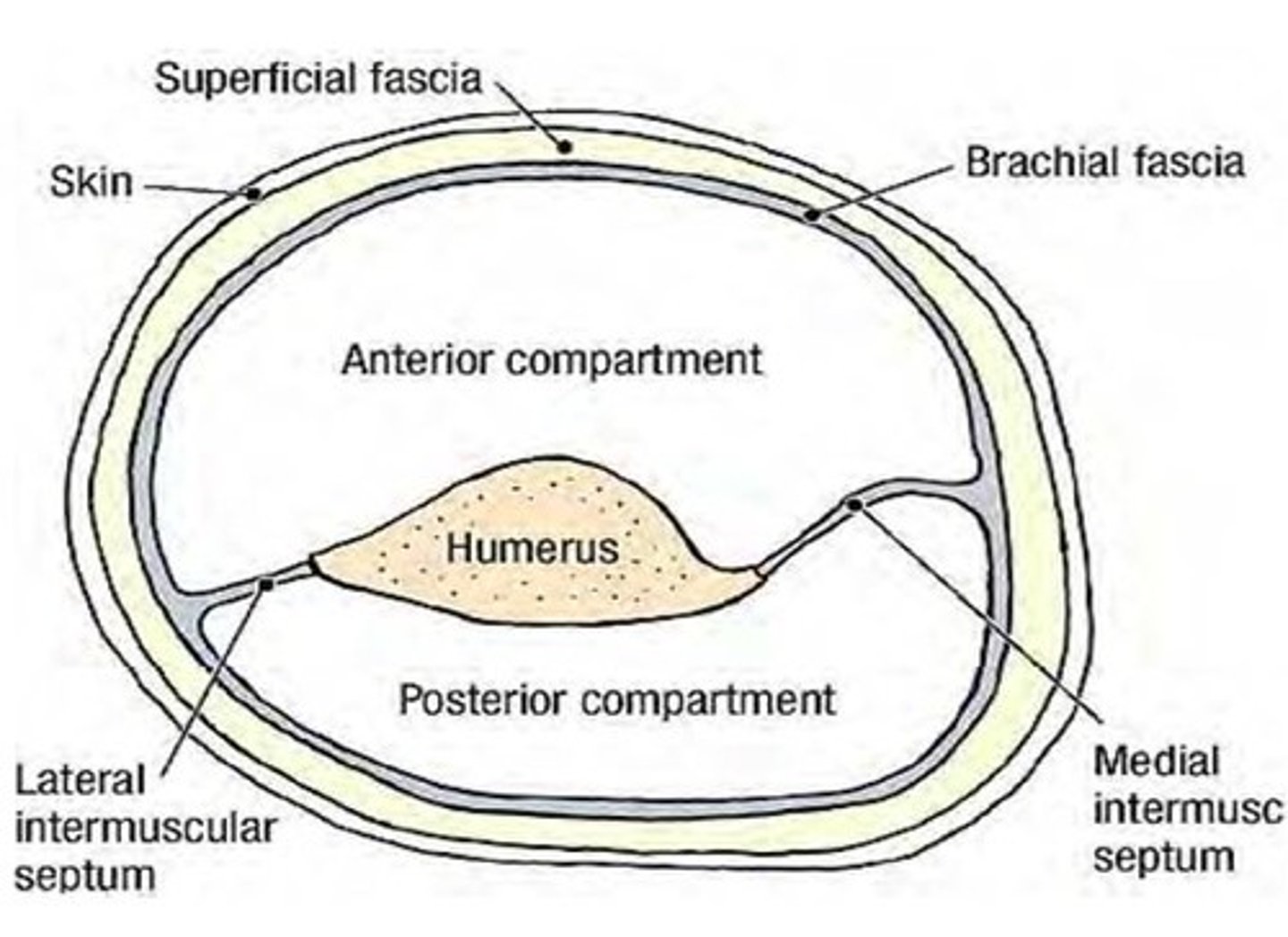
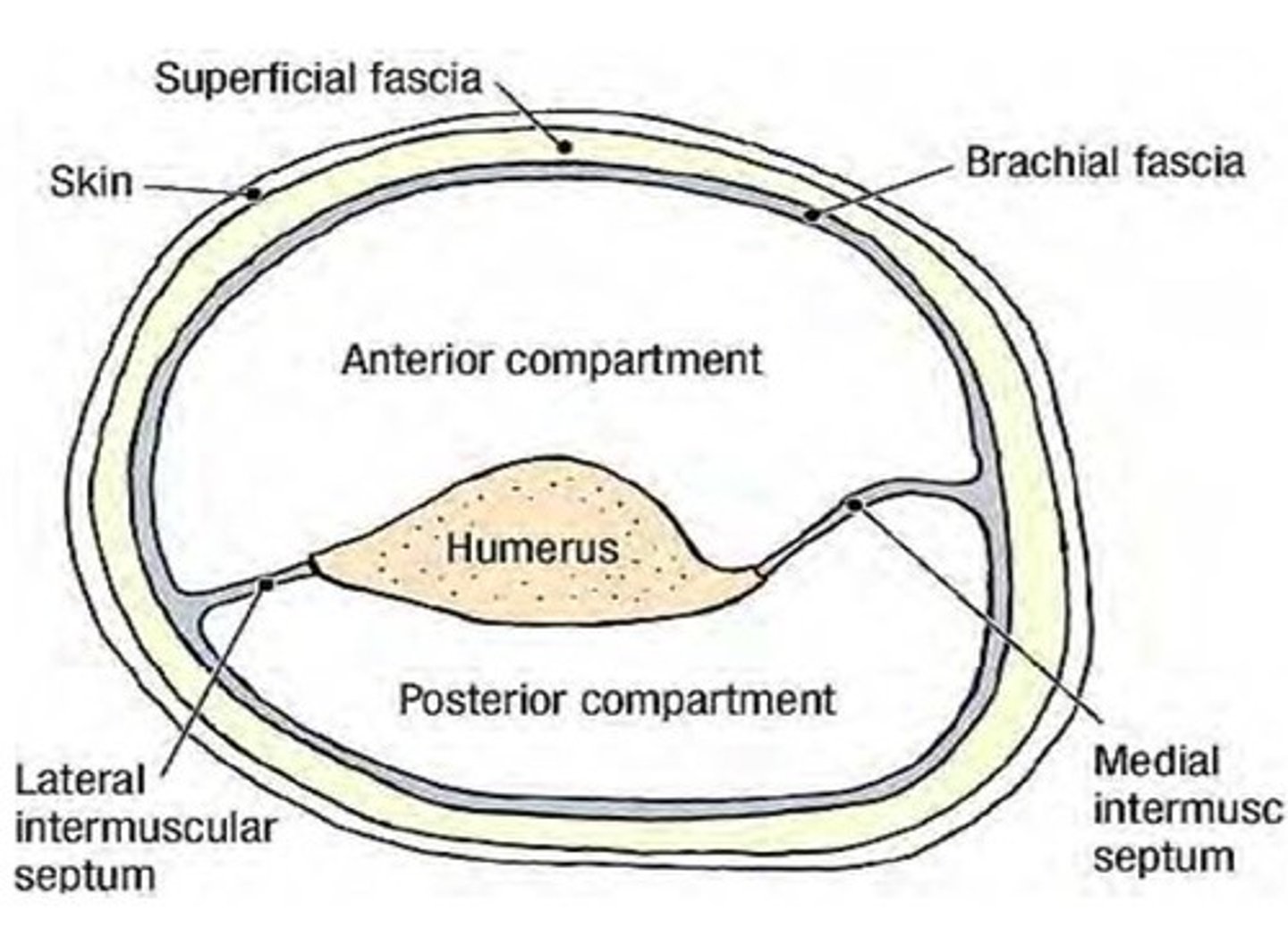
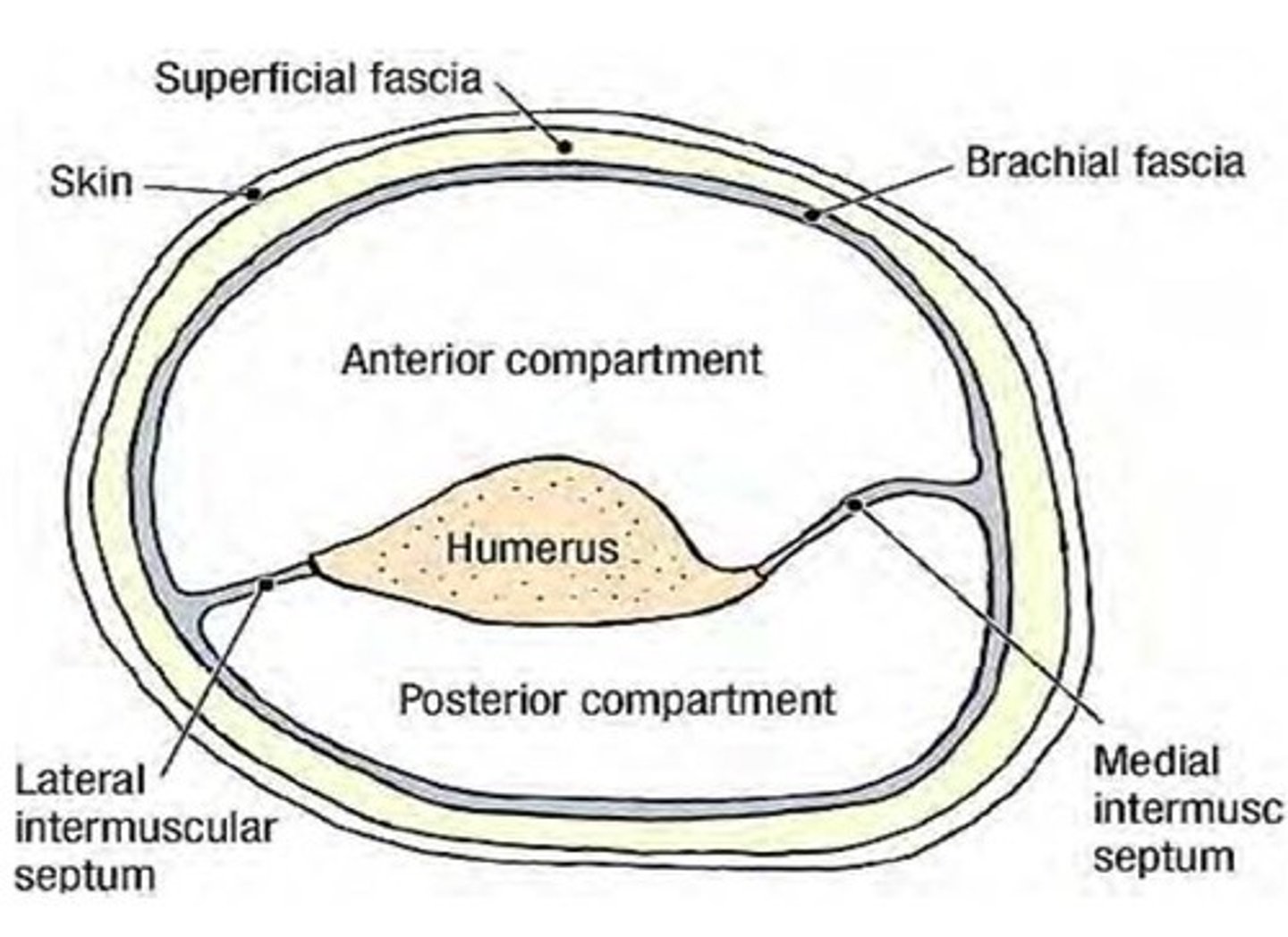
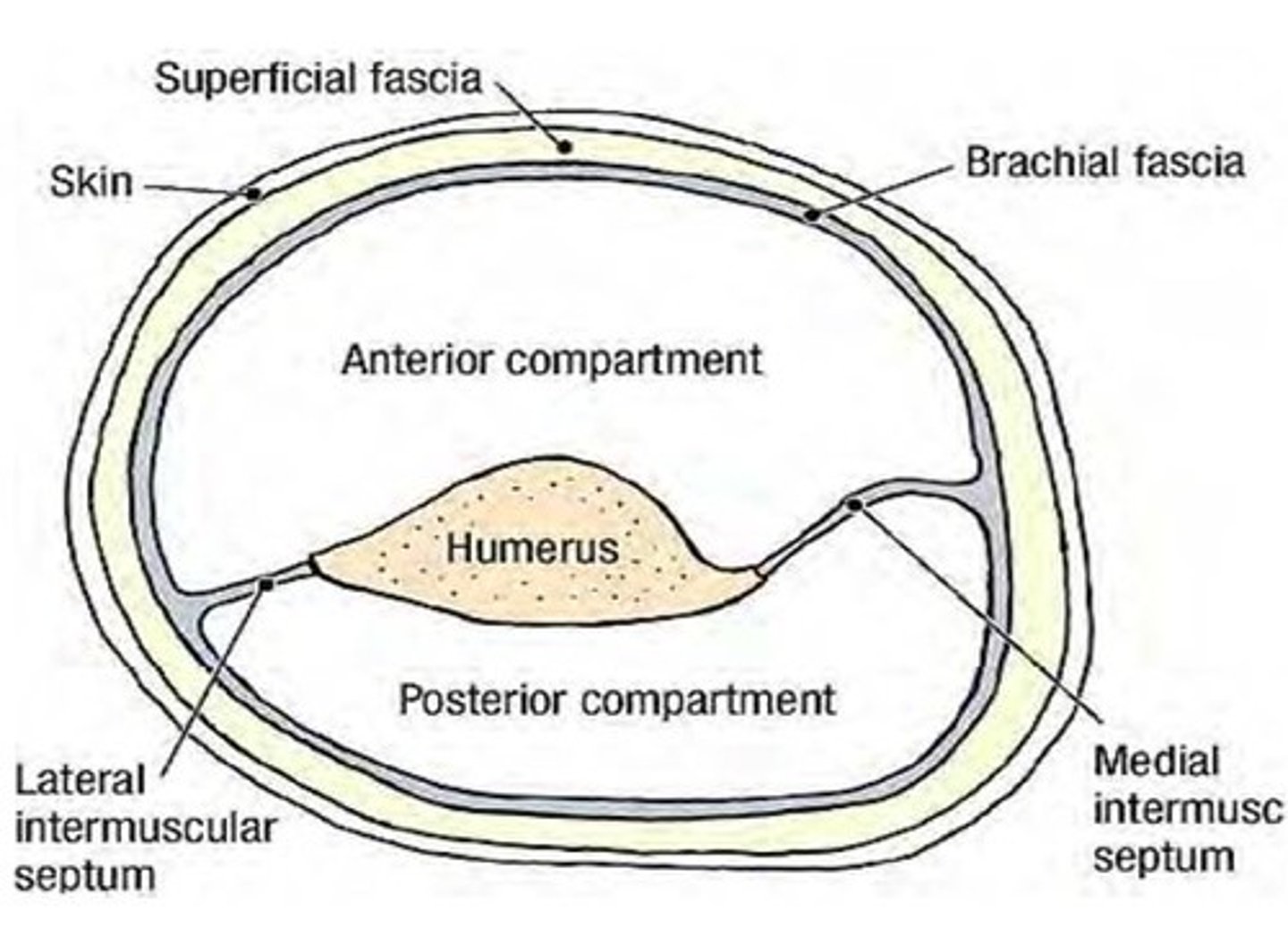
- Contains Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa
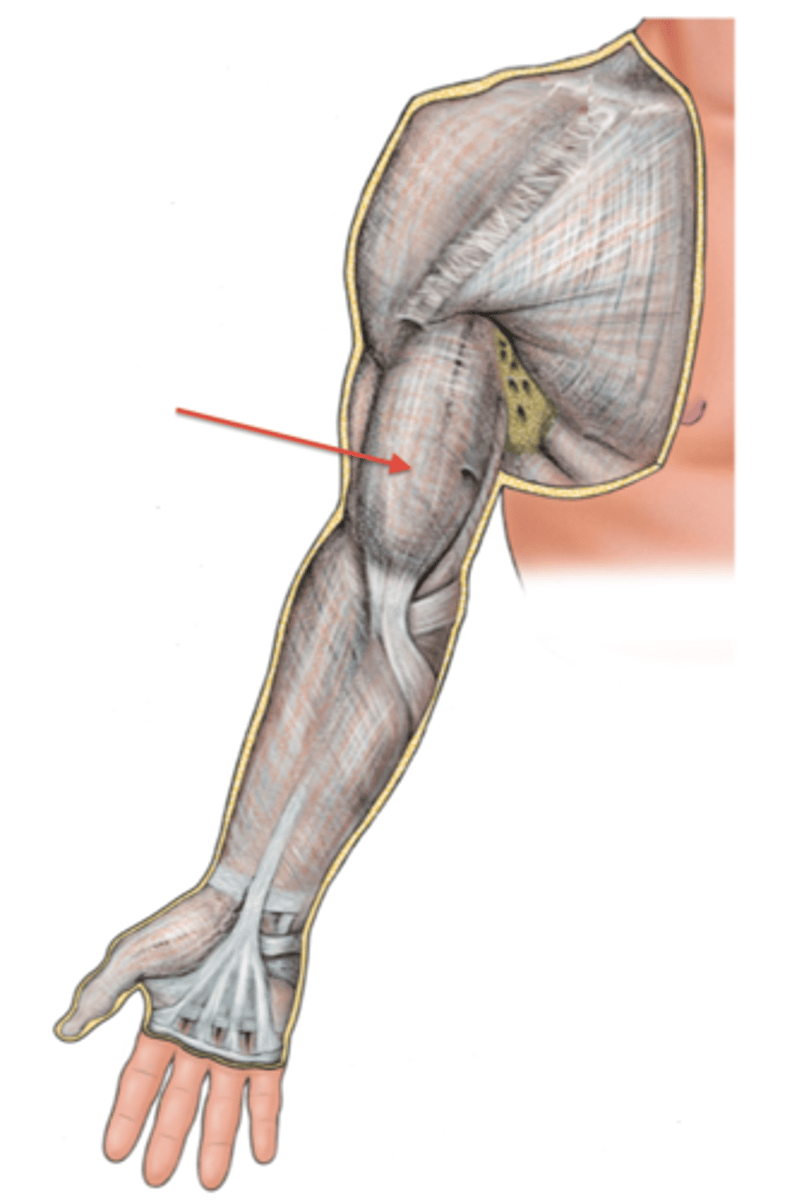
(Brachial Fascia:) Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa
extensions of brachial fascia that attach to the bone, forming fascial compartments that limit spread of infection and hemorrhage in the arm
-Anterior (flexor) fascial compartment
-Posterior (extensor) fascial compartment
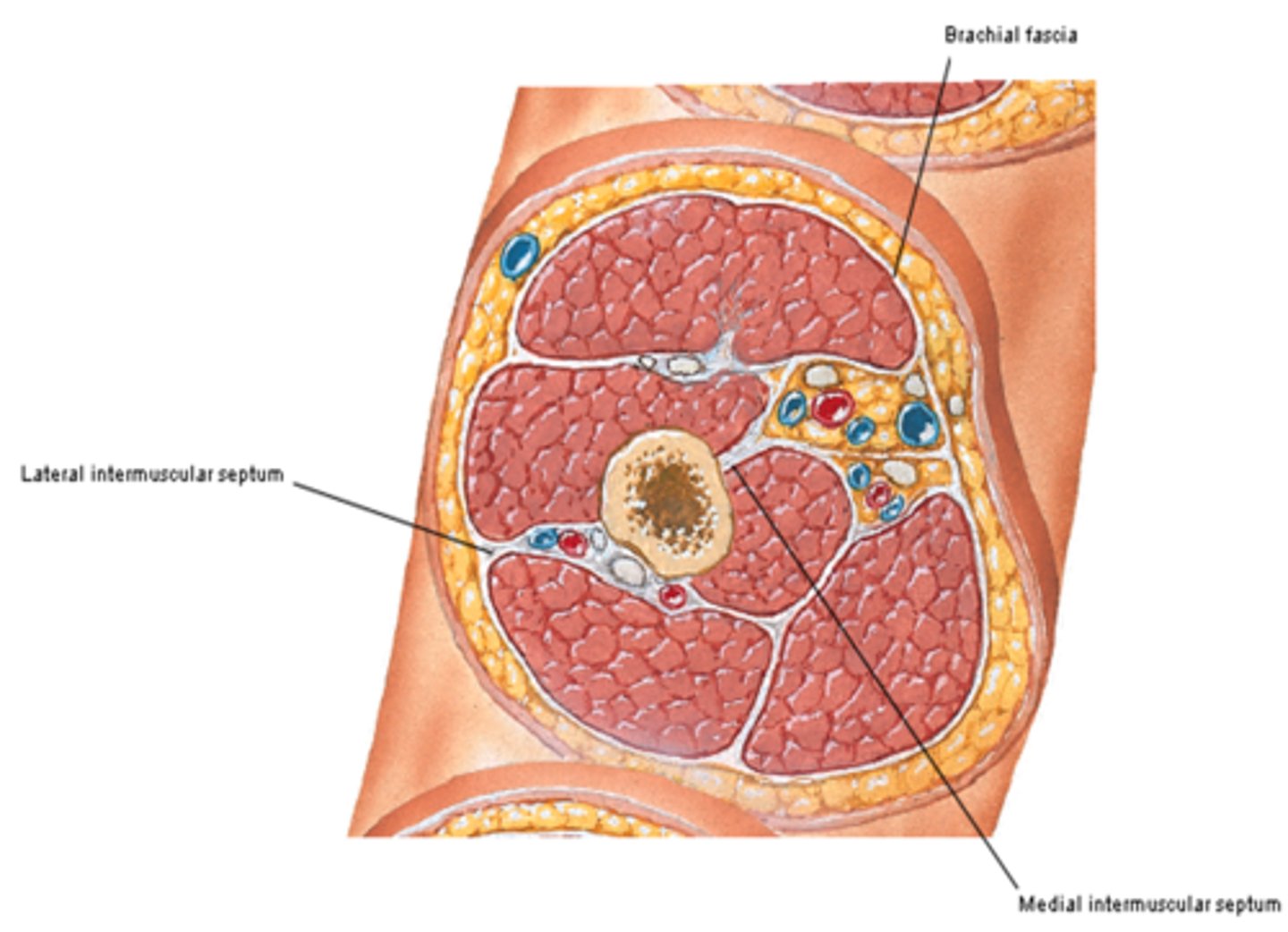
(Brachial Fascia's Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa:) Anterior (flexor) fascial compartment
contain muscles performing similar functions and sharing common innervation
(Brachial Fascia's Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa:) Posterior (extensor) fascial compartment:
contain muscles performing similar functions and sharing common innervation

(Upper Limb Fascia:) Fascia of forearm region
Antebrachial fascia
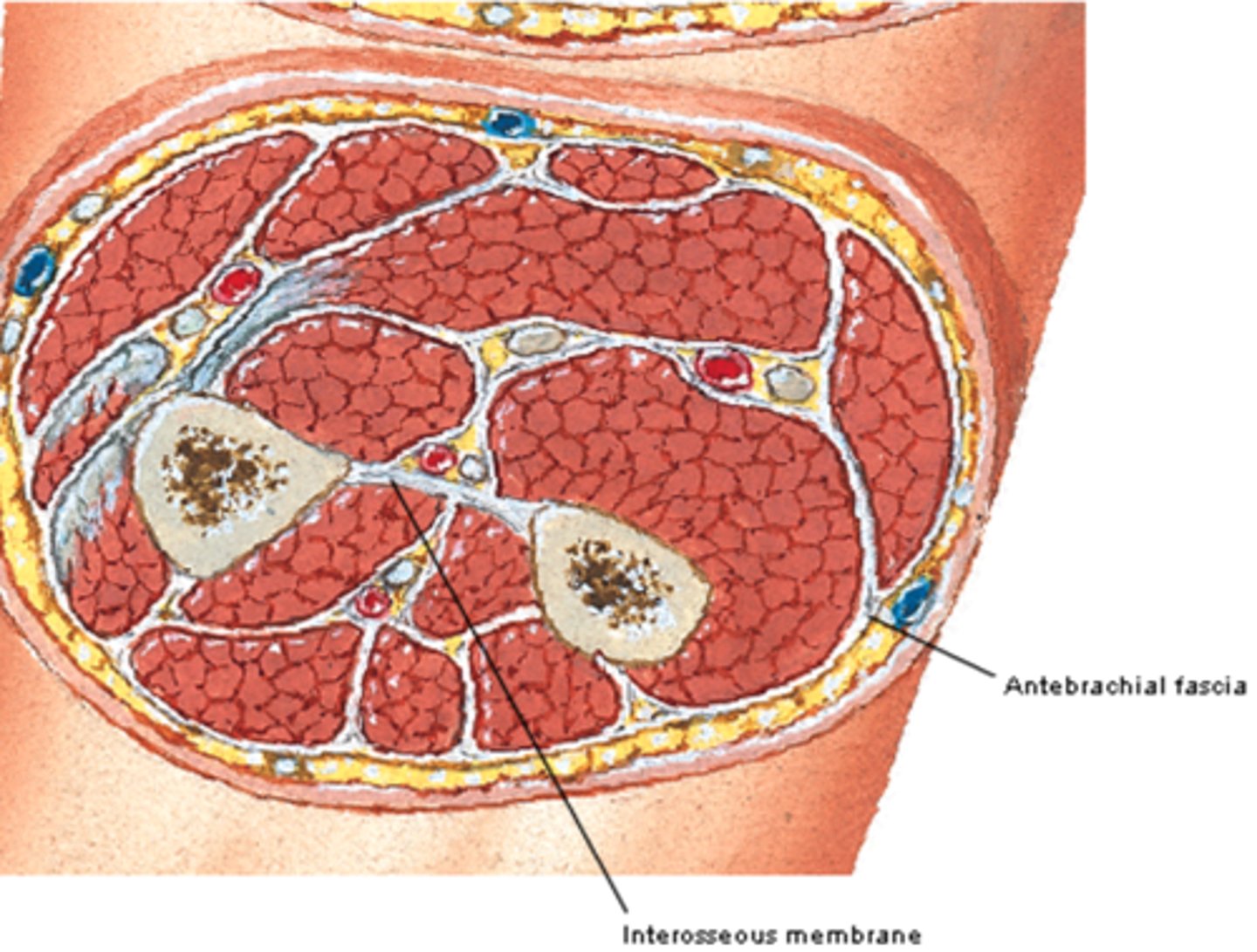
(Fascia of forearm region:) Antebrachial fascia
sheath of deep fascia that encloses the forearm like a sleeve deep to skin and superficial fascia. It is continuous superiorly with the brachial fascia, and it thickens inferiorly to form bands over the distal portion of the radius and ulna
-Contains: Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa and Transverse bands
(Antebrachial fascia:) Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa
extensions of brachial fascia that attach to the bone, forming fascial compartments that limit spread of infection and hemorrhage in the forearm
-Contains Anterior (flexor) fascial compartment and Posterior (extensor) fascial compartment
(Antebrachial fascia's Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa:) Anterior (flexor) fascial compartment
contain muscles performing similar functions and sharing common innervation. It is further divided into superficial and deep compartments
(Antebrachial fascia's Medial & Lateral intermuscular septa:) Posterior (extensor) fascial compartment
contain muscles performing similar functions and sharing common innervation. It is further divided into superficial and deep compartments
(Antebrachial fascia:) Transverse bands
-Extensor retinaculum
-Flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament)
-Palmar carpal ligament
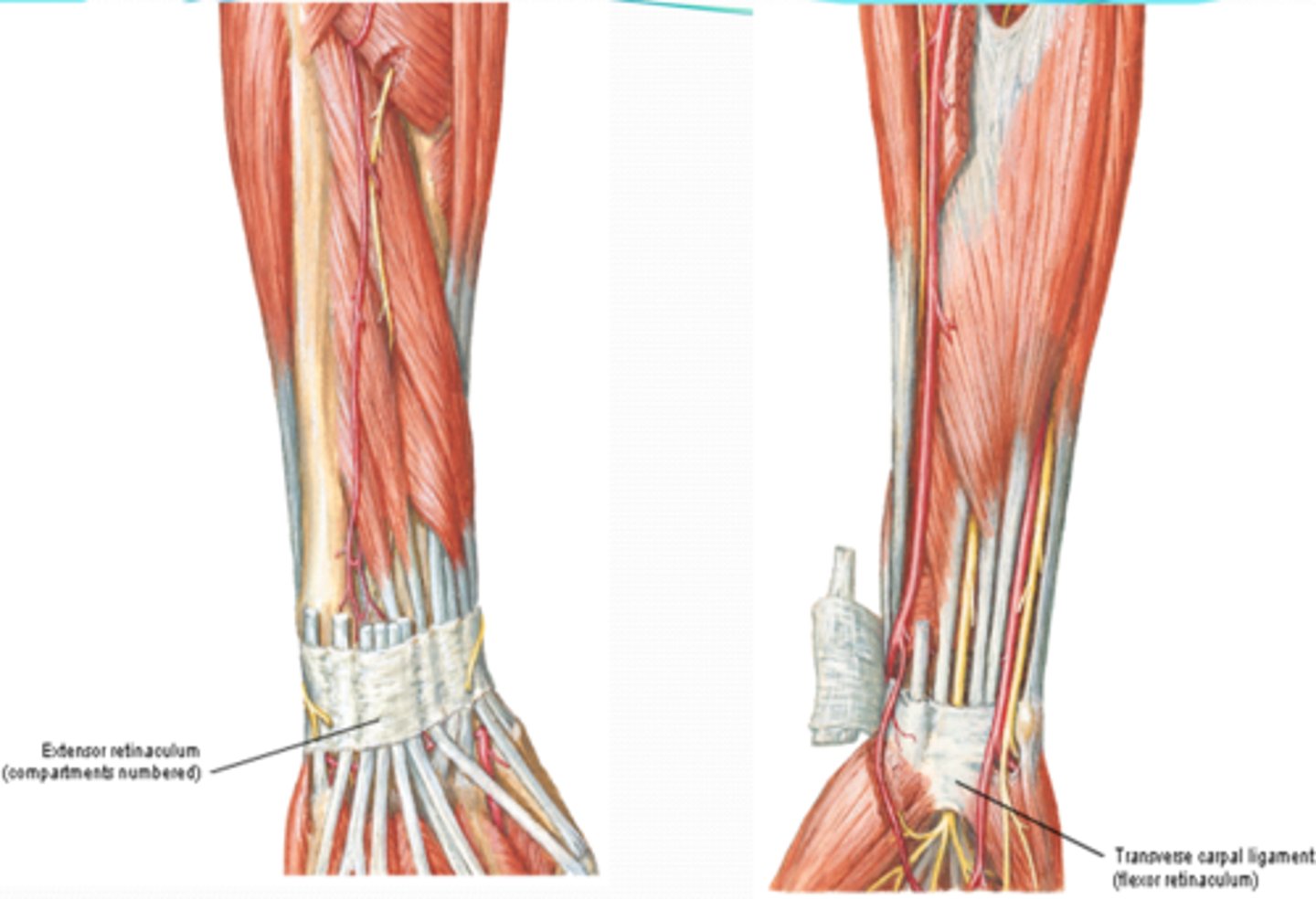
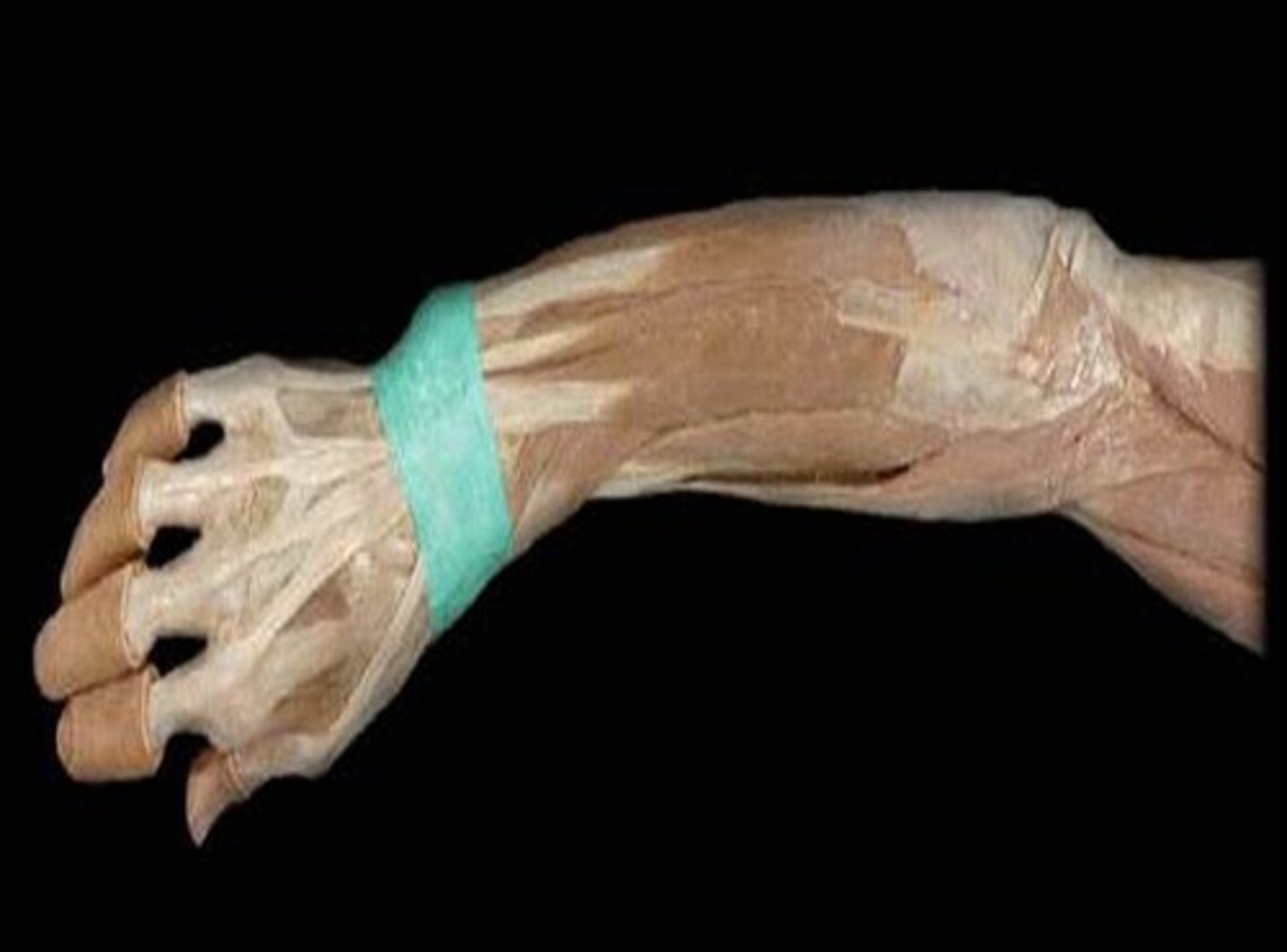
(Antebrachial fascia's Transverse bands:) Extensor retinaculum
in the posterior region, retains extensor tendons in place
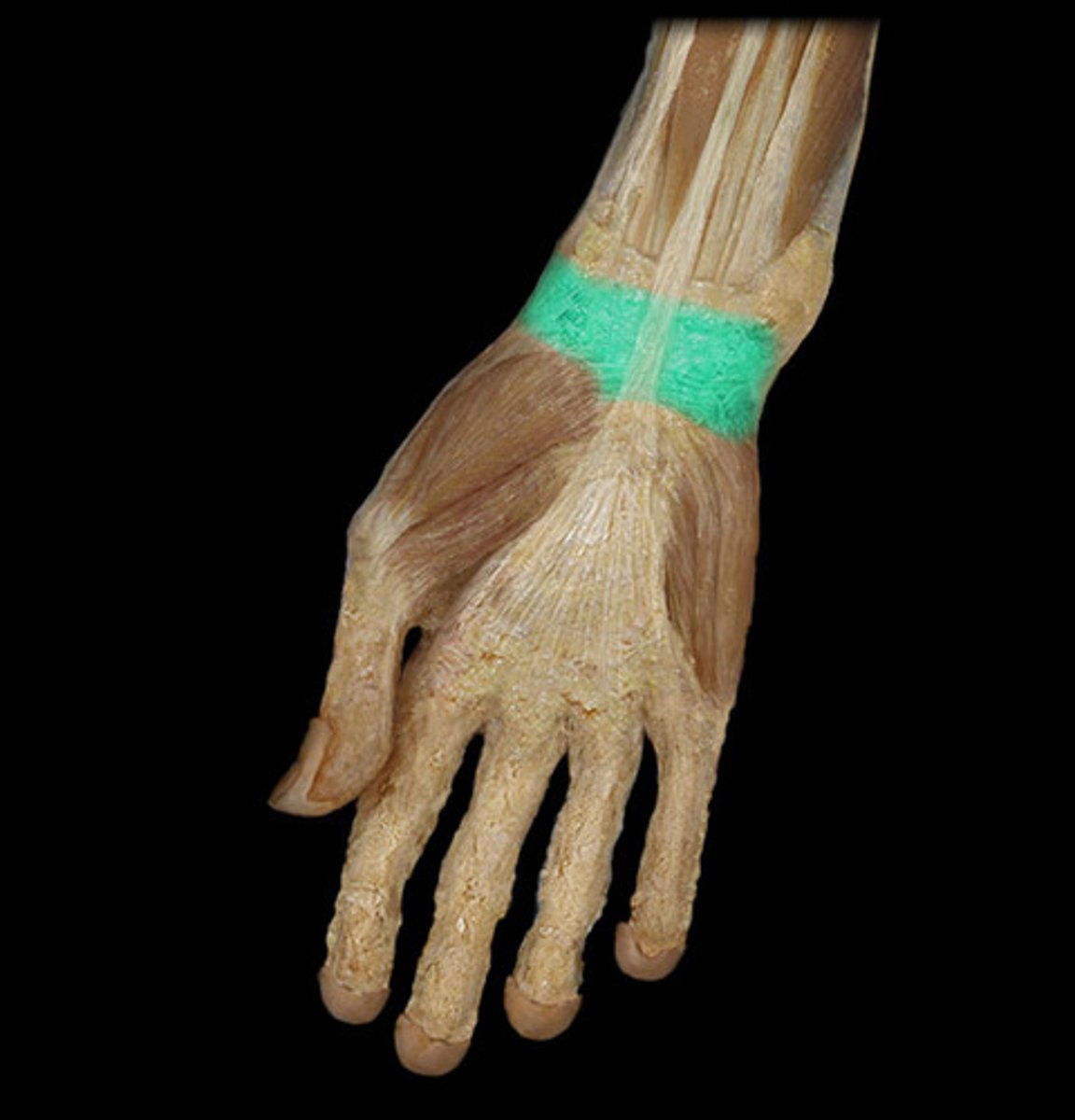
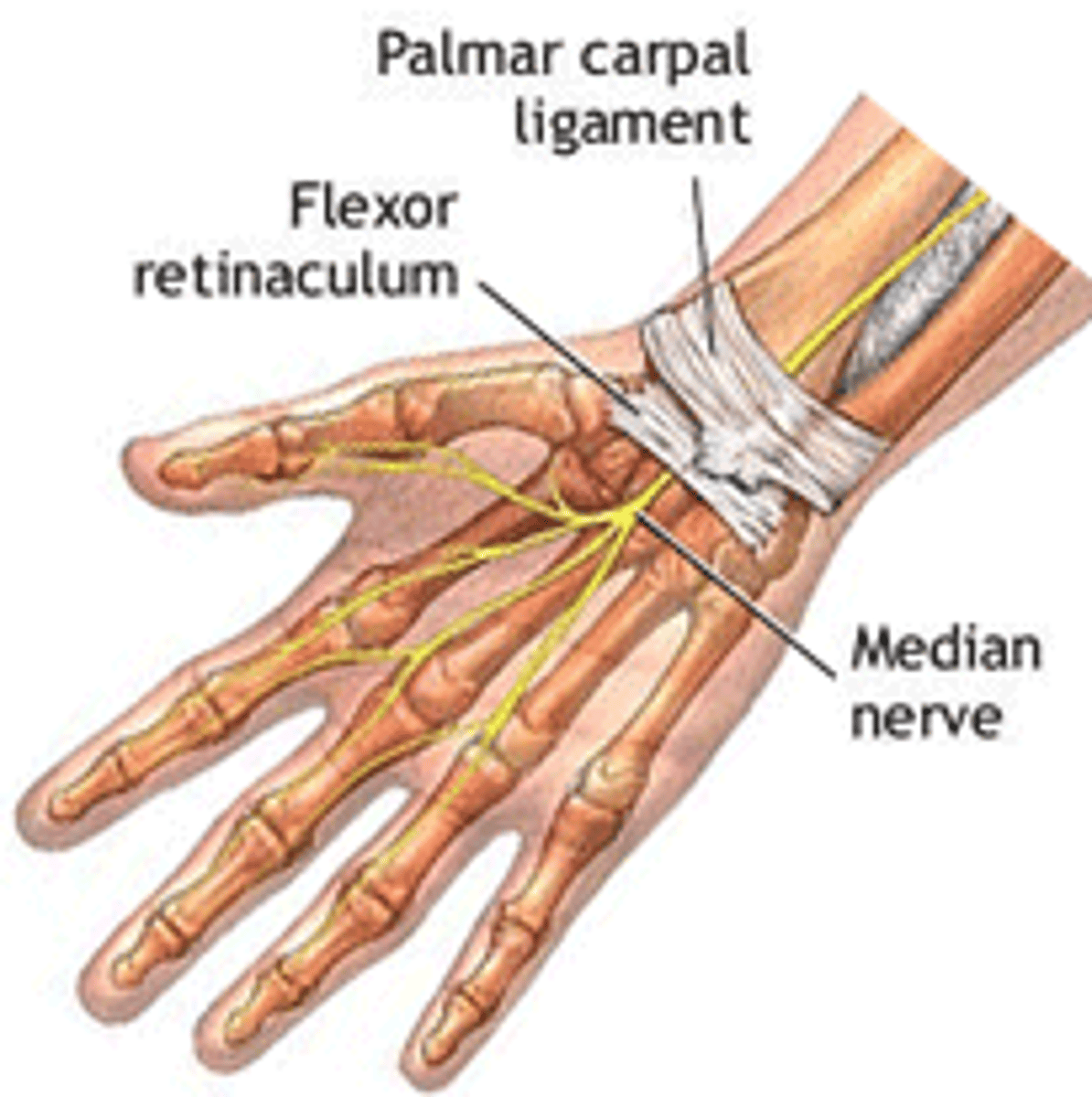
(Antebrachial fascia's Transverse bands:) Flexor retinaculum (transverse carpal ligament)
forms the roof of the carpal tunnel, which contains flexor tendons and the median nerve
(Antebrachial fascia's Transverse bands:) Palmar carpal ligament:
in the anterior region superficial to the flexor retinaculum, and continuous with the extensor retinaculum in the posterior region
(Upper Limb Fascia:) Fascia of palmar region
Palmar fascia
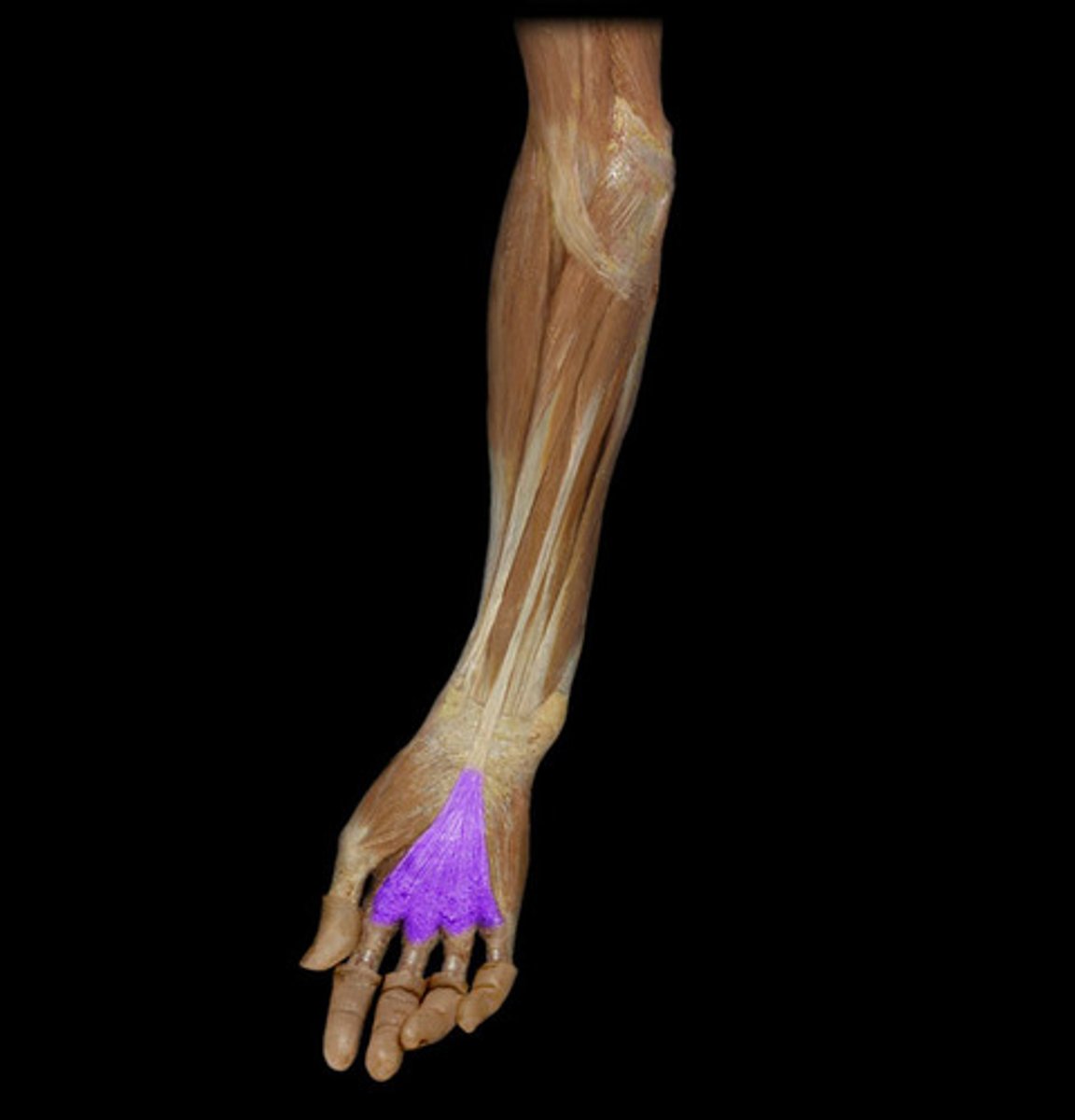
(Fascia of palmar region:) Palmar Fascia
inferior continuation of the antebrachial fascia onto the hand
Contains: Palmar aponeurosis, Thenar fascia, Hypothenar fascia
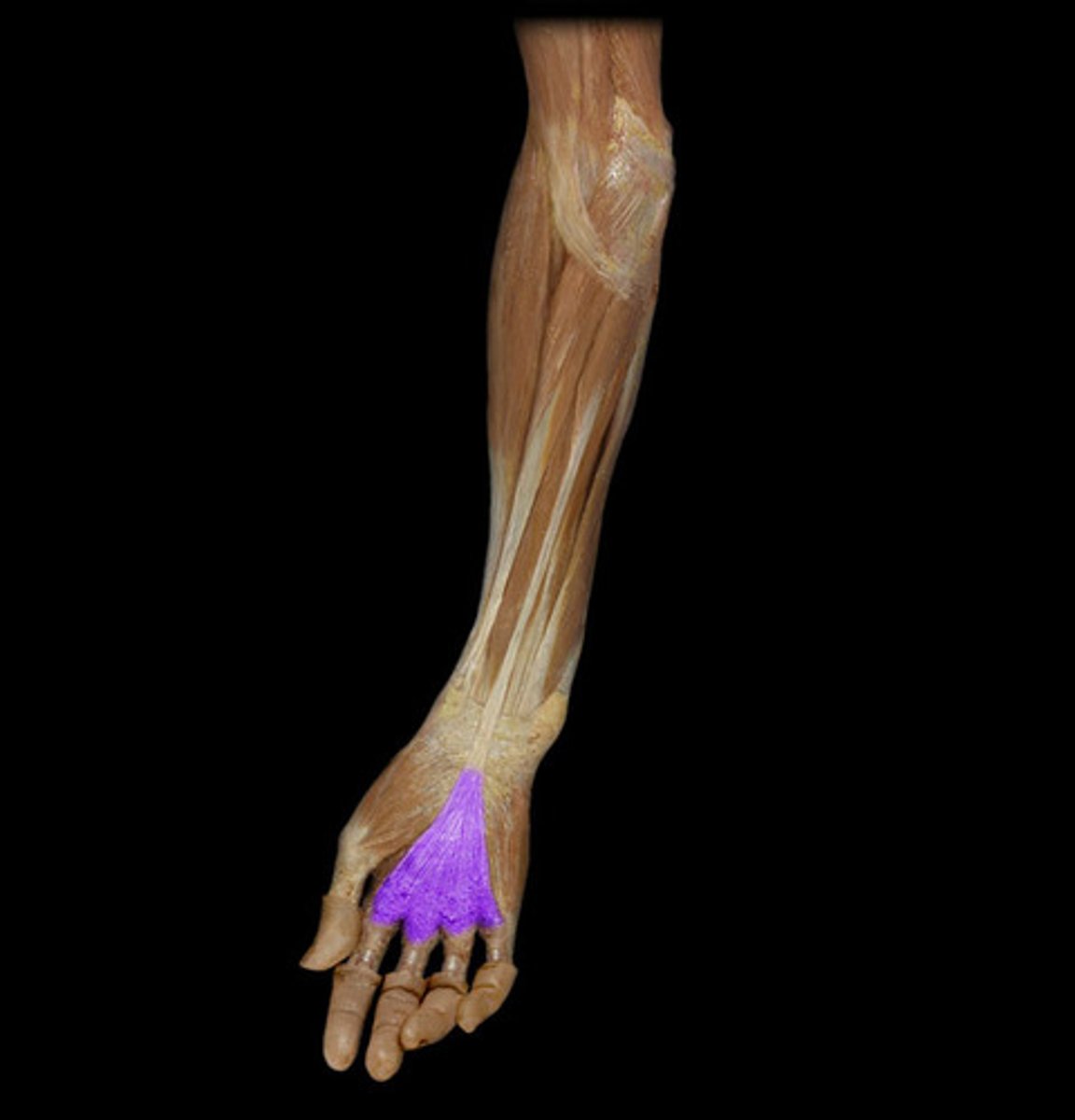
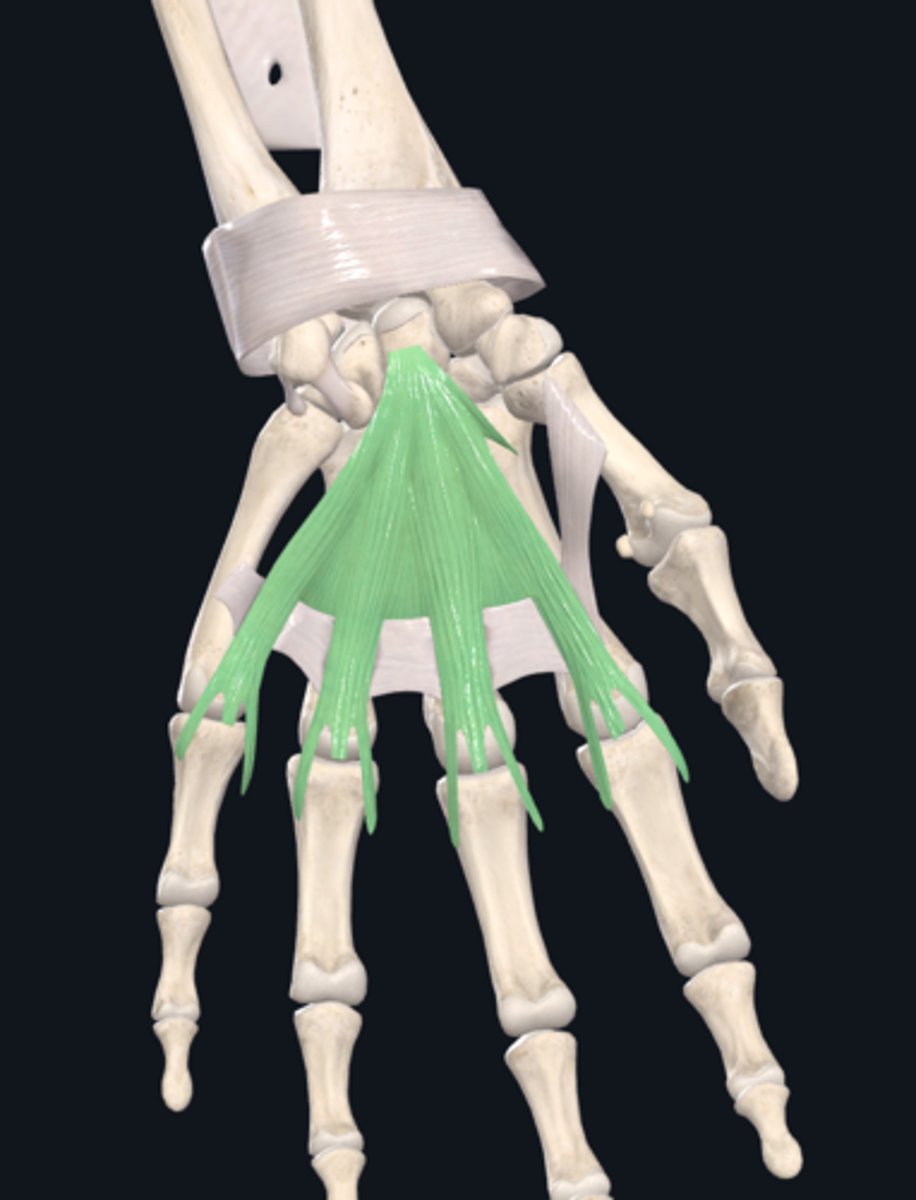
(Fascia of palmar region's Palmar Fascia:) Palmar aponeurosis
thick and strong, overlies the central compartment of the palm. Continuous superiorly with the flexor retinaculum and palmaris longus tendon (when present) and forms central compartment of hand
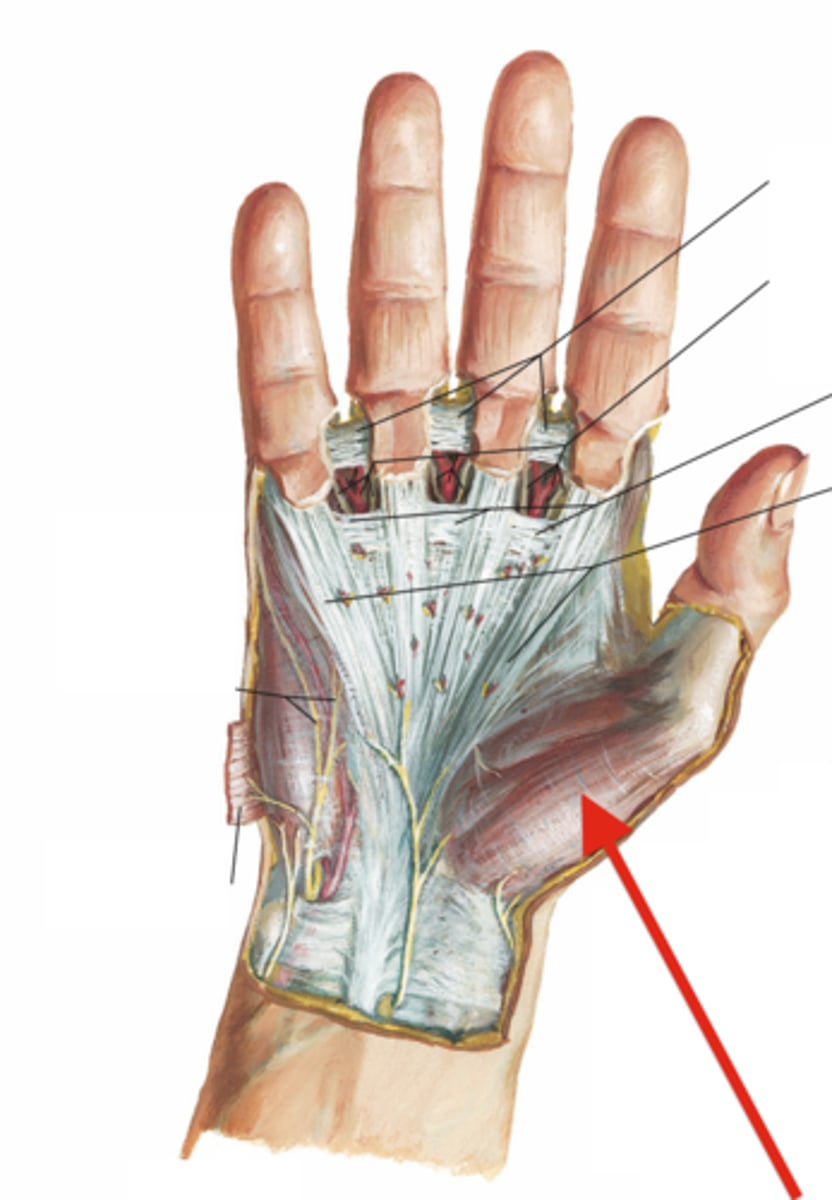
(Fascia of palmar region's Palmar Fascia:) Thenar fascia
forms lateral compartment of hand, containing the thenar muscles at the base of the thumb
(Fascia of palmar region's Palmar Fascia:) Hypothenar fascia
forms medial compartment of hand, containing the hypothenar muscles proximal to the base of the 5th finger
(Muscles of the pectoral region:) Anterior axioappendicular muscles
These muscles move the pectoral girdle
-Contains Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor, Subclavius muscle, Serratus anterior
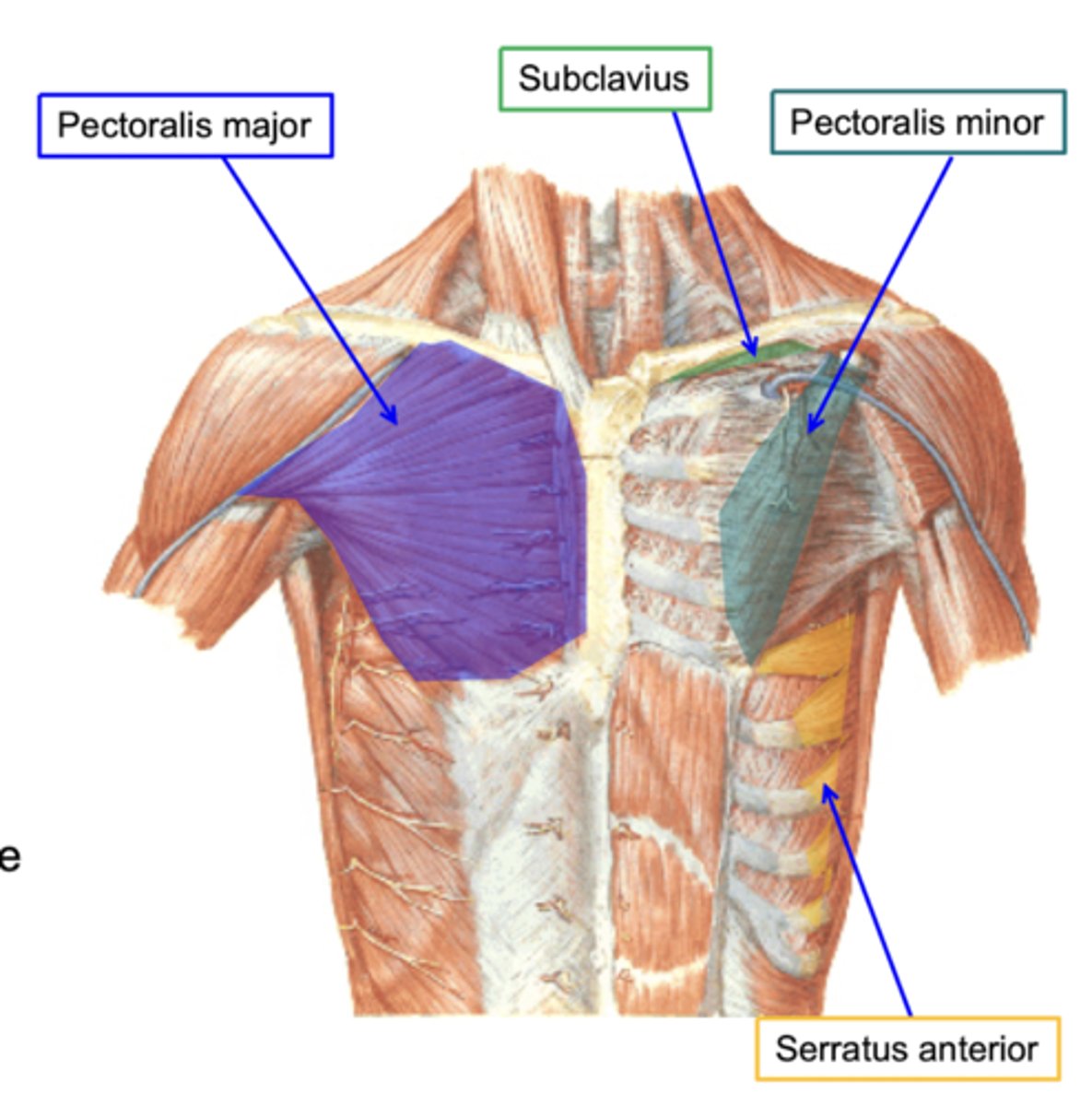
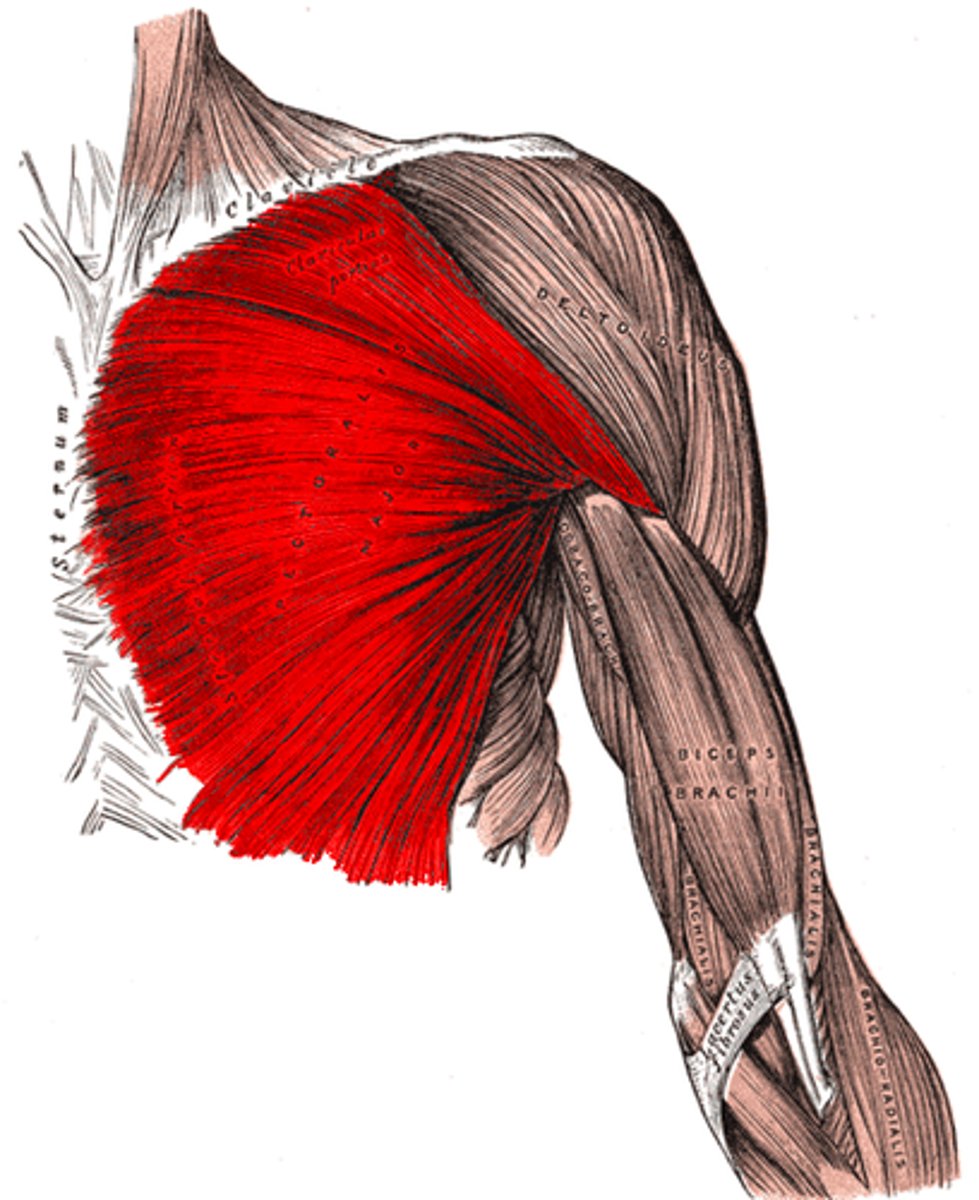
(Anterior axioappendicular muscles:) Pectoralis major
-Adduction and medial rotation of humerus. Draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly
-Medial (C8 – T1) & lateral (C5 – C7) pectoral n.
-Delto-pectoral groove: formed between pectoralis major and deltoid, allows passage for the cephalic vein
(Anterior axioappendicular muscles:) Pectoralis minor
-Stabilizes scapula
-Medial pectoral n. (C8 - T1)
-Forms a bridge with the coracoid process allowing the passage of nerves and vessels to the arm
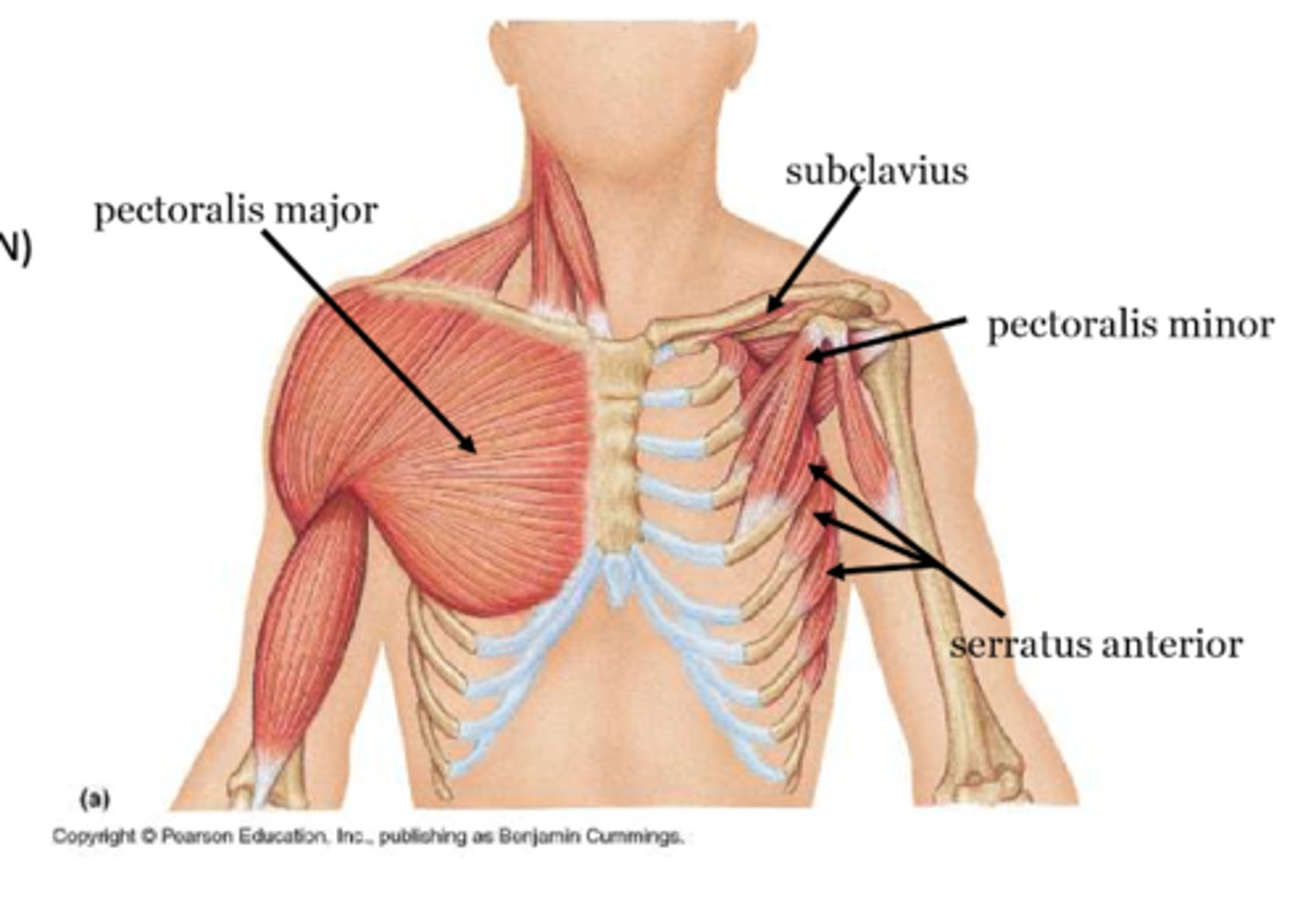
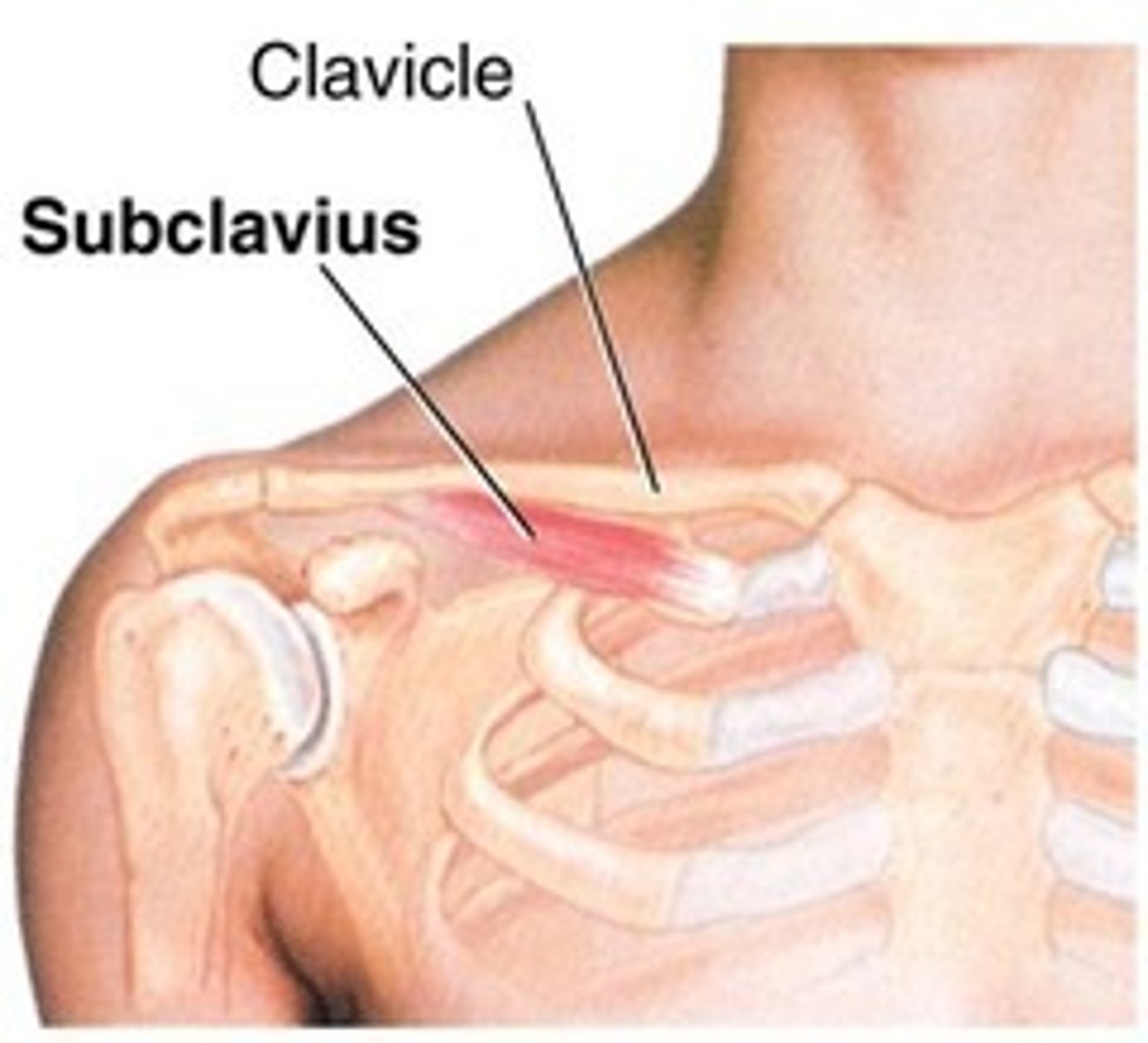
(Anterior axioappendicular muscles:) Subclavius muscle
-Anchors and depresses clavicle
-Nerves to subclavius (C5 - C6)
-Protects subclavian vessels and brachial plexus in case of fracture of the clavicle
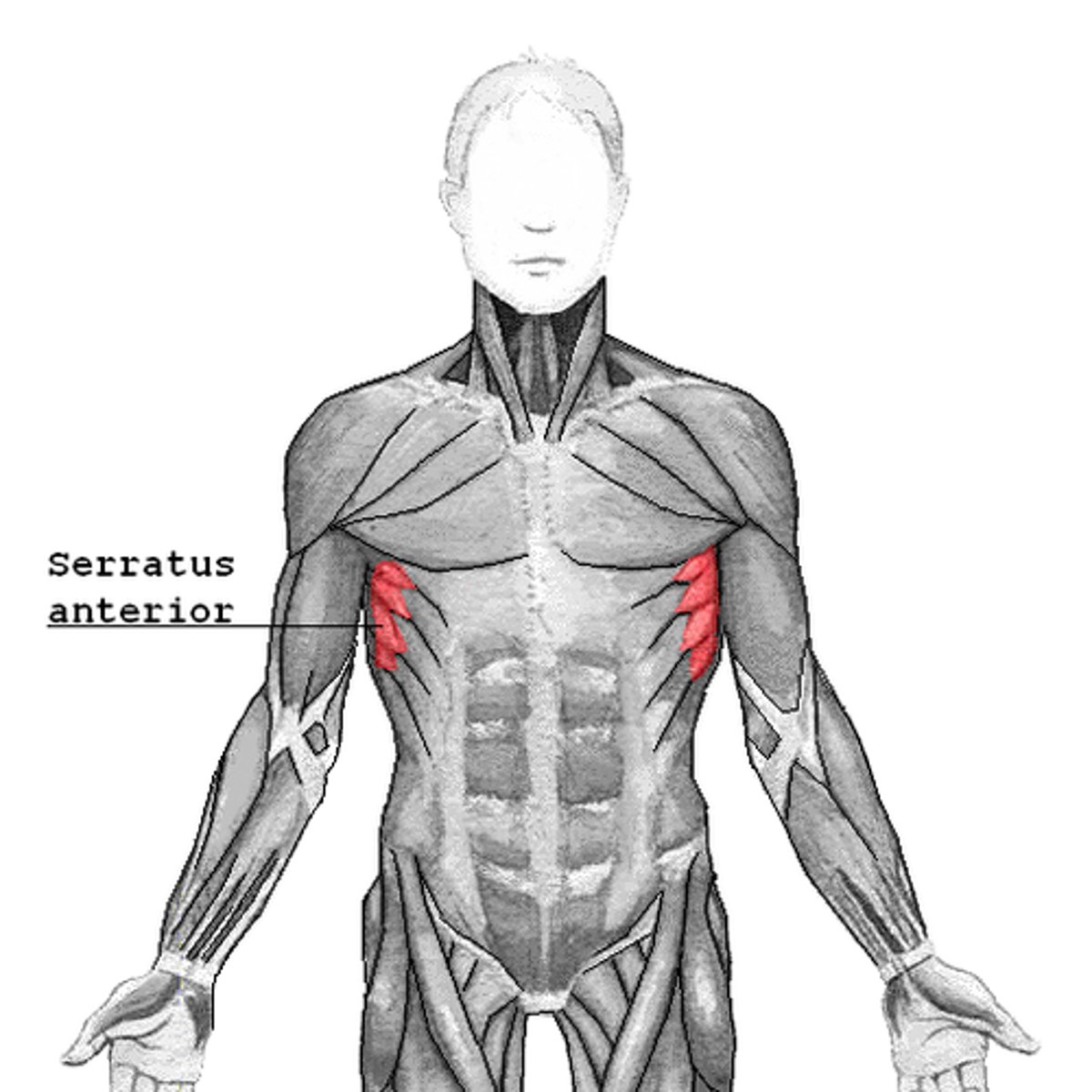
(Anterior axioappendicular muscles:) Serratus anterior
-Protracts and stabilizes scapula
-Long thoracic n. (C5 - C7)
(Muscles of Pectoral region:) Posterior axioappendicular and scapulohumeral muscles
-These are superficial and intermediate back muscles and can be divided into:
*Superficial posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder)
*Deep posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder)
*Scapulohumeral muscles (intrinsic shoulder)
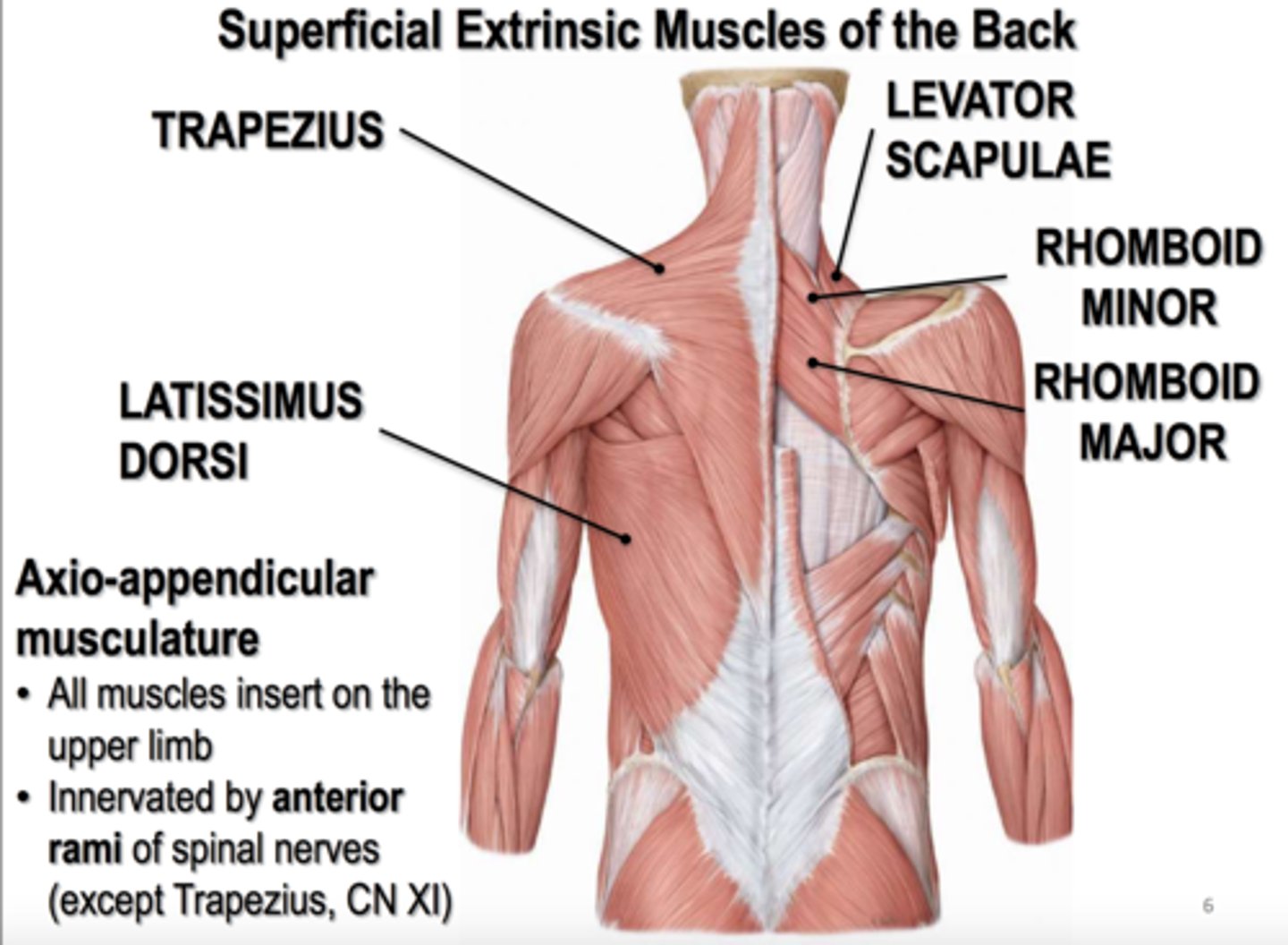
(Posterior axioappendicular and scapulohumeral muscles:) Superficial posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder)
Trapezius and Latissimus dorsi
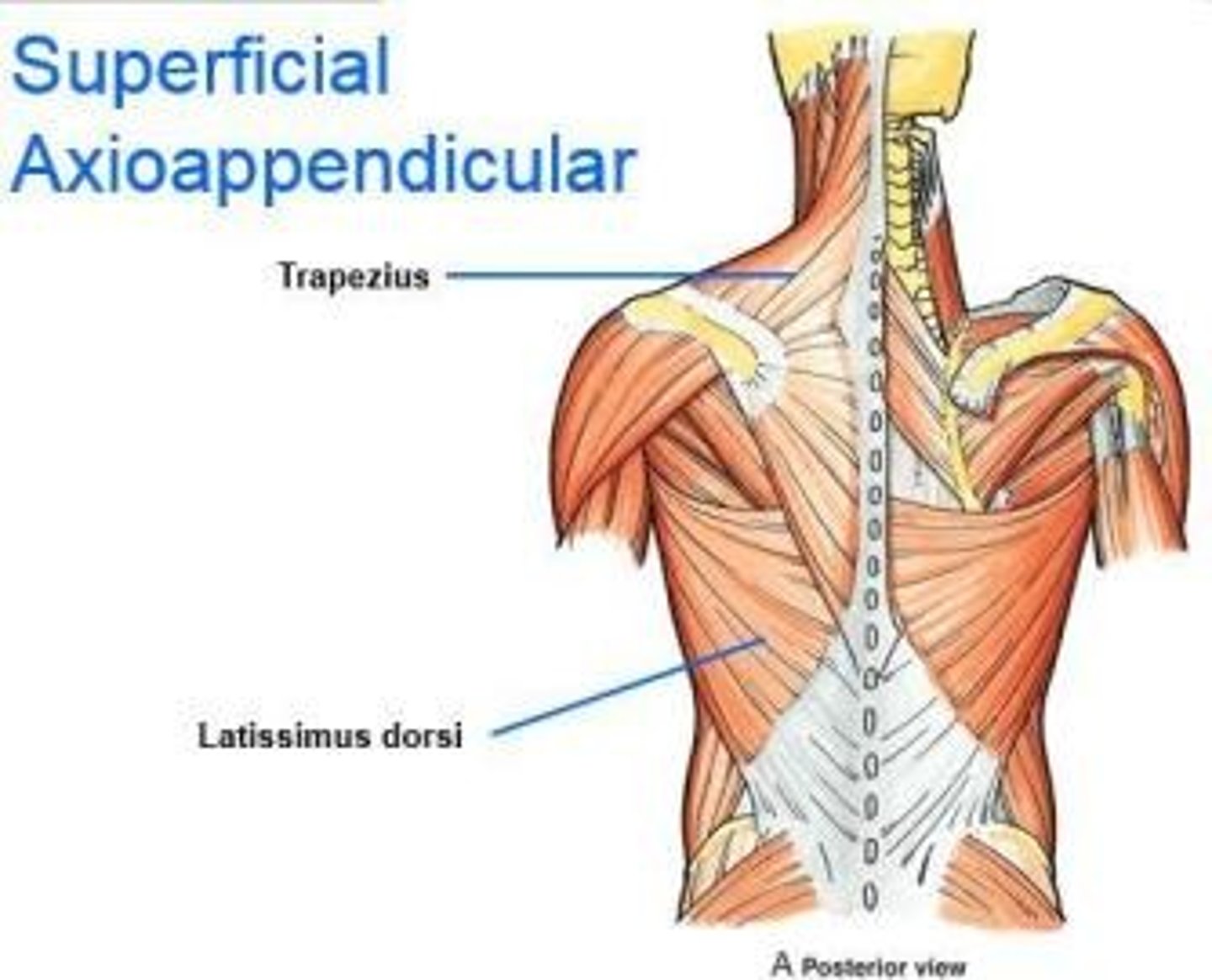
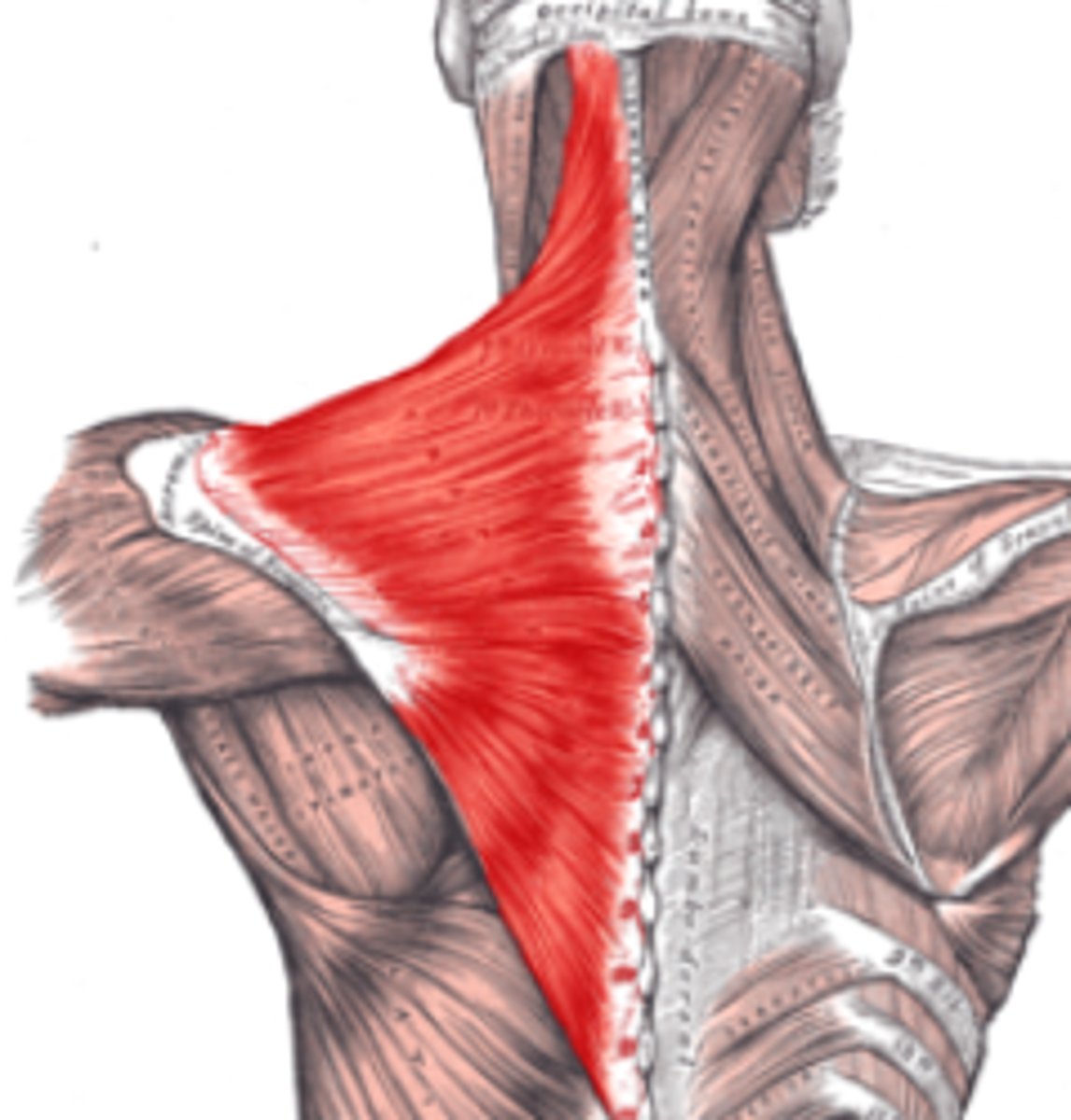
(Superficial posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder):) Trapezius
-Elevates, depresses, and retracts scapula
-Accessory nerve (CN XI)
(Superficial posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder):) Latissimus dorsi
-Extends, adducts, and medially rotates humerus
-Thoracodorsal n. (C6 - C8)
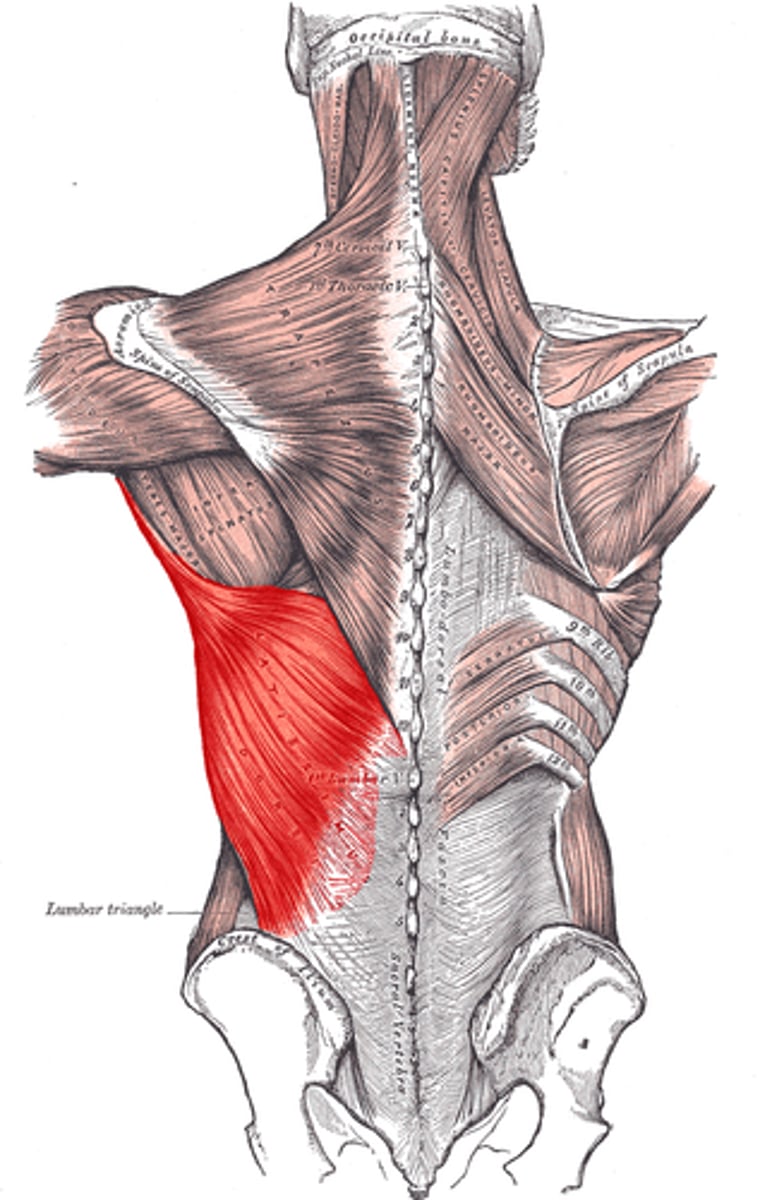
(Posterior axioappendicular and scapulohumeral muscles:) Deep posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder)
Levator Scapulae and Rhomboid minor and major
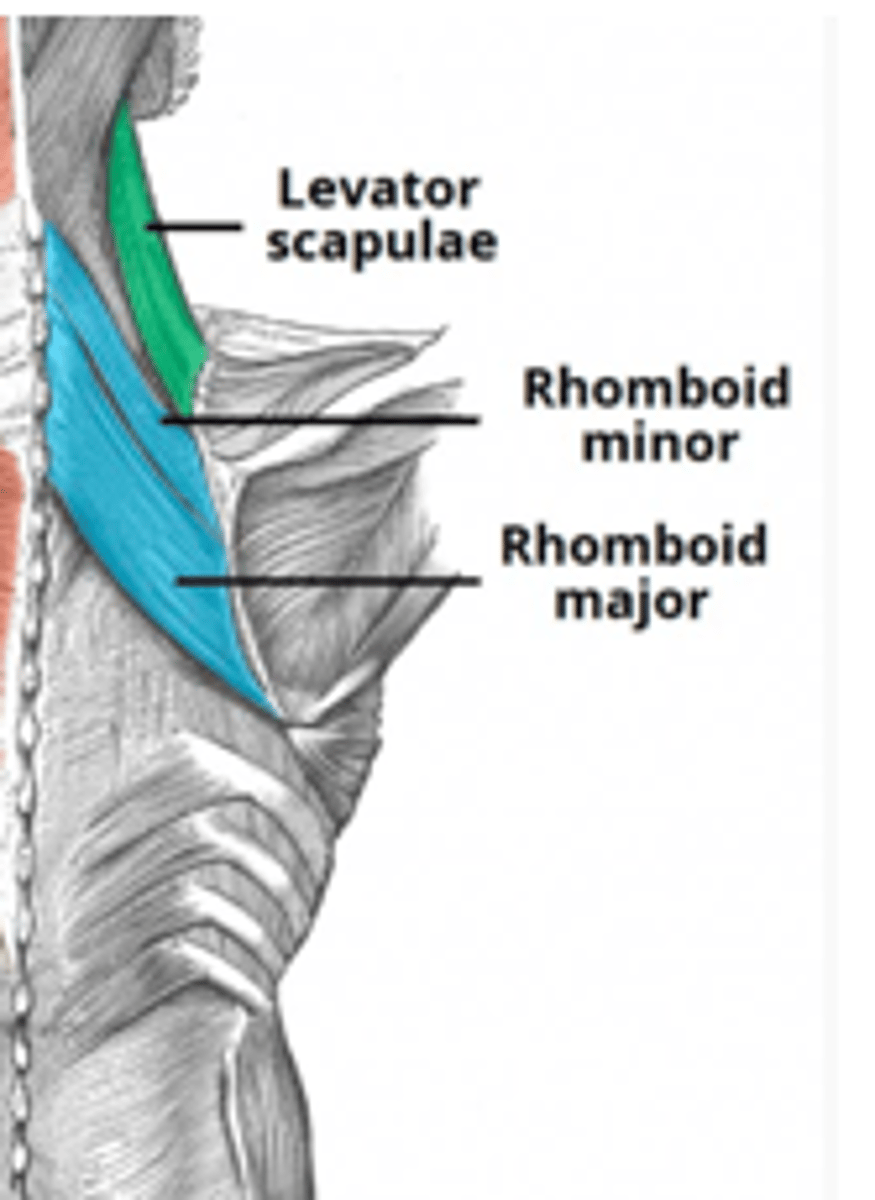
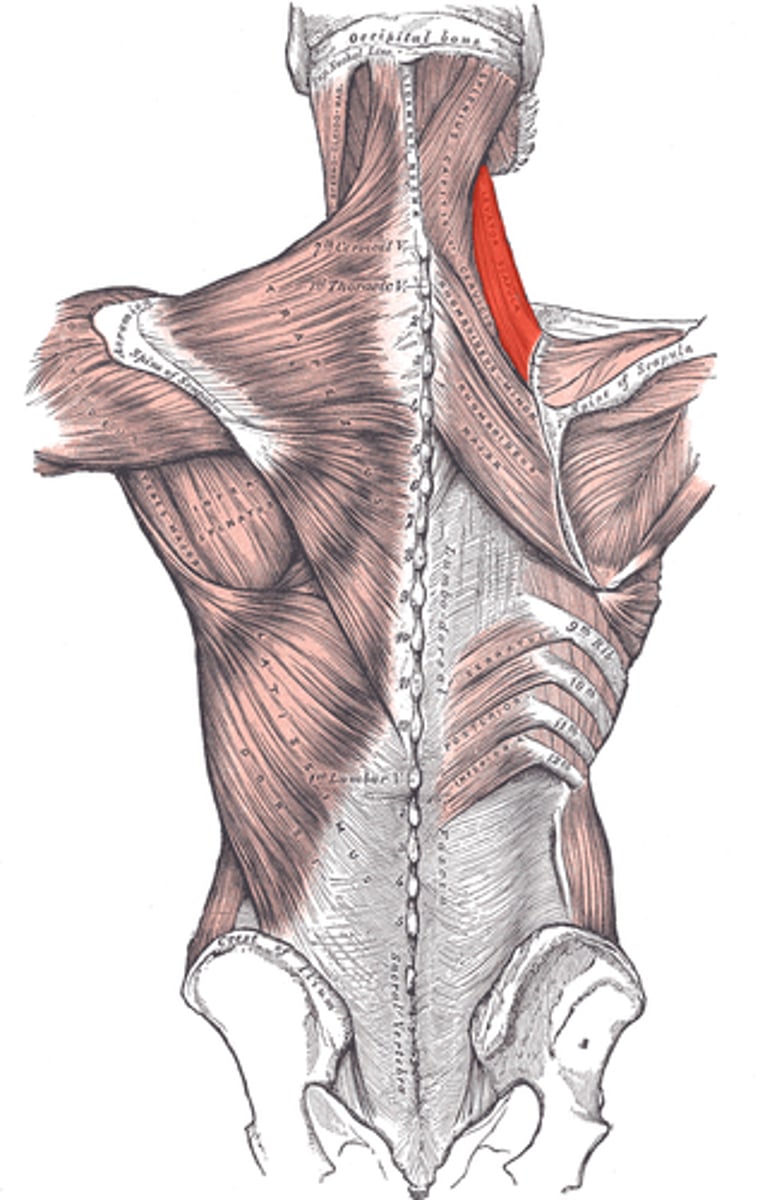
(Deep posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder):) Levator Scapulae
-Elevates and rotates scapula
-Dorsal scapular n. (C5)
(Deep posterior axioappendicular muscles (extrinsic shoulder):) Rhomboid Minor and Major
-Retract and rotates scapula
-Dorsal scapular n. (C5)
(Posterior axioappendicular and scapulohumeral muscles:)
Scapulohumeral muscles (intrinsic shoulder)
Deltoid and Teres Major
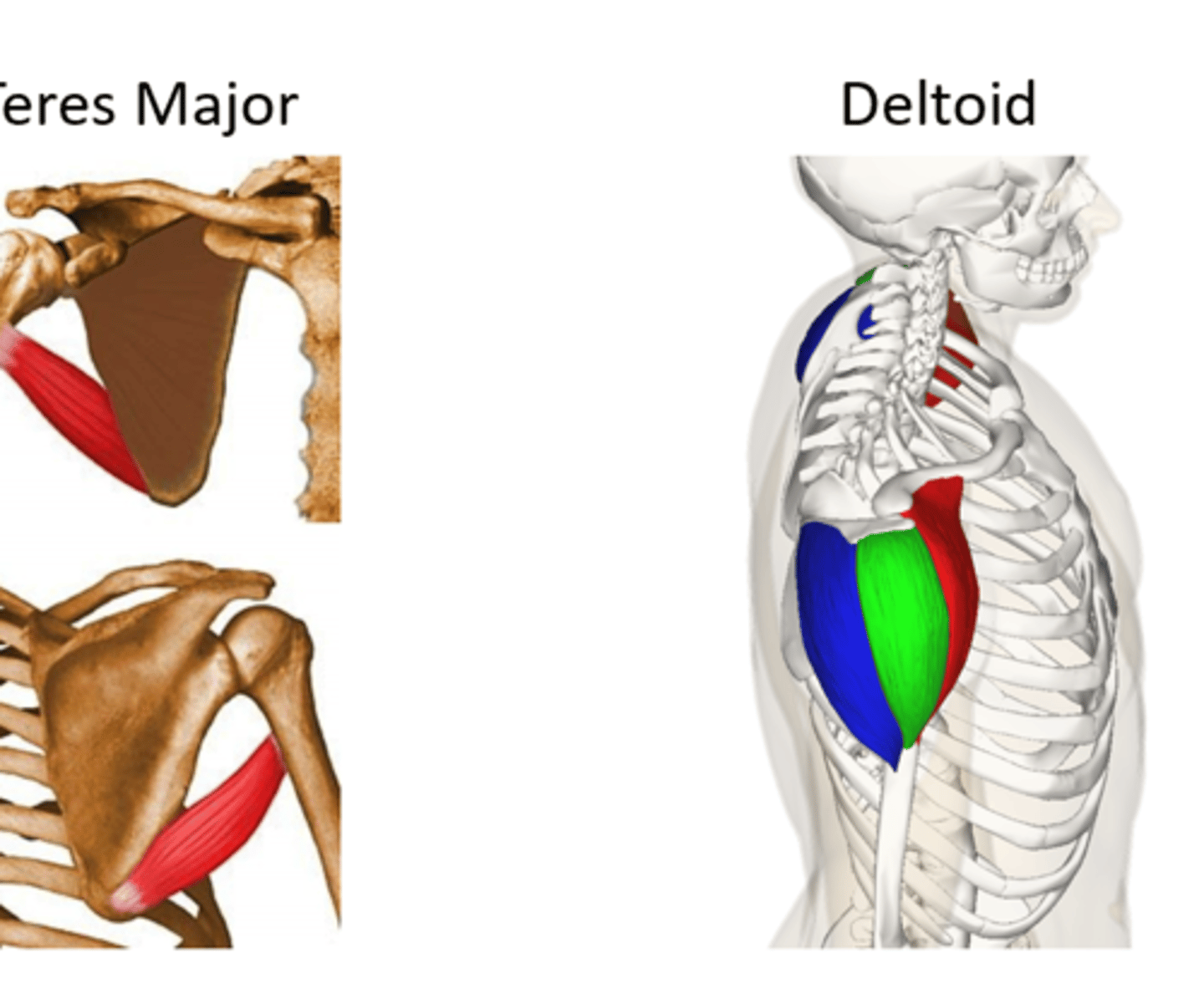
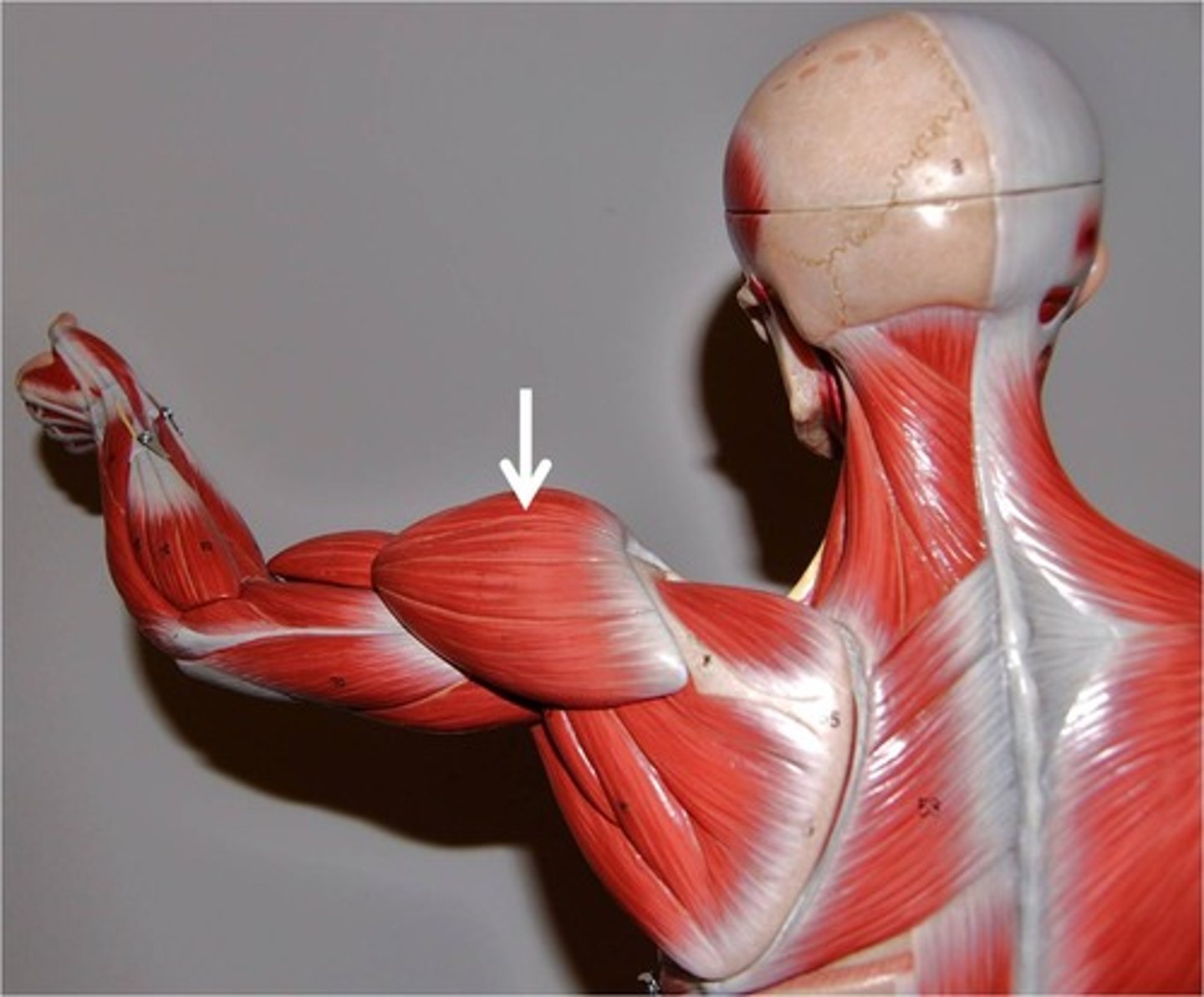
(Scapulohumeral muscles (intrinsic shoulder):) Deltoid
-Divided into anterior (clavicular), middle (acromial), and posterior (spinal) parts
-Flexes and medially rotates arm (anterior), abducts arm (middle), extends and laterally rotates arm (posterior)
-Axillary n. (C5 - C6)
-Abducts the arm after the initial 15˚. During the initial 15˚ is assisted by the supraspinatus muscle
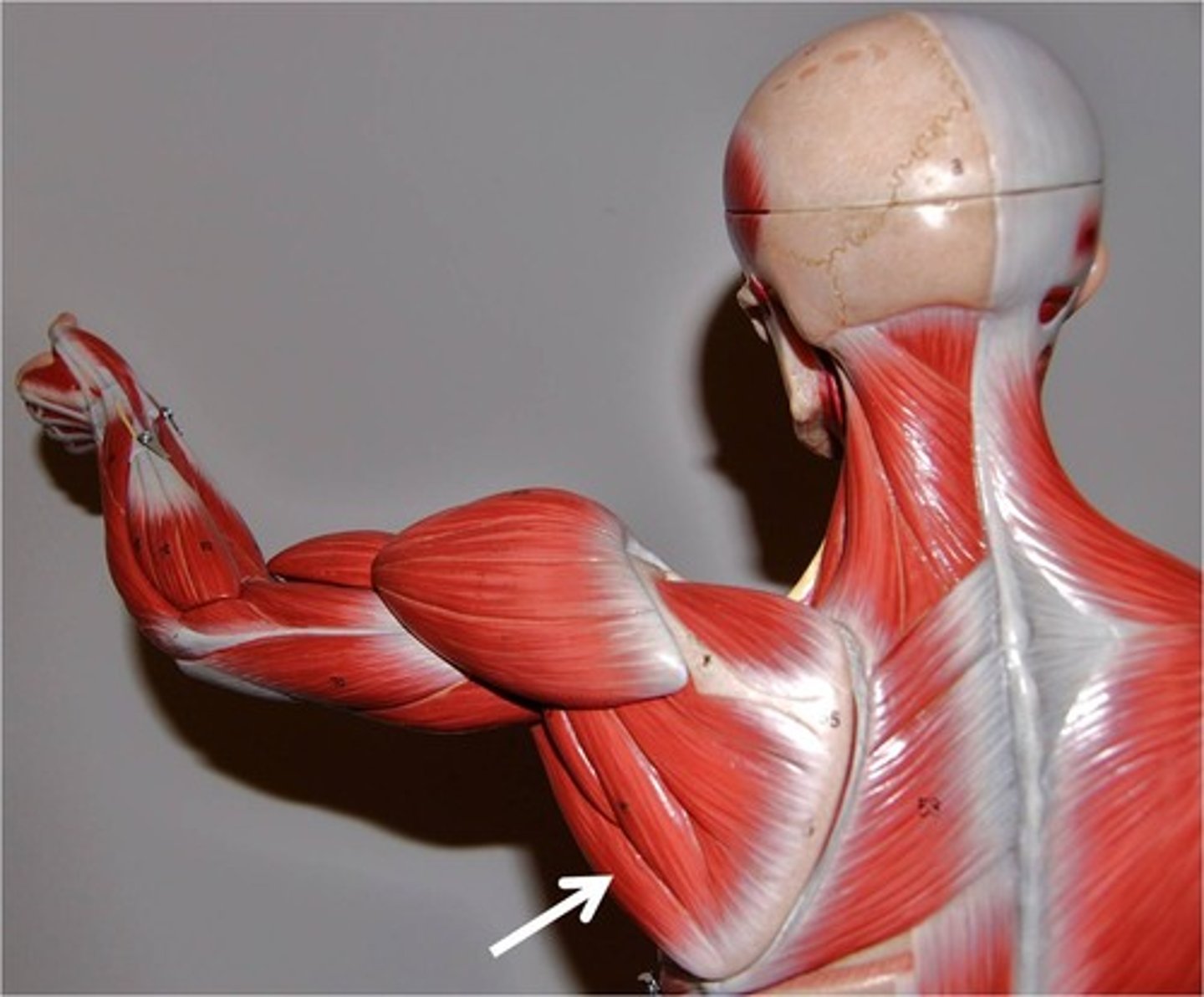
(Scapulohumeral muscles (intrinsic shoulder):) Teres Major
-Adducts and medially rotates arm
-Lower subscapular n. (C5 - C6)
(Scapulohumeral muscles (intrinsic shoulder):) Rotator cuff muscles
Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres Major, Subscalpularis
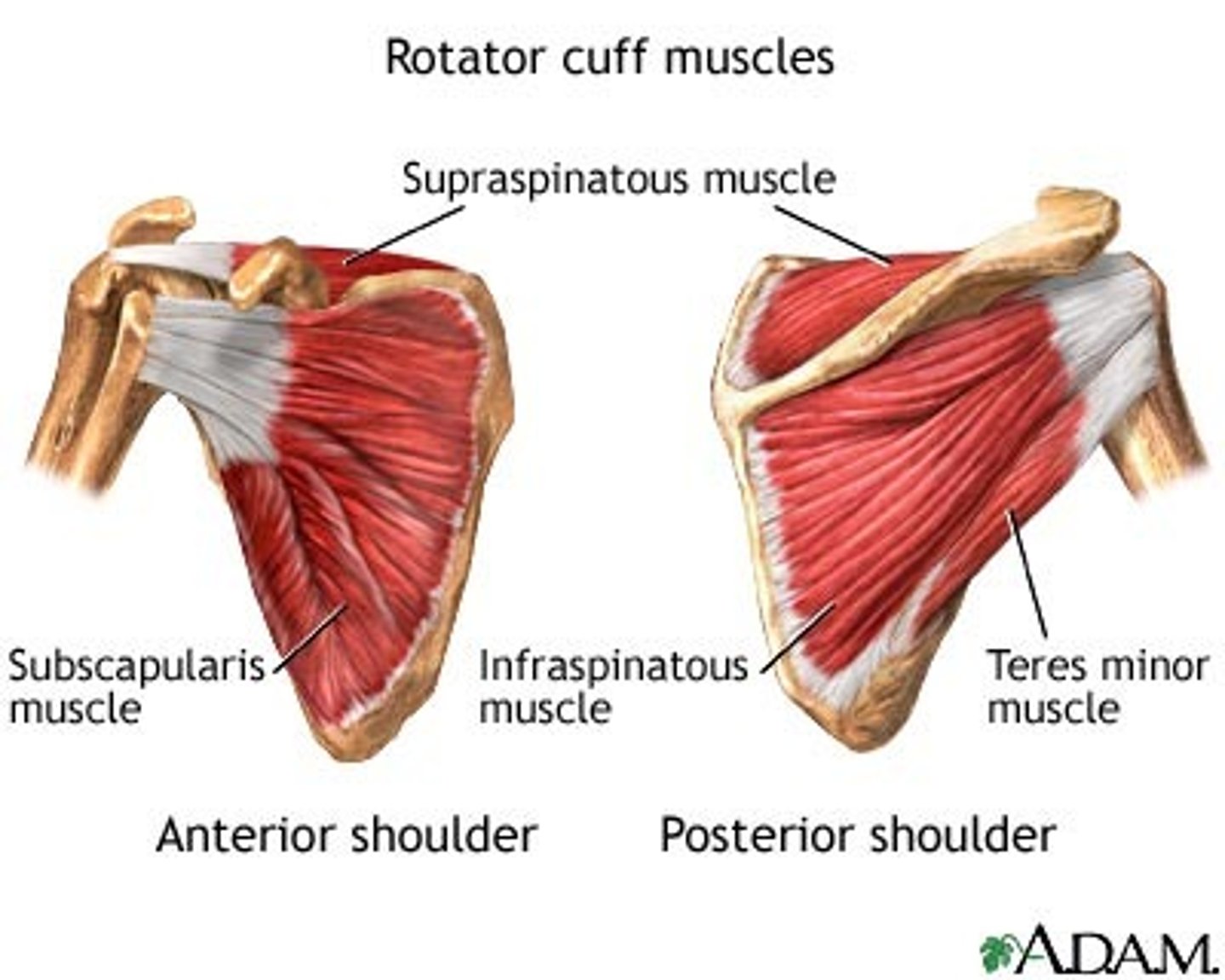
(Rotator Cuff Muscles:) Supraspinatus
-Abduction of arm (assists deltoid in the initial 15˚)
-Suprascapular n. (C5 - C6)
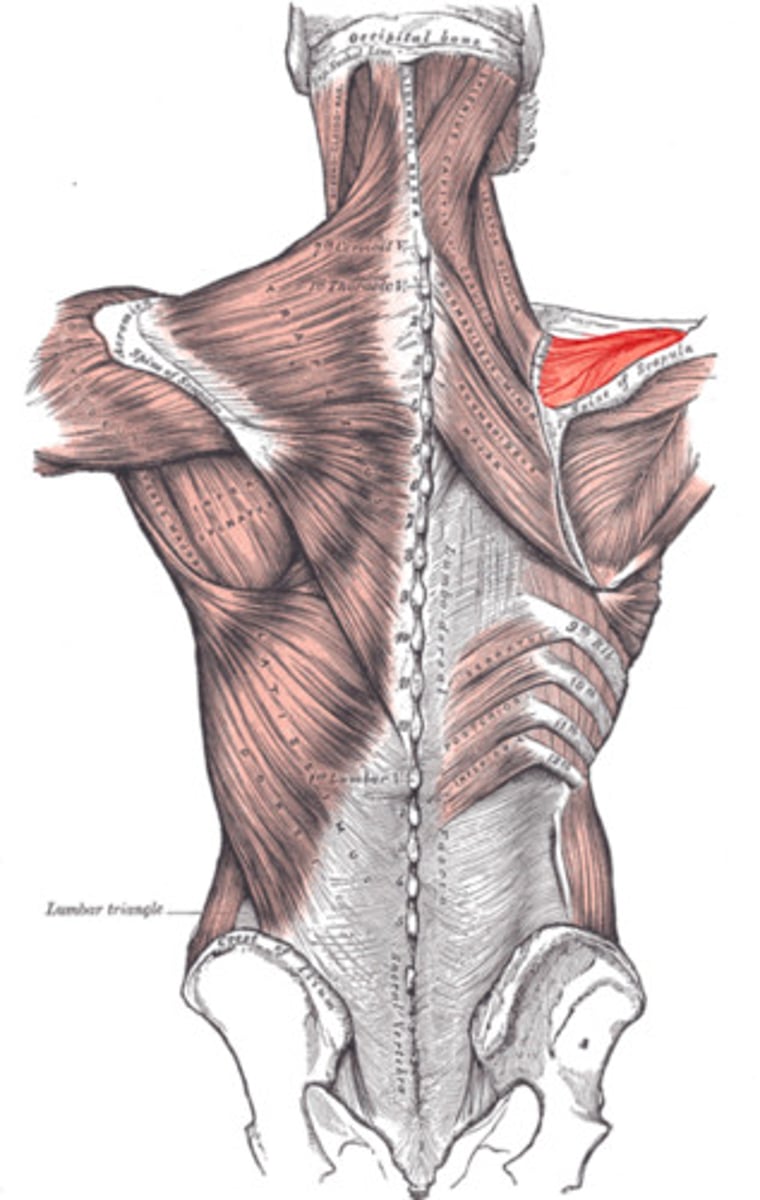
(Rotator Cuff Muscles:) Infraspinatus
-Laterally rotates arm
-Suprascapular n. (C5 - C6)
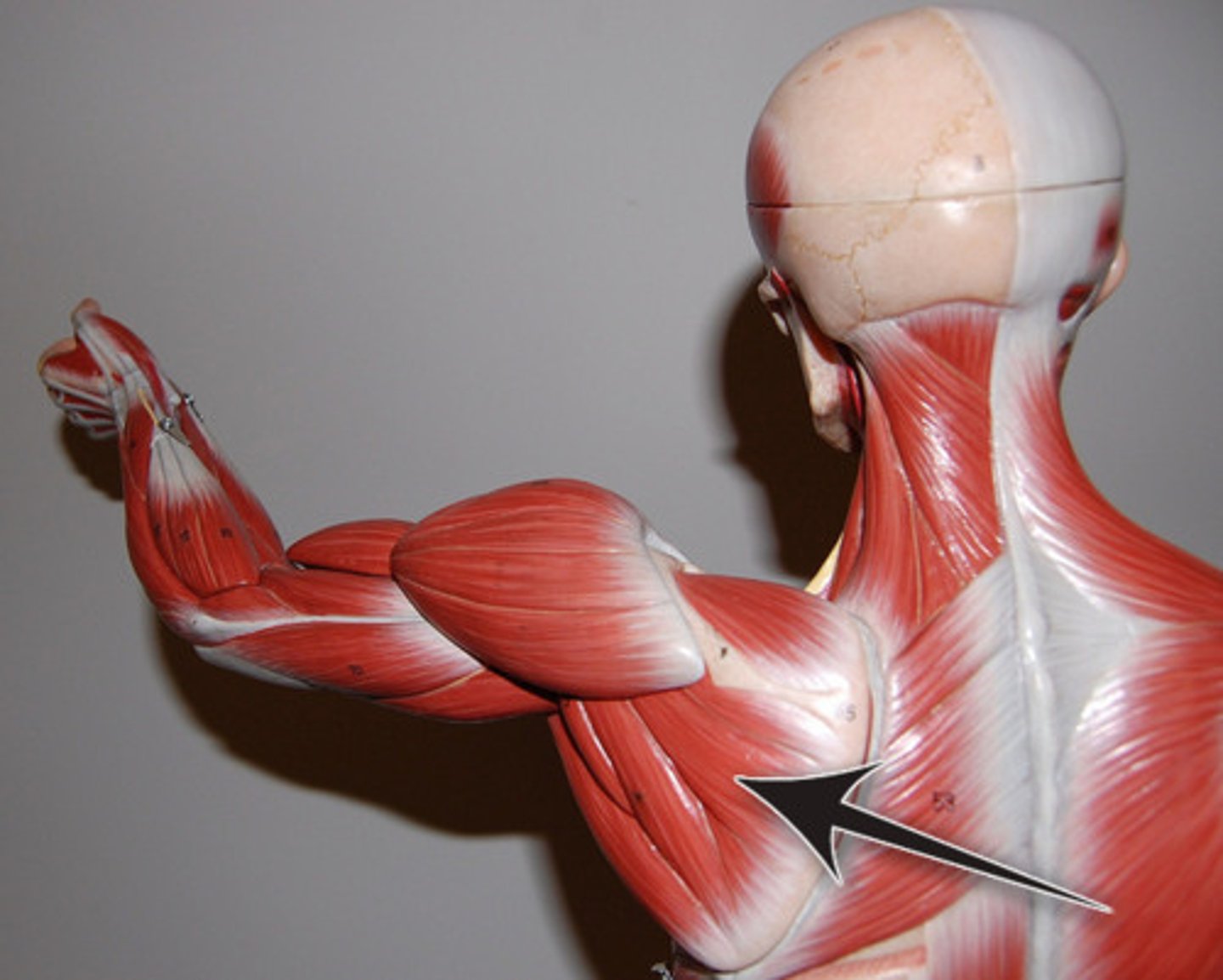
(Rotator Cuff Muscles:) Teres Major
-Laterally rotates arm
-Axillary n. (C5 - C6)
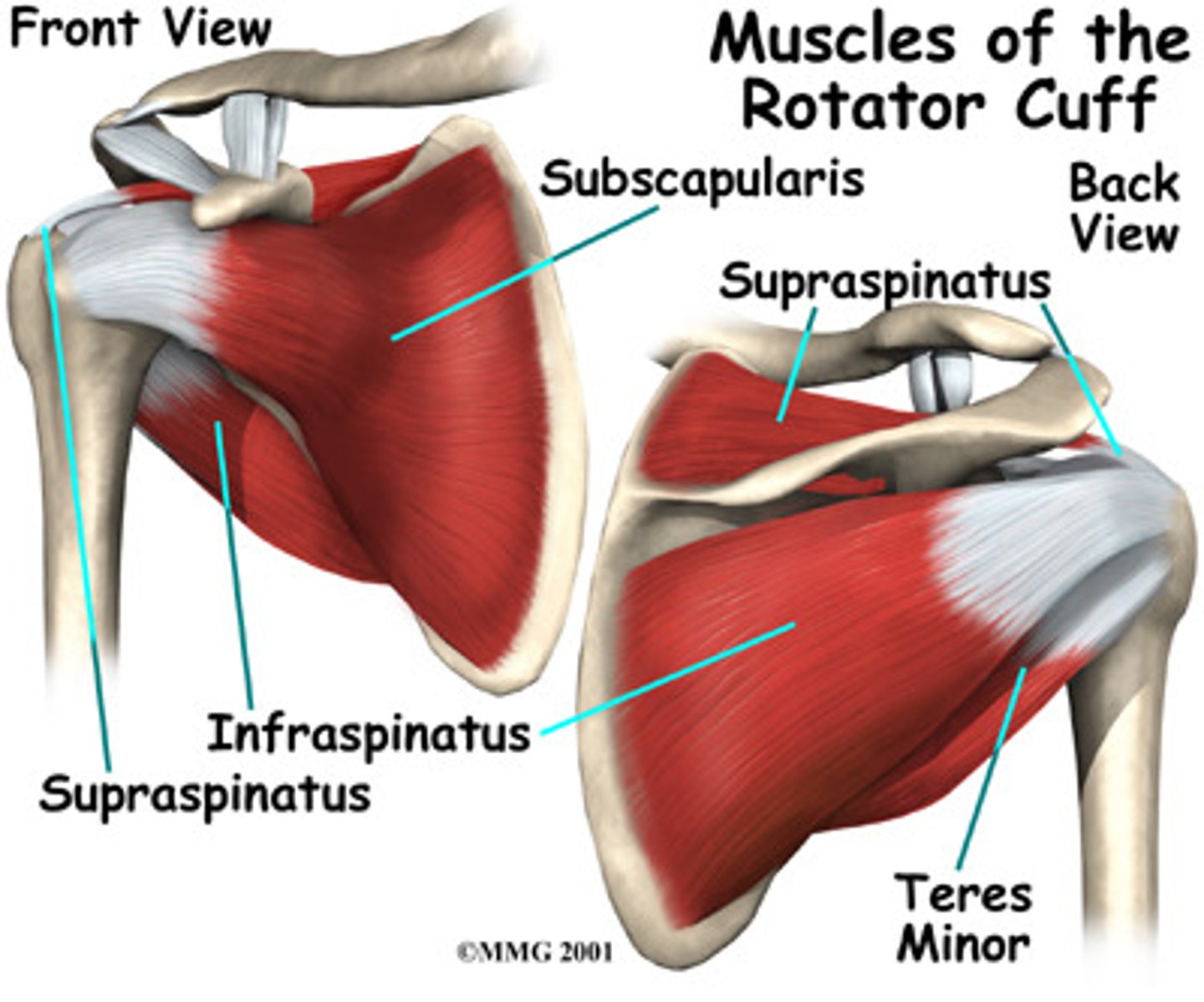
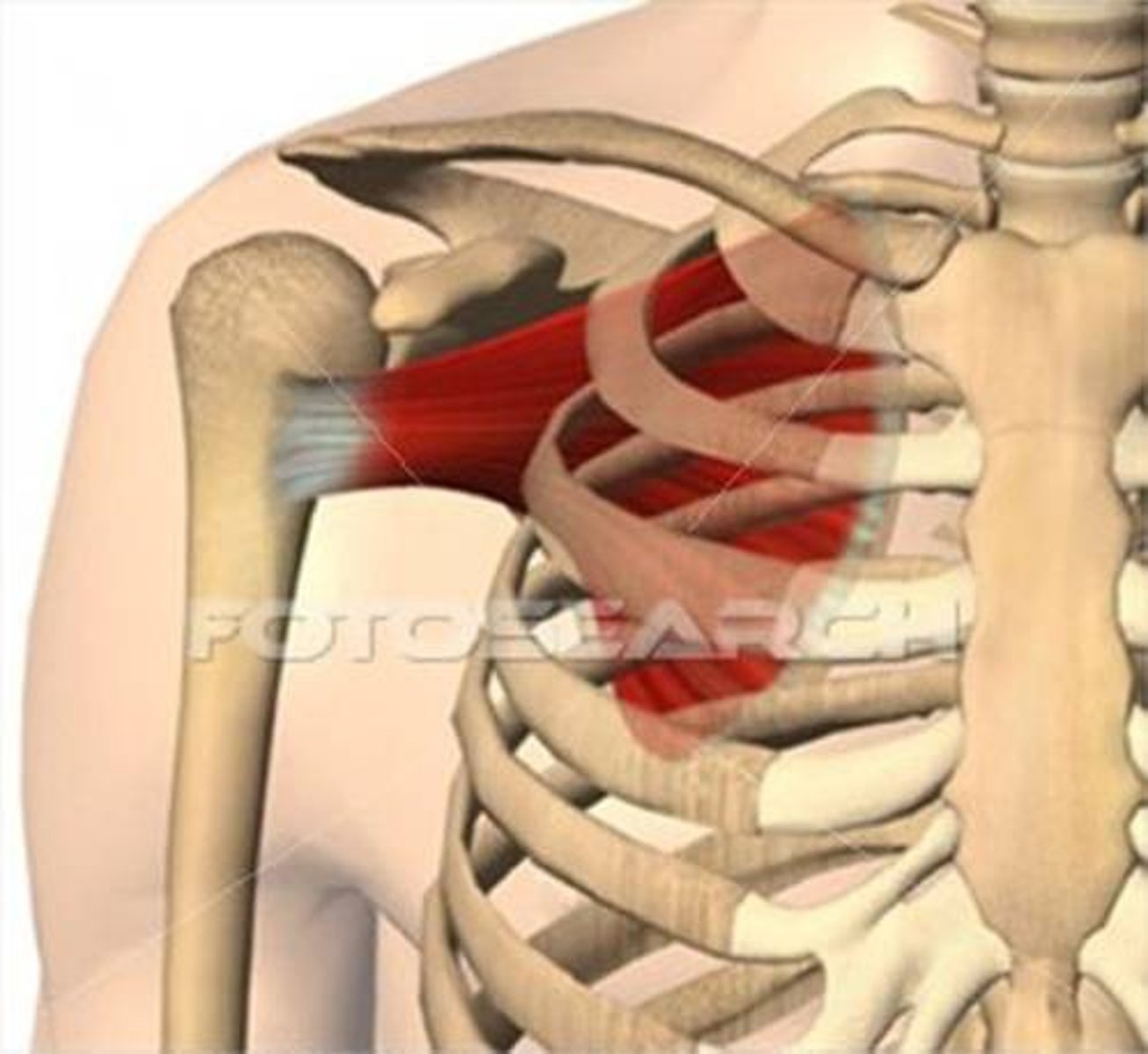
(Rotator Cuff Muscles:) Subscapularis
-Medially rotates arm
-Upper and lower subscapular nerves (C5 - C7)
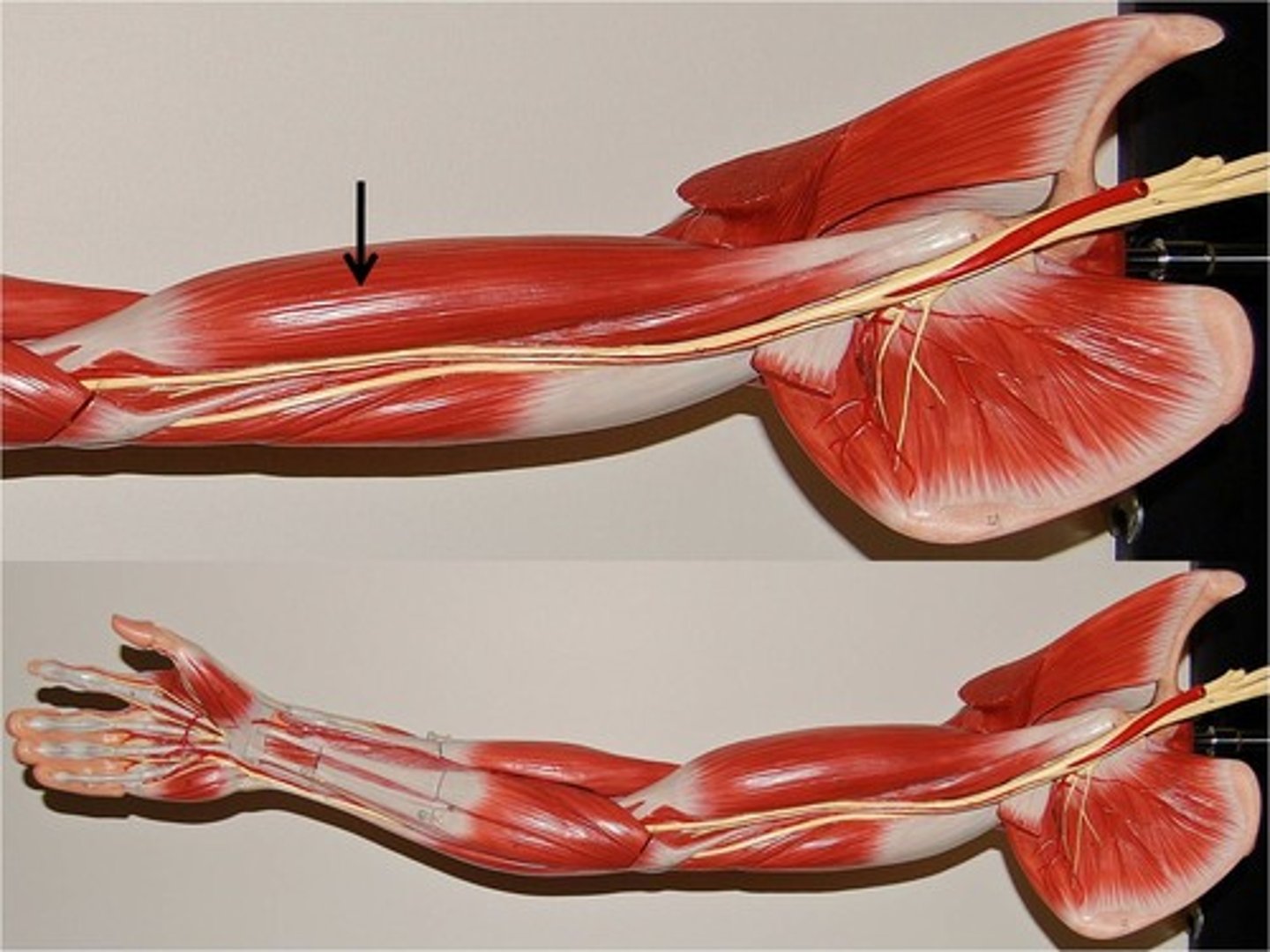
Muscles of the arm
•3 flexors in anterior compartment and 2 extensors in posterior compartment
•They act primarily at the elbow joint
Contains:
-Anterior compartment (flexor)
-Posterior compartment (extensor)
(Muscles of the arm:) Anterior compartment (flexor)
•Biceps brachii
•Brachialis
•Coracobrachialis
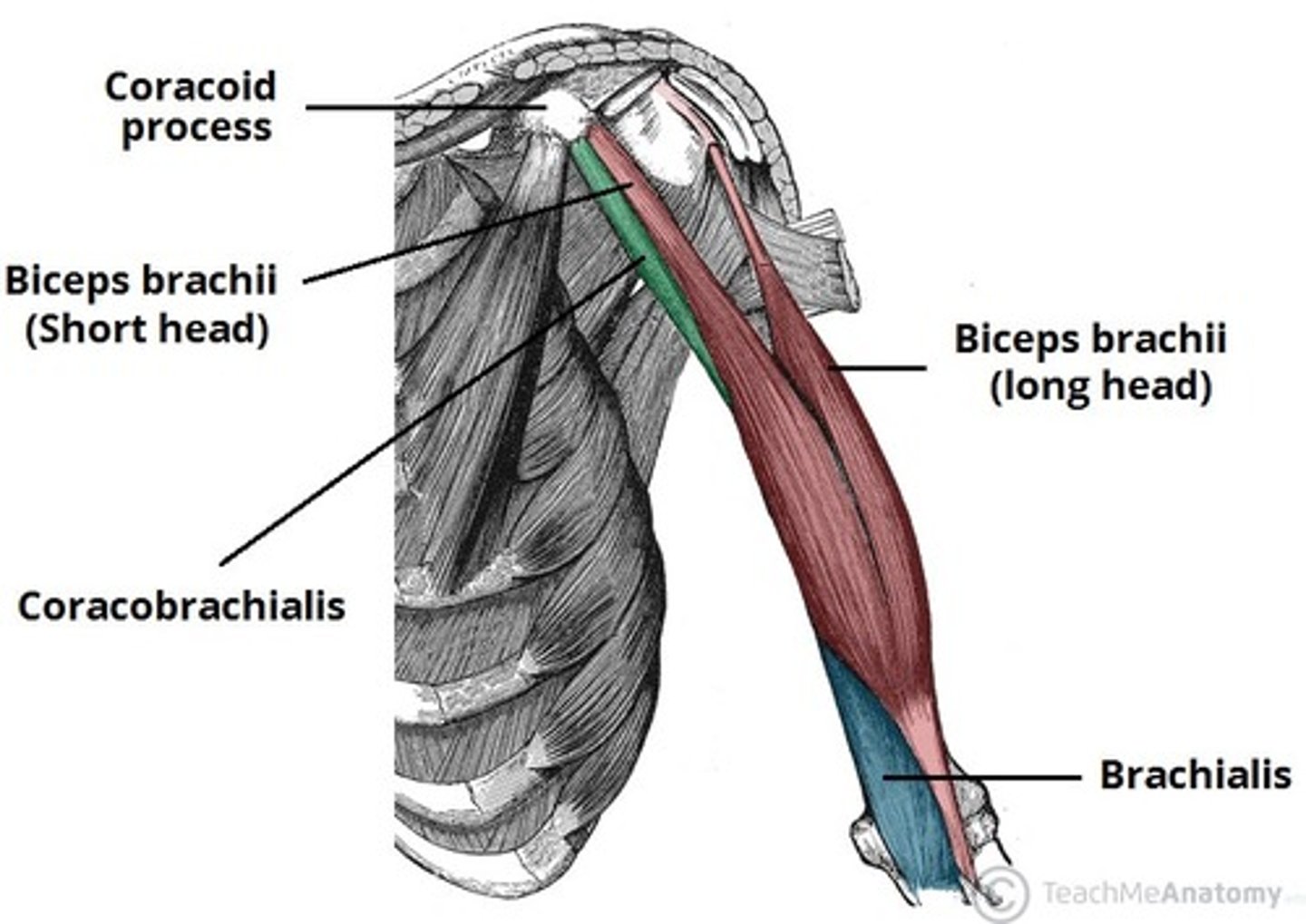
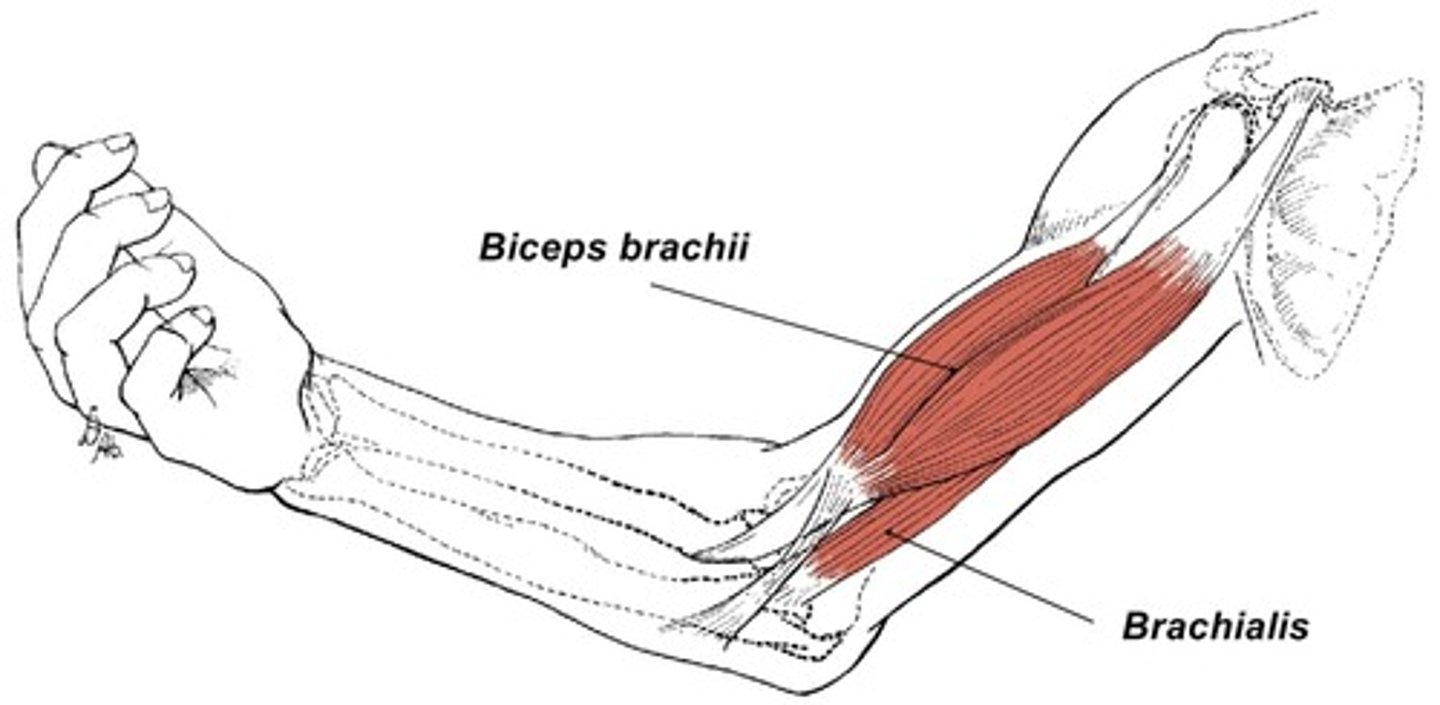
(Anterior compartment (flexor):) Biceps brachii
-Flexes and supinates forearm
-Musculocutaneous n. (C5 - C7)
-Bicipital aponeurosis: membranous band running from the biceps tendon across the cubital fossa and merges with antebrachial deep fascia. It is superficial to and protects the brachial a. and median n.
(Anterior compartment (flexor):) Brachialis
-Flexes forearm
-Musculocutaneous n. (C5 – C7)
-Deep to biceps brachii m. and is the main flexor of the forearm
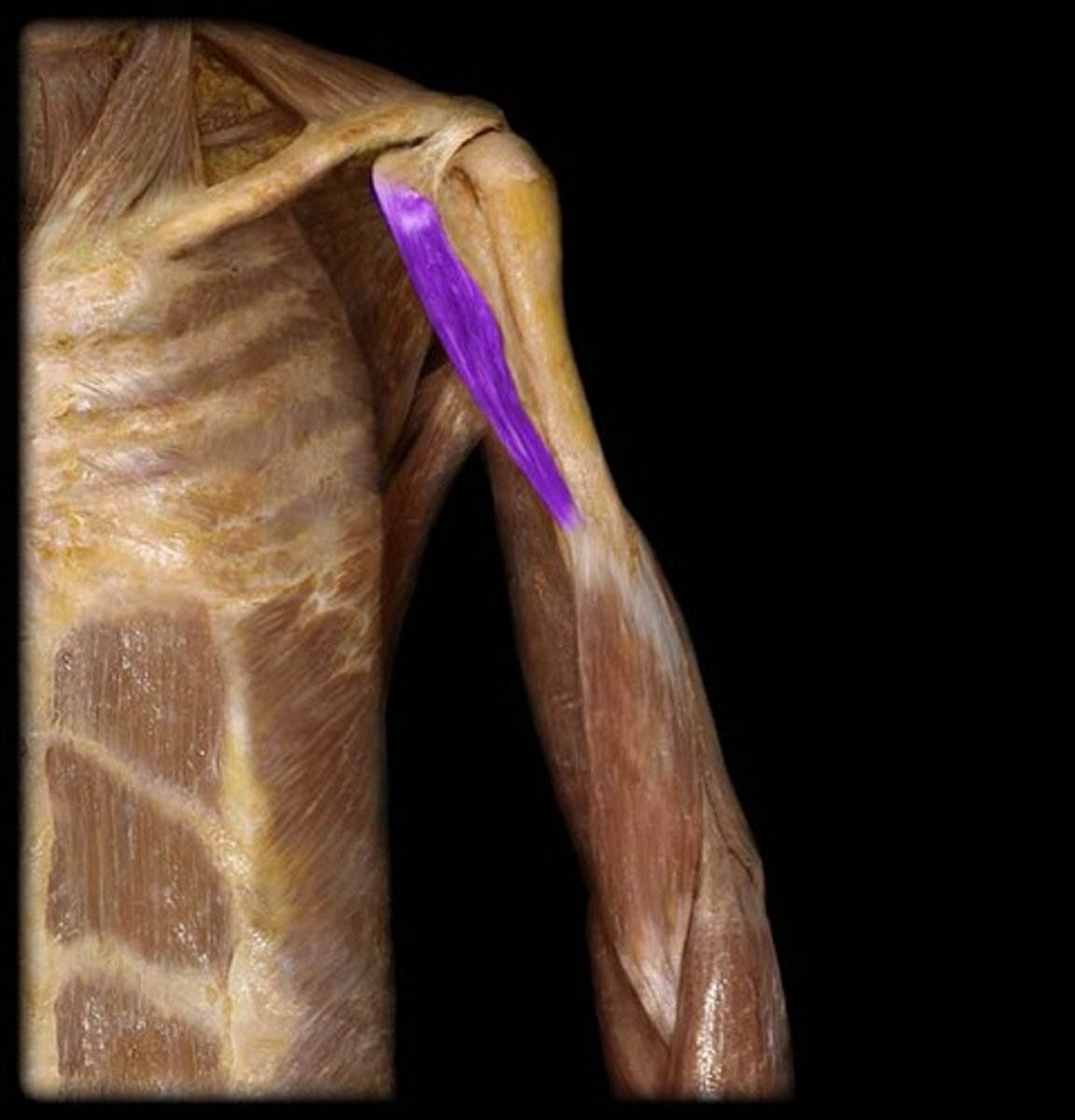
(Anterior compartment (flexor):) Coracobrachialis
-Flexes and adducts the arm
-Musculocutaneous n. (C5 - C7)
-Pierced by the musculocutaneous n. and located in the superomedial part of arm
(Muscles of the arm:) Posterior compartment (extensor)
Triceps brachii
Anconeus
(Posterior compartment (extensor):) Triceps brachii
-Extends forearm
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Long, medial, and lateral heads
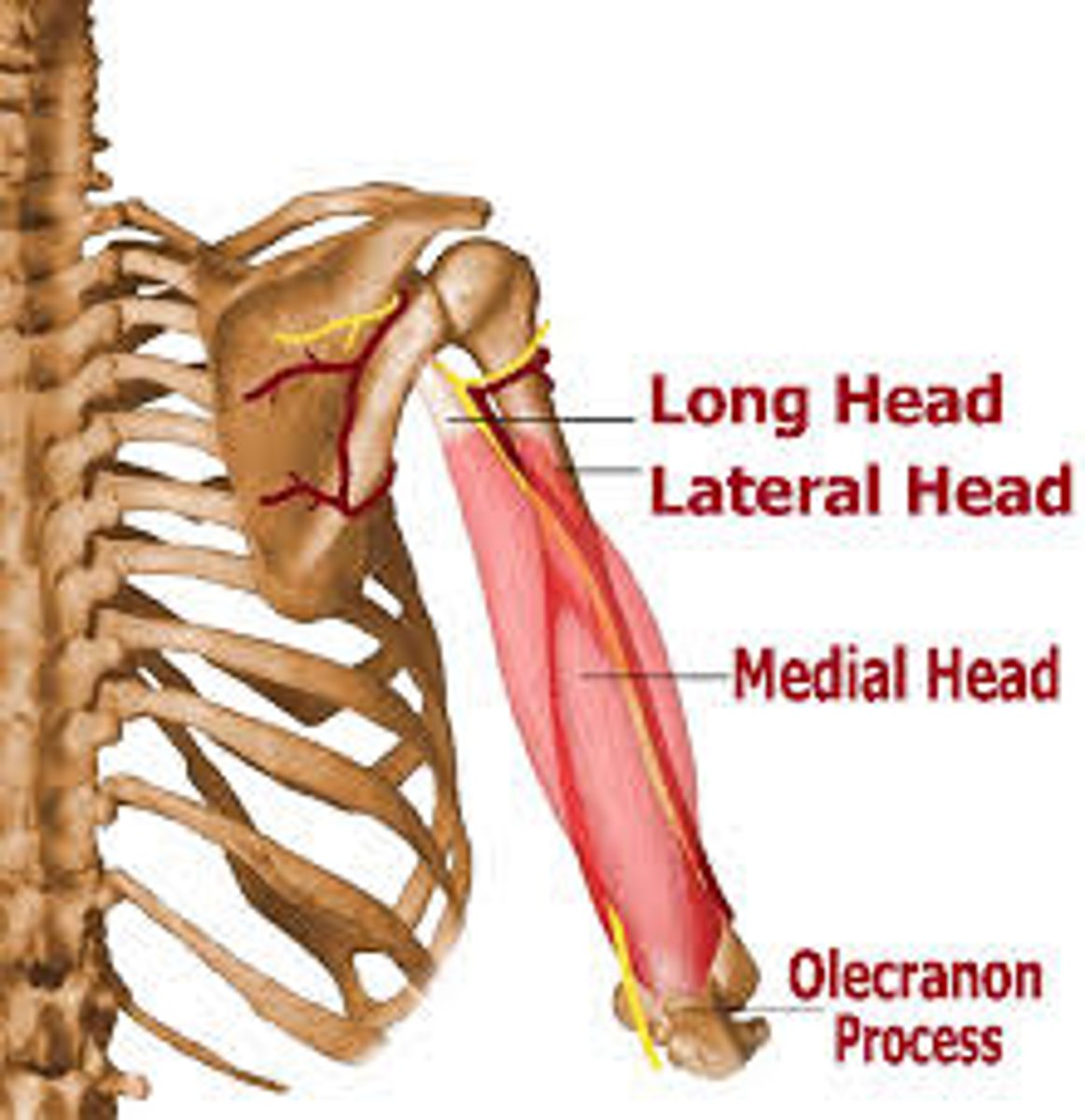
(Posterior compartment (extensor):) Anconeus
-Assists triceps in extending the forearm
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Located in the posterolateral aspect of the elbow
Muscles of the forearm
These muscles act on the wrist and fingers, but are located proximally in the forearm and distant from their site of action (like "remote control") to maximize their functionality
Muscles of the forearm has a flexor-pronator in...
anterior (actually anteromedial) compartment and extensor-supinator muscles in posterior (actually posterolateral) compartment
Flexor-pronator muscles of the forearm attach to
the medial epicondyle and supraepicondylar ridge
Extensor-supinator muscles of the forearm attach to
the lateral epicondyle and supraepicondylar ridge
Muscles of the forearm Anterior (flexor-pronator) compartment communicates with
central compartment of hand through the carpal tunnel without a fascial barrier
(Muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm (Flexors):) Superficial (1st) layer
Superficial (1st) layer: all muscles cross the elbow joint
-Pronator teres
-Flexor carpi radialis (FCR)
-Palmaris longus
-Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)
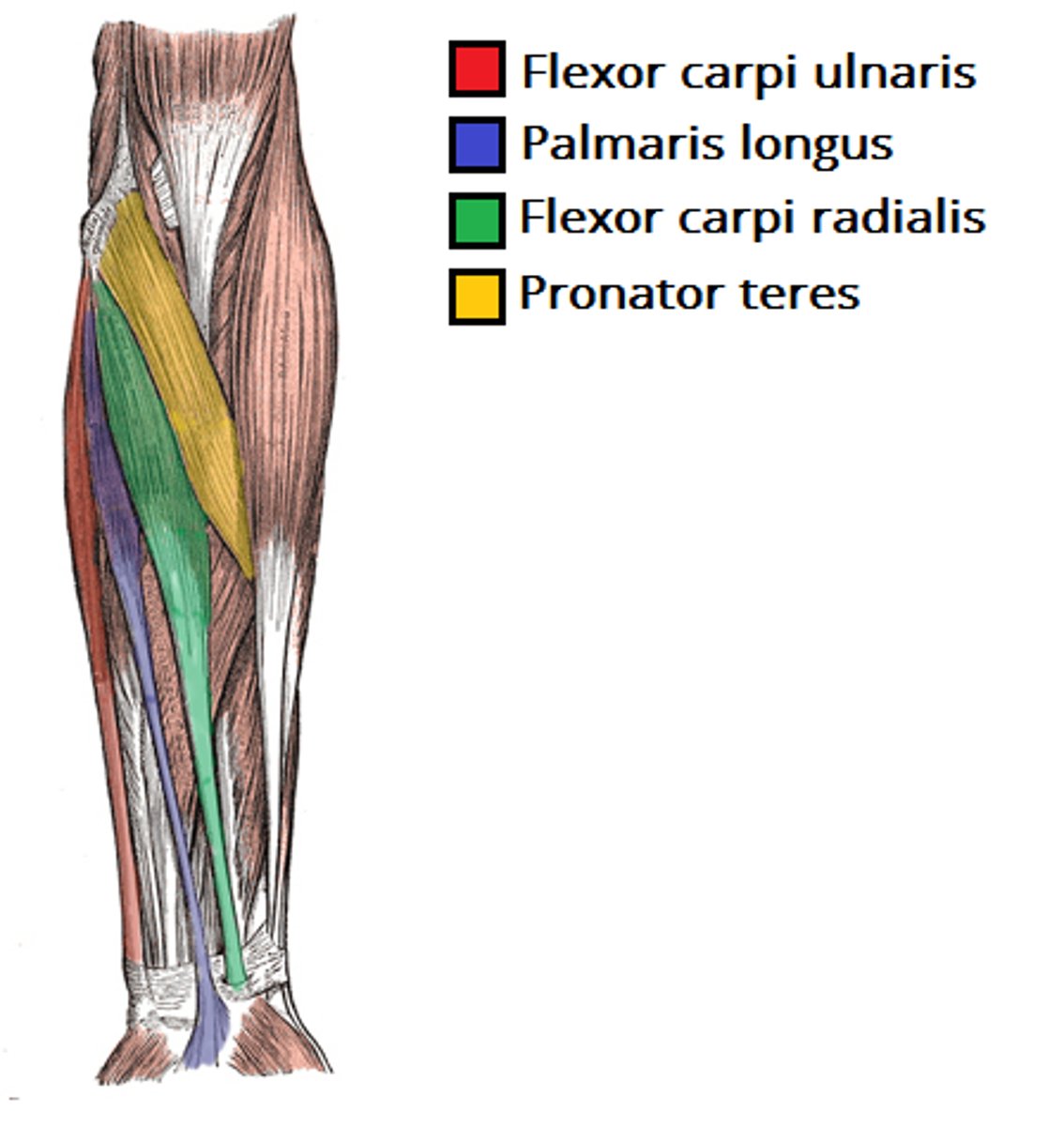
(Superficial (1st) layer:) Pronator teres
-Pronates forearm and flexes elbow
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Most lateral of this layer
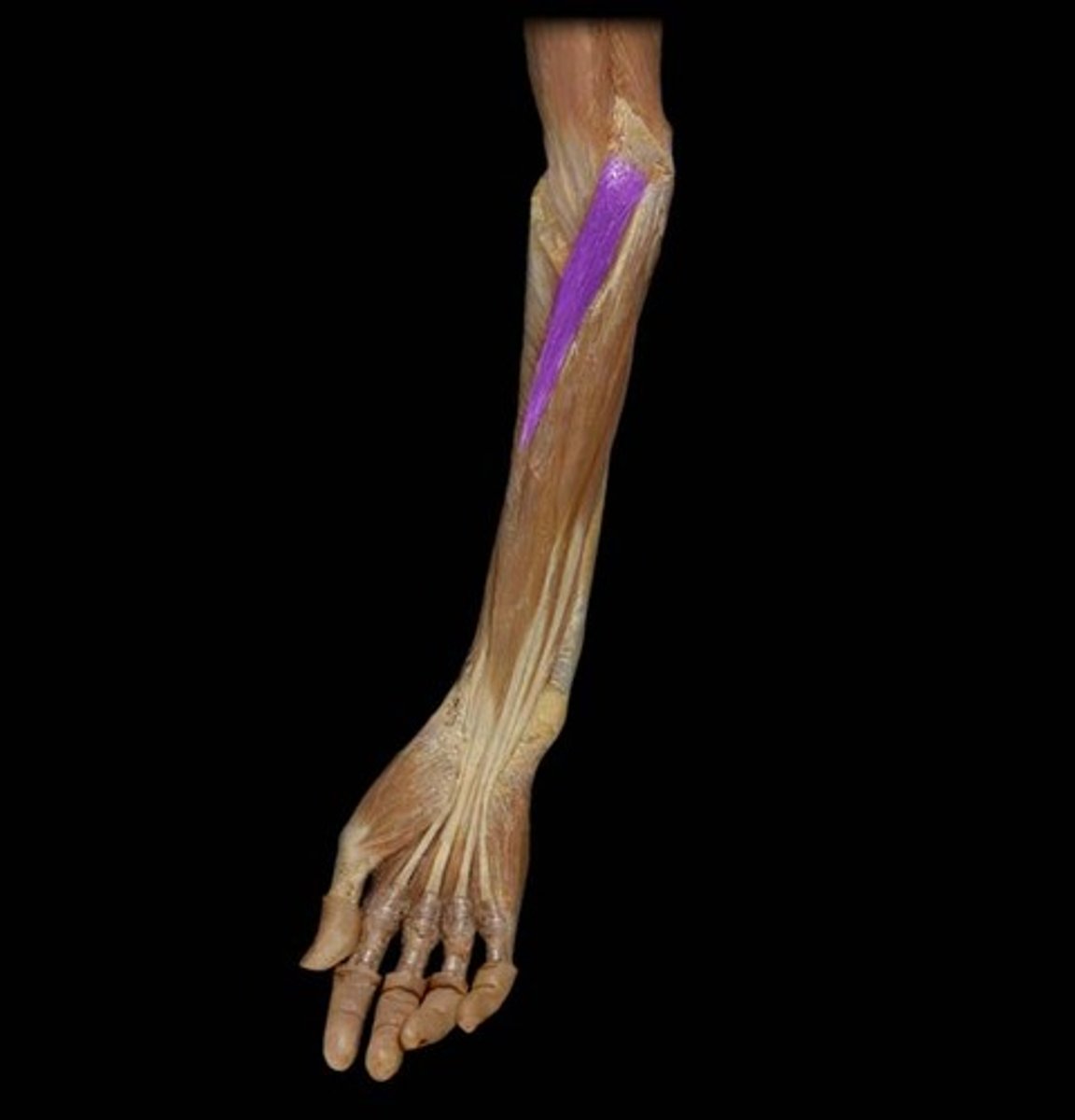
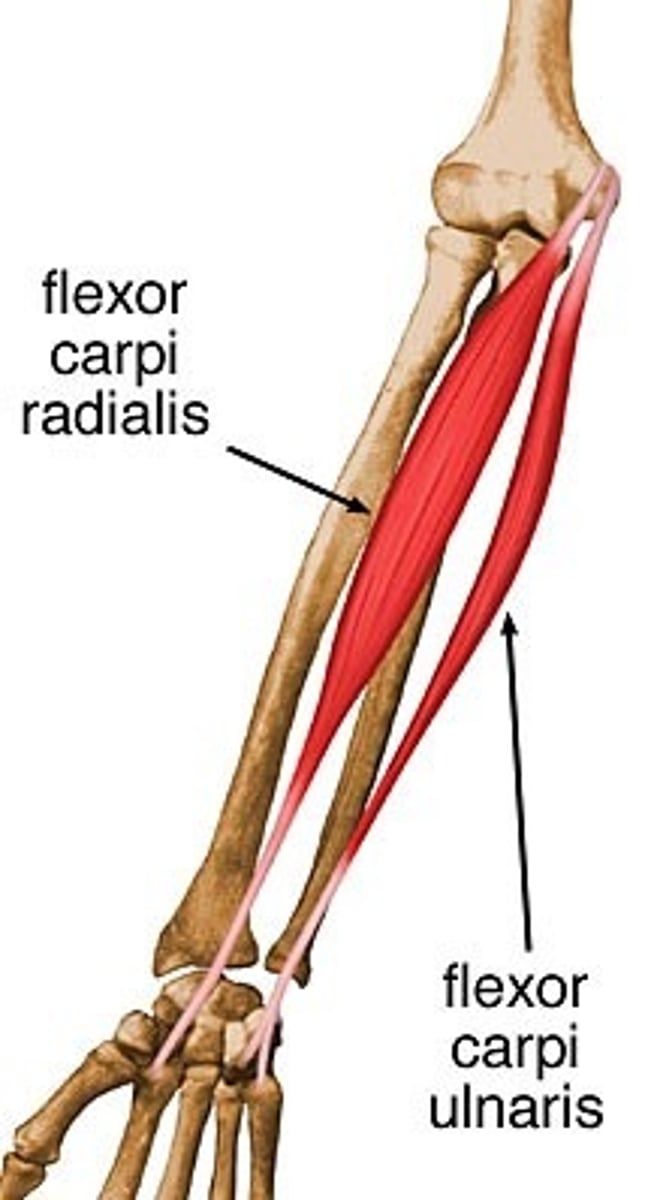
(Superficial (1st) layer:) Flexor carpi radialis (FCR)
-Flexes and abducts hand
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to pronator teres m.
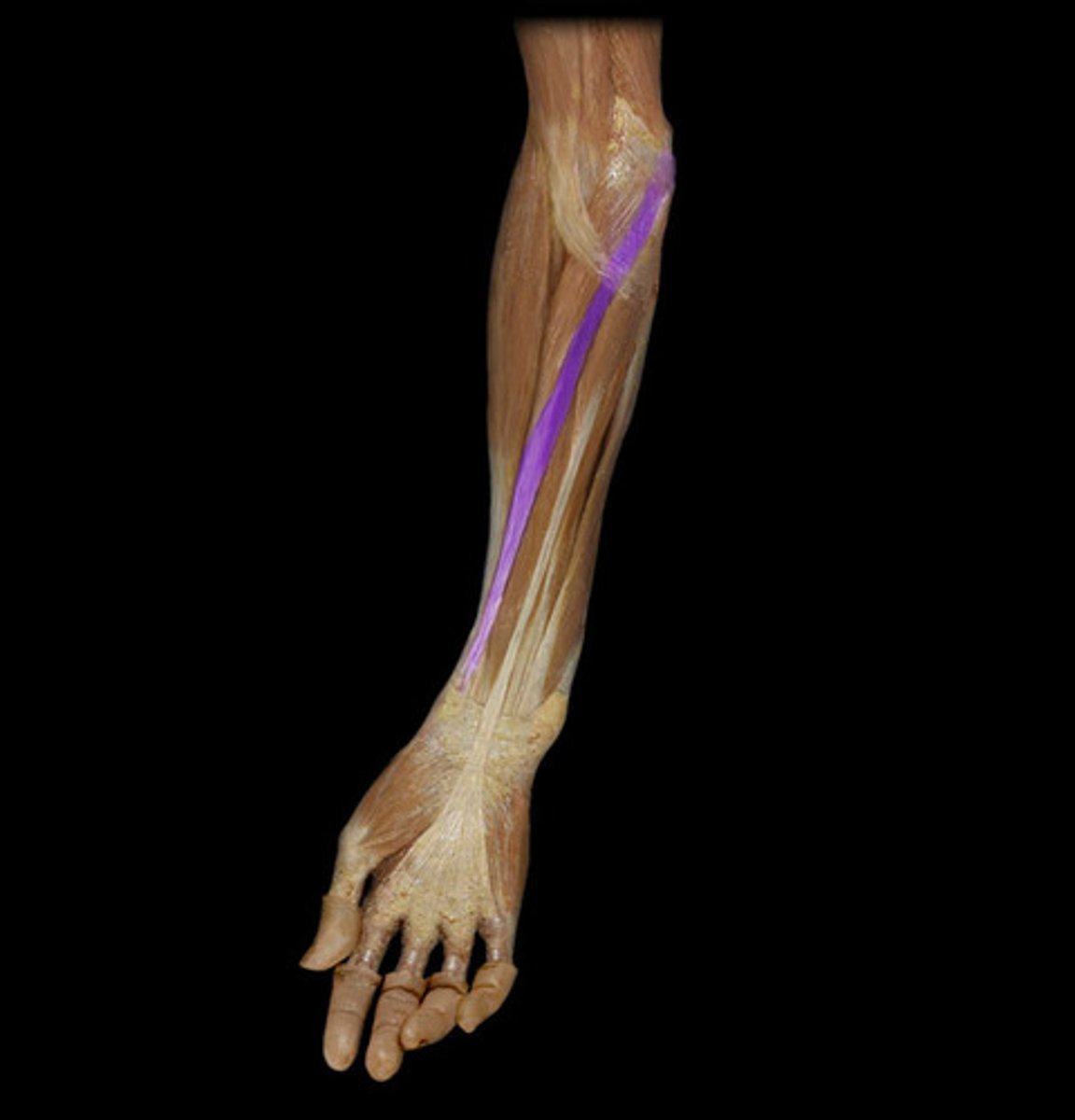
(Superficial (1st) layer:) Palmaris longus
-Flexes hand and tenses palmar aponeurosis
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to flexor carpi radialis m.
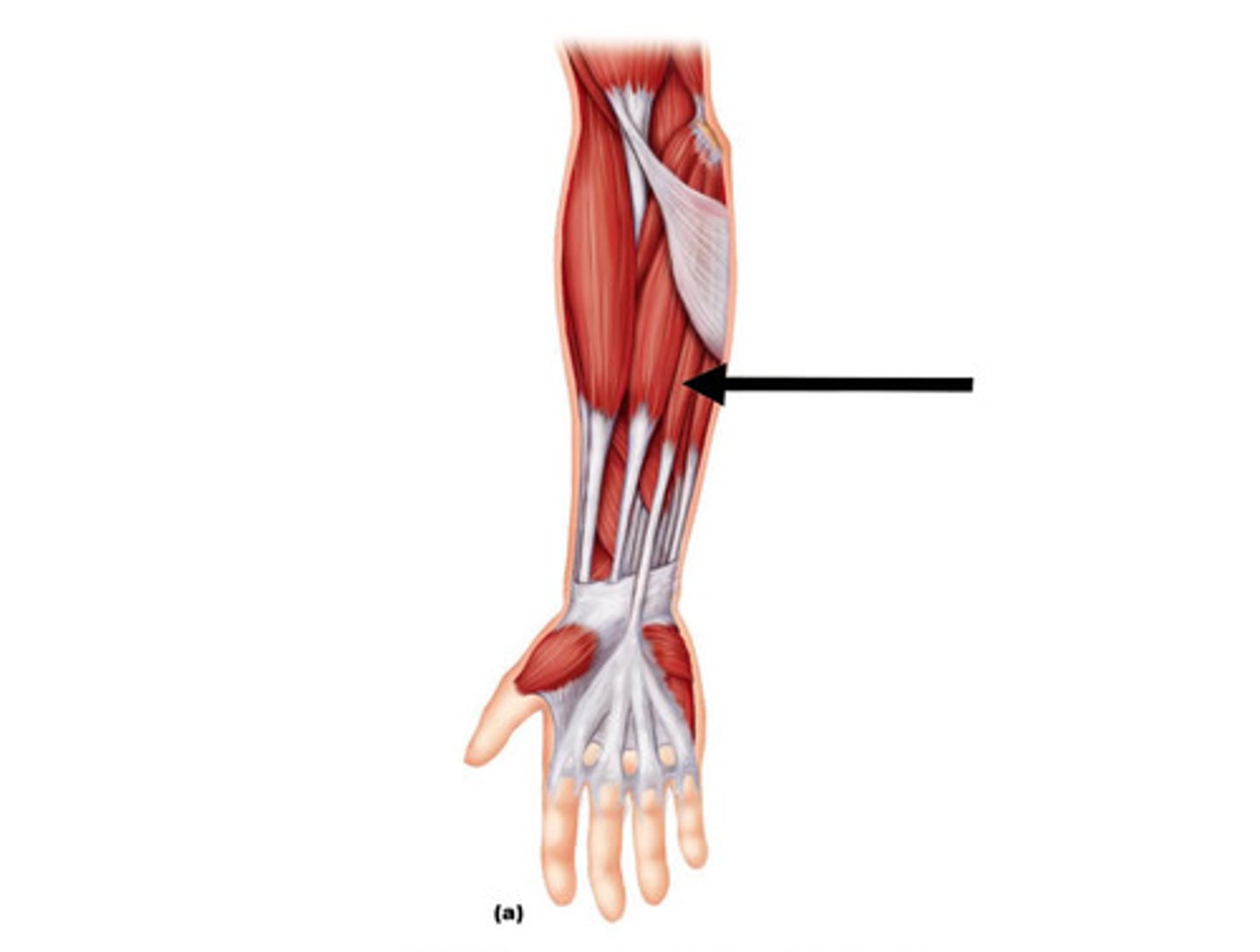
(Superficial (1st) layer:) Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU)
-Flexes and adducts hand
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-Medial to palmaris longus m.
(Muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm (Flexors):) Intermediate (2st) layer
Intermediate (2st) layer: cross the elbow joint
Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)
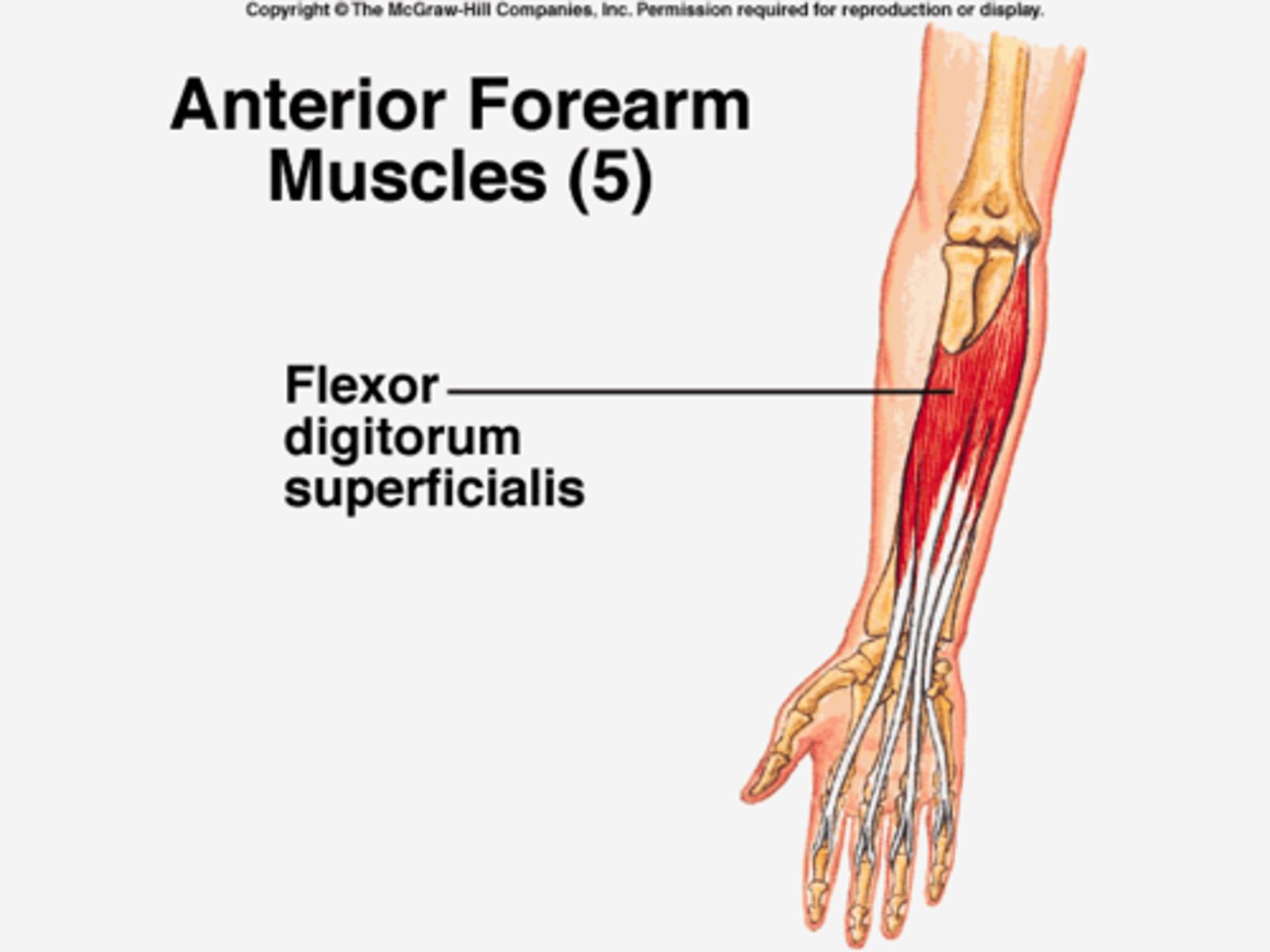
(Intermediate (2st) layer:) Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)
-Flexes proximal interphalangeal joints of 2nd - 5th digits
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Deep to muscles of the superficial layer
-Passes through the carpal tunnel
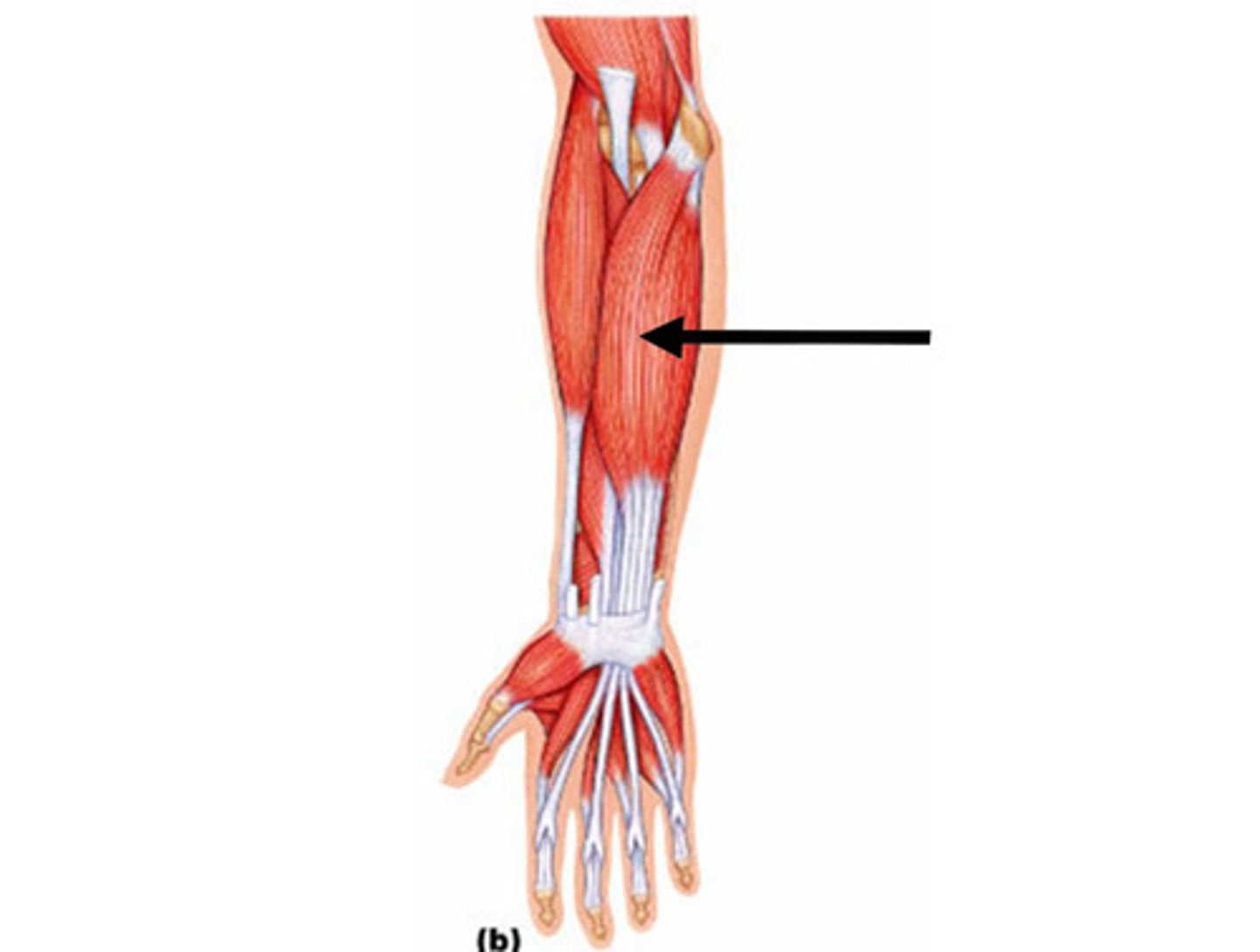
(Muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm (Flexors):) Deep (3rd) layer
Deep (3rd) layer: do not cross the elbow joint
-Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
-Flexor pollicis longus (FPL)
-Pronator quadratus
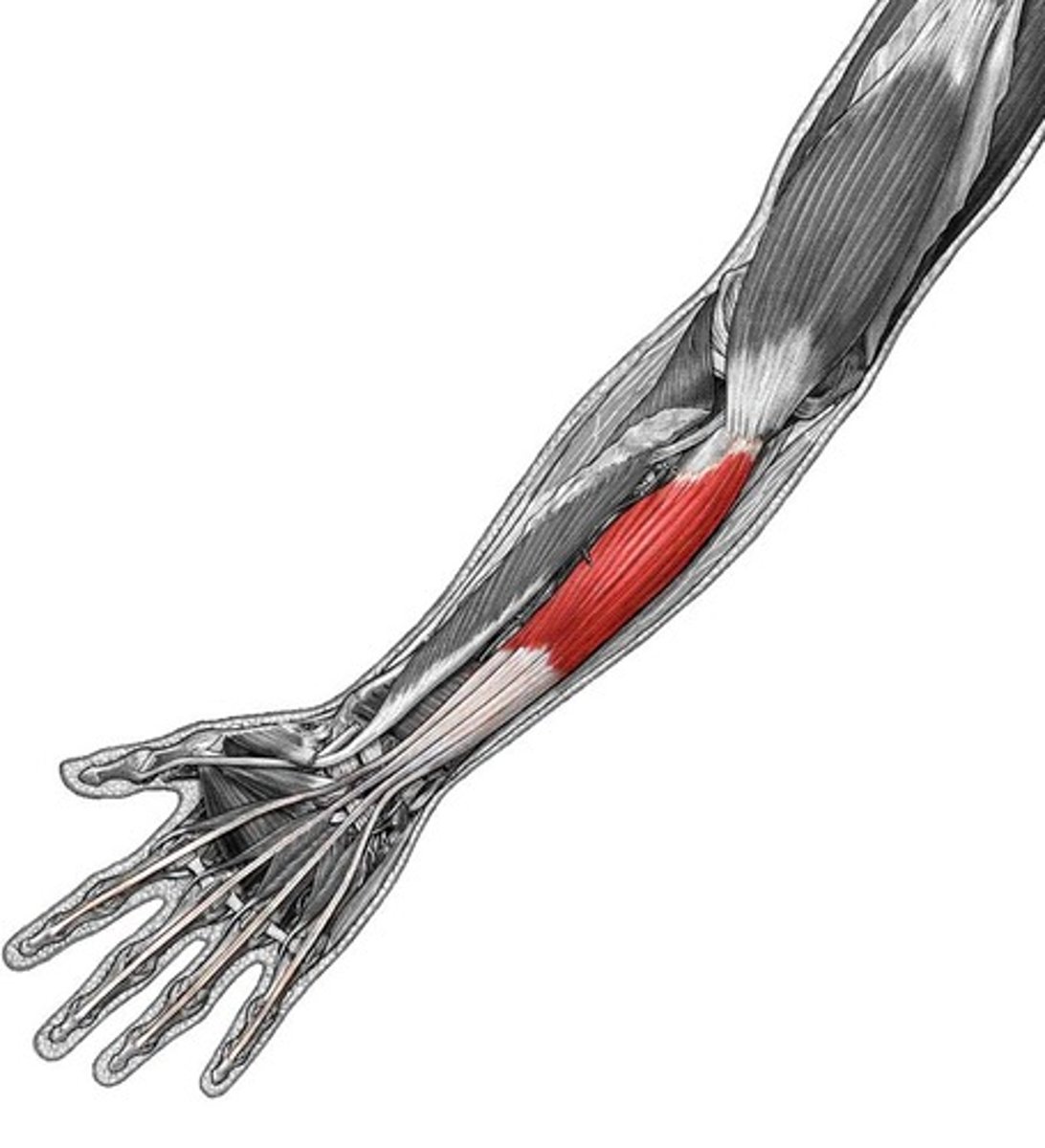
(Deep (3rd) layer:) Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)
-Flexes distal interphalangeal joints of 2nd - 5th digits
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1) & median n. (C5 - T1)
-Deep to FDS and in contact with the ulna
-Passes through carpal tunnel
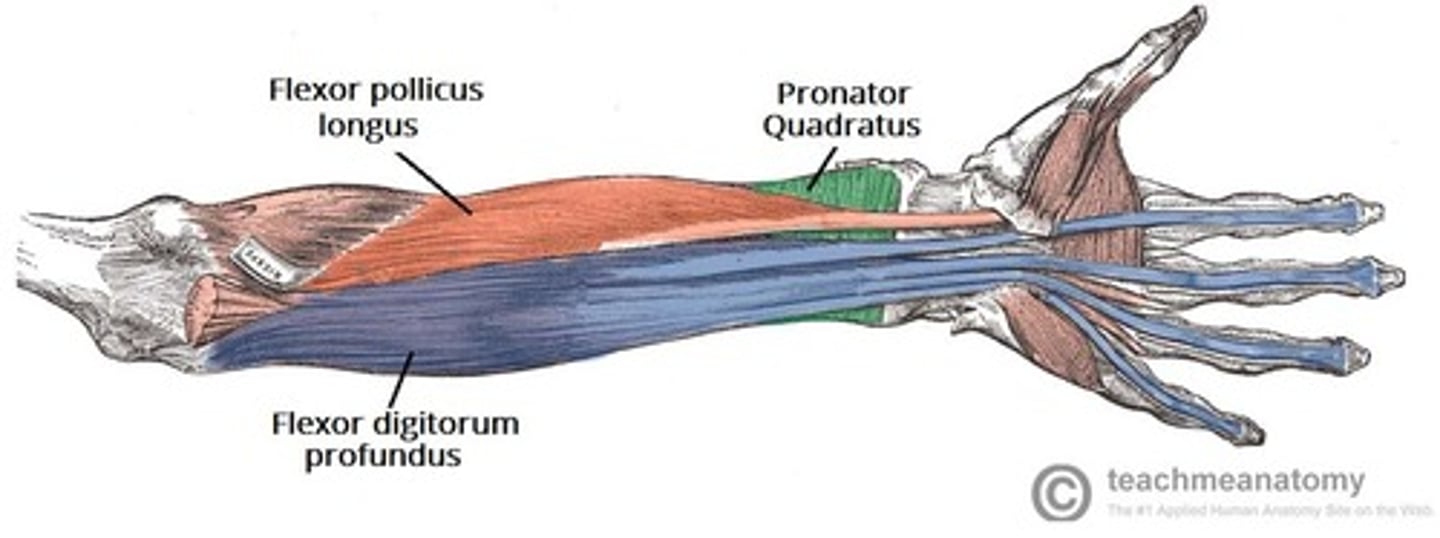
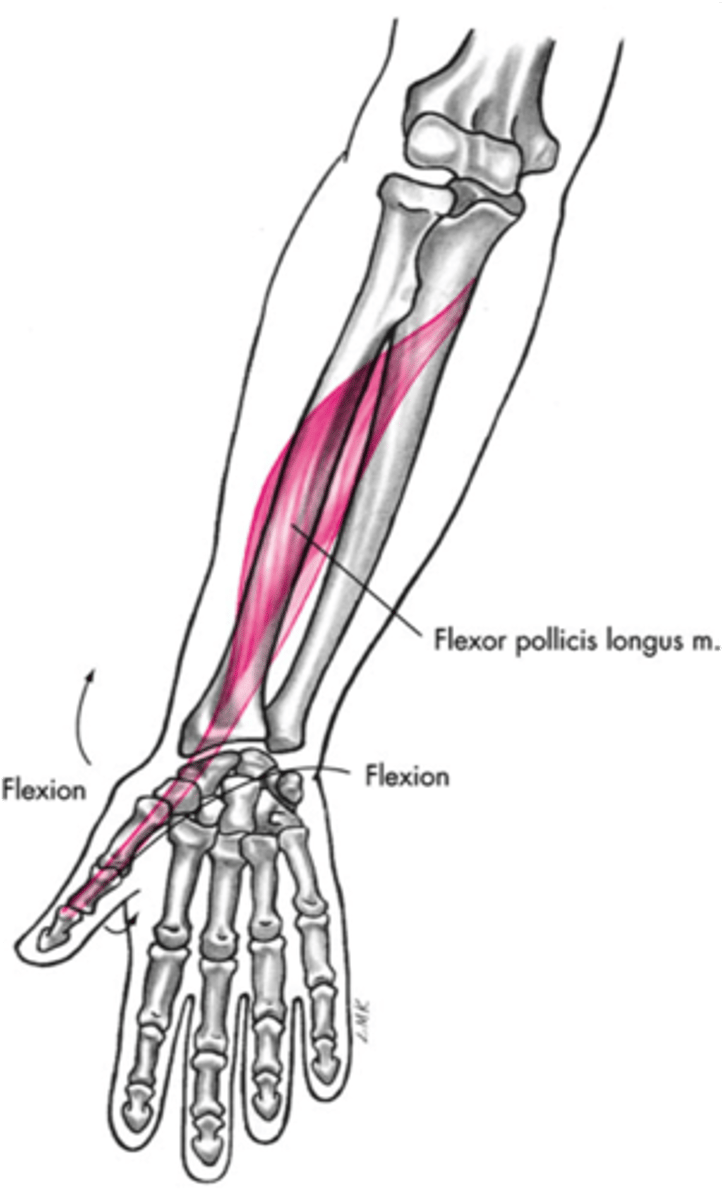
(Deep (3rd) layer:) Flexor pollicis longus (FPL)
-Flexes phalanges of 1st digit (thumb)
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Deep to FDS and in contact with the radius
(Deep (3rd) layer:) Pronator quadratus
-Pronates forearm
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Deep to FDP and FPL
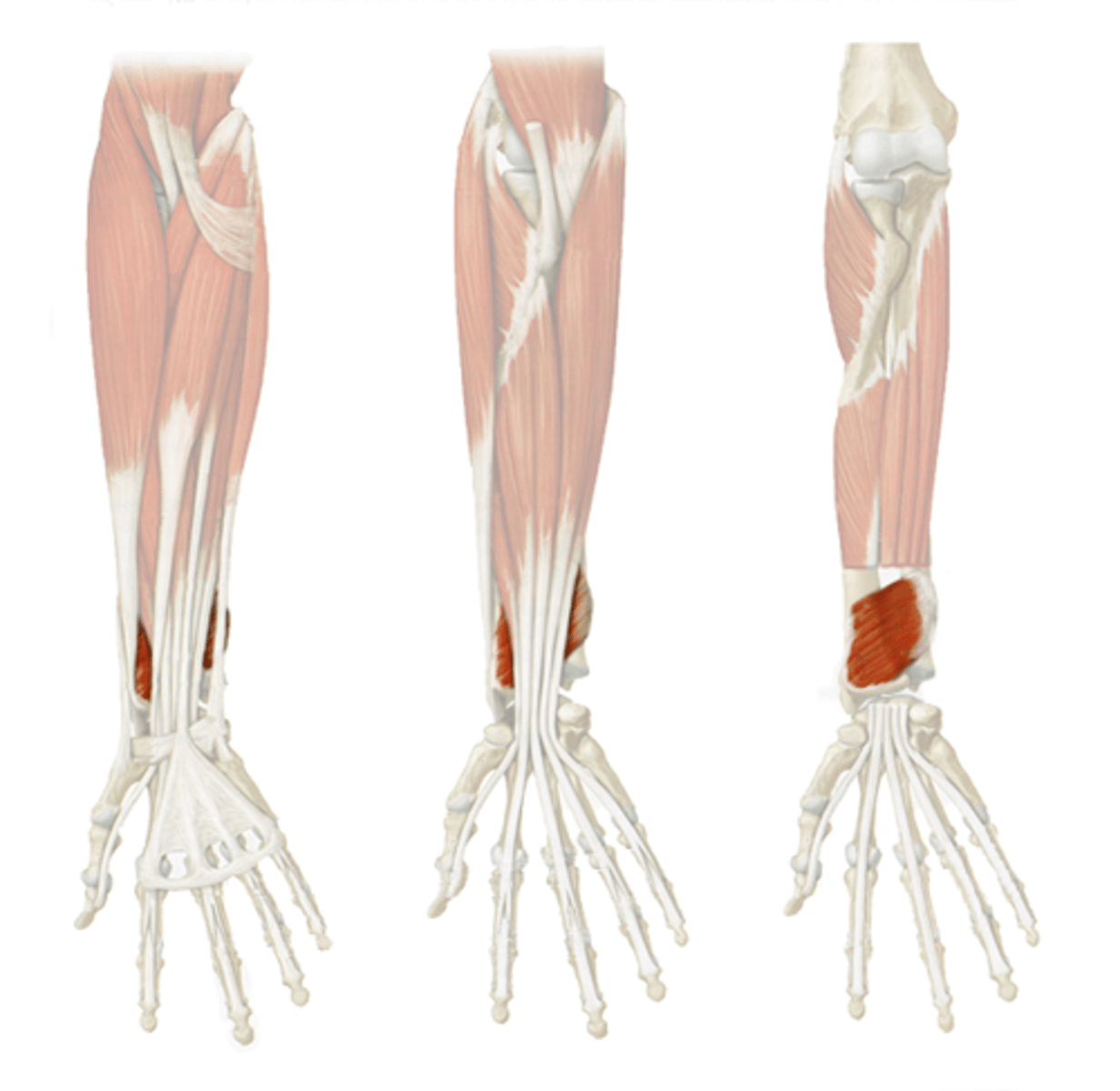
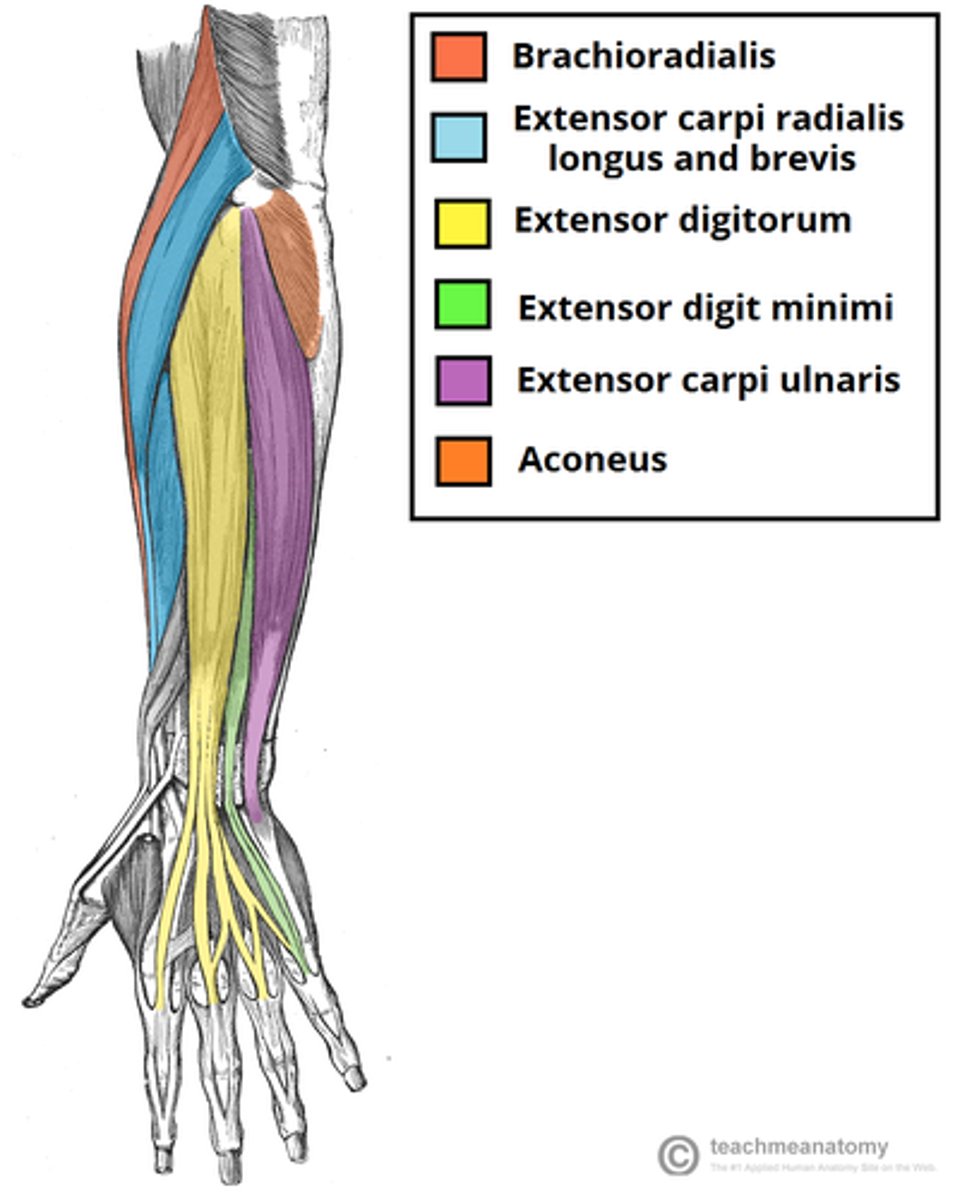
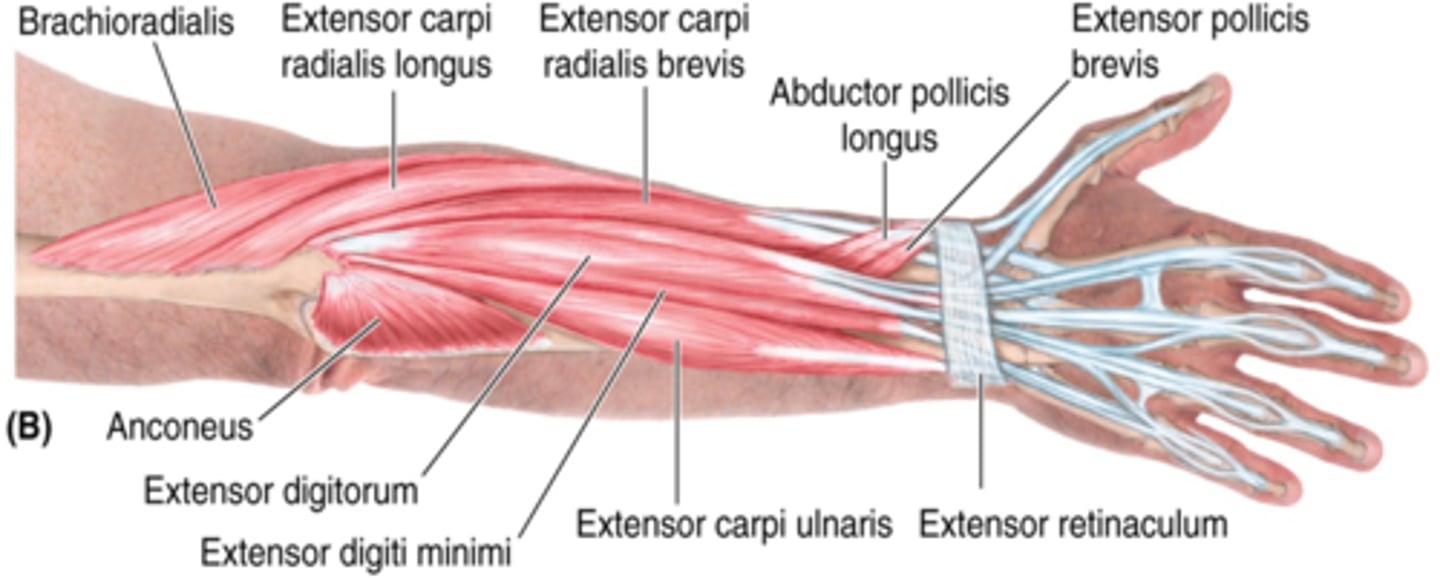
(Muscles of posterior compartment of the forearm (Extensors):) Superficial layer
-Brachioradialis
-Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL)
-Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB)
-Extensor digitorum
-Extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
-Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
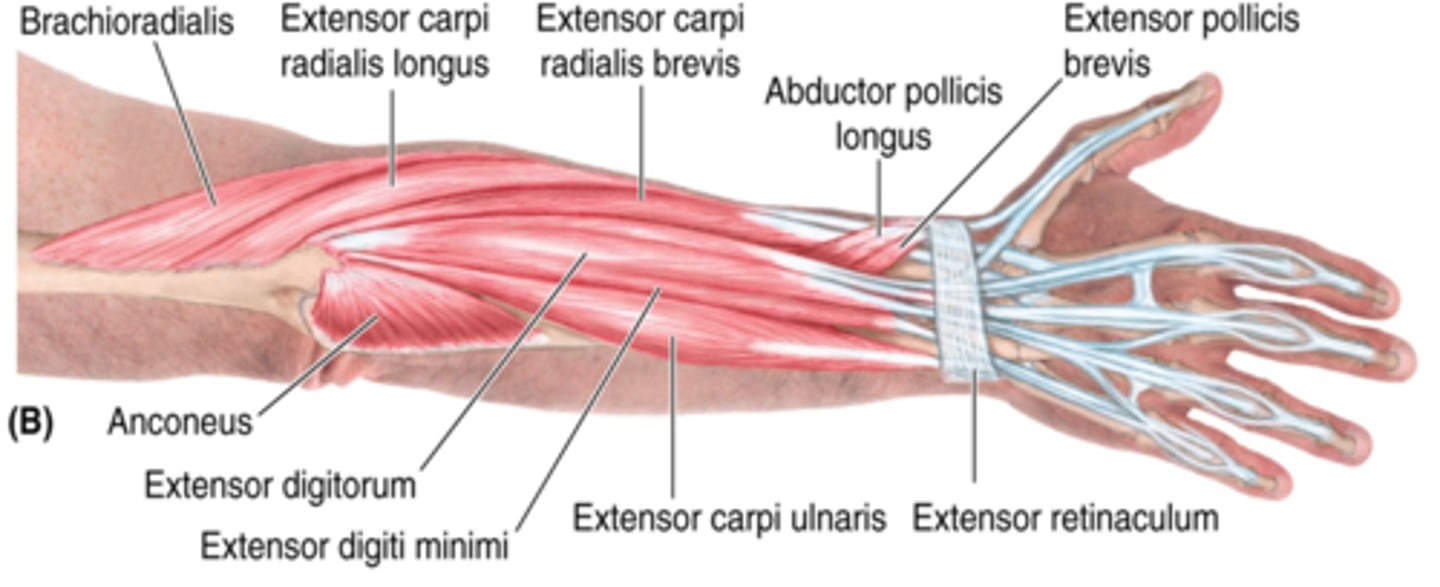
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Brachioradialis
-Flexes forearm
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-On anterolateral surface of forearm
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL)
-Extends and abducts hand
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to brachioradialis m.
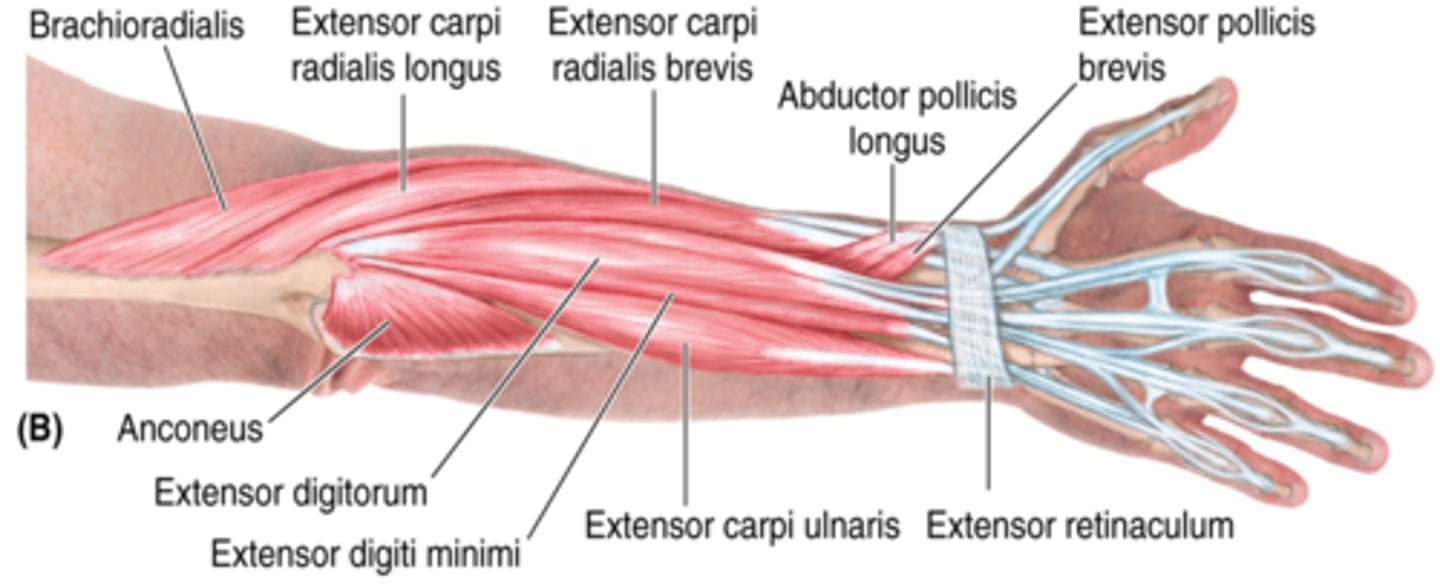
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB)
-Extends and abducts hand
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to ECRL
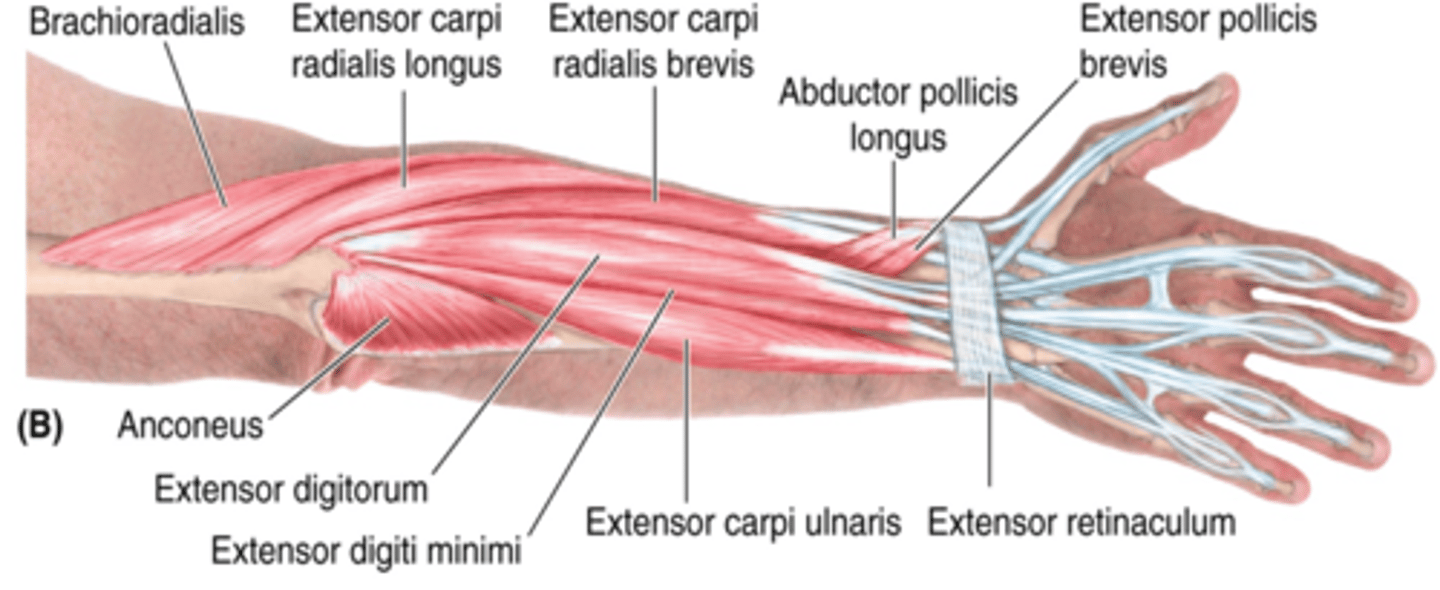
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor digitorum
-Extends 2nd - 5th digits
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to ECRB
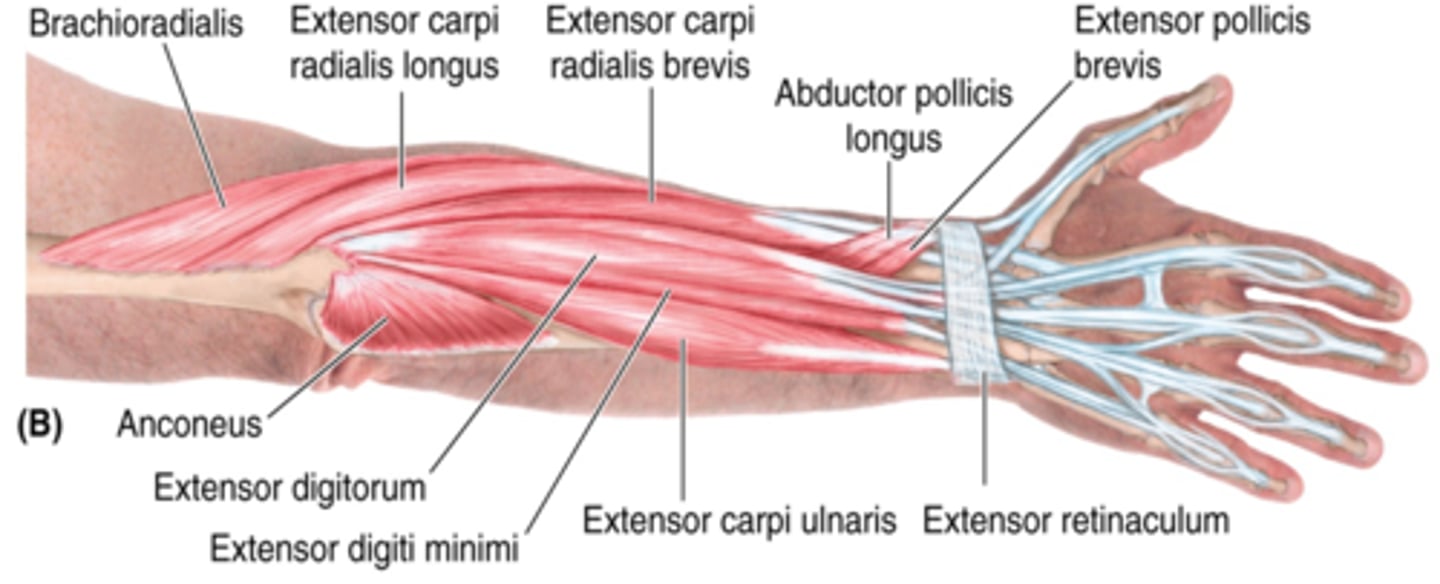
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor digiti minimi (EDM)
-Extends 5ht digit
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to extensor digitorum m.
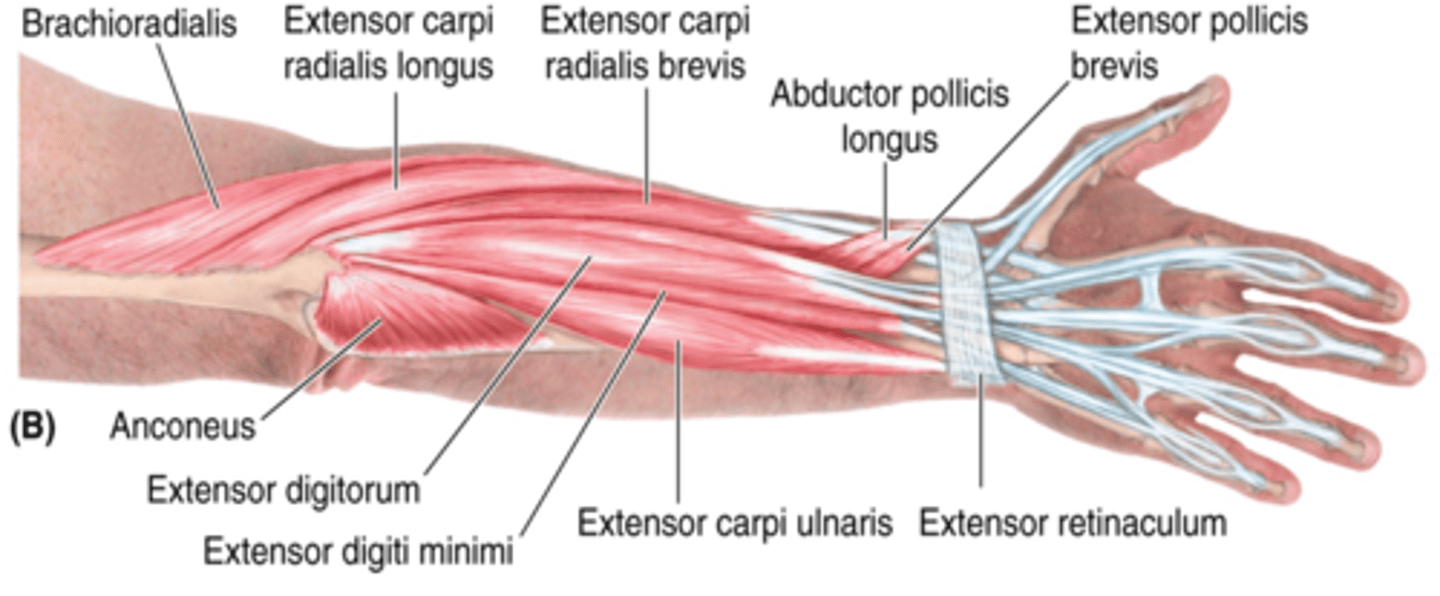
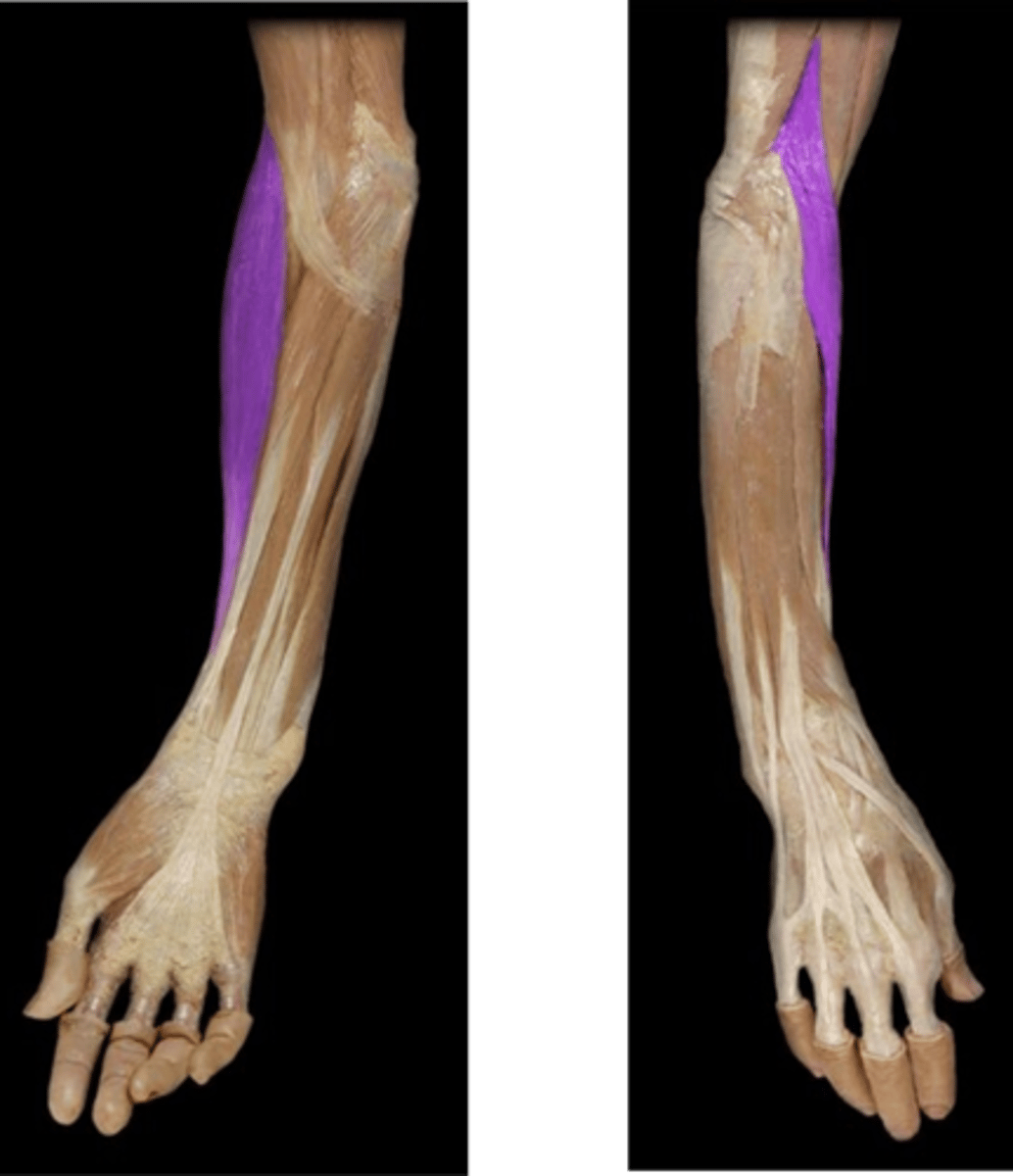
(Superficial layer of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU)
-Extends and adducts hand
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to EDM
(Muscles of posterior compartment of the forearm (Extensors):) Deep layer
-Supinator
-Abductor pollicis longus (APL)
-Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
-Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
-Extensor indicis
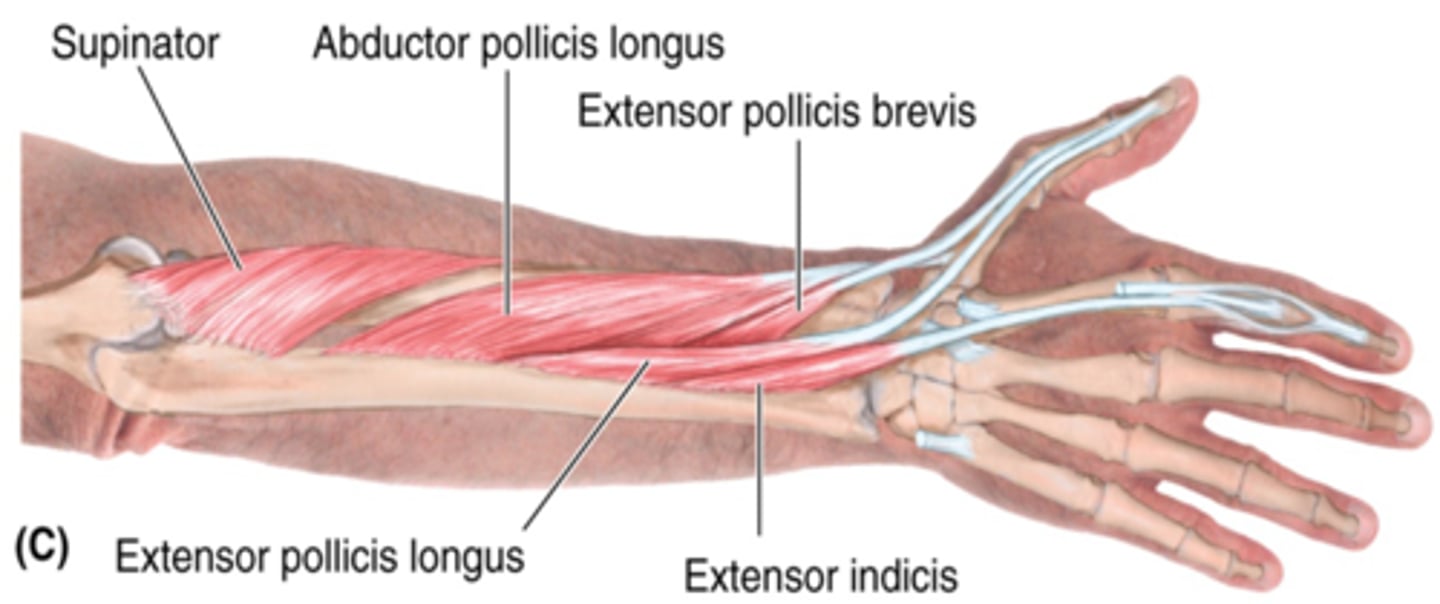
(Deep Layer of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Supinator
-Supinates forearm
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Lies deep in the cubital fossa, and the radial n. passes through its fibers
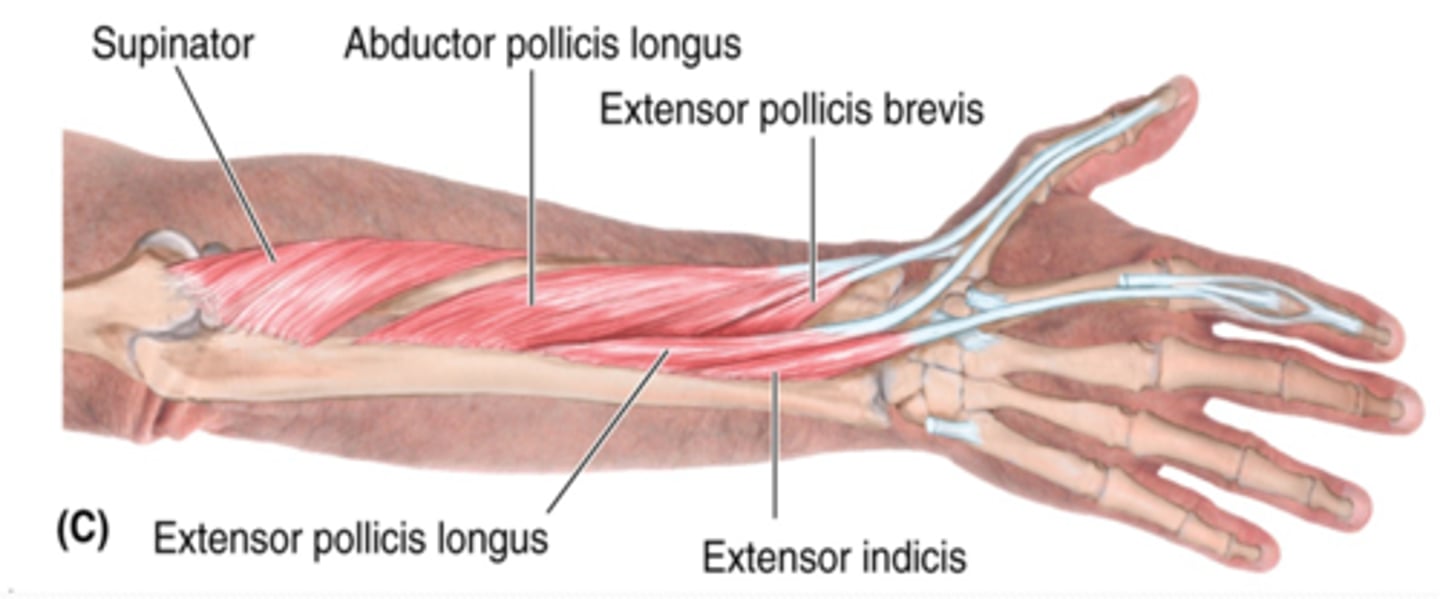
(Deep Layer of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Abductor pollicis longus (APL)
-Abducts and extends 1st digit (thumb)
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Distal to supinator
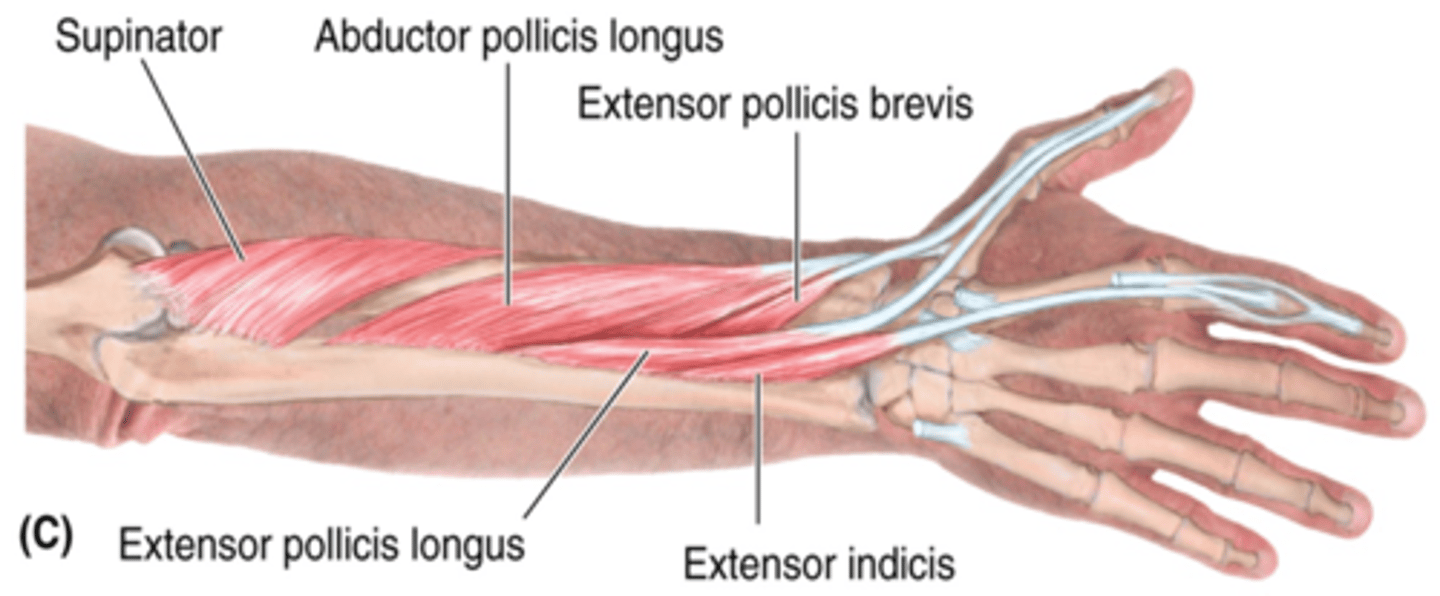
(Deep Layer of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor pollicis longus (EPL)
-Extends 1st digit (thumb)
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Distal and medial to APL
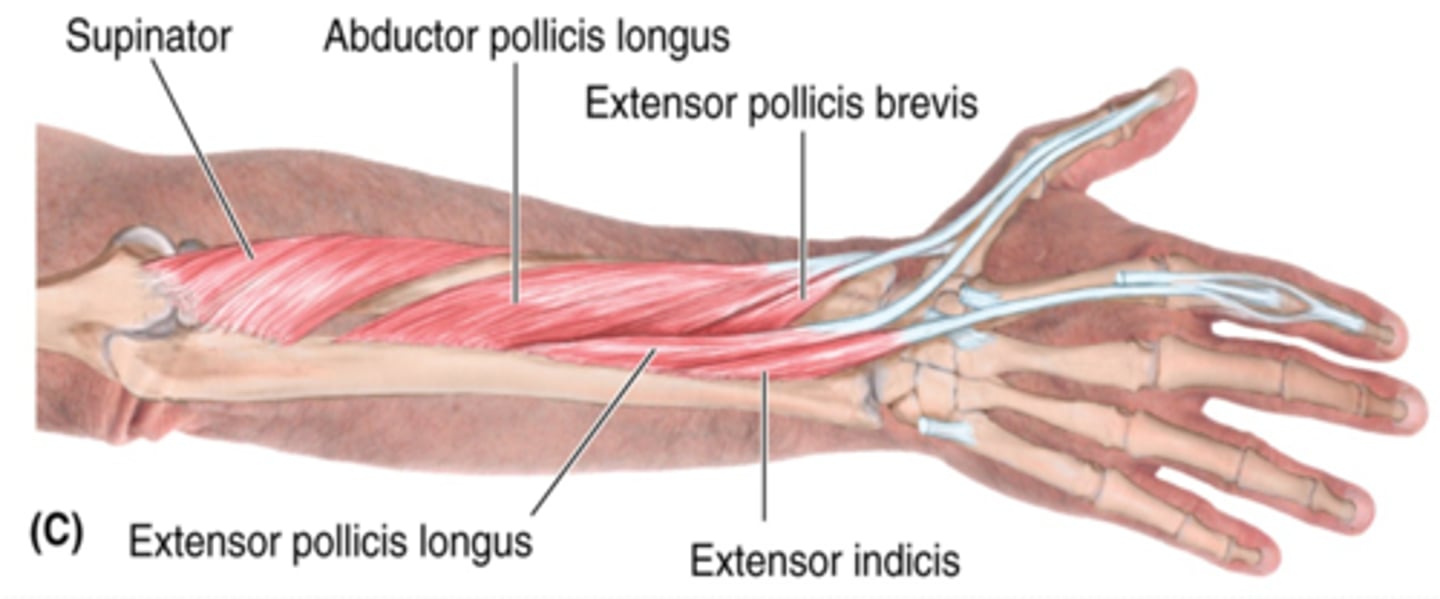
(Deep Layer of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB)
-Extends 1st digit (thumb)
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Distal to APL and lateral to EPL
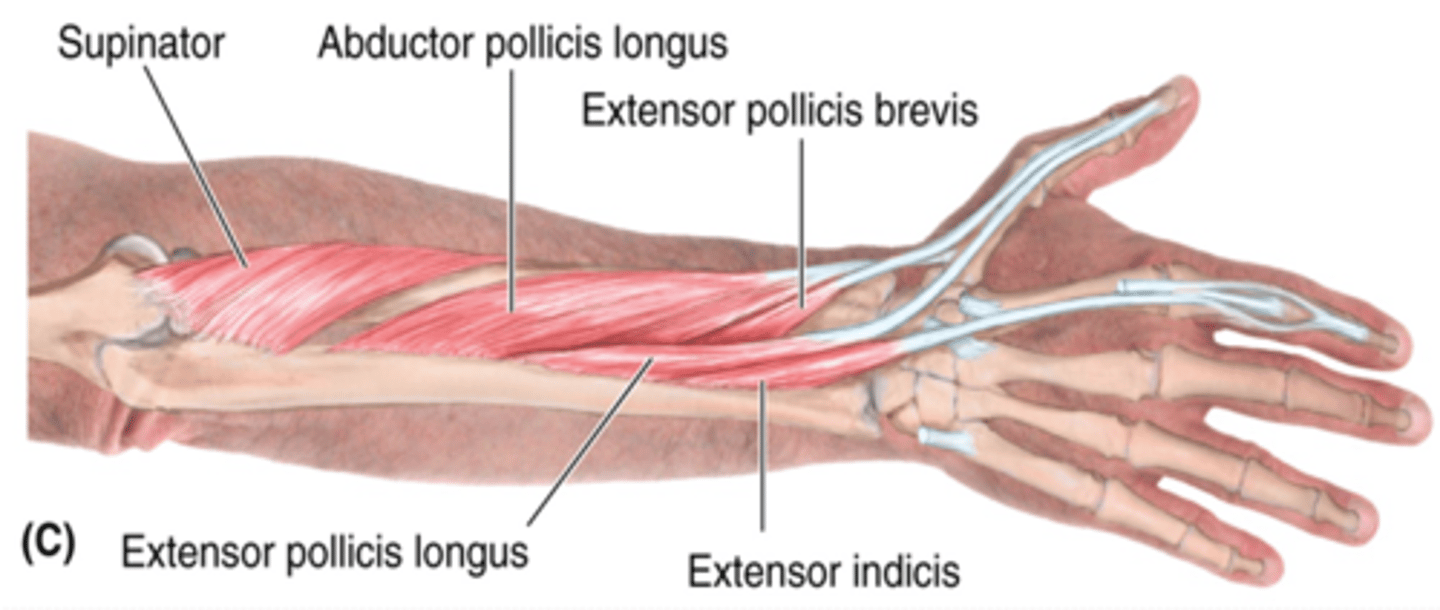
(Deep Layer of the muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm:) Extensor indicis
-Extends 2nd digit (index finger)
-Radial n. (C5 - T1)
-Distal to EPL
(Muscles of hand:) Muscles of thenar eminence
These muscles are responsible for opposition of thumb
-Abductor pollicis brevis (APB)
-Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
-Opponens pollicis
-Abductor digiti minimi
-Flexor digiti minimi
-Opponens digiti minimi

(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Abductor pollicis brevis (APB)
-Abducts 1st digit (thumb), helps opposition
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Forms anterolateral part of thenar eminence
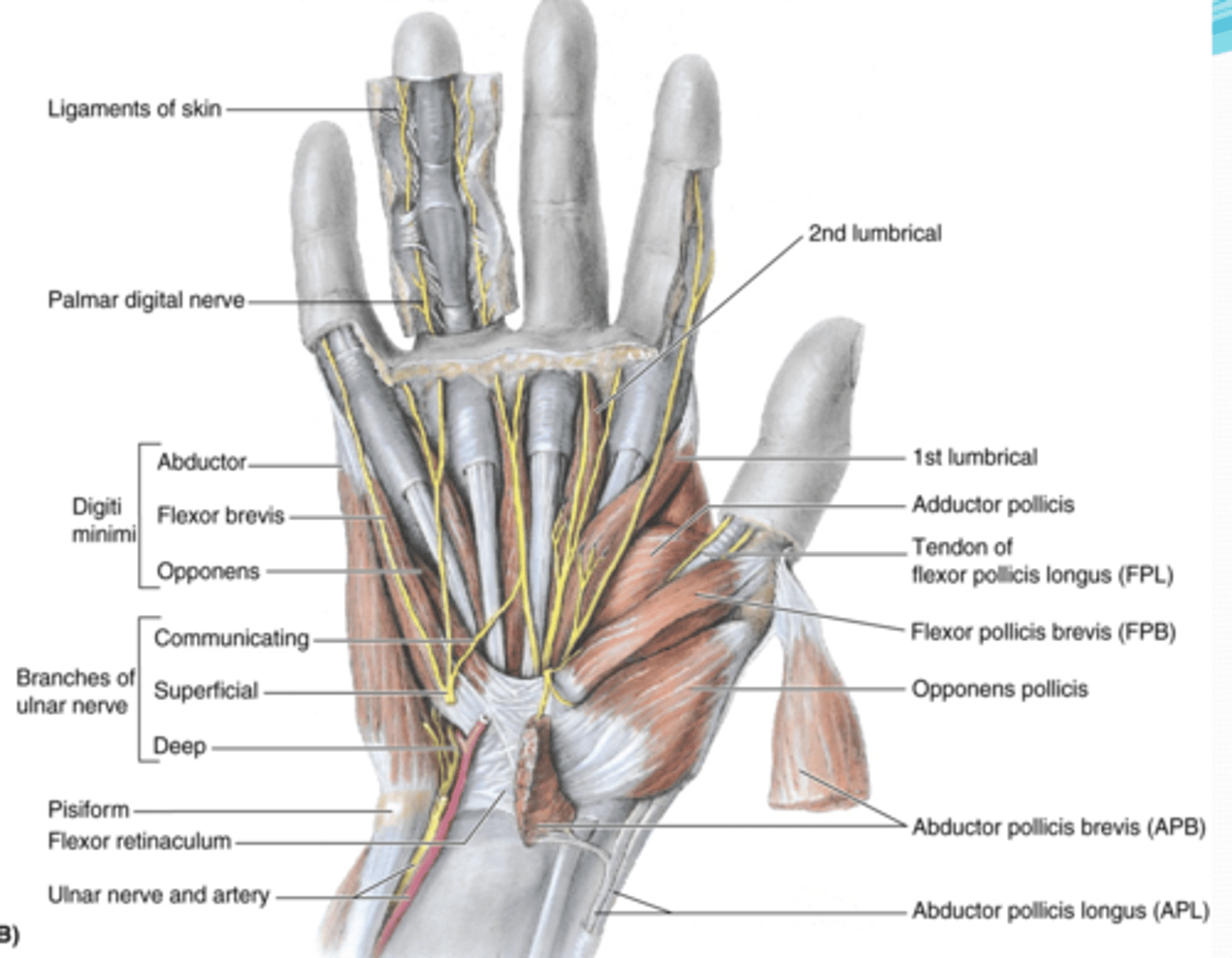
(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Flexor pollicis brevis (FPB)
-Flexes 1st digit (thumb)
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Medial to APB
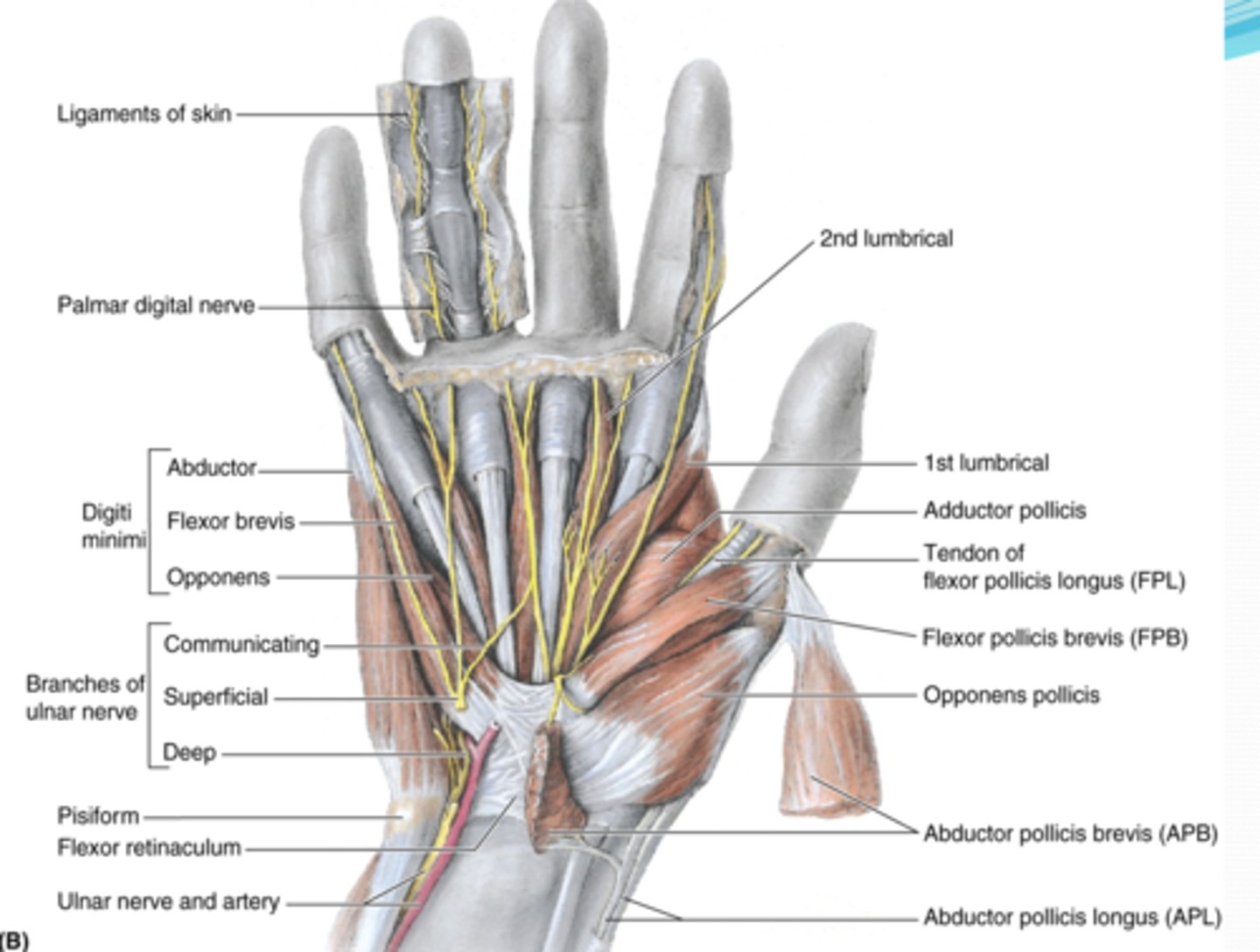
(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Opponens pollicis
-Opposes 1st digit (thumb)
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
-Deep to APB
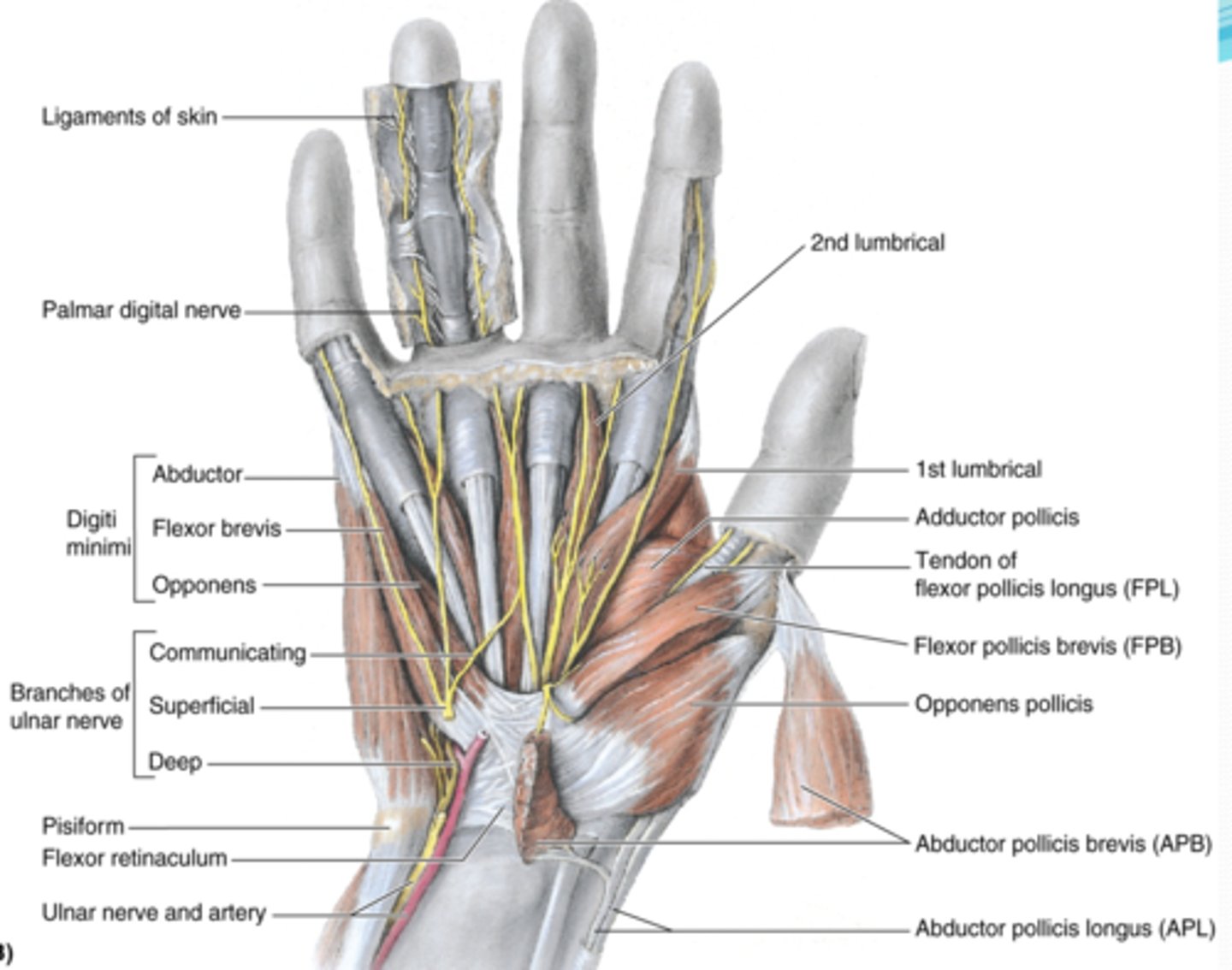
(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Abductor digiti minimi
-Abducts 5th digit
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-Most superficial of the hypothenar muscles
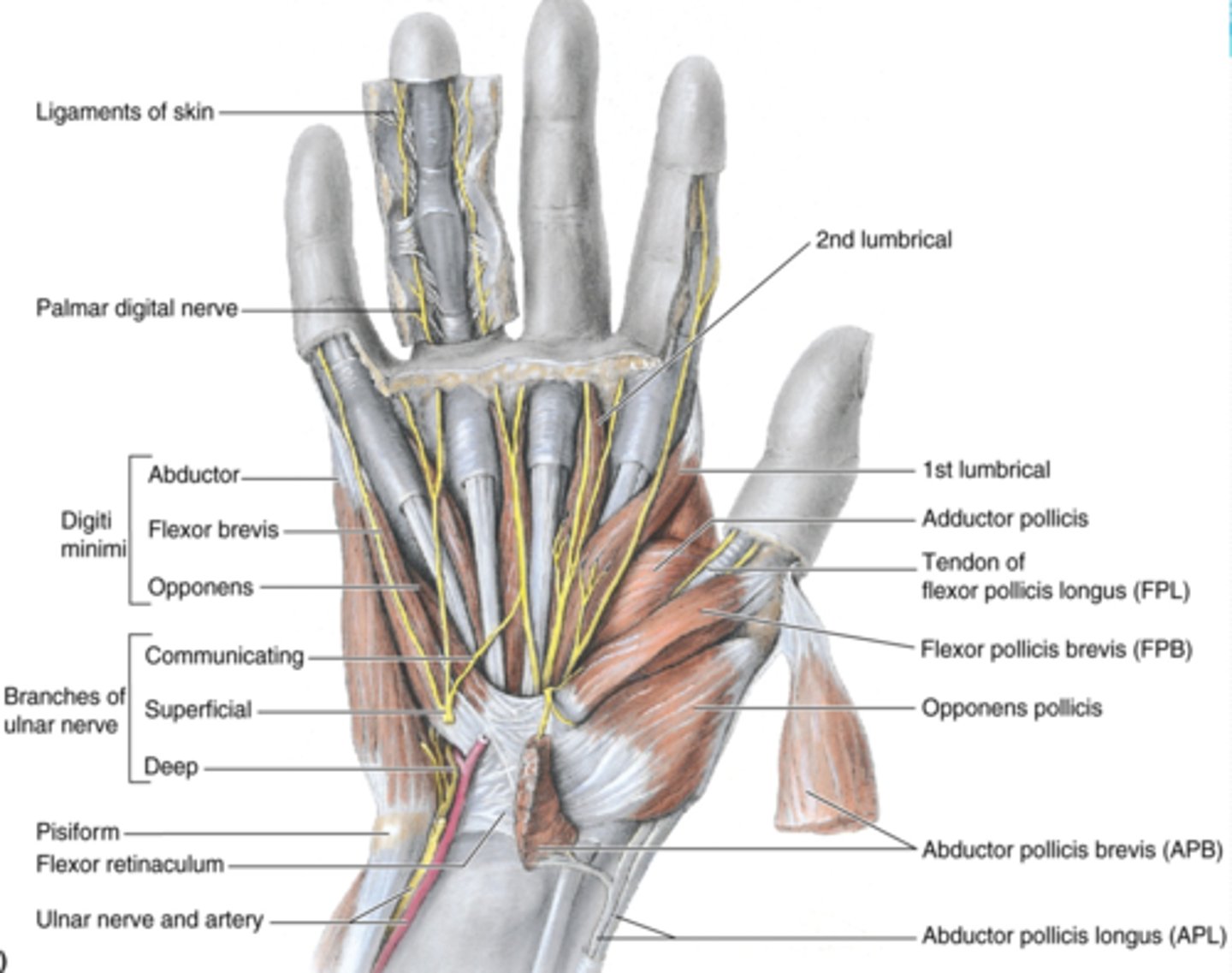
(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Flexor digiti minimi
-Flexes 5th digit
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-Lateral to abductor digiti minimi
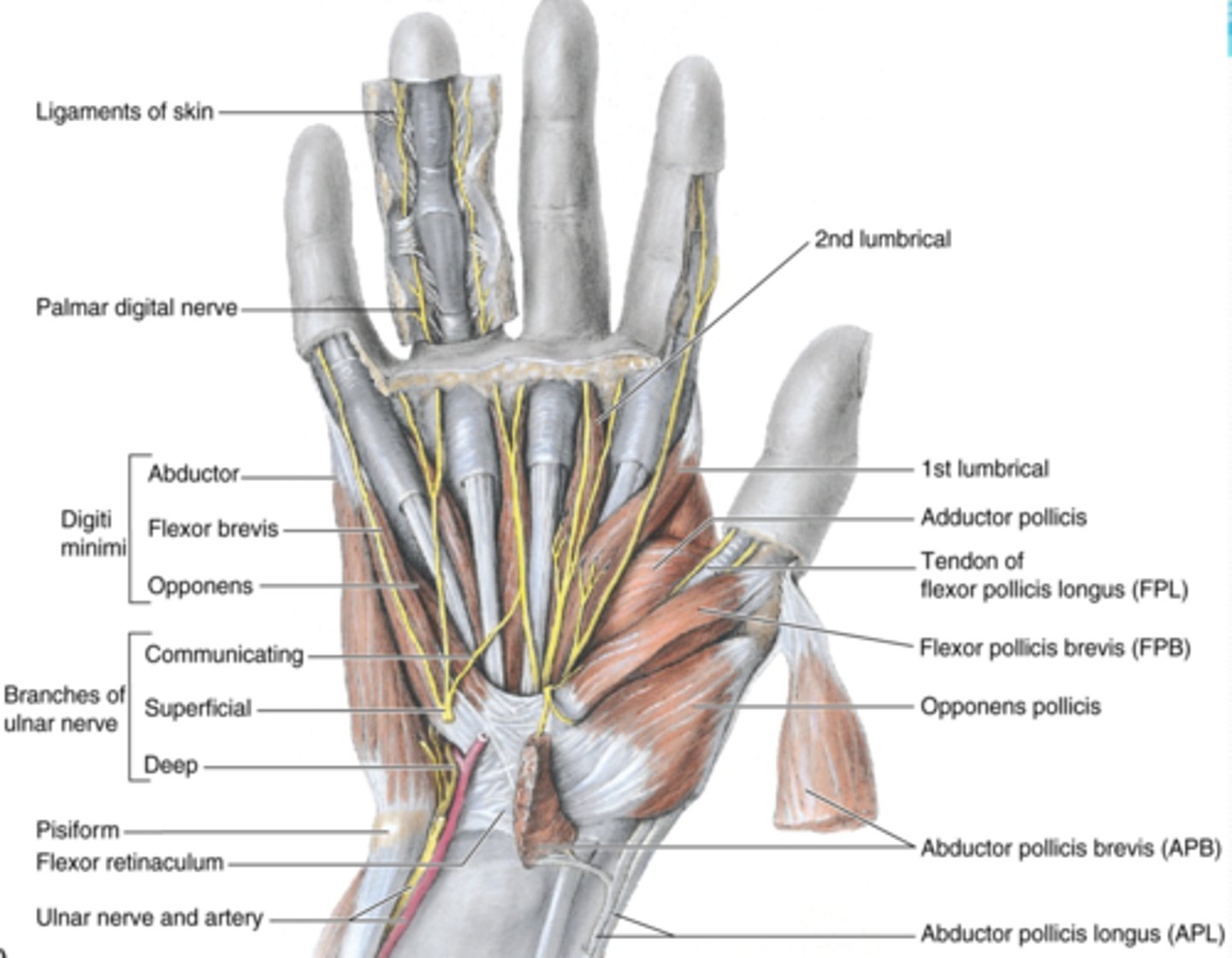
(Muscles of thenar eminence:) Opponens digiti minimi
-Rotates 5th digit bringing it into opposition with the thumb
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-Deep to abductor and flexor digiti minimi muscles
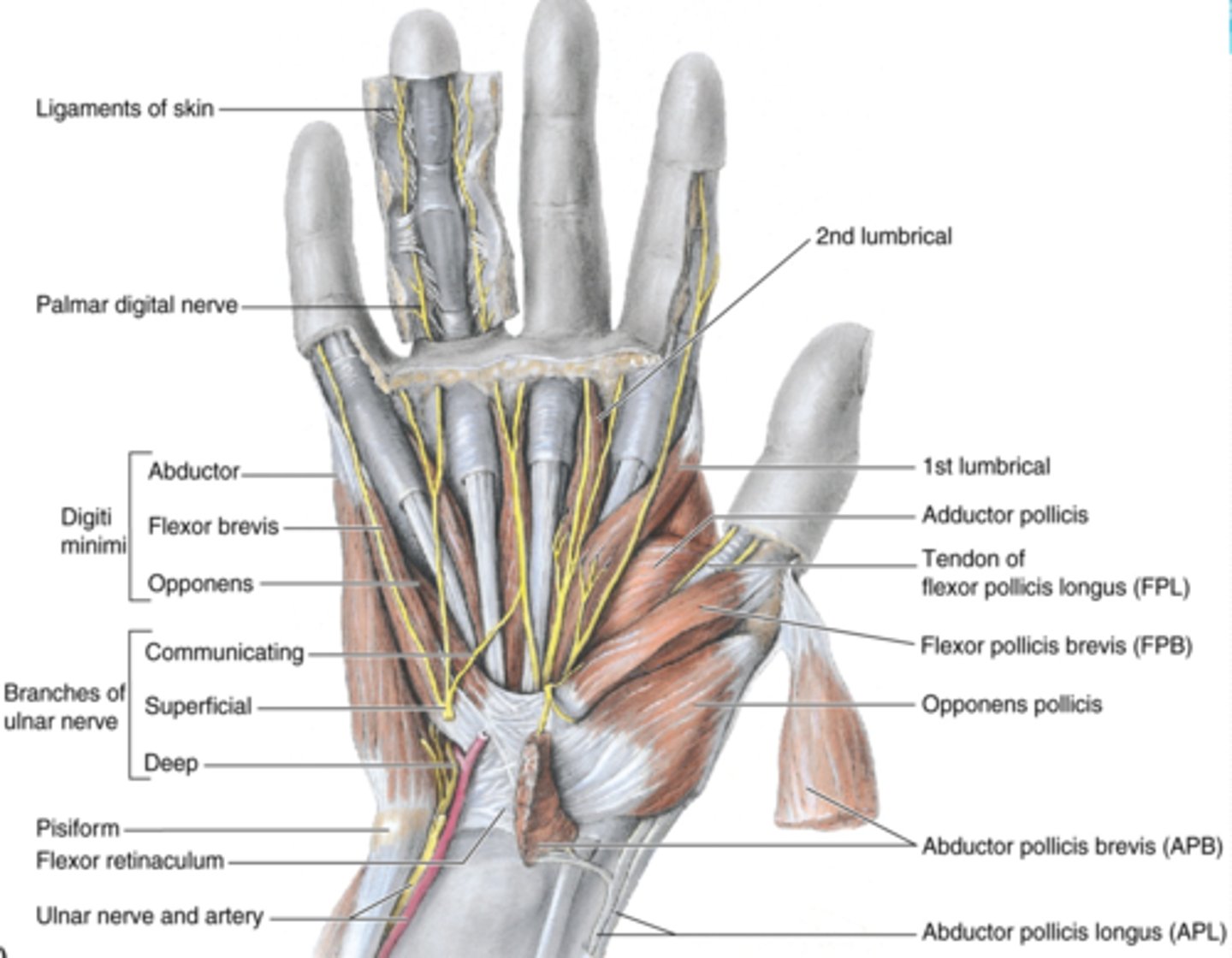
Short muscles of hand
lumbricals, dorsal interossei (4) , palmar interossei (3)
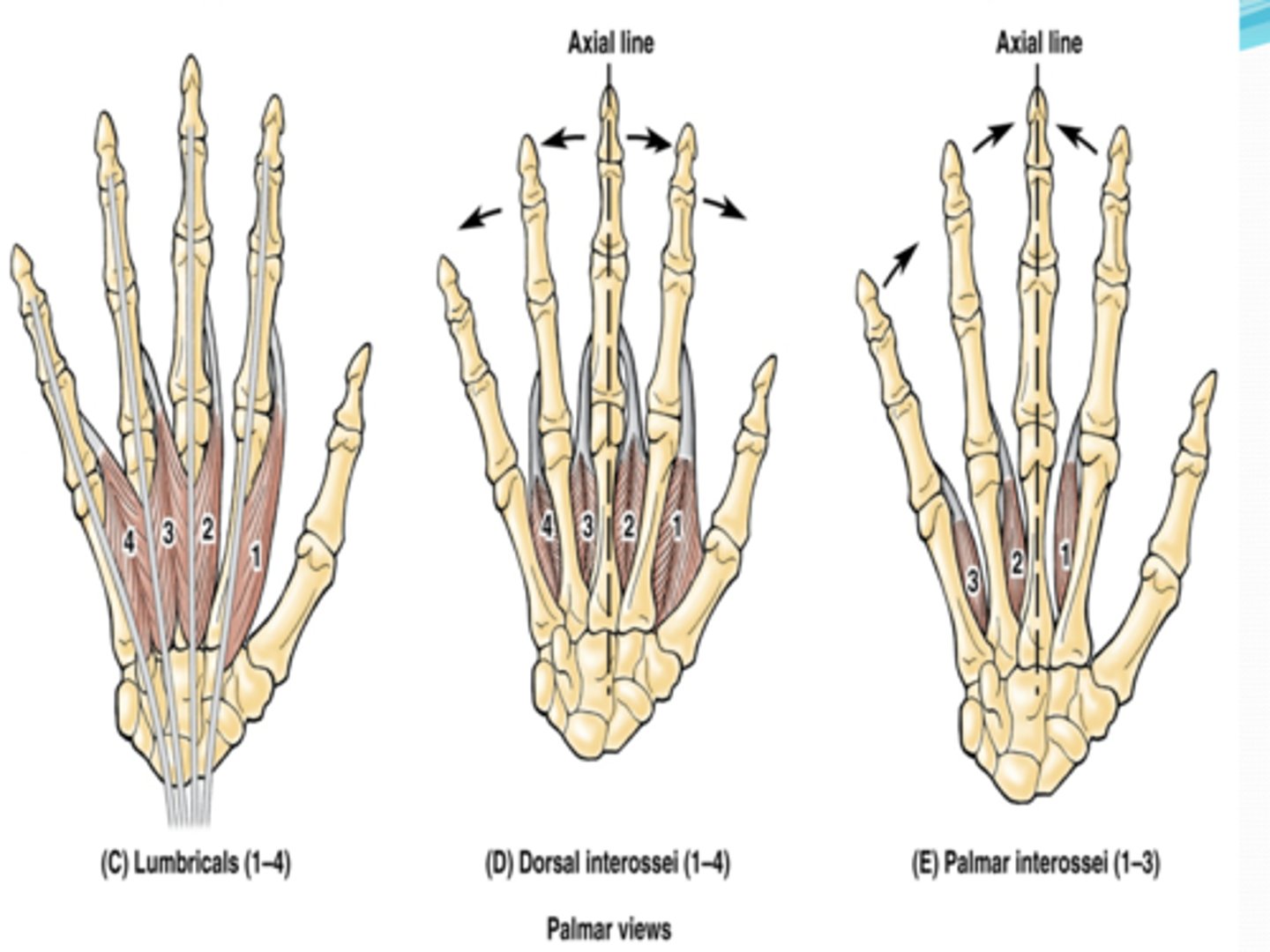
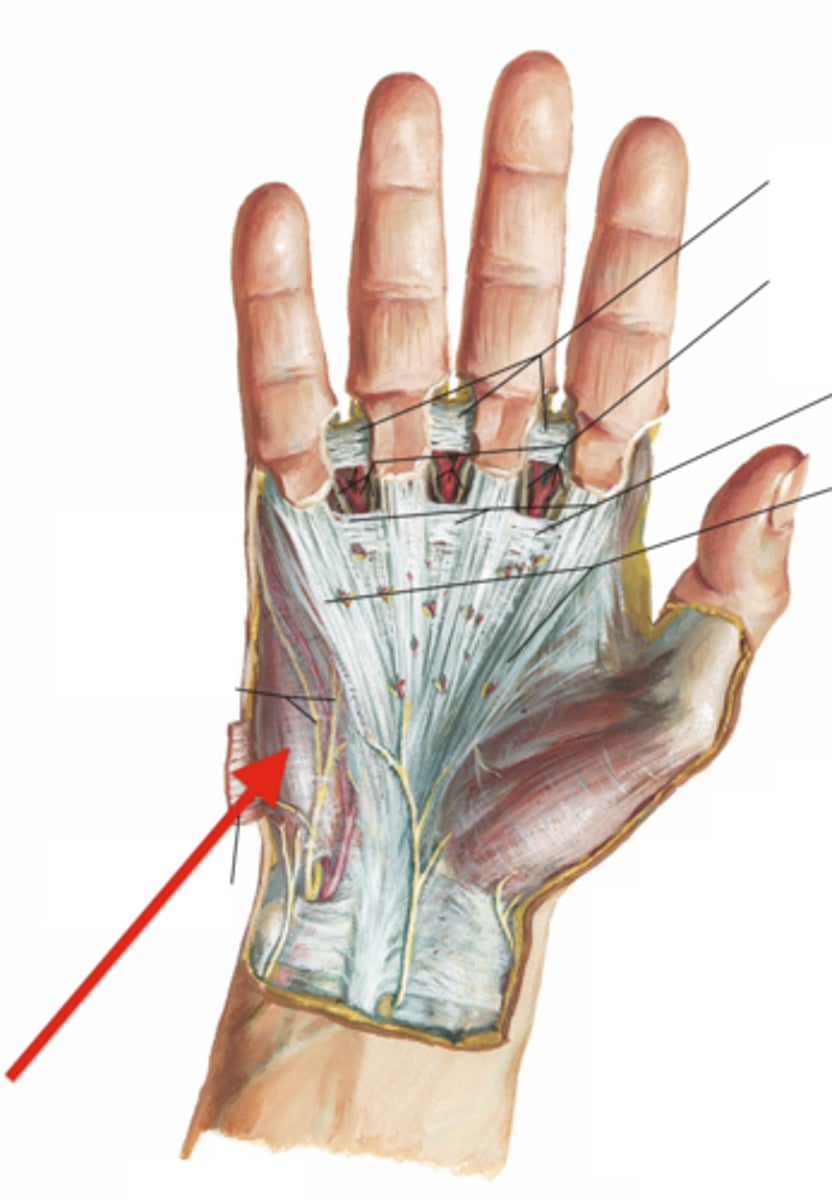
(Short muscles of hand:) Lumbricals
-Flex fingers at metacarpophalangeal joints and extend interphalangeal joints of 2nd - 5th digits
-Median n. (C5 - T1)
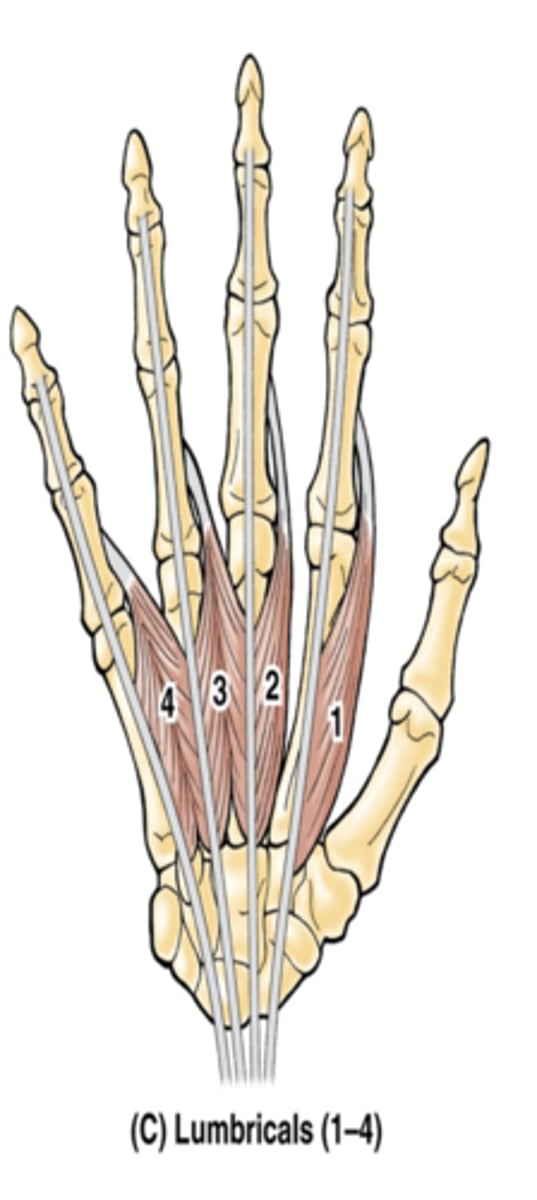
(Short muscles of hand:) Dorsal interossei (4)
-Abduct fingers
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-Between the metacarpal bones
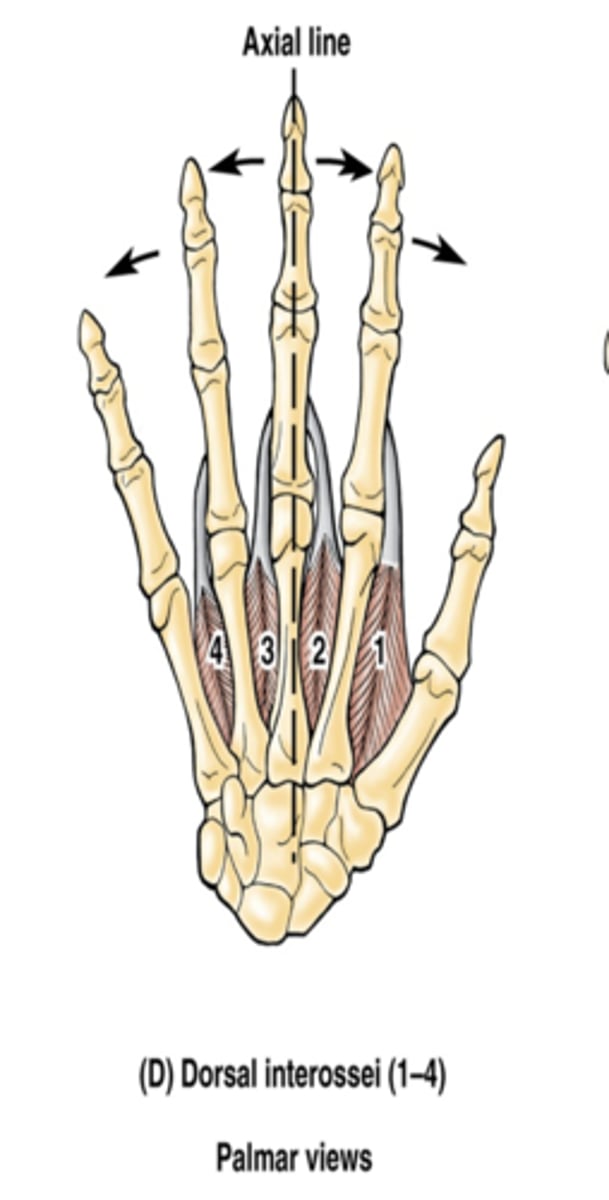
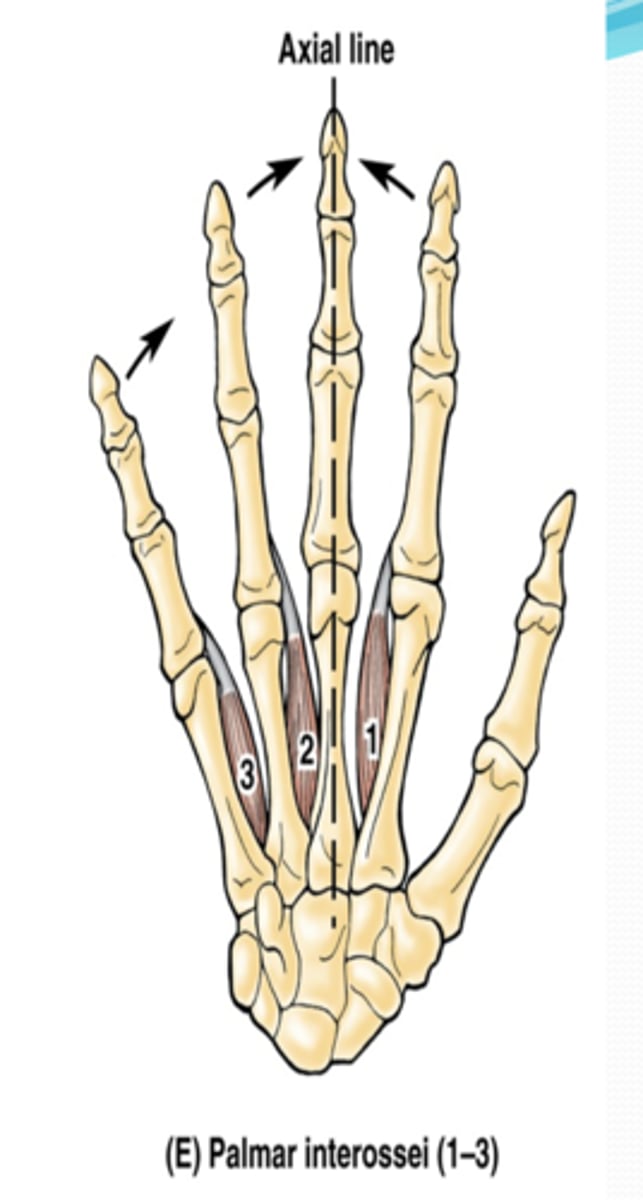
(Short muscles of hand:) Palmar interossei (3)
-Adduct fingers
-Ulnar n. (C7 - T1)
-On the palmar surface of metacarpal