Physics Paper 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/190
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
191 Terms
1
New cards
What is the formula to work out kinetic energy?
Kinetic energy = ½ x mass x speed²
2
New cards
What is the standard unit for mass?
Kilograms
3
New cards
What is the standard unit for speed?
Metres per second (m/s)
4
New cards
What is the standard unit for kinetic energy?
Joules
5
New cards
What is the standard unit for elastic potential energy?
Joules
6
New cards
What is the standard unit for the spring constant?
Newtons per metre (N/m)
7
New cards
What is the standard unit for extension in the elastic potential energy equation?
Metres
8
New cards
What is the formula for gravitational potential energy
G.P.E = mass x gravitational field strength x height
9
New cards
What is the standard unit for mass?
Kilograms
10
New cards
What is the standard unit for gravitational field strength?
N/kg
11
New cards
What is the standard unit for specific heat capacity?
Joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/Kg°C)
12
New cards
What is this the definition of:
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
The amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
Specific Heat Capacity
13
New cards
What is defined as the rate at which energy is transferred or work is done?
Power
14
New cards
What is the standard unit for power?
Watts
15
New cards
What is the equation that links power, energy transferred and time?
Power= energy transferred/time
16
New cards
What is the equation that links power, work done and time?
Power= work done/time
17
New cards
What is energy transferred the same as?
Work Done
18
New cards
An energy transfer of 1 joule per second is equal to a power of?
1 Watt
19
New cards
If two electric motors both lift the same weight, the same height which will do it faster?
The most powerful one
20
New cards
Energy can be transferred, stored or dissipated but cannot be
Created or destroyed
21
New cards
In what type of system is there no net change to the total energy?
Closed
22
New cards
How can we reduce unwanted energy transfers?
\-Lubrication
\-Use of thermal insulation
\-Use of thermal insulation
23
New cards
How does increasing the thermal conductivity of a material affect the rate of energy transfer by conduction?
It increases it
24
New cards
What factors affect the rate of cooling of a building?
\-Thickness of walls
\-Thermal conductivity of walls
\-Thermal conductivity of walls
25
New cards
How do you work out efficiency from input and output energy?
Efficiency = Useful output energy transfer/ Total input energy transfer
26
New cards
How do you work out efficiency from power input and output
Efficiency = Useful power output/Total power input
27
New cards
What are the three main types of fossil fuels?
Coal, Oil, Gas
28
New cards
Name the main non-renewable energy resources?
Fossil fuels, Nuclear fuel
29
New cards
Name 6 renewable energy resources
Biofuel, Wind, Hydro-electricity, Geothermal, Tidal, Solar, Water waves
30
New cards
What type of resource is one that is being replenished as it is used?
Renewable
31
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for an open switch
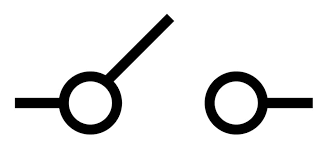
32
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a closed switch
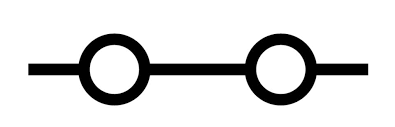
33
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a cell
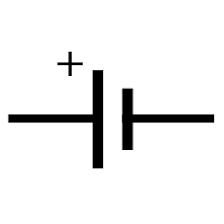
34
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a battery
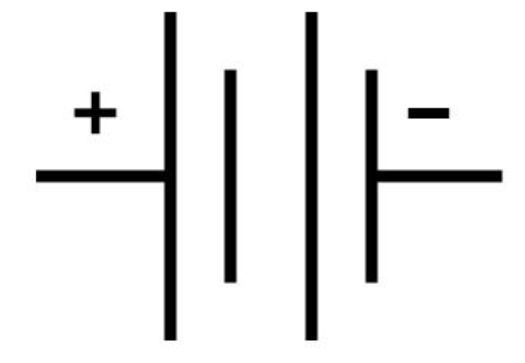
35
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a diode
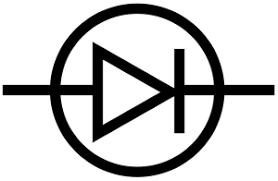
36
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a resistor
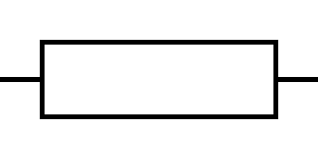
37
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a variable resistor
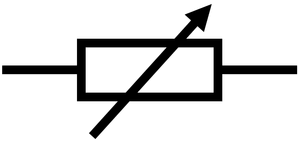
38
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a LED
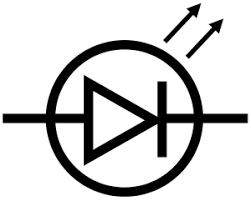
39
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a lamp
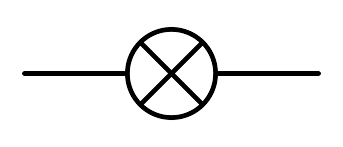
40
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a fuse

41
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a voltmeter
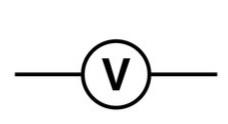
42
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for an ammeter
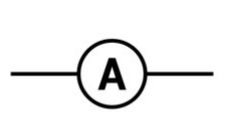
43
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a thermistor
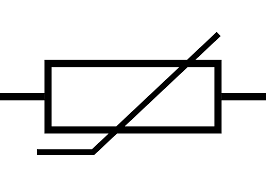
44
New cards
Draw the circuit symbol for a LDR
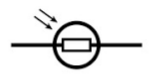
45
New cards
What is required for an electrical charge to flow through a closed circuit?
A potential difference
46
New cards
What is the flow of electrical charge?
Electric current
47
New cards
What equation links charge flow, current and time?
Charge flow = Current x Time
48
New cards
What is the standard unit for current?
Amps
49
New cards
What is the standard unit for Charge flow?
Coulombs
50
New cards
What is the standard unit for time?
Seconds
51
New cards
What is the equation that links resistance, potential difference and current?
Potential difference = Current x Resistance
52
New cards
What two things does the current flowing through a component depend on?
Resistance, Potential Difference
53
New cards
If you increase the resistance of a component what happens to the current, for a set potential difference
Decreases
54
New cards
What is the standard unit for resistance?
Ohms
55
New cards
What is the standard unit for potential difference?
Volts
56
New cards
How are current and potential difference linked in an ohmic conductor
They are directly proportional
57
New cards
Through which component is resistance constant?
Ohmic conductor
58
New cards
How does the resistance of a filament lamp change as the temperature increases?
It increases
59
New cards
How does the current flow in a diode?
In one direction only
60
New cards
What can you tell me about the resistance in a diode?
Very high in the reverse direction
61
New cards
How does the resistance of a thermistor change as the temperature increases?
It decreases
62
New cards
How does the resistance of an LDR change as light intensity increases?
It decreases
63
New cards
What could LDR’s be used for
Switching lights on when it gets dark
64
New cards
What could a thermistor be used for?
In a thermostat to control heating
65
New cards
What is the current like in a series circuit?
The same everywhere
66
New cards
What is the total resistance of two components in a series circuit?
It is the sum of the resistance of each component
67
New cards
What is the total resistance of two resistors connected in parallel?
Less than the resistance of the smallest resistor
68
New cards
What type of supply is the mains electricity in the UK?
AC
69
New cards
What is the frequency of the domestic electricity supply in the UK?
50Hz
70
New cards
What is the voltage of the domestic electricity supply in the UK?
230V
71
New cards
What type of potential difference varies between a positive and negative value?
Alternating
72
New cards
What type of potential difference is only found in the positive?
Direct
73
New cards
How are most electrical appliances connected to the mains?
Using a three-core cable
74
New cards
What colour is the live wire?
Brown
75
New cards
What colour is the neutral wire?
Blue
76
New cards
What colour is the earth wire?
Green and Yellow Stripes
77
New cards
What does the live wire carry?
The alternating potential difference from the supply
78
New cards
What does the neutral wire do in a plug?
Completed the circuit
79
New cards
What does the earth wire do in a plug?
It is a safety wire to stop an appliance becoming live
80
New cards
What is the potential difference between the live wire and the earth?
230V
81
New cards
What is the voltage of the neutral wire
At or close to 0V
82
New cards
What is the voltage of the earth wire
0V, unless there is a fault
83
New cards
What equation links power, potential difference and current?
Power = Potential difference x Current
84
New cards
What equation links current, resistance and power?
Power = (Current)² x Resistance
85
New cards
What does the amount of energy an appliance transfers rely on?
\-How long the appliance is switched on for
\-The power of the appliance
\-The power of the appliance
86
New cards
What is done when charge flows in a circuit?
Work
87
New cards
What equation links energy transferred, power and time?
Energy transferred = Power x Time
88
New cards
What equation links charge flow, potential difference and energy transferred
Energy transferred=charge Flow x Potential Difference
89
New cards
What is the National Grid?
A system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers
90
New cards
What is transferred from power stations to consumers using the National Grid?
Electrical power
91
New cards
What happens when an insulating material is rubbed against other materials?
Electrically charged
92
New cards
When electrons move from the material onto another, what charge will that material become?
Negative
93
New cards
What charge will the material become if it loses electrons?
Positive
94
New cards
What will two objects do if they carry the same charge?
Repel
95
New cards
What will two objects of opposite charge do?
Attract
96
New cards
What does a charged object create?
Electric Field around itself
97
New cards
When is the electric charge most strongest?
When it is close to the charged object
98
New cards
What happens to the charge when the object is moved away from the charge object?
The weaker the field
99
New cards
What will a second charged object experience when placed in a field?
Force
100
New cards
What will happen to the force if the objects distance from each other decreases?
Stronger