A&P - 9.3 Cartilaginous Joints
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
cartilaginous joint - general characteristics
articulating surfaces are united by cartilage (tough but flexible type of connective tissue)
no joint cavity
can synarthrotic or amphiarthrotic
types of cartilaginous joints
synchondrosis
symphysis
synchondrosis
cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by hyaline cartilage
rigid bridge of hyaline cartilage unites the bones of a synchondrosis joint
can be temporary or permanent
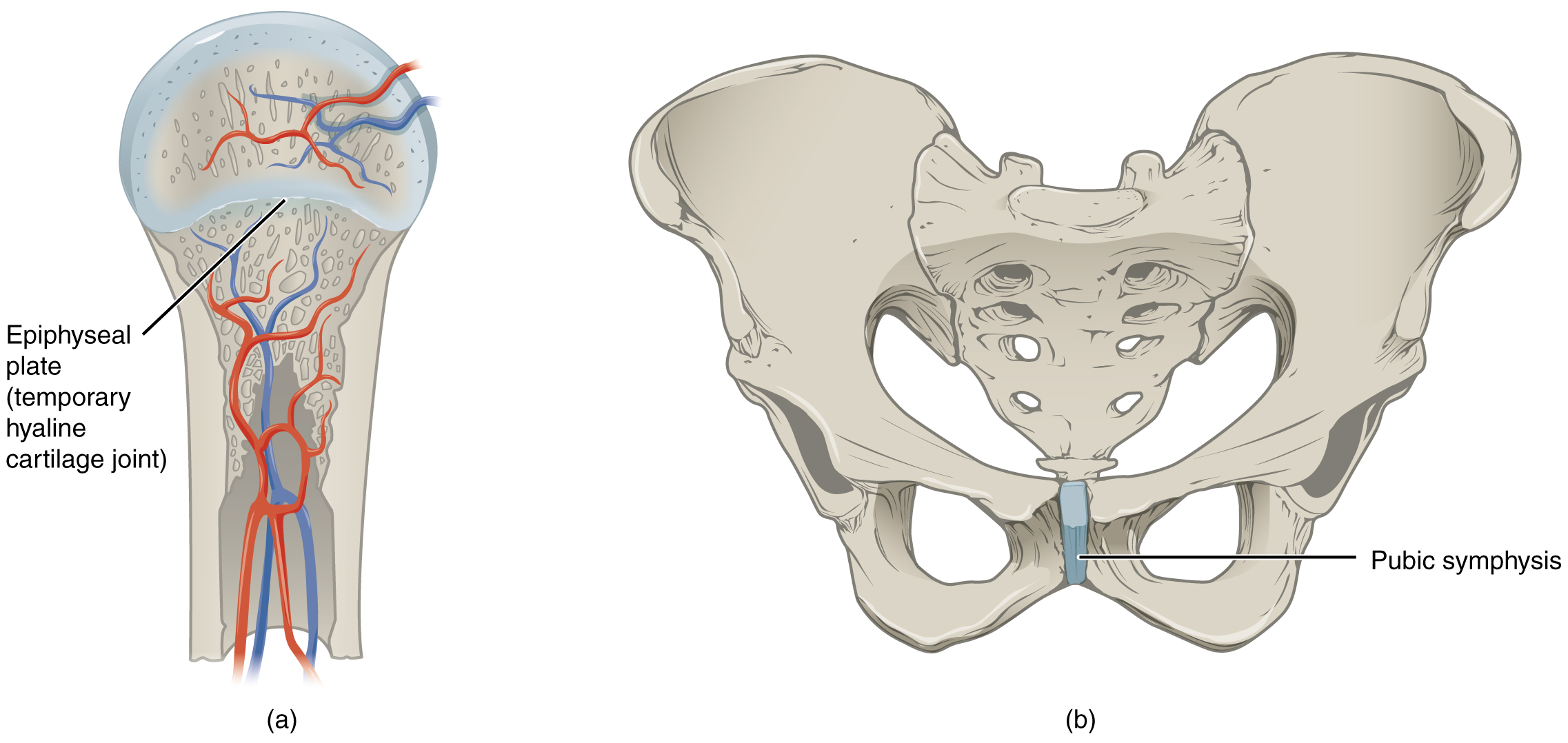
temporary synchondrosis
growing layers of cartilage where once bone growth stops the cartilage disappears and is replaced by bone
due to lack of movement between bone and cartilage it’s functionally classified as a synarthrosis
example:
epiphyseal plate (growth plate) of a growing long bone
region of growing hyaline cartilage that unites the diaphysis (shaft) of the bone to the epiphysis (end of the bone)
permanent synchondrosis
retain their hyaline cartilage and thus do not ossify with age
due to lack of movement between bone and cartilage it’s functionally classified as a synarthrosis
example:
thoracic cage
first sternocostal joint - where the first rib is anchored to the manubrium by its costal cartilage (articulations of the remaining costal cartilages to the sternum are all synovial joints)
formed where the anterior end of the other 11 ribs is joined to its costal cartilage
symphysis
cartilaginous joint where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage
articulating bones are separated by a wedge or pad of fibrocartilage
gap separating bones at a symphysis may be narrow or wide
functionally classified as an amphiarthrosis
fibrocartilage has a much greater ability to resist pulling and bending forces when compared with hyaline cartilage
gives it the ability to strongly unite the adjacent bones but can still allow for limited movement to occur
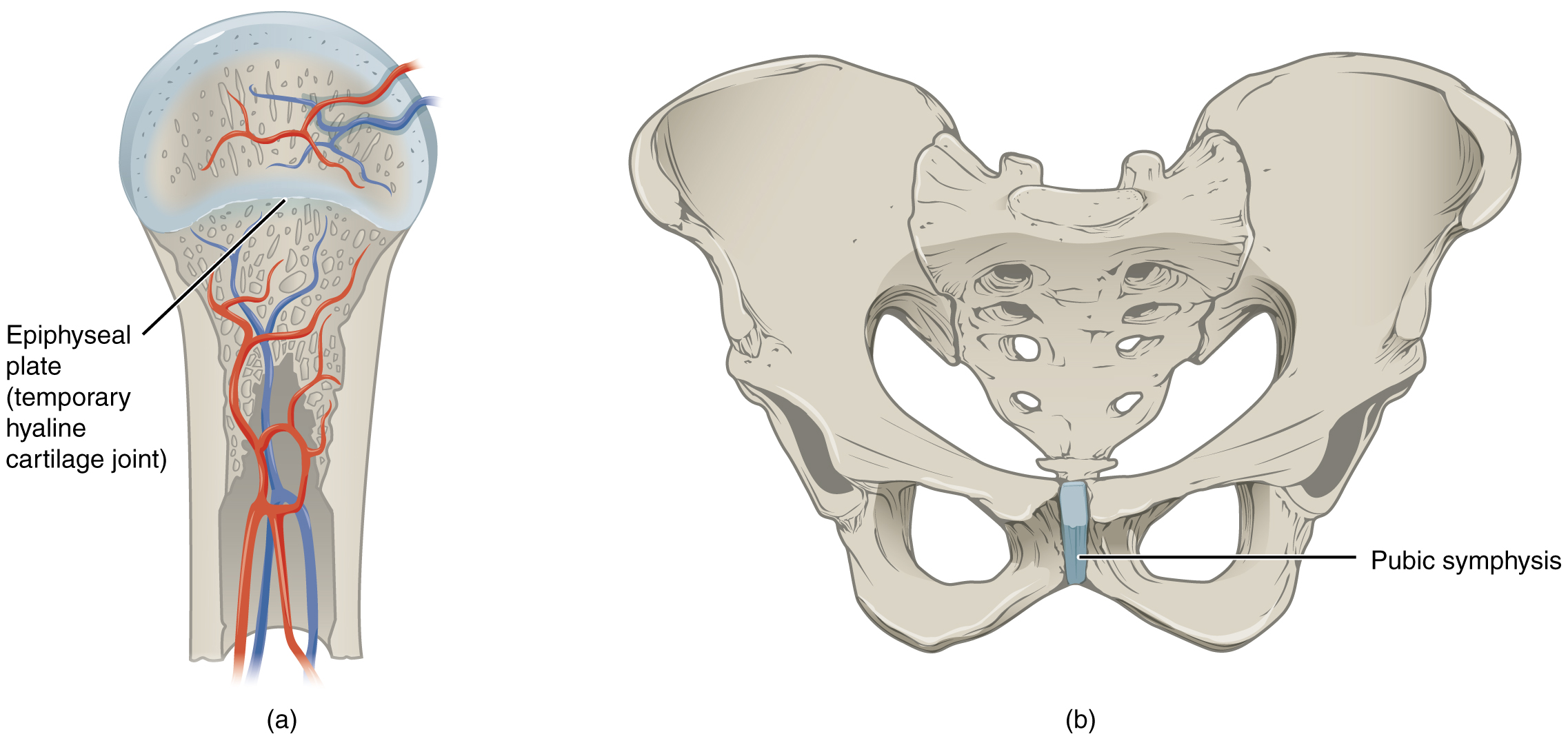
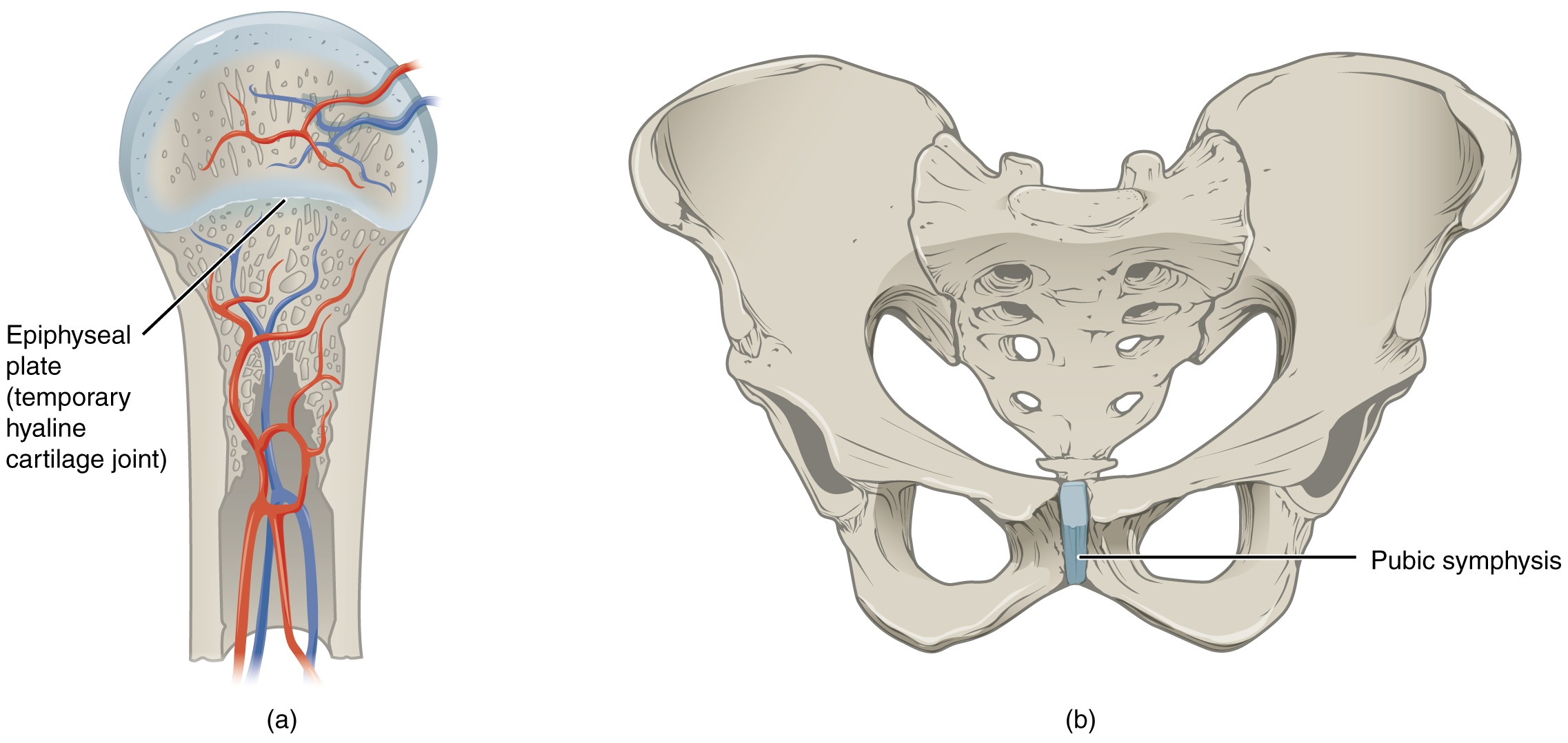
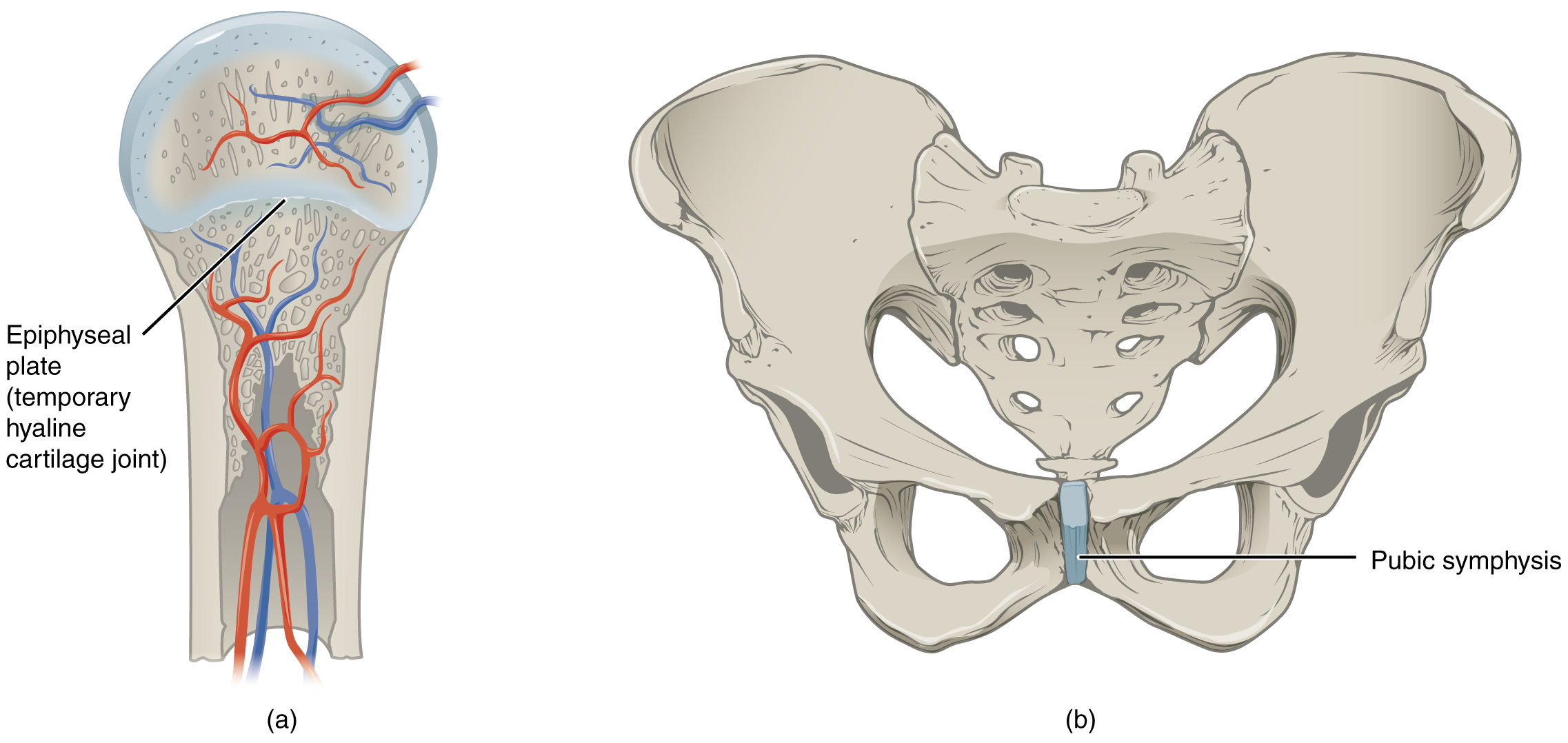
examples of narrow gap between bones
pubic symphysis
pubic portions of the right and left hip bones of the pelvis are joined together by fibrocartilage across a narrow gap
manubriosternal joint
fibrocartilage unites the manubrium and body portions of the sternum
examples of wide gap between bones
intervertebral symphysis
located between the bodies of adjacent vertebrae of the vertebral column
thick pad of fibrocartilage called an intervertebral disc strongly unites the adjacent vertebrae and provides cushioning between the vertebrae (important when carrying heavy objects or during high impact activities such as running or jumping)
width is important because it allows for small movement between the adjacent vertebrae