Chapter 5 - General Psychology
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Perception
The processing organization, and interpretation of sensory signals in the brain
Sensation
The detection of physical stimuli and the transmission of this information to the brain
Bottom-up processing
Perception based on the physical features of the stimulus
Top-down processing
The interpretation of sensory information based on knowledge, expectations, and past experiences
Transduction
The process where sensory stimuli are converted to neural signals the brain can interpret
Qualitative information
Sensory receptors to the differences by firing in different combinations
Quantitative information
Sensory receptors respond to the differences by firing at different rates
Absolute threshold
The minimum intensity of stimulation necessary to detect a sensation half the time
Difference threshold
The minimum amount of change required to detect a difference between two stimuli
Sensory adaptation
A decrease in sensitivity to a constant level of stimulation
Signal detection theory (SDT)
A theory of perception based on the idea that the detection of a stimulus requires a judgement - it isn’t an all-or-nothing process
Hit
When a signal is presented and the participant detects it
Miss
When a signal is presented and the participant doesn’t detect it
False Alarm
When the participant reports there was a signal that wasn’t presented
Correct Rejection
When a signal isn’t present it and the participant doesn’t detect it
Response bias
a participant’s tendency to report or not report detecting a signal in an ambiguous trial
Retina
The thin inner surface of the back of the eyeball, which contains the sensory receptors that transduce light into neural signals
Cones
Retinal cells that respond to higher levels of light and result in color perception
Rods
Retinal cells that respond to low levels of light and result in black-and-white perception
Fovea
The center of the retina where cones are densely packed
Gestalt perceptual grouping laws
proximity, similarity, good continuation, closure, illusory contours, and common fate
Proximity
The closer two figures are to each other, the more likely we are to group them and see them as part of the same object
Similarity
Grouping figures according to how closely they resemble each other
Good continuation
grouping together smooth and continuous edges or contours
Closure
Completing figures that have gaps
Illusory contours
Seeing contours, shapes, and cues to depth when they don’t exist
Common fate
Seeing things that move together as belonging to the same group
Object constancy
Correctly perceiving objects as constant in their shape, size, color, and lightness, despite raw sensory data that could mislead perception
Binocular depth cues
Cues of depth perception that rise from the fact that people have two eyes
Monocular depth cues
Cues of depth perception that are available to each eye alone
Binocular disparity
A depth cue; because of the distance between the two eyes, each eye receives a slightly different retinal image
Convergence
A cue of binocular depth perception; when a person views a nearby object, the eye muscles turn the eye inward
Motion parallax
A monocular depth cue observed when moving relative to objects, in which the objects that are closer, appear to move faster than the objects farther away
Audition
Hearing; the sense of sound perception
Eardrum
A thin membrane that marks the beginning of the middle ear; sound waves cause it to vibrate
Vestibular sense
Perception of balance determined by receptors in the inner ear
Order of structures that information travels through to the primary auditory cortex
Eardrum, ossicles, cochlea, auditory nerve
Temporal coding
A mechanism for encoding low-frequency auditory stimuli in which the firing rates of cochlear hair cells match the frequency of the sound wave
Place coding
A mechanism for encoding the frequency of auditory stimuli in which the frequency of the sound wave is encoded by the location of the hair cells along the basilar membrane
Gustation
The sense of taste
Olfaction
The sense of smell
Taste buds
Sensory organs in the mouth that contain the receptors for taste
Olfactory epithelium
A thin layer of tissue within the nasal cavity that contains the receptors for smell
Olfactory bulb
The brain center for smell, located below the frontal lobes
Haptic sense
The sense of touch
Sound wave
A pattern of changes in air pressure during a period of time; it produces the perception of a sound
Accommodation
The automatic, reflex process where the eye changes the shape of its lens to shift focus between distant and near objects
Color afterimages
Optical illusions where colors continue to appear after staring at an object for several seconds and then looking away
Cornea
The thick, transparent outer layer of the eye
Figure-ground
the cognitive ability to distinguish an object from its background in a visual scene
Ganglion cells
The cells that make up the optic nerve
Iris
a circular muscle that determines the eye’s color and controls the pupil’s size
Lens
A transparent, biconvex structure behind the iris that changes shape to focus light onto the retina for clear sight
Linear perspective
Seemingly parallel lines appear to converge in the distance
Opponent Process Theory
Human color vision is governed by three neural channels (red-green, blue-yellow, and black-white) that respond in opposing pairs
Optic Chiasm
an X-shaped neural structure where optic nerves from both eyes meet and partially cross that enables binocular vision and depth perception
Optic nerve
A bundle of over 1 million retinal ganglion cell axons that transmits electrical visual signals from the retina at the back of the eye to the brain's visual cortex
Phi phenomenon
a perceptual illusion where stationary, alternating lights or images shown in rapid succession are perceived as moving
Pupil
The adjustable, black circular aperture located in the center of the iris that controls the amount of light entering the eye
Receptor
Rod and cone cells in the retina that transduce light energy into visual, electrochemical signals
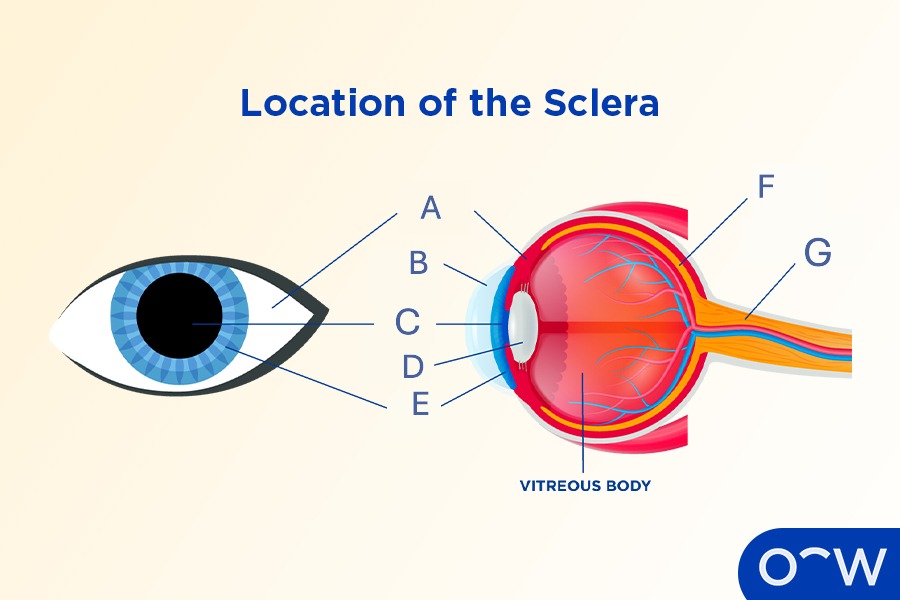
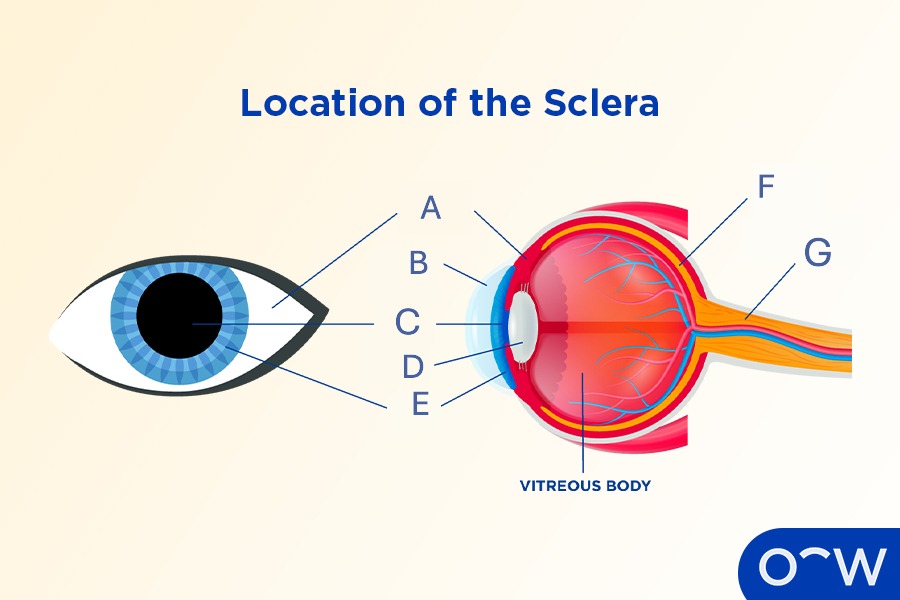
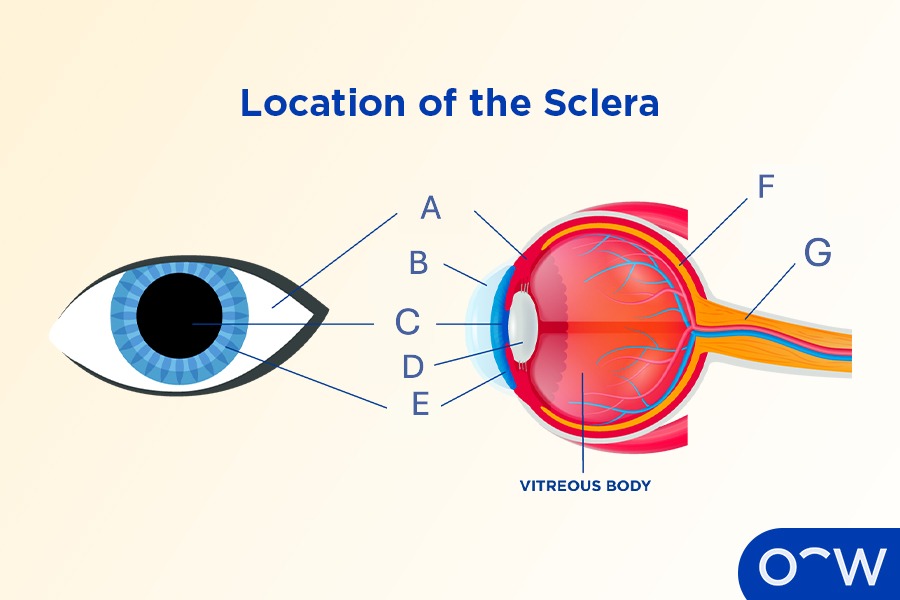
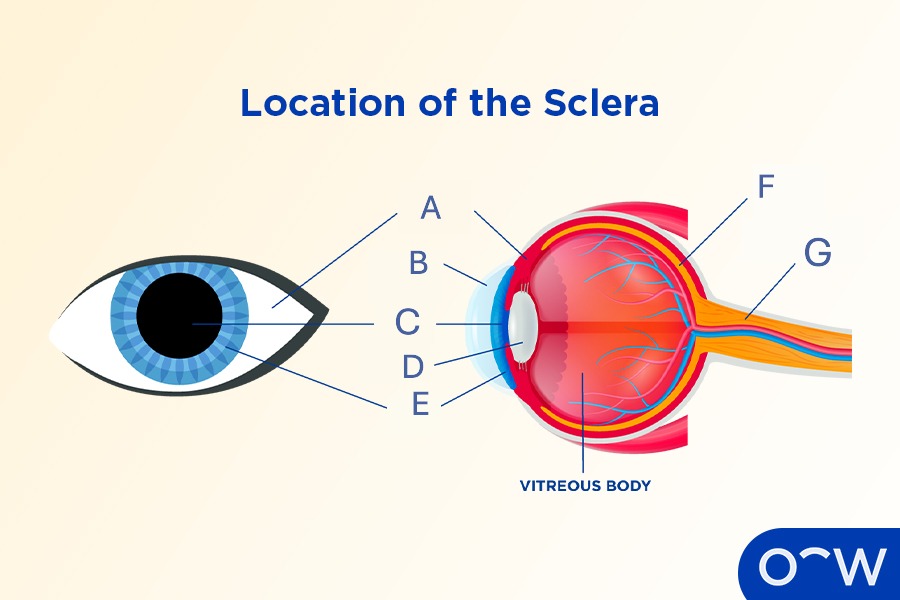
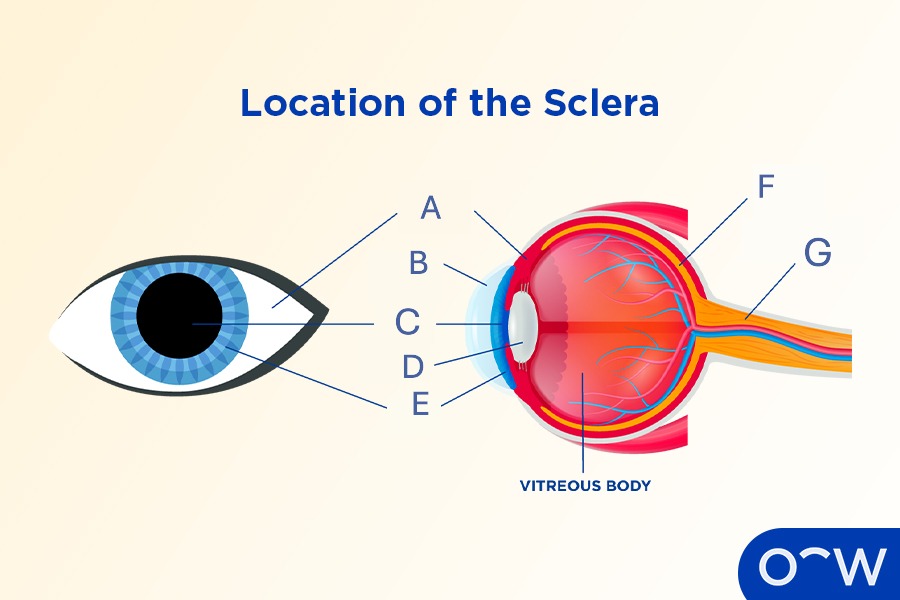
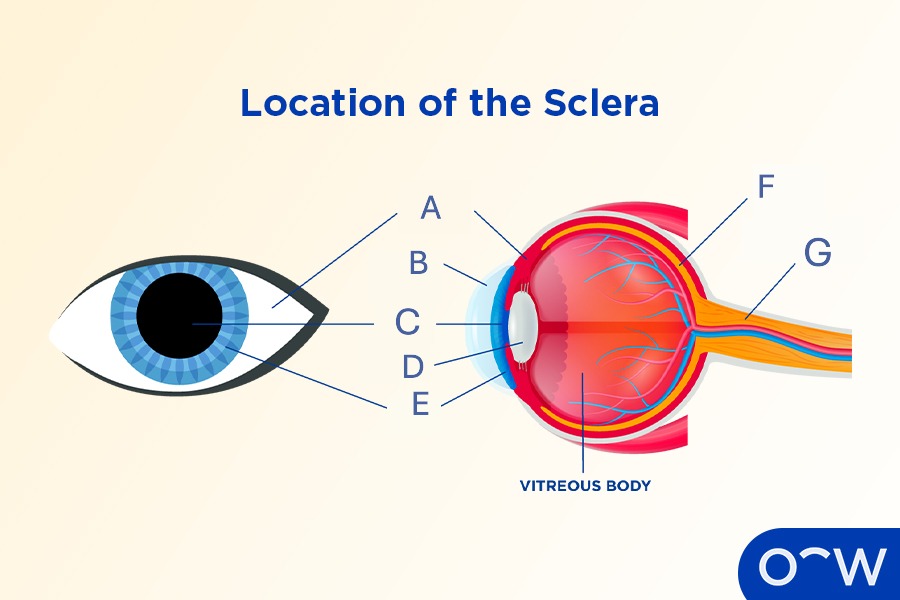
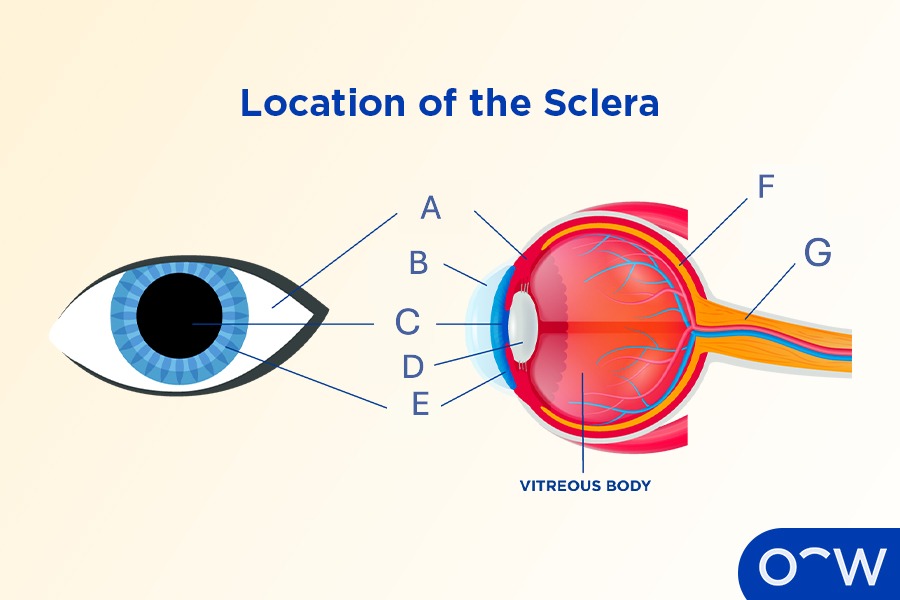
Sclera
The opaque, tough, fibrous outer layer that covers most of the human eyeball
Transduction
The process where sensory receptor cells convert physical energy into electrical neural signals that the brain can interpret
Trichromatic theory
Color vision results from activity in three types of cones sensitive to different wavelengths
Visual Cortex
The primary region in the occipital lobe at the back of the brain responsible for processing, interpreting, and integrating visual information received from the eyes