asthma and copd meds
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
beta 2 receptor:
what type of receptor
related to what neurotransmitter?
symp or parasymp?
activation leads to?
adrenergic receptor
related to epi
symp
bronchodilation
m3 receptor:
what type of receptor
related to what neurotransmitter?
symp or parasymp?
activation leads to?
muscarinic receptor
acetylcholine AcH
parasymp
activation leads to bronchoconstriction and mucus prod
most effective tx for airway remodeling and how
inhaled corticosteroids
- suppress inflammation, reduce eosinophils, prevent fibrosis
what are essential for relieving acute asthma sx and what do they directly affect
broncodilators
reduce SM contraction
what do corticosteroids target and why are they essential for long-term asthma management
they are potent immunomodulators
trigger release of inflammatory mediators, leading to immediate sx and long term structural airway changes
what do we need to measure for copd
eosinophils
the primary treatment for copd
is it reversible
bronchodilators
highly variable but bronchodilators can partially improve
preferred route of delivery for asthma & COPD
inhaled
does inhaled route have low or high systemic absorption
lower
is inhaled route slow or rapid onset and what med is especially important for this
rapid
bronchodilator - acute attack tx
optimal particle size for airway deposition is between?
2-5µm
what happens in inhaled route if particles are too small? too large?
too small - exhaled
too large - trapped in upper airways
are inhaled meds subject to first pass metabolism
no
what inhaled route is easier to use during resp distress
nebulizer
what inhaled route is easier for older people that have problems with timing with metered dose inhaler
dry powder inhaler
is dry powder inhaler used for acute attack
no
traditional pressured metered dose inhaler (pMDI) vs hydrofluoroalkane propelled inhaler (HFA)
- what is used as propellant and which is worse for environment
- small or large particles to treat what area of lungs?
- which has higher systemic absorption
- which is used more now
pmdi: chlorofluorocarbons (bad from environment)
hfa: hydrofluoroalkane (safe)
pmdi: larger particles, get trapped in upper airways
hfa: smaller particles, reach parenchyma
pmdi lower systemic absorption, hfa higher absorption
hfa used now
inhaled route that is delivered as micronized powder and requires minimized inspiratory flow
difficult for kids
dry powder inhalers
inhaled route that is vibration or stream of o2
- deliver much higher doses than mdi
- useful in acute exacerbation and good for kids
nebulizer
inhaled route tool
- large volume chamber that attaches to metered dose inhaler
- reduces the velocity of particles entering the upper airways and the amount of drug that lands in the oropharynx
- helpful for patients who have trouble timing an MDI (children, elderly, other)
space chambers "spacers"
which is preferred inhaled or oral
ALWAYS oral
for inhaled route, how much higher do doses need to be
20x
what drug must be given orally
theophylline
oral or parenteral drugs that are used for exacerbations
corticosteroids
route used for treatment of severe acute exacerbations
parenteral
how are biologics typically delivered and in what population is this useful
subq
severely ill pts who cannot absorb from gi tract
oral vs inhaled onset of action
albuterol and formoterol
albuterol: oral 30 min, inhaled 5 min
formoterol: oral 30-60 min, inhaled 5 min
bronchodilator moa
relax airway smooth muscle reversing obstruction and restoring airflow
- can also prevent bronchoconstriction when used prophylactically.
do bronchodilators treat underlying inflammation
no
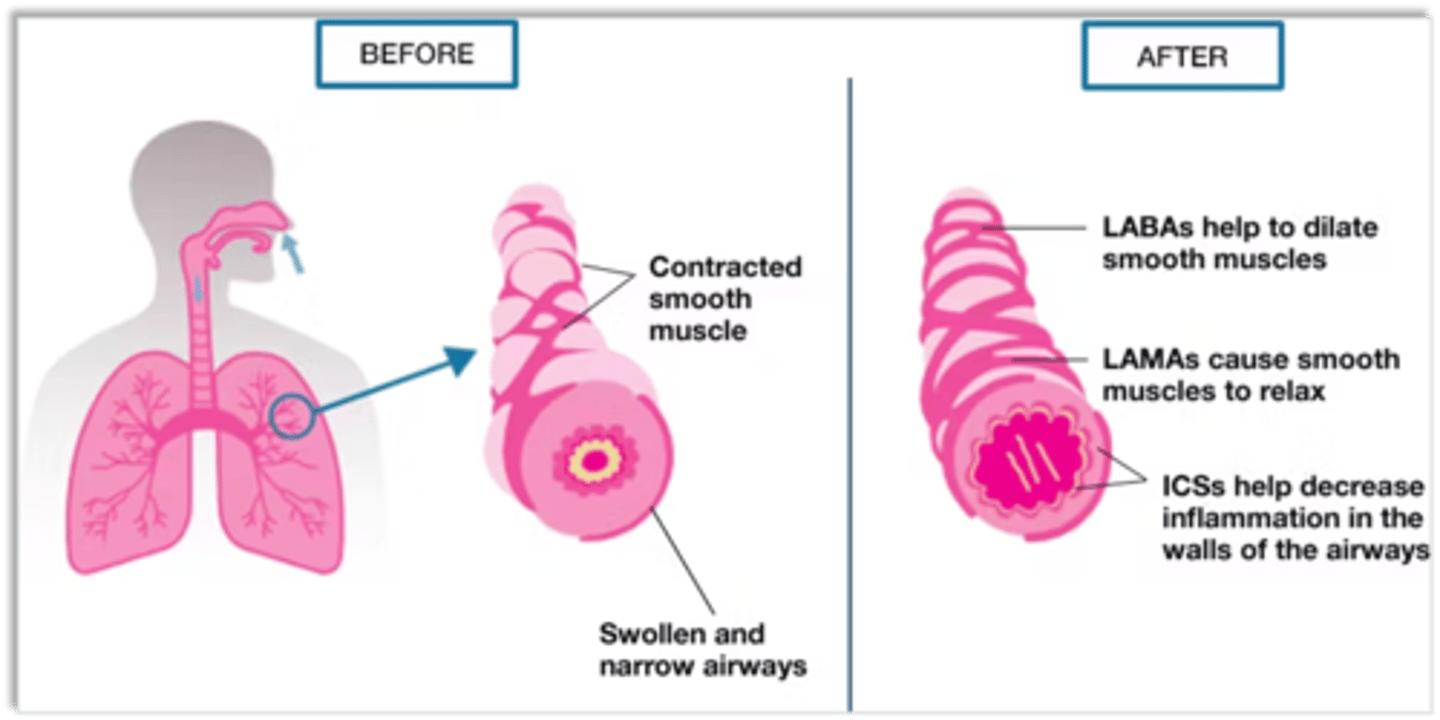
2 classes of bronchodilators
b2 adrenergic agonists sympathomimetics
anticholingeric agents (muscarinic receptor antagonists)
how b2 agonist cause muscle relaxation
bind to b2 receptors on airway SM --> trigger signaling kinase increase cyclic amp (CAMP) and increase protein kinase A --> muscle relaxation
what is bronchodilator of choice for asthma b2 agonist or anticholinergic agent
b2 agonist
what 2 things does b2 agonist inhibit release of
release of constrictive mediators from mast cells --> reduce airway swelling by decreasing microvascular leakage, improve mucociliary clearance
reduce ach release from nerves causing vagal constriction
types of b2 agonists
SABA - short acting beta 2 agonist
LABA - beta 2 agonist
types of SABAs
albuterol, levalbuterol
can b2 agonists be used for monotherapy
no!!!
LABA examples
formoterol
LABA vs SABA onset of action and duration
LABA variable onset, long duration up to 24 hr
SABA rapid onset short duration
what is the only LABA that can be used for rescue therapy and why
formoterol, rapid onset of action
are SABAs used for rescue inhaler
yes!
b2 agonist that combines synergistic meds in same device for better adherence, consistent delivery and better outcomes
ICS SABA
SABA SAMA
ICS LABA
LABA LAMA ICS
LABA LAMA
combo inhalers
bronchodilators that are combos with other bronchodilators (ex. SABA/SAMA, LABA/LAMA) are often used for what condition
copd
side effects of b2 agonists
muscle tremors
tachycardia
palpitations
hypokalemia (↑ risk of arrythmia) * rare
ventilation-Perfusion (V/Q) mismatch
metabolic effects (increase in free fatty acids, insulin, glucose, pyruvate and lactate) * only seen with large systemic doses
tolerance
what can occur with b2 agonist use with time and what can prevent this
tolerance
ics can prevent
studies have shown that the more frequently patients use beta-2 agonists what occurs
more likely they are to die
- not causal, more frequent use indicates more severe asthma
what is contraindicated in pts with covid due to what side effect
LABA salmeterol
using with paxlovid --> increased CV risk - QT prolongation and tachycardia
what is contraindicated with b2 agonist and what are examples of these meds? what does using them together cause
non selective beta blocker (propranolol, nadolol)
block bronchodilation and bronchospasm
what conditions should we be careful using b2 agonists with
heart disease / arrhythmias
severe hypertension
hyperthyroidism
diabetes (may ↑ glucose)
hypokalemia
pheochromocytoma
muscarinic antagonist moa
competitive antagonism of endogenous acetylcholine (Ach) at muscarinic receptors causing inhibition of bronchial smooth muscle constriction
what does ach do to resp system, what do antimuscarinics do
bronchoconstriction and tracheobronchial mucus secretion
- antimuscs antagonize these effects --> bronchodilation and decreased mucus secretion
- also prevent structural fibrosis and neutrophilic inflammation caused by Ach
do antimuscarinics have a significant effect on chronic inflammation associated with asthma & COPD
NO
which is more effective in asthma b2 agonist or antimusc
b2
when can antimusc be used with asthma
pt maxed out on b2 agonist
acute severe asthma attack
which is more effective in copd b2 agonist or antimusc
antimusc
what is one of the few reversible elements in copd and what drug targets this
increased vagal tone
antimusc
what drug can reduce air trapping and improve exercise tolerance in copd
antimusc
what antimusc is most commonly used in copd and why?
what does consistent use do
LAMA - only dosed once daily compared to SABA 3-4x a day
improved lung function and health status
do antimusc affect disease progression
no
most popular SAMA
ipratropium bromide
what are commonly used in copd pts due to additive effects
anticholinergic + b2 agonist - SABA/SAMA and LABA/LAMA
what is used in copd pts with high eosinophils
LABA/LAMA/ICS
tiotropium bromide, aclidinium bromide, and glycopyrrolate bromide are examples of
LAMAs
side effects of anticholinergics
rebound increase in airway --> responsiveness after discontinuation (need taper)
bitter taste --> noncompliance
glaucoma
bronchoconstriction
mydriasis, dry mouth, urinary retention
what conditions are contraindicated for anticholinergics and what effect do they have
don't DRIP
Drain eyes - increase glaucoma pressure
Retain urine - BPH/obstruction
Impair intestines - ileus/obstruction
Paralyze - exacerbate myasthenia gravis
what medication contraindicates anticholinergic use and what occurs with combined use
other anticholinergics (diphenhydramine, oxybutynin, amitriptyline)
additive anticholinergic effects - inc urinary retention, constipation, confusion
nebulized ipratropium side fx
may precipitate glaucoma in elderly
ipratropium bromide rare side fx
paradoxical bronchoconstriction
phosphodiesterase inhibitors moa
increases cAMP which leads to smooth muscle relaxation and reduced inflammatory cell activity
phosphodiesterase inhibitor class
antiinflammatory, not bronchodilator
phosphodiesterase inhibitor is used for
copd, being studied for ashtma
what does phosphodieseterase do normally and what does inhibiting it do
enzyme that breaks down cAMP and gAMP --> act as second messengers in cells to regulate SM tone, inflammatory cell activation, cardiac contractility, platelet aggregation
inhibition: SM relaxation and decreased inflammatory cell activity
predominant phosphodiesterase isoform in inflammatory cells
PDE4
nonselective PDE4 inhibiter with oral administration
metabolized CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 enzymes
roflumilast
what pts is roflumilast used for
add on tx for pts with copd who have maxed out therapeutic algorithm and keep having exacerbations
does roflumilast impact sx and lung function? what does it do
no
only reduces exacerbation rate
FEV1 required for roflumilast
less than 50% predicted
do CYP3A4/CYP1A2 inhibitors inc or dec roflumilast levels?
what about CYP inhibitors?
increase both
side effects of roflumilast and contraindications
GI: nausea, diarrhea, weight loss
neuropsychiatric: anxiety, insomnia, depression, rarely suicidal ideation
headache
caution w severe liver disease, significant weight loss, uncontrolled depression
example of methyxanthine
theophylline
methylxanthine aka theophylline moa
and how effective is it
weak, non-selective PDE inhibitor → ↑ cAMP → mild bronchodilation
- not very effective, we have other meds that work a lot better
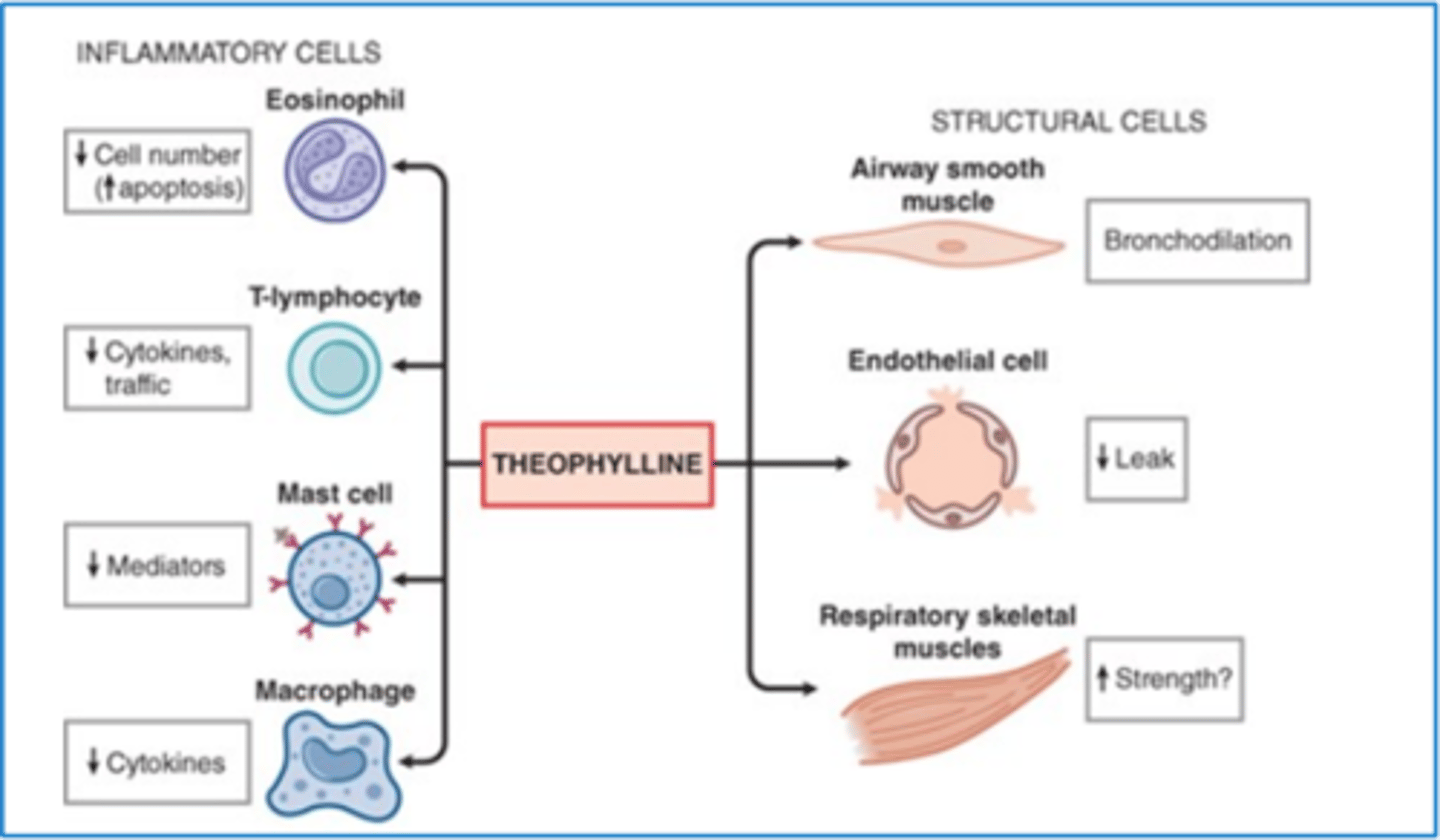
how is methylxanthine aka theophylline monitored and why? where is it metabolized?
must check levels and modify dose accordingly until optimal levels are achieved and then if change in clearance is suspected
narrow therapeutic range: 5-15 mg/L
- large variation in dosing amounts patients due to differences in plasma clearance
- metabolized in the liver via CYP1A2 - many factors can affect clearance
routes of methylxanthine aka theophylline administration and which is not recommended?
IV - used for many years in the treatment of acute severe asthma
Oral immediate-release (tablet or elixir) - wide fluctuations in plasma levels (not recommended)
Slow-release oral - twice daily recommended
what conditions are methylxanthine aka theophylline used for and are they the best option
bronchodilator for copd (others are superior)
acute severe asthma via IV (less effective than inhaled b2 agonist)
controller for asthma (ICS more effective, can be added to ICS)
methylxanthine aka theophylline side fx and what levels indicate toxicity risk
GI: nausea, vomiting
CNS: headache, irritability, insomnia → seizures at high levels
Cardiac: tachycardia, arrhythmias
Other: tremor, reflux, diuresis
Toxicity risk ↑ if levels > 15 mg/L
when is magnesium sulfate used as a bronchodilator and what is it often added to
acute severe asthma - only for life threatening attacks NOT routine use
beta 2 agonists - when added gives improvement in lung function
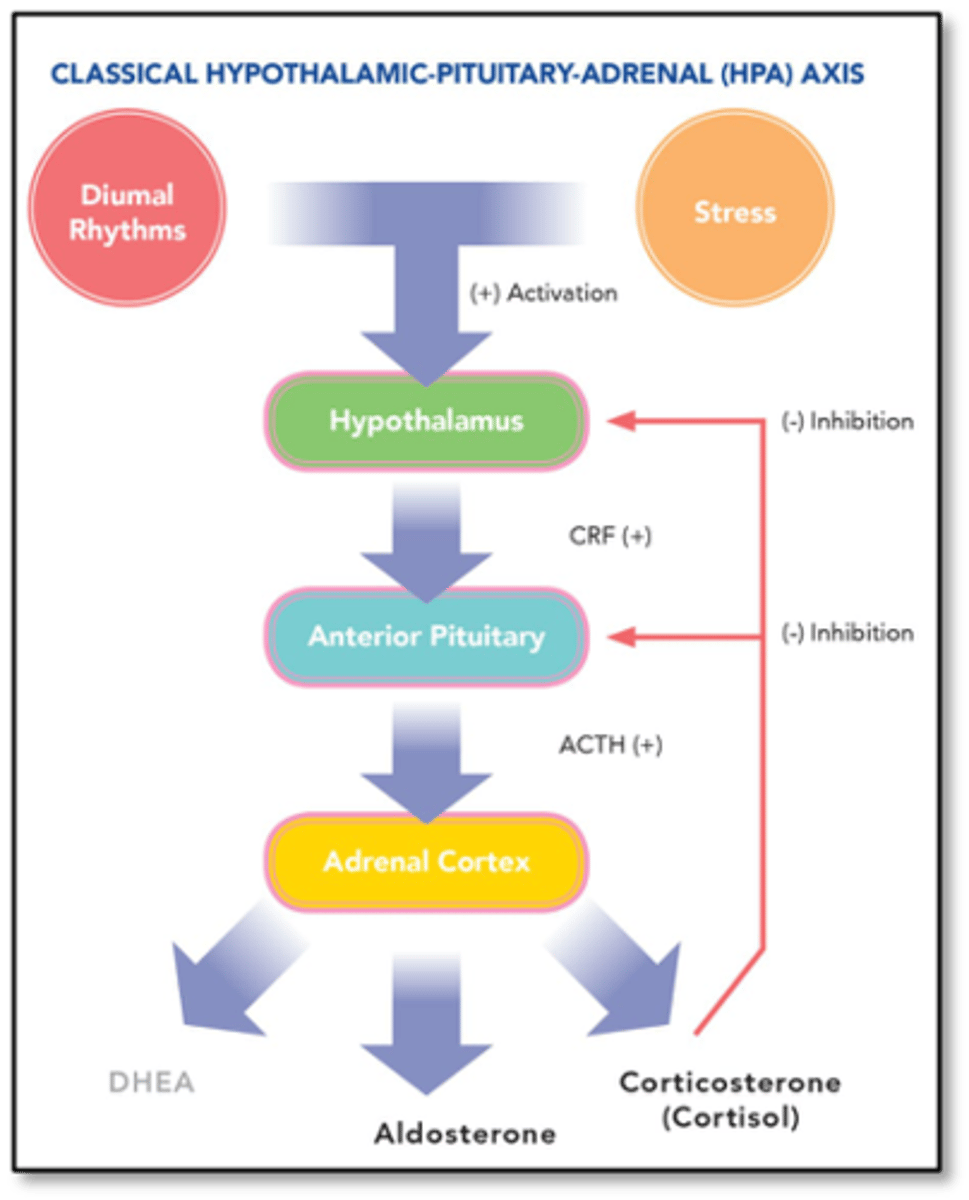
what does hpa axis control and how does it do this
HPA axis controls release of cortisol
- when there is enough, it negative feedbacks hypothalamus CRH (cortisol releasing hormone) and pituitary ACTH release that stimulate cortisol production
functions of cortisol
maintain BP
glucose metabolism
modulate immune system, inflammation, stress
maintain vascular reactivity
what does ACTH released by pituitary gland control production of
cortisol and aldosterone
how does RAAS system control aldosterone
juxtaglomerular cells of RAAS in the kidney sense a drop in blood pressure and release renin --> converts angiotensinogen which stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex
what does aldosterone release do and under what conditions will this occur
stimulates sodium reabsorption and raises bp
glucocorticoid vs mineralocorticoid effects
glucocorticoid - anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive
mineralocorticoid - sodium retention, potassium loss, fluid balance regulation
all corticosteroids have what 2 effects
glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid activities
relative potency of a corticosteroid (glucocorticoid vs mineralocorticoid effect) is compared to the potency of what drug
hydrocortisone
corticoidsteroid moa
CCSs enter target cells and bind to glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) in the cytoplasm
- binds to target genes and increases transcription
- interact with protein transcription factors to repress them (which is anti-inflammatory)
corticosteroid effects with asthma
what do they do to inflammatory cells, airway inflammation, vascular permeability, mucus secretion, and beta 2 receptor response
decrease inflammatory cells: reduce eosinophils, mast cells, and cytokine release
decrease airway inflammation: suppress cytokine and mediator production
decrease vascular permeability: stabilize endothelium, reducing edema
decrease mucus secretion: decrease mucus gland activity
increase beta-2 receptor response: enhance receptor expression and bronchodilation
what does pt need to do after taking ics and what does it do
rinse their mouth
- reduces systemic absorption and thrush risk
what is the cornerstone of asthma management and every pt should be on
ICS
is ics useful for copd
no much less effective than for astma
who can ics reduce exacerbations in and at what eosinophil level? who is it contraindicated in?
how should it be given
pts with T2 inflammation
eosinophils of over 300 cells/microliter
pneumonia or mycobacteiral infx risk
always give as triple inhaler ics-laba-lama
how do beta 2 agonists and steroids work in synergy
steroids inc number of b2 receptors in lungs and make them more receptive --> better bronchodilation
beta agonists help steroid receptors move into cell nucleus where steroids can turn off inflammation genes more effectively