amines
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
primary amines
have 1 alkyl group attached
secondary amines
have 2 alkyl groups attached
tertiary amines
have 3 alkyl groups attached
how primary amines can be formed
by nucleophilic substitution between halogenoalkanes and ammonia
need excess ammonia
reaction mechanism between bromoethane and ammonia
forms primary amine
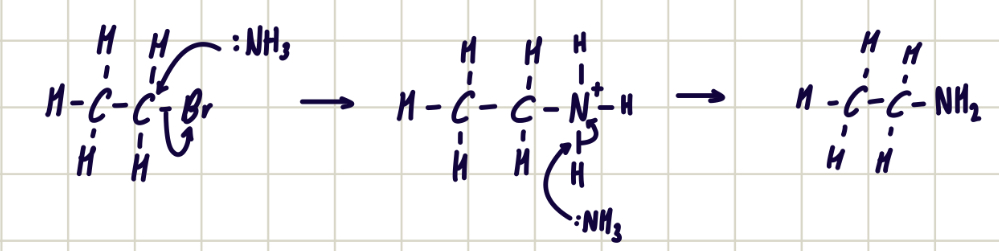
reaction mechanism between bromoethane and ethylamine
forms secondary amine
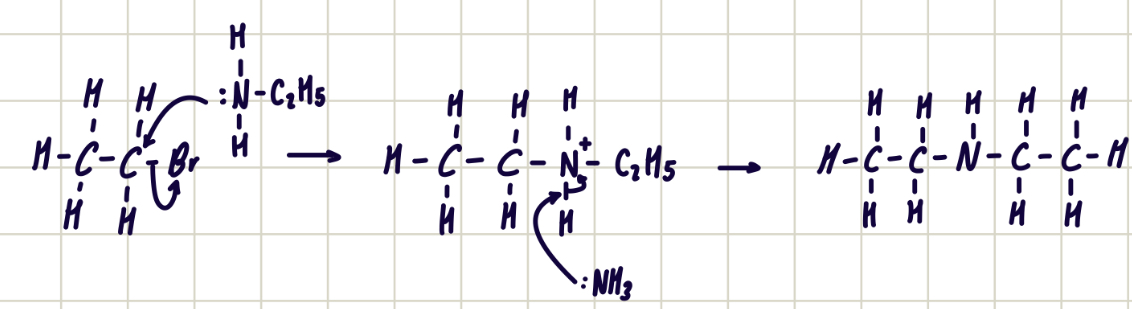
reaction mechanism between bromoethane and diethylamine
forms tertiary amine
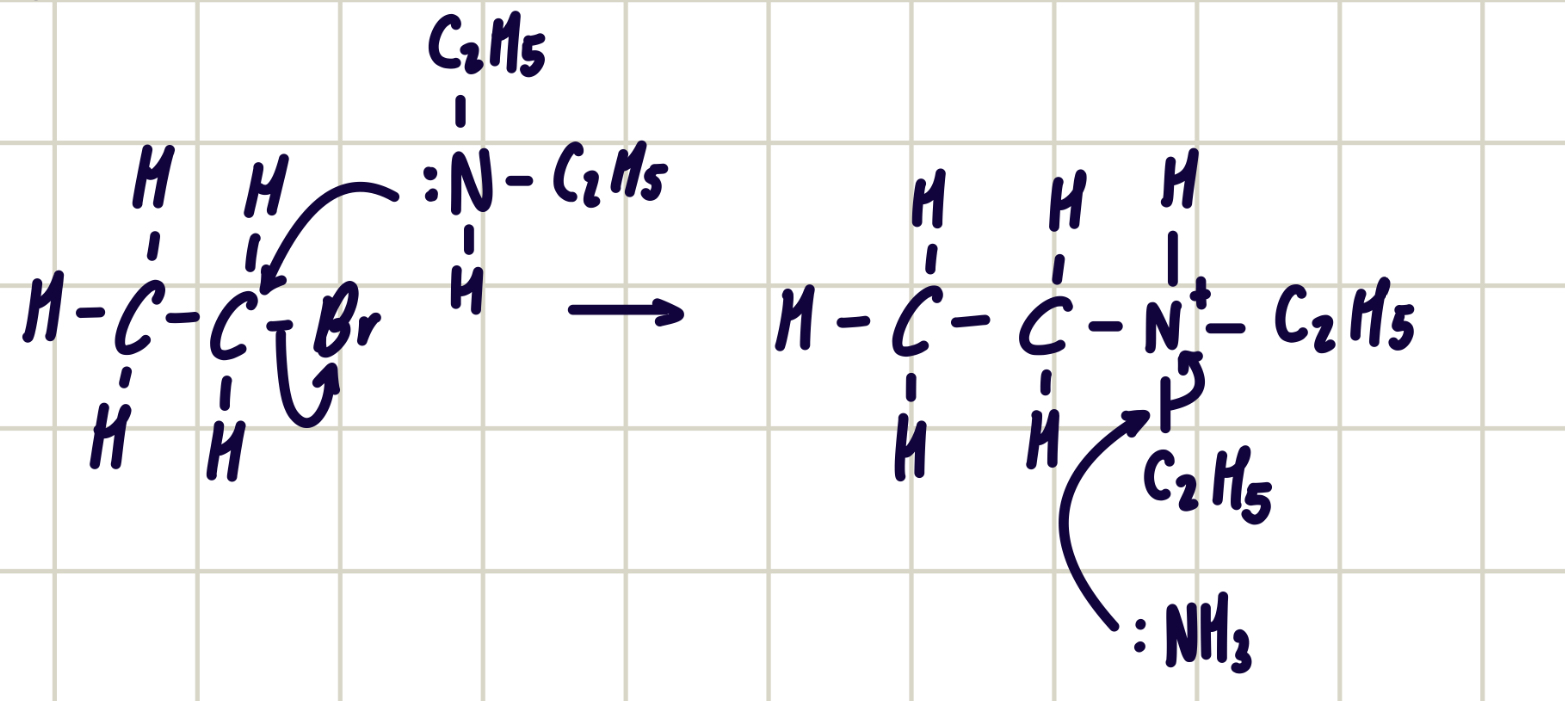
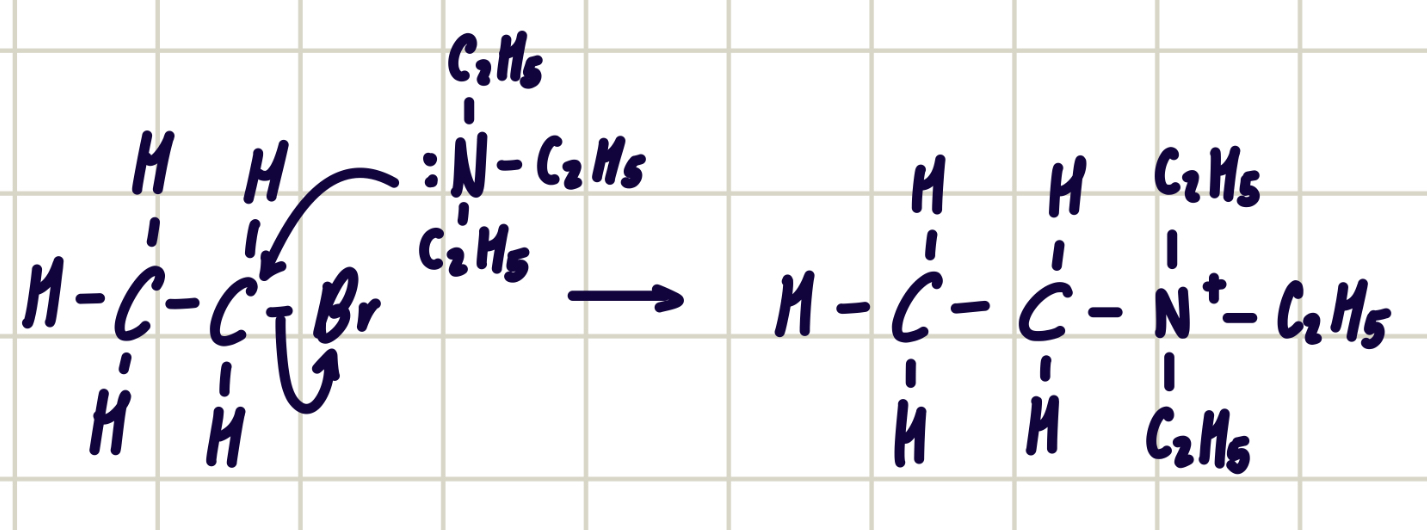
reaction mechanism between bromoethane and triethylamine
forms quaternary ammonium salt
what are quaternary salts used as?
cationic surfactants
e.g. in hair conditioner and fabric softners
preparing amines from nitriles
convert halogenoalkane to nitrile using KCN in aqueous ethanol and heat under reflux
CH₃CH₂Br + CN⁻ ———> CH₃CH₂CN + Br⁻
reduce nitrile to amine using LiALH₄ in ether
CH₃CH₂CN + 4[H] ———> CH₃CH₂CH₂NH₂
advantages and disadvantage of preparing amines from nitriles
advantage
only single product formed
disadvantages
two step reaction, therefore low yield
KCN is toxic
Disadvantages of preparing amine from halogenoalkanes
further substitution reactions occur and other products formed
impure products
reducing nitroarenes to aromatic/phenyl amines
reagent: tin catalyst and conc. HCl
conditions: heat under reflux
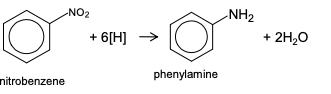
reaction of acyl chloride with primary amine
change in functional group: acyl chloride to secondary amide
reagent: primary amine
conditions: room temp.
observation: nvc
reaction mechanism of ethanoyl chloride with ethylamine
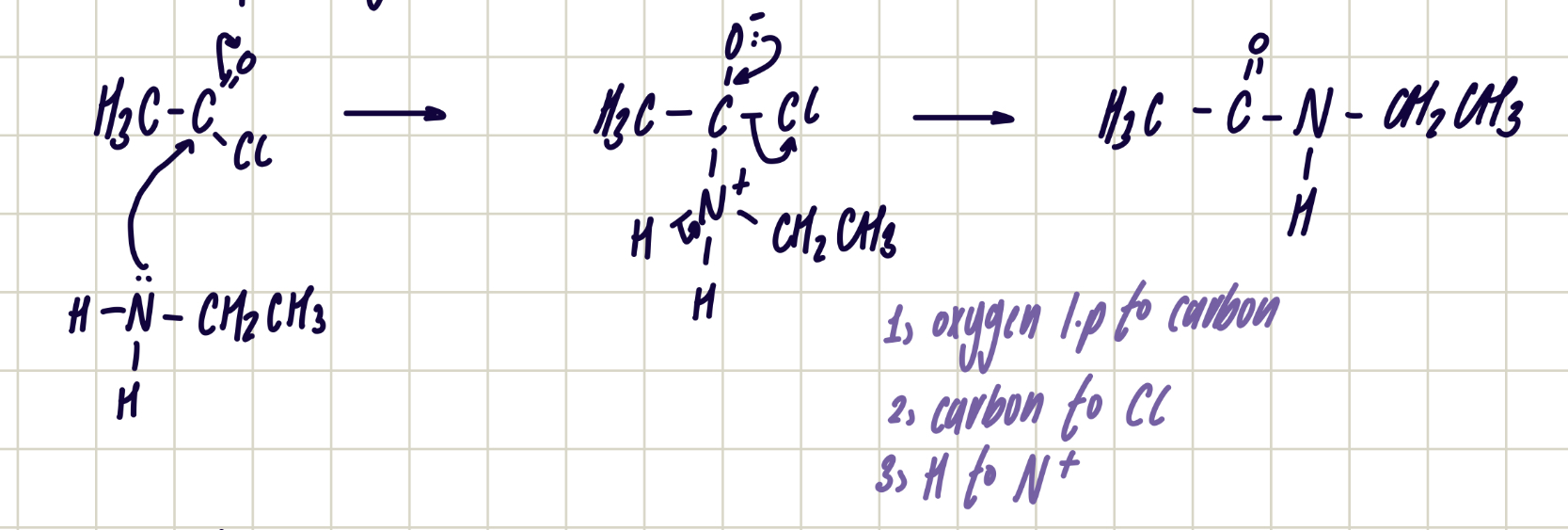
reaction of acid anhydride with primary amine
change in functional group: acid anhydride to secondary amide
reagent: primary amine
conditions: room temp.
observations: nvc
reaction equation of ethanoic anhydride and methylamine
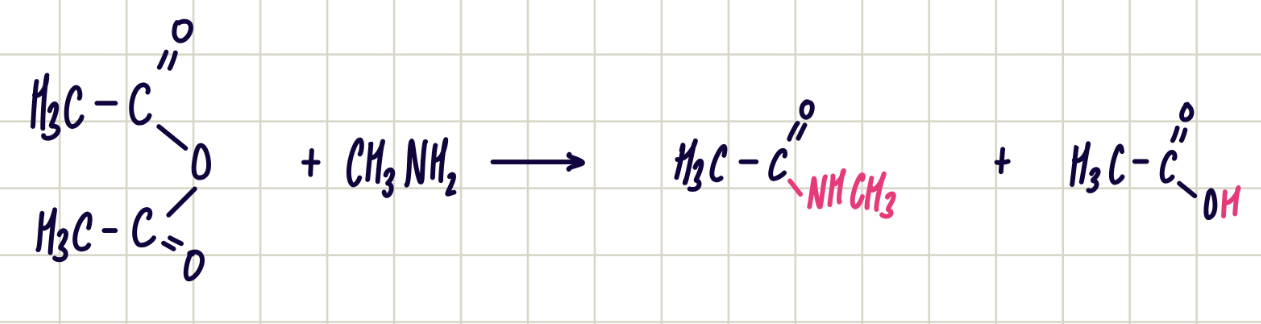
explain why aliphatic amines are stronger bases than ammonia
the alkyl groups are electron releasing and they push electrons towards N atom
inductive effect pushes electrons
positive inductive effect
therefore making lone pair of electrons on N atom more readily available to accept protons
explain why secondary amines are stronger bases than primary amines
secondary amines have more alkyl groups that are substituted onto the N
so more electron density is pushed onto the N atom
since the inductive effect of alkyl groups is greater than H atoms
positive inductive effect
therefore making the l.p of electrons on the N atom more readily available
overall order of base strength
strongest
secondary amines
primary amines
ammonia
aromatic amines
weakest
explain the base strength of aromatic amines
aromatic amines do not form basic solutions
this is bc the l.p of electrons on the N delocalise with the ring of electrons in the benzene
this means that the l.p on the N atom is less able to accept p+