NUR 317 Exam 5 - Osteomyelitis
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Osteomyelitis
Severe infection of bone, bone marrow, and surrounding soft tissue
Most common microorganism is Staphylococcus aureus, but can be caused by variety of organisms
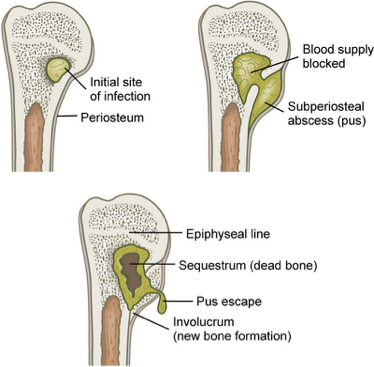
Indirect entry osteomyelitis
Usually one organism
Hematogenous – seeding from source of infection
Blunt trauma
Direct entry osteomyelitis
Usually more than one organism
Via open wound
Foreign body presence
Acute osteomyelitis local manifestations
Pain that worsens with activity and is unrelieved by rest
Swelling
Restricted movement
Acute osteomyelitis systemic manifestations
Fever
Night sweats
Chills
Restlessness
Nausea
Malaise
Drainage (late)
Chronic osteomyelitis clinical manifestations
Infection lasting more than 1 month
Or – has failed to respond to initial antibiotic treatment
Continuous and persistent or process of exacerbations and remissions
Local manifestations become more common
Systemic manifestations become less common
Scar tissue develops
Osteomyelitis diagnostic studies
Bone or soft tissue biopsy
Blood and/or wound cultures
WBC count
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
C reactive protein
X-rays/ MRI/ CT scans
Bone scans
Acute osteomyelitis interprofessional care
IV antibiotic therapy
Surgical debridement and decompression
IV antibiotics:
For 4-6 weeks or longer
Antibiotics may be continued at home or may need
Variety of antibiotics depending on microorganism
Not all SNF’s accept all medications
Oxacillin, clindamycin, vancomycin, ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, linezolid
Chronic osteomyelitis interprofessional care
Surgical removal
Antibiotics
Acrylic bead chains
Intermittent or constant antibiotic irrigation of bone
Negative pressure wound therapy
Hyperbaric O2
Amputation
Osteomyelitis subjective data
Past health history
Bone trauma, open fracture, open or puncture wounds, other infections
Medications
Use of analgesics or antibiotics
Surgery or other treatments
Bone surgery
IV drug and alcohol abuse, malaise
Anorexia, weight loss, chills
Weakness, paralysis, muscle spasms
Local tenderness, increase in pain
Irritability, withdrawal, dependency, anger
Osteomyelitis objective data
Restlessness, high spiking temperature, night sweats
Diaphoresis, erythema, warmth, edema
Restricted movement, wound drainage, spontaneous fractures
Labs – WBC, cultures, ESR
X-ray – sequestrum, involcurum
Osteomyelitis overall goals
Satisfactory pain and fever management
No complications associated with osteomyelitis
Adherence to treatment plan
Maintain a positive outlook on outcome of disease
Osteomyelitis acute care
Mobility – bedrest, repositioning
Assess and treat pain
Dressing care
Proper positioning/support of affected limb
Antibiotic therapy (potentially high dose)
Educate on side effects
May need to monitor peak and trough levels
Osteomyelitis complications and associated conditions
Septicemia
Septic arthritis
Pathologic fractures
Amyloidosis
Osteomyelitis
Continued psychologic and emotional support
Patient and family are often frightened and discouraged
Collaboration with MSW
If patient going home vs SNF:
Long term antibiotic administration
Teaching regarding antibiotic administration
Teaching regarding management of CVAD
Wound care/dressing changes