👑MASTER SET Surgery and Hospital Care
1/451
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
452 Terms
>50yo
CBC, CMP and EKG are typically ordered prior to surgery for patients _____ to rule out asymptomatic disease (ie. anemia, DM)
ASA I
Healthy, non-smoker, no or minimal alcohol use
Which ASA classification?
ASA II
-current smoker
-social alcohol drinker
-pregnancy
-obesity BMI >30 and <40
-well controlled DM/HTN
-mild lung disease
Which ASA classification?
ASA III
one or more moderate to severe diseases
-poorly controlled DM/HTN
-COPD
-morbid obesity BMI >40
-actie hepatitis
-alcohol dependence or abuse
-implanted pacemaker
-moderate reduction ejection fraction
-end stage renal disease with dialysis
-history >3 months MI, CVA, TIA, CAD/stents
Which ASA classification?
ASA IV
-recent <3 months MI, CVA, TIA, CAD/stents
-ongoing cardiac ischemia or valve dysfunction
-severe reduction of ejection fraction
-shock, sepsis, DIC, ARD, ERSD without dialysis
Which ASA classification?
ASA V
-ruptured abdominal or thoracic aneurysm
-massive trauma
-intracranial bleed with mass effect (brain herniation)
-ischemic bowel and significant cardiac pathology or multiple organ dysfunction
Which ASA classification?
ASA VI
A declared brain-dead patient whose organs are being removed for donor purposes
Which ASA classification?
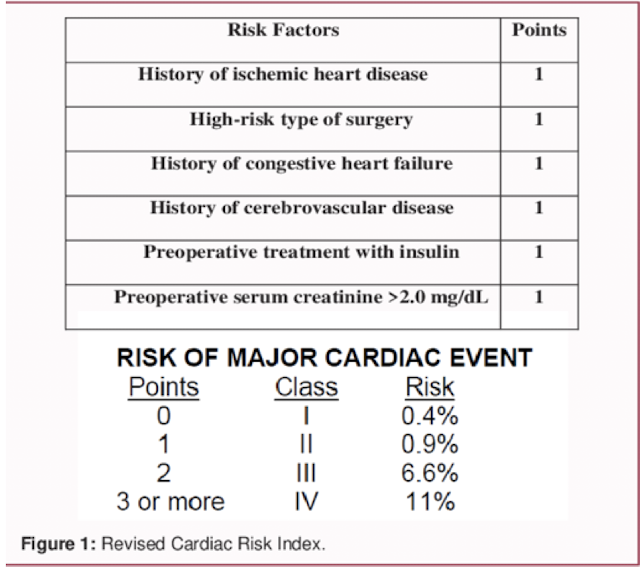
RCRI (Revised Cardiac Risk Index)
• Hx of ischemic heart disease
• Hx of CHF
• Hx of Cerebrovascular disease
• High-risk operation
• Preoperative treatment with insulin
• Preoperative serum creatinine >2.0mg/dl
Does this patient care increased risk for developing postoperative cardiac complications?
smoking
What is significantly associated with postoperative pneumonia, surgical site infection (SSI) and death?
most surgeons require cessation for a specific time prior to elective surgery
postoperative pulmonary complications (PPC)
pneumonia and ventilator dependency are primary ____ related to age, elevated ASA, functional dependence, COPD, smokers, CHF, Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
high risk patients benefit from pre-op respiratory therapy, baseline studies and smoking cessation
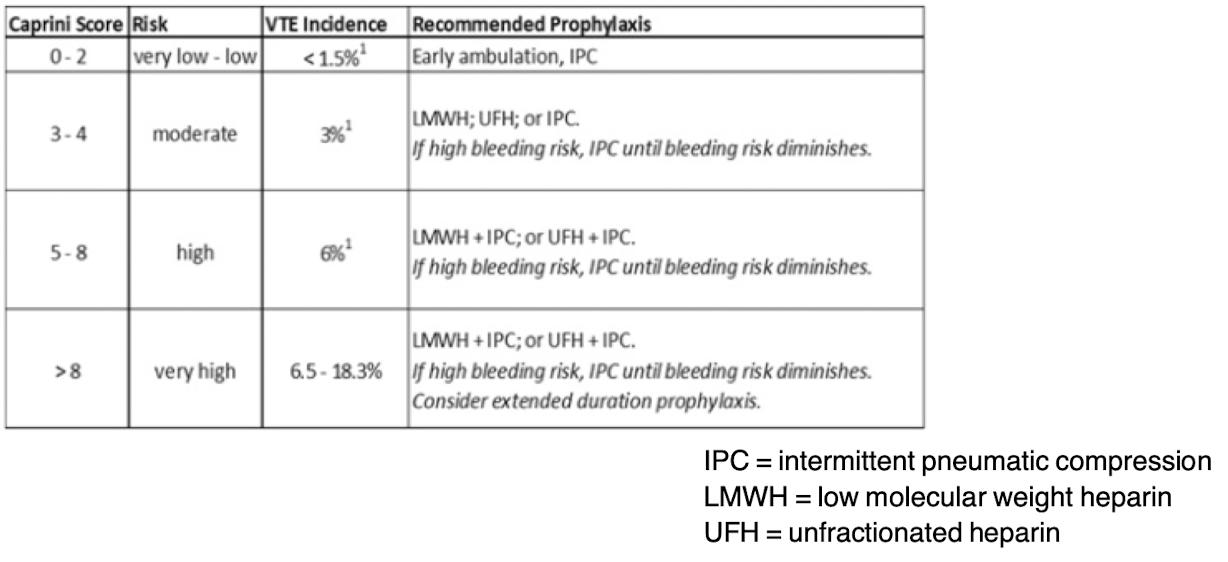
Caprini Model
What is the preoperative risk assessment for VTE for use in all elective general surgery patients?
>140mg/dL
Sole predictor of surgical site infection (SSI) is post-operative hyperglycemia _______
<3mg/dL
hypoalbuminuria ____ carries a 5X risk for surgical site infection (SSI) postoperative
assess for malnutrition preoperative
severe obesity
____ with BMI >50kg/m2 increases operative time and can result in increased post op mortality, wound complications, pulmonary insufficiency, & renal failure
Informed consent
-discuss all possibilities including alternative procedures
-caution all risks: infection, poor outcomes including death
-native/preferred language
Informed consent
• Procedure
• Alternative
• Risk
• Question
• Answer
PARQA of preoperative _____
2 hours
-clear liquids only, medications with sip of clear liquid as prescribed
-NO orange juice, NO hard candy, NO gum
NPO guidelines _____ prior to surgery/procedure
6 hours
-formula/non-human milk
-non-clear juice/drinks
-gum/hard candy
-light meal (toast, fruit, juice, broth, apple sauce)
NPO guidelines _____ prior to surgery/procedure
8 hours
Last regular meal must be _______ prior to surgery/procedure
NPO guidelines
Pre-Round
• What happened overnight?
• Any new labs/imaging/information?
• Any changes in vitals? I/O’s?
• Any changes in ambulation/mobility?
• Does staff have any new concerns?
Physically check on and examine patient!
Preop Holding
• Day of surgery: update the H&P (within 30 days) + preop note
• Check for any same day/admission labs, medical updates
• Check for all consents (surgery & anesthesia)
• Pre meds & Antibiotic prophylaxis
• Discuss expectations and postop care
• Check consent, mark patient, confirm NPO status
Last opportunity to talk with patient and family
1 hour
Pre-op prophylactic antibiotics to prevent SSI during operative procedure should be administered ______ before incision
consider holding until AFTER culture with concern for abscess or septic joint to avoid altering specimen ID
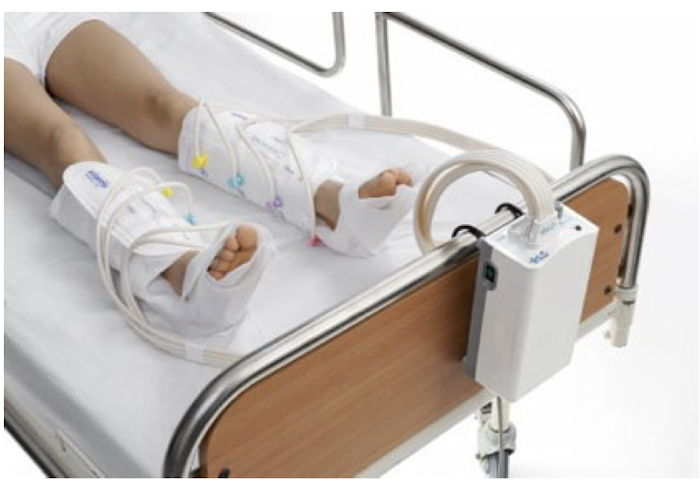
Sequential Compression Devices (SCDs)
• Increase mean and peak femoral vein velocity in the leg
• Affect systemic coagulation and fibrinolytic mechanisms by causing the dissolution of fibrin by enzymatic action
• Use CAUTION with patients who have CHF or PAD
Time Out
mandatory “pause with a purpose” that reduces surgical errors
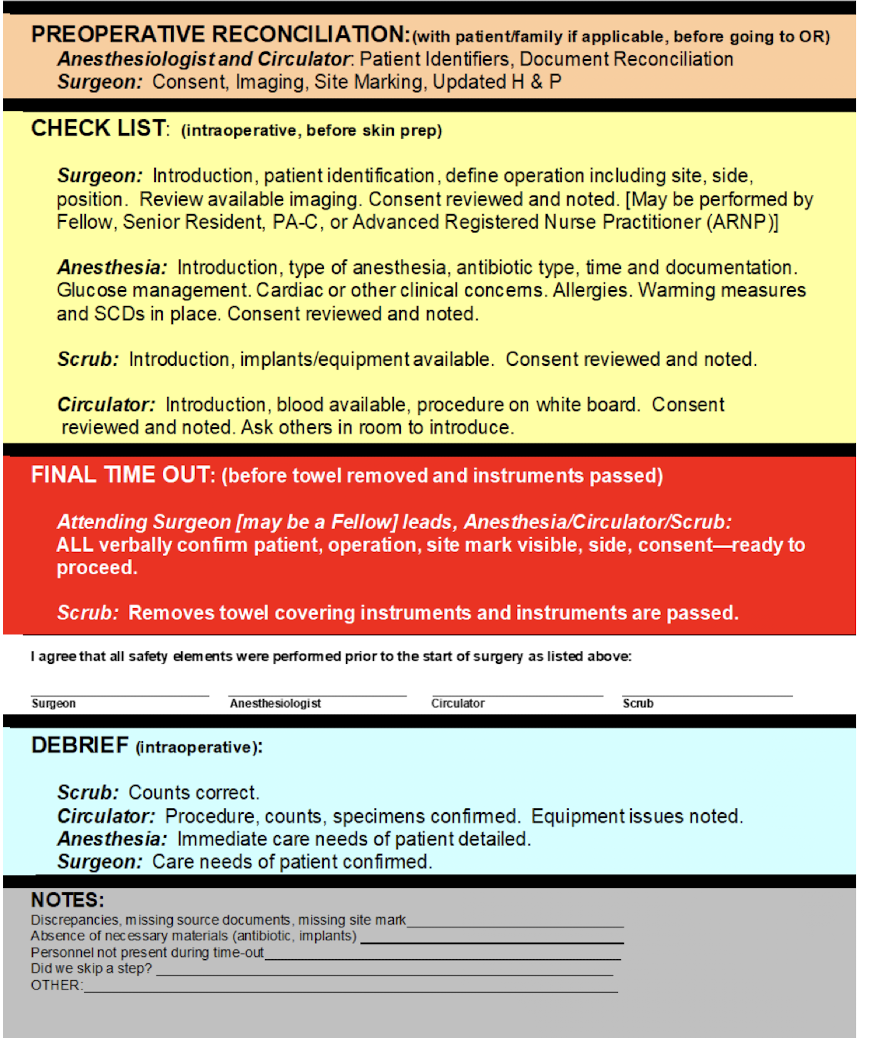
wrong site surgery
_____ performed on wrong side or body part is a sentinel event: an unintended event that involves death or serious physical or psychological injuries or risk
Scrub
• No Jewelry (earrings, necklace)
• No acrylic/fake nails
• All hair covered, including beards
• MUST have eye protection
• Surgical mask
• Must wear hospital scrubs
• Wet vs dry scrub
• Gown/Glove
sterile field
Respect the BLUE!!! 12-18 inches away if unsterile
• Patients prep night before/morning of (shower/wipes)
• Room (clean) and instruments (sterile)
• NEVER argue, just go re scrub, glove
• NEVER reach over blue
• “Dirty” cases at the end of the day
Respect the ________
Clean technique
• Giving an injection (IM/SQ)
• Inserting/Removing a peripheral IV
• Removing a urinary catheter
• Emptying a urinary catheter drainage bag
• Cleansing and dressing an abrasion
• Putting on exam gloves
Sterile/Aseptic technique
• Performing a joint/deep injection
• Placing/inserting a urinary catheter
• Inserting/Removing a Central Line
• PICC line insertion
• Lumbar puncture (LP)
• Donning sterile gloves
MAC (Monitored Anesthesia Care)
IV sedation (often Propofol), patient is unconscious but able to maintain airway and quick recovery
-Anesthesia tech or CRNA administered only
General anesthesia
Reversible state of unconsciousness with loss of sensation of the entire body, unable to maintain an airway
Sedation anesthesia
Decreased level of consciousness or relaxed state, but not fully unconscious, able to maintain an airway
Conscious sedation
IV sedation and analgesic (Fentanyl and Versed), patient is conscious and able to breath on their own
-Dentists, Surgeons, GI docs (colonoscopy)
Open
Cutting through skin or mucous membrane and any body layers necessary for exposure
Abdominal hysterectomy, open appendectomy
Percutaneous
Entry by puncture or minor incision of instrumentation through skin or muscles and any layers necessary to reach procedure
Needle biopsy or liver or breast, percutaneous abscess drainage
Percutaneous endoscopic
Entry by puncture or minor skin incision of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and necessary layers
Arthroscopy, laparoscopic cholecystectomy
Via natural or artificial opening
Entry of instrumentation through a natural or artificial opening to reach site
Endotracheal intubation, foley catheter placement, EGD, colonoscopy
Open with percutaneous endoscopic assistance
Cutting through skin or mucous membrane and other body layers AND entry by puncture or minor incision of instrumentation through skin or muscle and layers necessary
Laparoscopic-assisted vaginal hysterectomy
External
Procedures performed directly on the skin or mucous membrane procedures performed indirectly by application of external force through skin or mucous membrane with no entry into the body
Closed reduction of a fracture
Endovascular
Cutting through skin entry into vascular structure with small incision and introduction of a catheter
Uterine artery embolization, endovascular repair of AAA
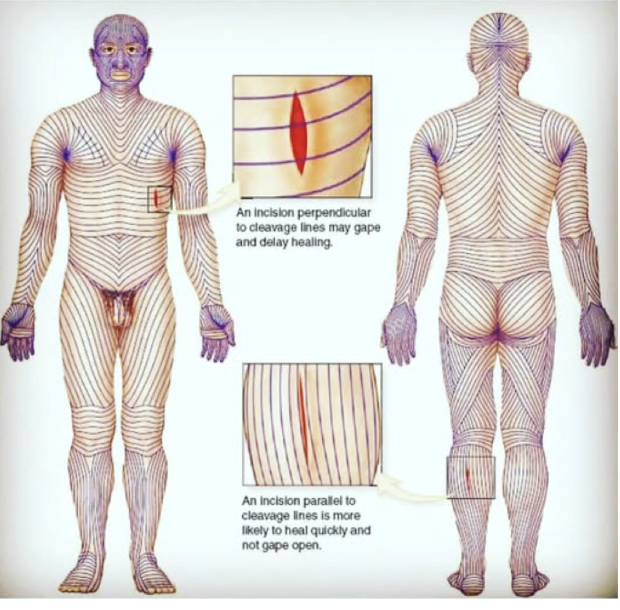
Langer’s lines
cleavage lines, are topological lines drawn on a map of the human body parallel to the natural orientation of collagen fibers in the dermis
-generally perpendicular to underlying muscle fibers, prevents gaping, allows for better cosmesis
Lateral Abdominal Wall
• Skin
• Subcutaneous tissue
• Superficial fascia layer
• Camper’s fascia (fatty)
• Scarpa’s fascia (membranous)
• Deep Fascia
• Musculoapoeurotic Layers and Investing fascia
• External oblique (lateral)
• Internal oblique (lateral)
• Transverse abdominis (lateral)
• Rectus abdominis (central)
• Fascia transversalis
• Pre-peritoneal fatty tissue/extraperitoneal fat
• Parietal peritoneum
Layers of __________
arcuate line
There is NO posterior rectus sheath below the ______
Site of Pfannenstiel incision (C-Section)
Inguinal triangle (Hesselbach)
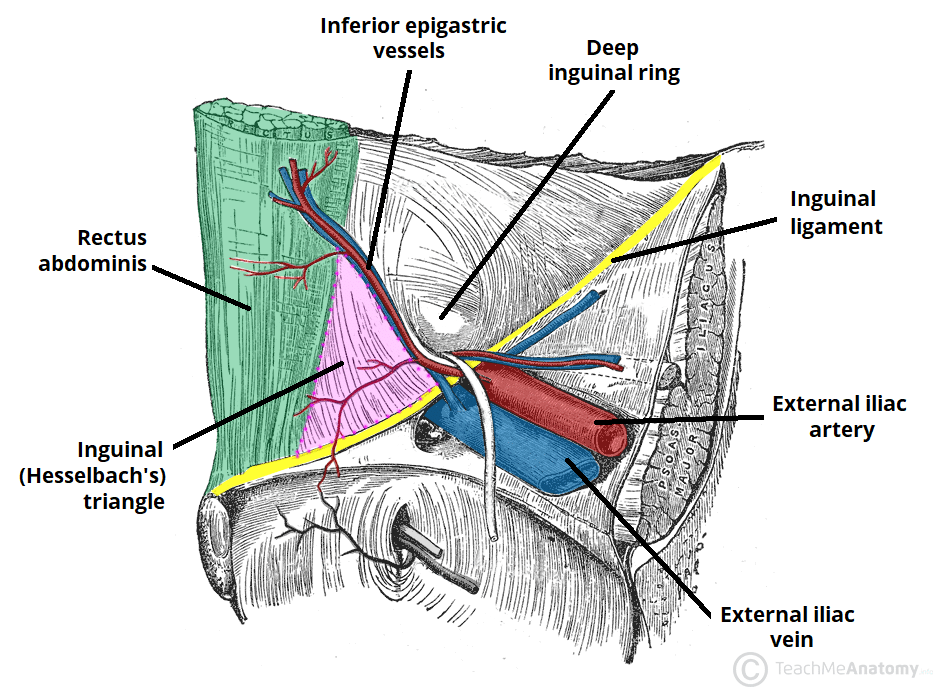
Vessels and nerves at risk for injury in anterior abdominal wall
Calot’s triangle
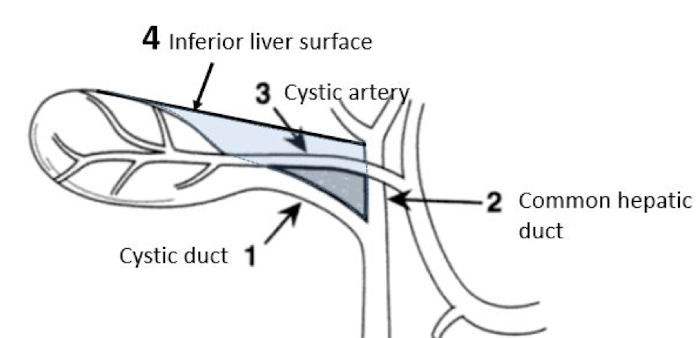
Vessels and nerves at risk for injury in anterior abdominal wall
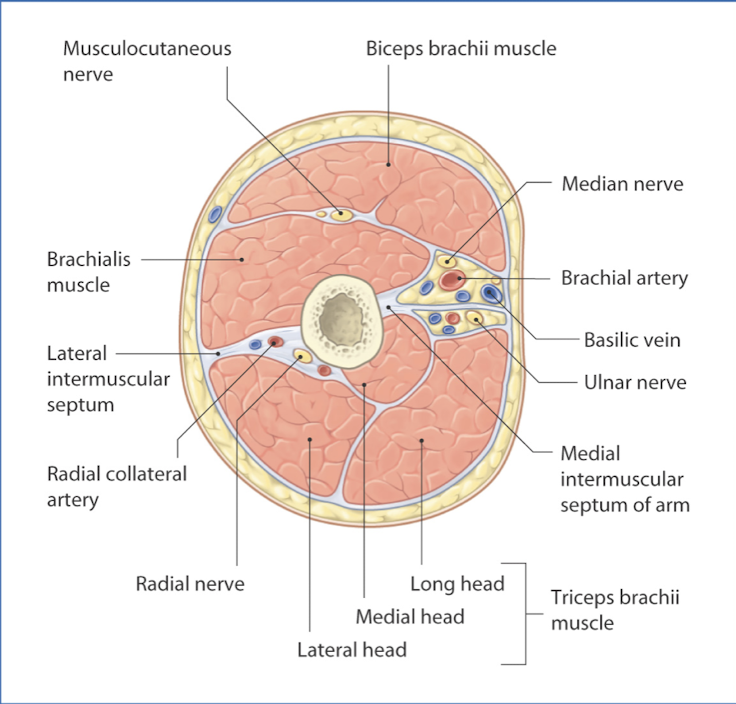
Extremity layers
• Skin (epidermis/dermis)
• Superficial fascia
• Adipose
• Deep fascia
• Epimysium covers muscle
• Periosteum covers bone
• Neurovascular bundles
• Compartments (anterior and posterior)
Meticulous hemostasis
• Assist natural clotting process, apply pressure
• Thermal coagulation
• Tourniquets
• Vasoconstrictive substances (Epinephrine)
• Apply procoagulants (thrombin and collagen, (TXA) tranexamic acid)
• Takes place pre-op, intra-op, post-op
Blood management
Perfusion to support organs
• Maintenance of sufficient blood supply to tissues
• Support of vital organ functions
• Tissue handling/technique: avoid hemostatic closures/damage with electrocautery
Blood management
Dead space
cavity or pocket remaining after the closure of a wound that is not obliterated by the operative technique permitting the accumulation of blood, pus, serum or air
-can be caused by retraction or dissection of tissue
Prevention:
• Careful suture placement in all tissue planes
• Minimal tension on sutures to prevent tissue devitalization
• Drains or packing to prevent fluid accumulation
• Pressure dressings
• Wound care/checks
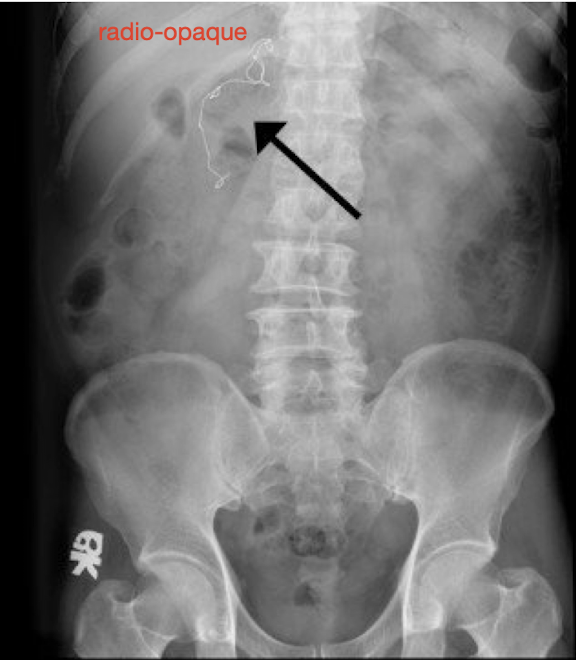
Surgical count
Counting all sponges and instruments in sequence during closure to prevent retained surgical instruments before and after operative procedure
-NEVER cut/alter a sponge or towel (radio-opaque detectable by XRAY)
-should be documented before and after and shift change
Admission criteria
“>2 midnights” rule: Patient benefits from +2 nights to qualify for inpatient status, otherwise goes to obs (observation status)
Risks: living alone and unable to care for self, unable to walk, medical comorbidities
Indications: requires parenteral medications, supplementation O2/ventilation, unstable/abnormal labs or vitals, course of illness expected to worsen or deteriorate
Level of care
• Observation/CDU (clinical decision unit)
• Med/Surg (staying overnight)
• Med/Surg telemetry (monitoring units)
• PCU (progressive care unit)
• ICU “The Unit” SICU, MICU, CV/CICU, Neuro-ICU, NICU, PICU
Close the loop with primary/accepting provider name, number and conversation during hand-off when you are admitting patients
Admit Orders
A – Admit to
D – Diagnosis
C – Condition/Code status
V – Vitals (frequency)
A – Activity
N – Nursing Instructions
D – Diet
I – IV fluids
M – Medications
A – Allergies
L – Labs studies
S – Special studies/consults/instructions
Post-op pain control
Trend towards:
• Regional blocks
• Epidural/Spinal blocks
• Multimodal pain control (APAP, Gabapentin)
• NSAIDs/Toradol
• Local infiltration
Trend AWAY from use of opioids (increased risk tolerance)
ERAS (Enhanced Recovery After Surgery)
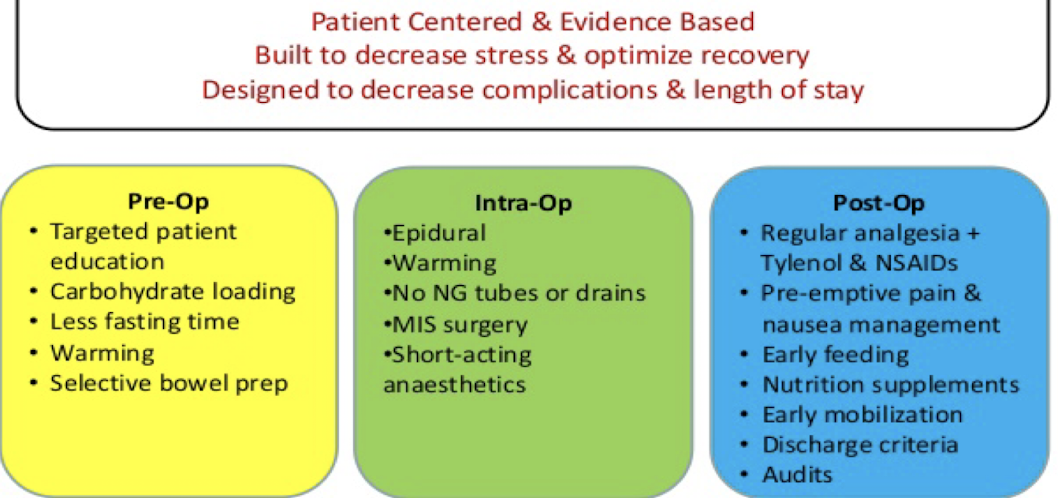
Discharge criteria
• Pain control (PO meds)
• Wound concerns/Bleeding
• Tolerating PO (oral intake) without N/V
• Mobility/Safety
• GI? Flatus vs BM (especially general surgery)
• Any things specific to your service!!!
• Work with RN Case Managers, Social Workers
AVS (After Visit Summary)
Patient education & information with clear post-operative instructions after procedure or hospitalization
-wound care, drains, medications
-medication reconciliation
-appointments and referrals (dates and times)
-Indications for prompt re-evaluation by surgeon/provider and ER precautions (contact information for on-call surgeon)
Admission
-Care plan created
-Orders are placed, plan is set in motion
-Notify consult services need to evaluate and treat based on orders
-Admission documents are completed
Steps:

Critical orders: patient status, level of care, code status, admitting diagnosis
Daily Rounding
-Every day the new data creates an evolving care plan with the interprofessional team
-Attending provider makes the ultimate decisions on plan of care
-New data is collected, new orders are placed, and new documentation is created
Steps:

Discharge Planning
-Patient no longer deemed needing inpatient care
-A plan is set and the team gets all needs met to set patient up for a successful transition to next phase of care
Steps:
• Write DC orders
• Provide DC instructions
• Patient education performed
• Complete DC medication reconciliation
• Prescribe any new medications
• Write Discharge Summary
• Update Problem List
• Complete billing & coding
enteral nutrition (feeding tube)
• Evaluate if feeding is appropriate to care plan
• Dietician Consult
• ________ always preferred route
• Healthy/stable patients can generally go up to 7 days without feeding if the gut is unusable (fluids/electrolytes/glucose managed parenterally), plan IV methods at day 6 if bowels are still shut down
• Sick patients require earlier aggressive intervention
Malnutrition causes lean muscle loss, alterations in respiratory mechanics, impaired immune functions and intestinal atrophy and can lead to poor wound healing, infection and increased morbidity/mortality
FASTHUGSBID - Feeding
serum albumin
rough estimate of patient’s nutritional status/prognostic indicator long-term
_____ levels <3.5mg/dL correlates with increased morbidity and mortality and increased length of hospital stay
FASTHUGSBID - Feeding
Analgesia
• Mild Pain: OTC Tylenol, Ibuprofen, Heat/Ice, Distraction
• Moderate Pain: Above + prescription pain meds, muscle relaxers, nerve blockers, low dose opioids (Tramadol, Flexeril, Neurontin, Norco, +/- Oxycodone)
• Severe Pain: Above + Higher dose/ IV opioids (Oxycodone, Morphine, Dilaudid, Fentanyl)
FASTHUGSBID- __________
*preferred instead of sedative to reach sedation goal, always start with mild treatments and stack on as needed
Sedation
Common medications:
• Fentanyl/ Opioids
• Propofol
• Precedex
• Benzodiazepines
• Ketamine
- Can help reduce agitation
- Can increase respiratory depression
- Decreases gastric motility (constipation)
- AVOID for alcohol/drug withdrawal
FASTHUGSBID- __________
Caprini Score
-Assess with ___________ for VTE risk
-Virchow’s Triad risk factors: Immobilization, Cancer, Pregnancy, Critical illness, Surgery, Smoking, Obesity, Trauma, OCPs, prior VTE
Prophylaxis:
• Ambulation, TED hose
• SCDs (sequential compression devices)
• LMWH (low molecular weight heparin), Heparin
**evaluate meds DAILY and change as indicated
FASTHUGSBID- Thromboprophylaxis
Delirium
an altered state of consciousness with episodes of confusion that can develop over hours or days
Tx: address underlying cause (remove medications, treat infection)
-encourage mobility (PT/OT), proper sleep wake cycles, lights on/windows open, glasses and hearing aids, reassure and reorient frequently
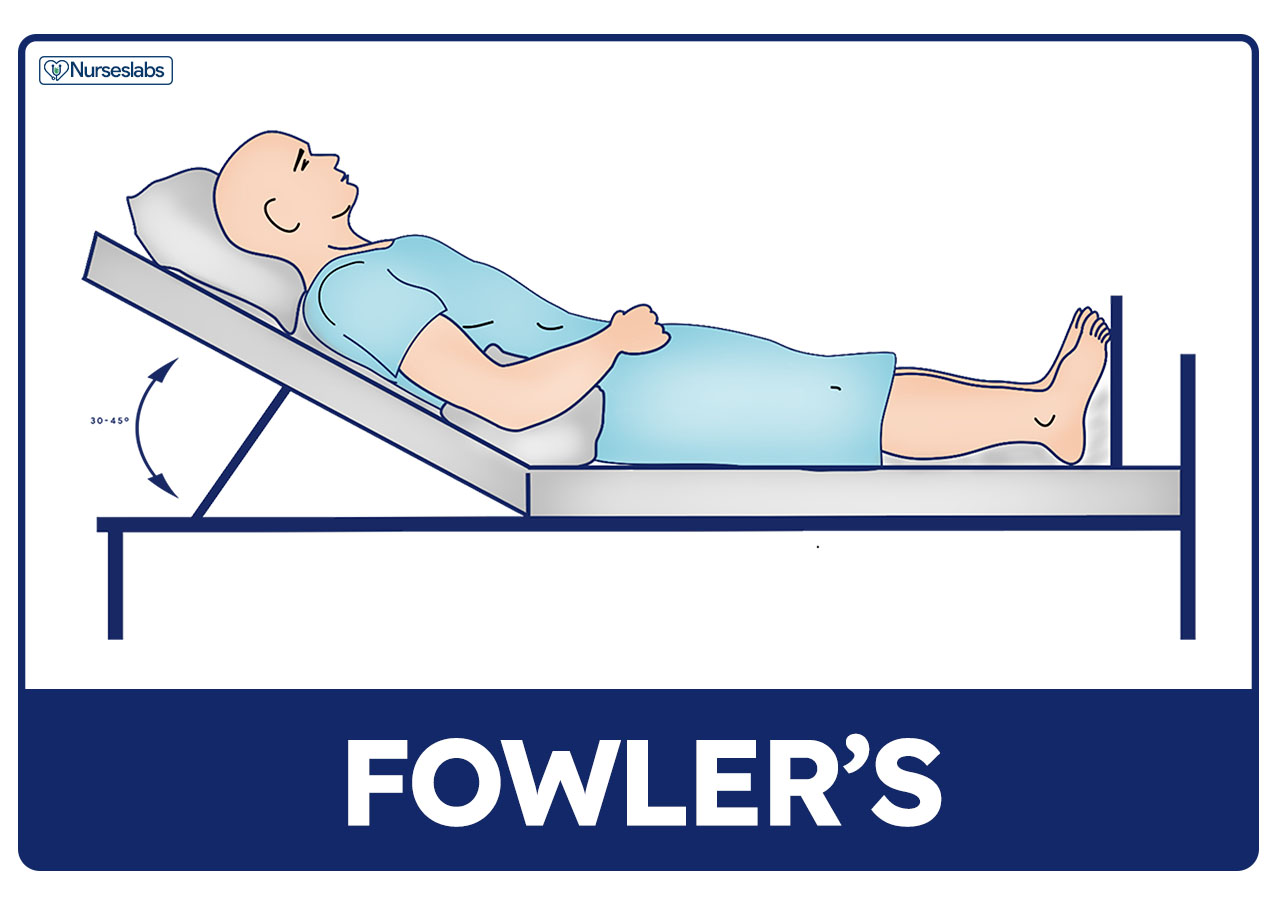
30 degrees
ensure head of bed is elevated to _______ to reduce risk of aspiration and GERD
*repositioning patients is key, closely watch ventilated/sedated patients on enteral (tube) feeding
FASTHUGSBID - Head of Bed
Pantoprazole (PPI)
gastric stress ulcer formed due to impaired mucosal protection and hypersecretion of acid
-consider in patients with 1 major (coagulopathy, mechanical ventilation >48hr) or 2 minor risk factors
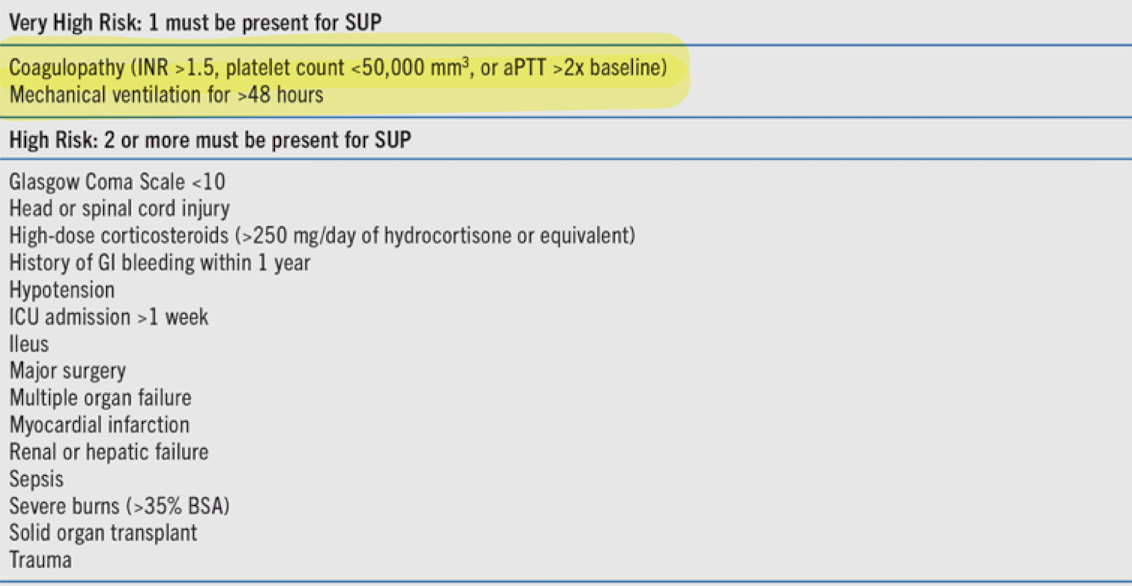
Prophylaxis: ________ (first line); H2 Blockers (Famotidine), Sucralfate
FASTHUGSBID- Ulcer prophylaxis
<150mg/dL
hyperglycemia results in increased morbidity and mortality, can develop in response to acute metabolic stress due to inflammation and cytokine production
Tx: insulin therapy (short-acting first, titrate slowly to avoid hypoglycemia) to combat high levels
Glycemic control goal _____ in critical care setting
FASTHUGSBID - Glycemic control
Spontaneous breathing trial (SBT)
daily assessment of the intubated patient’s ability to breathe with little to no ventilator support
-performed to evaluate whether patient can be extubated
-assess for hemodynamic stability, lung disease stable/resolving and patient showing signs of self management (spontaneous breaths)
FASTHUGSBID - ___________
Bowel care
every patient should be evaluated and placed on ______ regimens (except surgical patients with bowel disorders)
-goal to prevent constipation/decreased bowel motility
Risk factors: pain medications, minimal PO intake, immobility
FASTHUGSBID - ___________
Indwelling catheters
all _____ should be carefully monitored for time of placement and removal indications
-remove lines within guidelines and caution for infections
*CLABSI (Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection) and
CAUTI (Catheter-Associated Urinary Tract Infection) are leading causes of Hospital-Associated Infection
FASTHUGSBID - ___________
Deescalation

FASTHUGSBID - ___________
Medication Reconciliation
-review with patient and family the name, dosage, frequency, timing, and duration of all medications patient is taking at home; check allergies and intolerances
Readmission
____ <30 days for 6 major conditions:
1. Acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
2. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
3. Heart failure (HF)
4. Pneumonia
5. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery
6. Elective primary total hip/ total knee arthroplasty (THA/TKA)
HRRP (hospital readmissions reduction program) hospitals are penalized for repeat admissions and rewarded for safety and efficiency
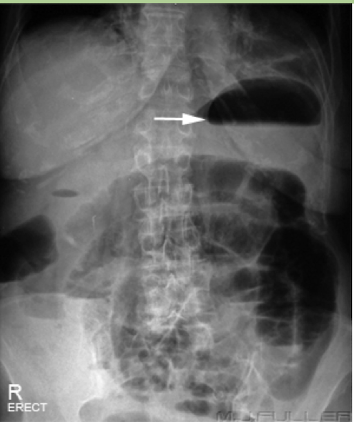
Gastric Bubble
common normal finding
Abdominal Radiograph
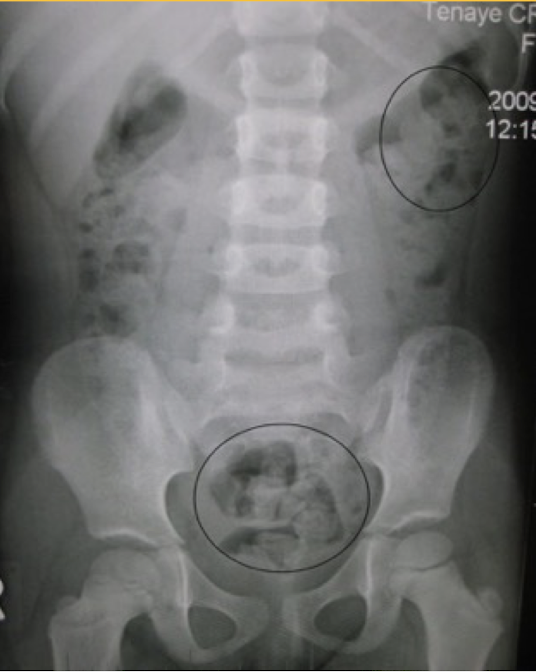
Constipation
mottled appearance of fecal material
Abdominal Radiograph
Pneumoperitonem
free air under the diaphragm
abnormal finding, perforated until proven otherwise
Abdominal Radiograph
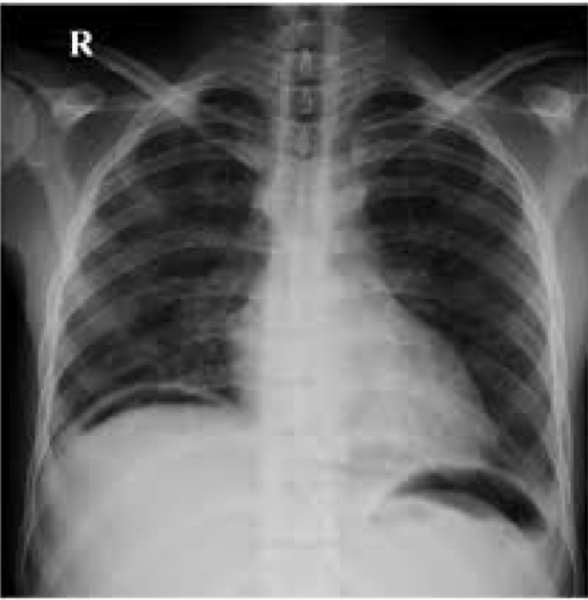
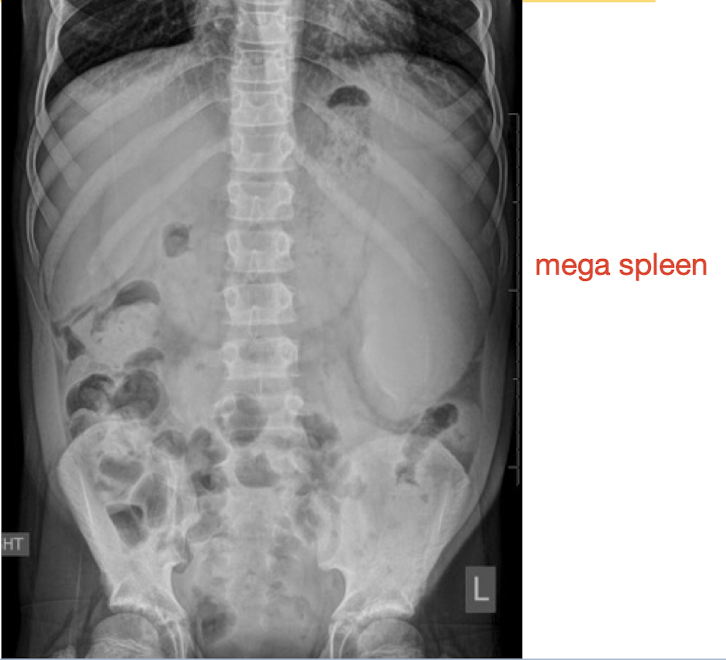
Organomegaly
abnormal finding
Abdominal Radiograph
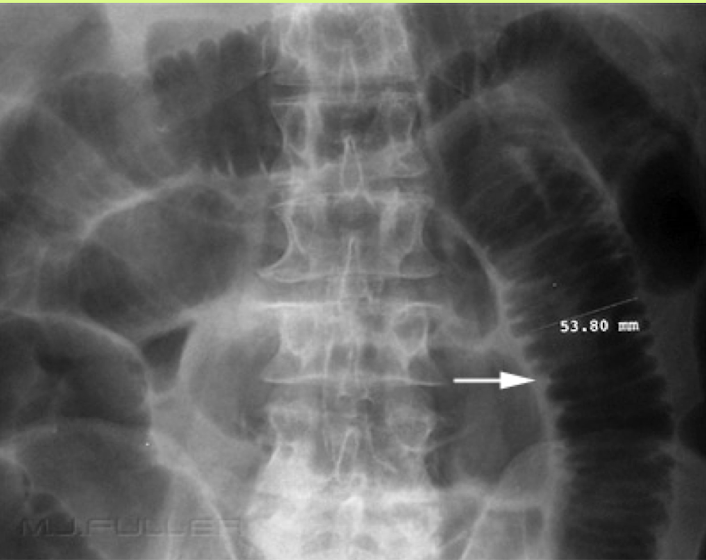
Valvulae
travel entire width of the small bowel
3cm for small bowel is normal width
Abdominal Radiograph
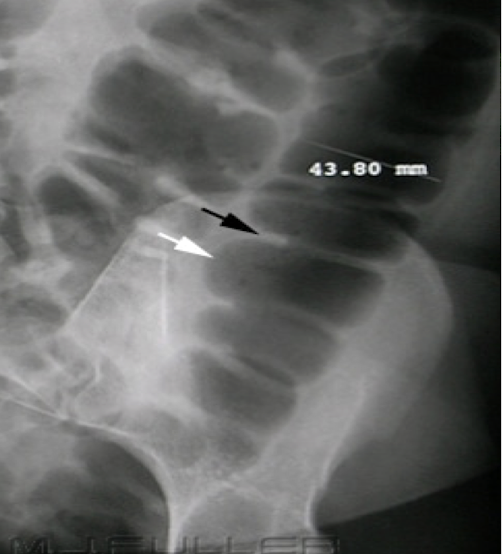
Haustra and Plicae
travel partial width of large bowel/colon
6cm for colon and 9cm for cecum is normal width
Abdominal Radiograph
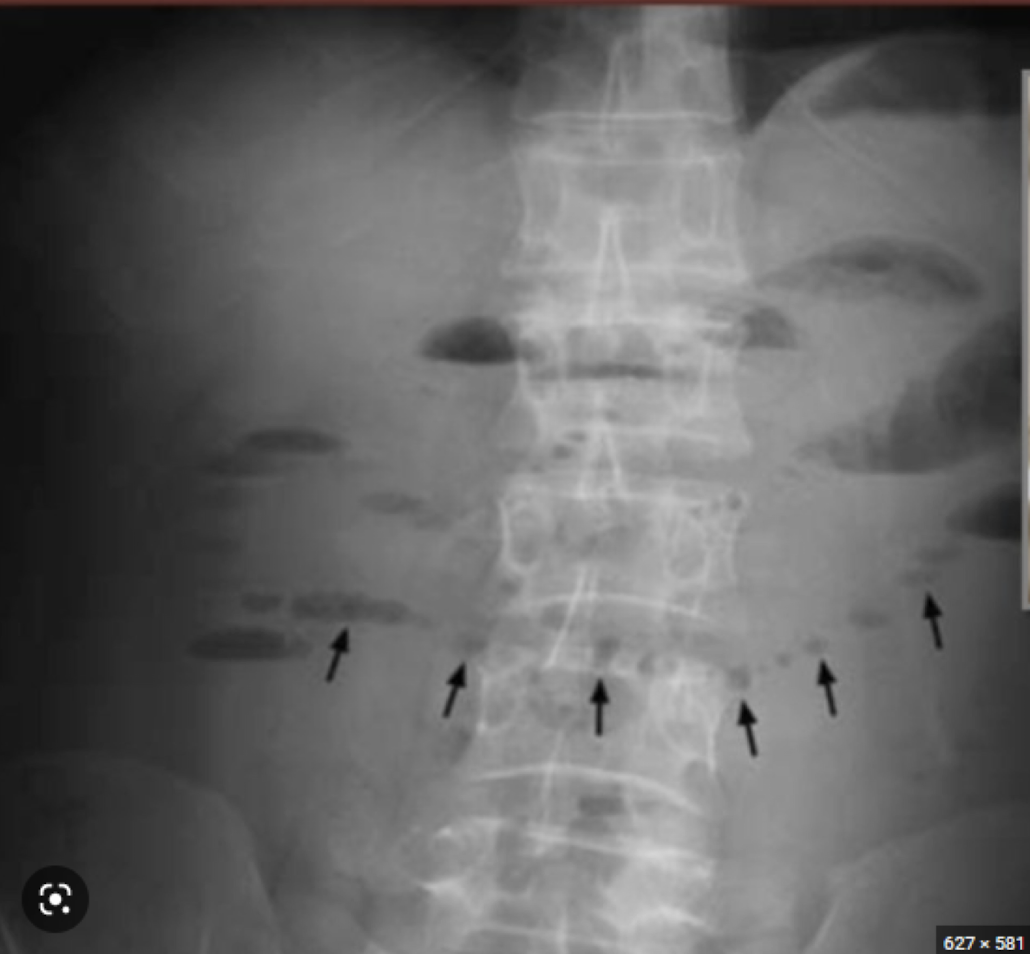
Small bowel obstruction (SBO)
dilation and multiple bubbles, air fluid levels
Abdominal Radiograph
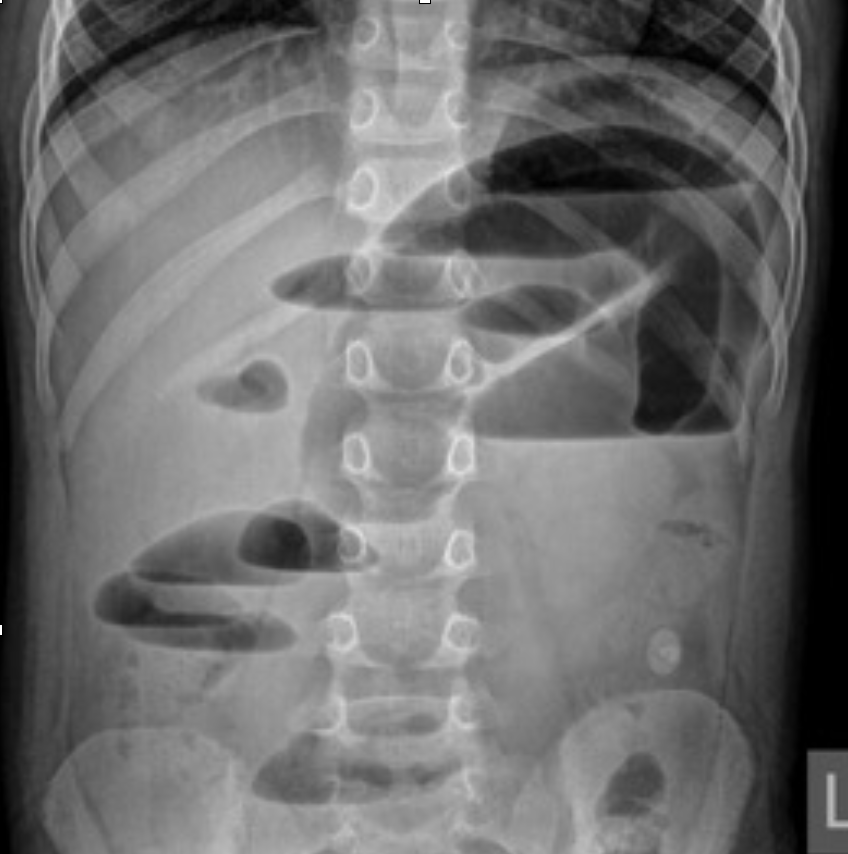
Small bowel obstruction (SBO)
“string of pearls” finding
Abdominal Radiograph
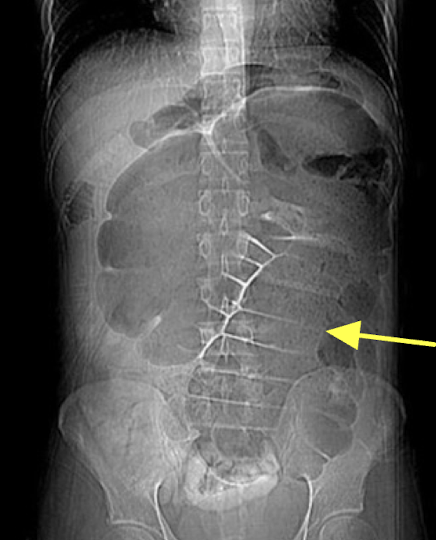
Cecal volvulus
section of twisted bowel causing obstruction and strangulation
Abdominal Radiograph
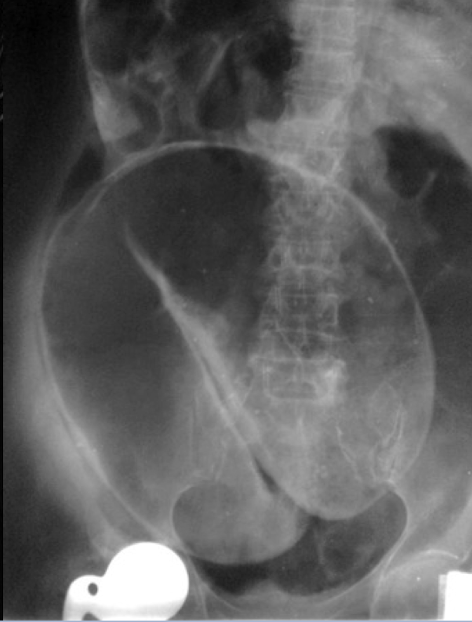
Sigmoid volvulus
“coffee bean” sign
section of twisted bowel causing obstruction and strangulation
Abdominal Radiograph
KUB (kidney, ureter & bladder)
XRAY optimized to assess the urogenital system ± GI system
Abdominal Radiograph
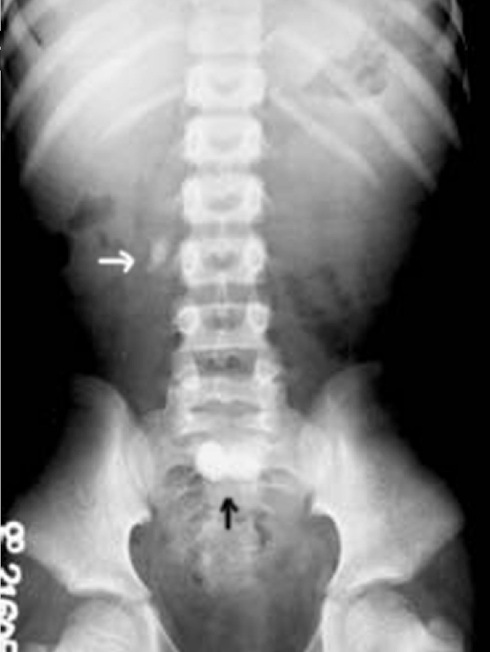
IVP (IV pyelogram)
XRAY using IV contrast material to assess kidney, ureters and bladder (less commonly used)
*CT Urogram is more common for assessing flank pain
Abdominal Radiograph
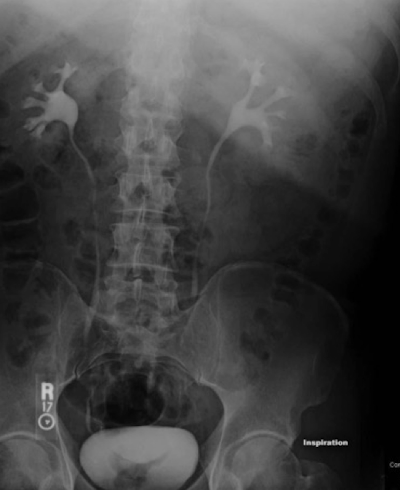
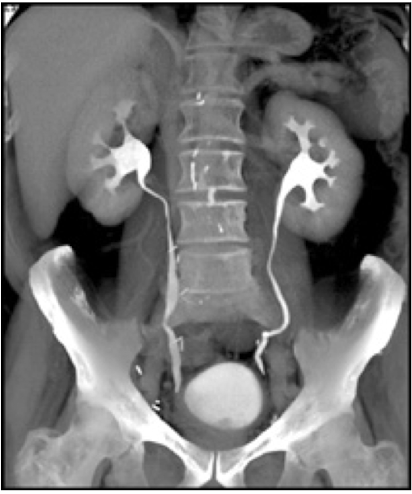
CT urography
CT scan using an IV contrast material to assess kidney, ureters, and bladder
Abdominal Radiograph
E-FAST (Extended Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma)
bedside ultrasound protocol design to detect peritoneal fluid, pericardial fluid, pneumothorax and/or hemothorax in trauma patient
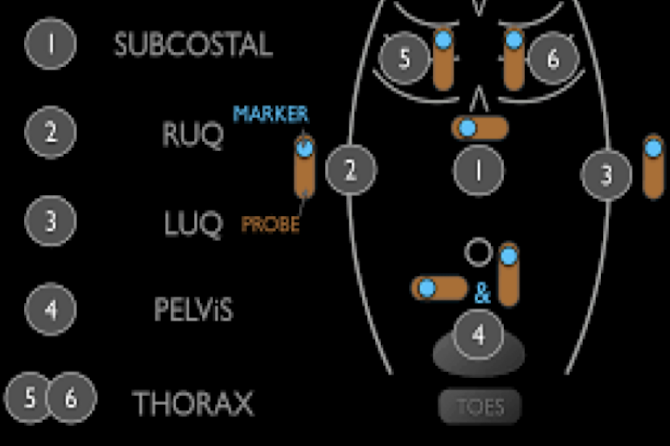
RUSH Exam
ultrasound to quickly assess any patient with undifferentiated shock and hypertension
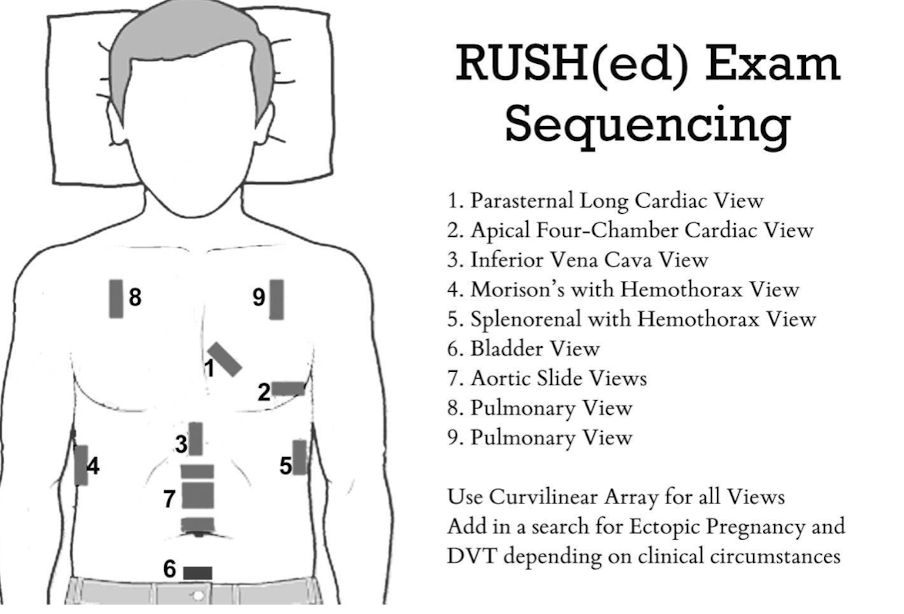
Appendix
“doughnut sign” or “bullseye sign” of ______ on ultrasound due to concentric alternating echogenic and hypoechoic bands
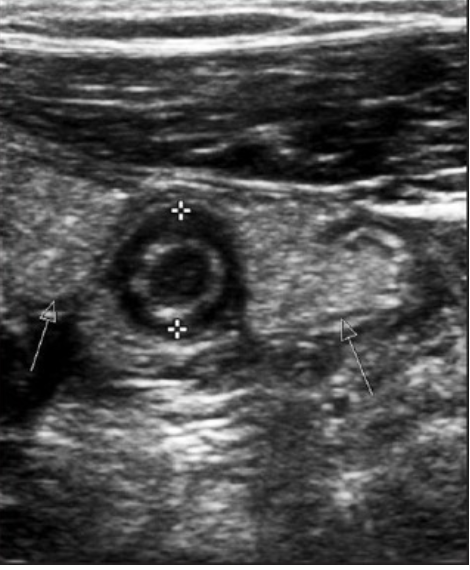
Cholelithiasis
formation of gallstones in gallbladder
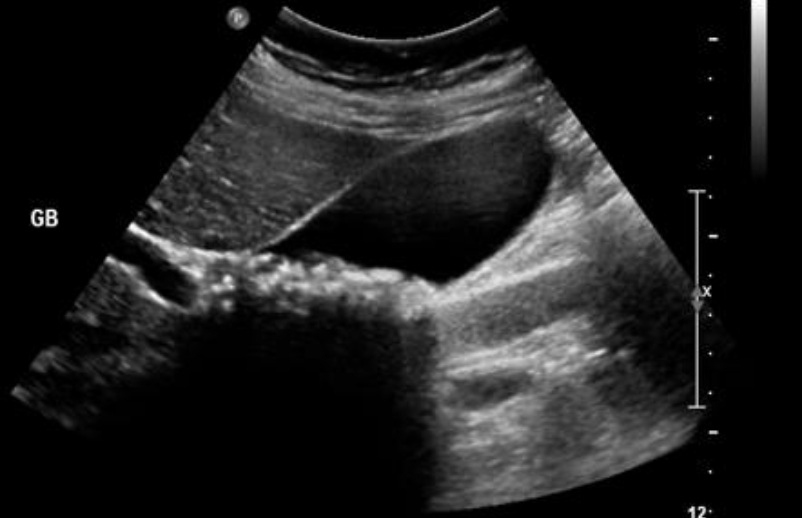
Cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder
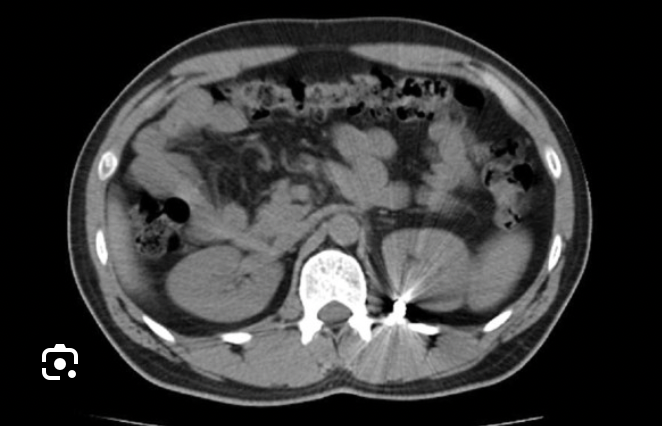
transverse
Which CT view?
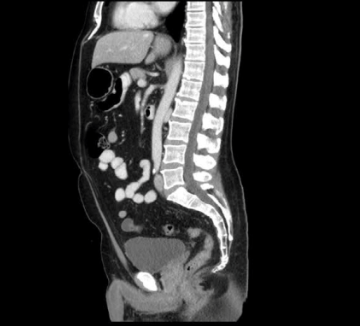
sagittal
Which CT view?
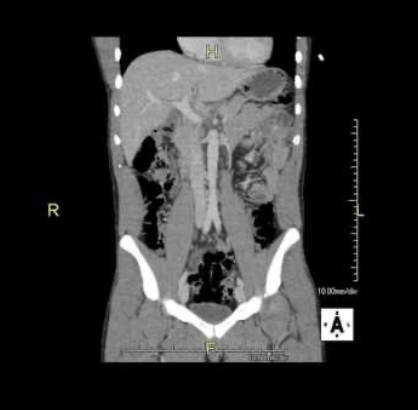
coronal
Which CT view?
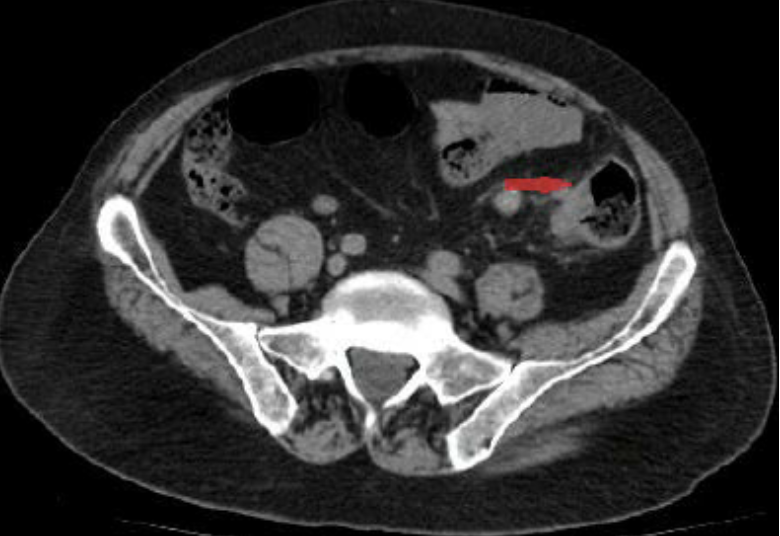
Acute appendicitis
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
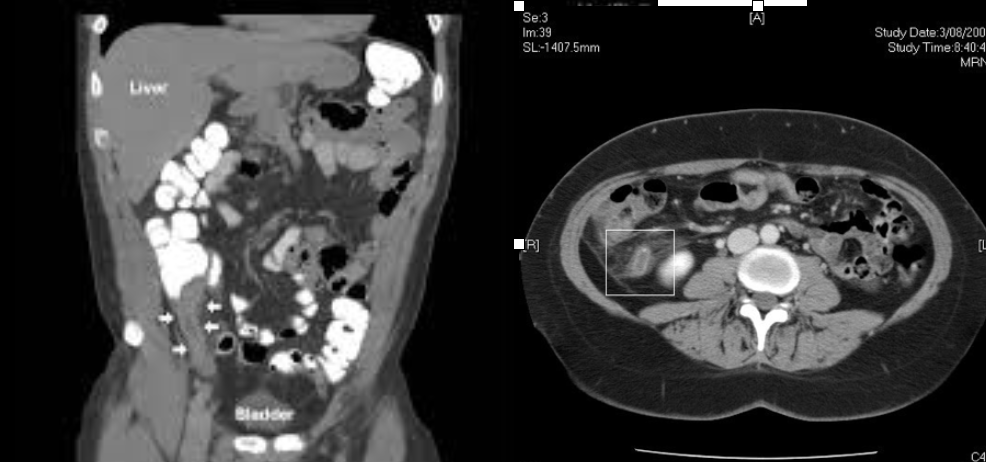
Diverticulitis
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
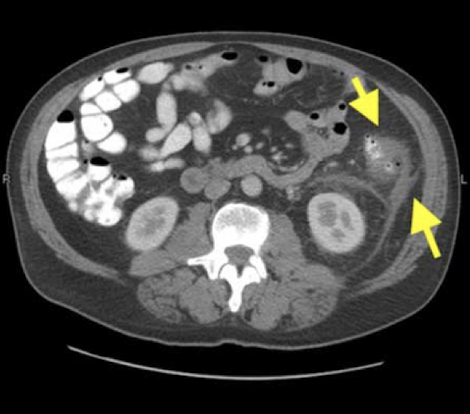
Intra-abdominal abscess
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast
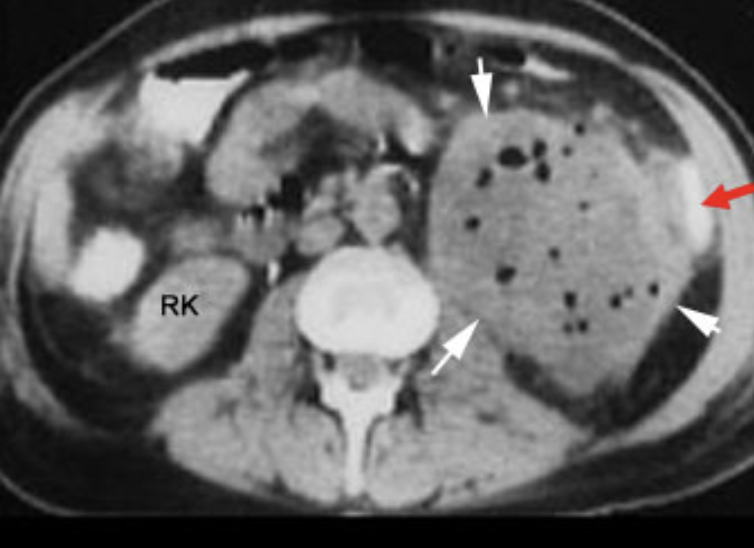
Colonic mass
CT Abdomen/Pelvis IV contrast