Shapes of Molecules
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what are shapes of molecules determined by
number of electron pairs around the central atom
why does the largest bond angle possible exist between covalent bonds
each electron pair naturally repels
how does the presence of a lone pair reduce the angle between covalent bonds
provide additional repulsive forces
reduces bond angle by 2.5 degrees per lone pair
name all shapes of molecules
linear
bent
trigonal planar
triangular pyramid
tetrahedral
trigonal bipyramid
octahedral
number of bonding pairs and lone pairs in a linear shape
linear: 2 bonding pairs, 0 lone pairs
bond angle of a linear molecule
180
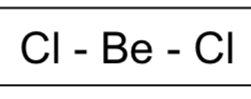
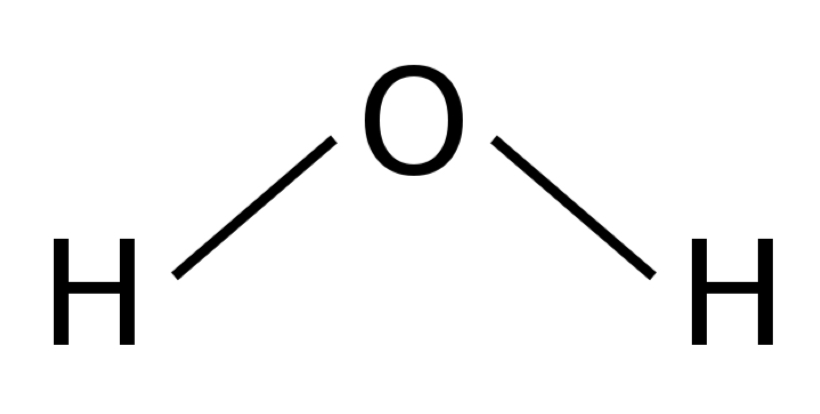
how many bonding and lone pairs are there in bent molecules
2 bonding pairs
2 lone pairs
bond angle of a bent/v-shaped molecule
104.5
(tetrahedral with 2 lone pairs)
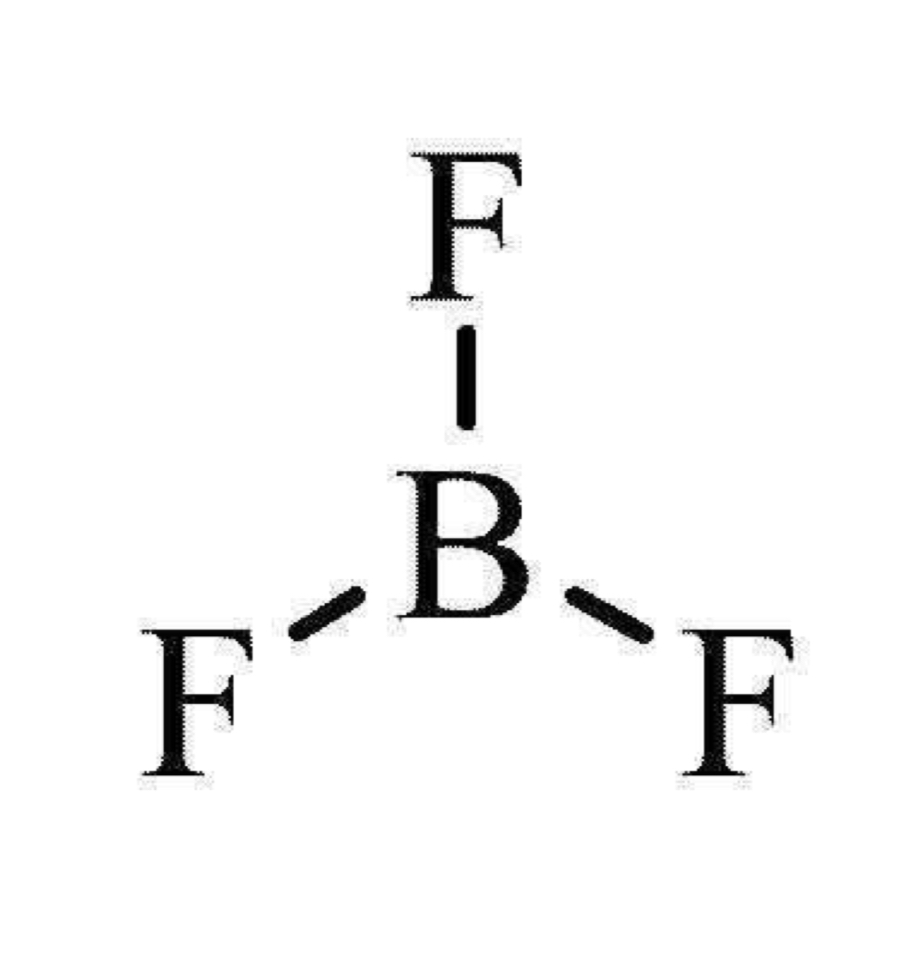
number of bonding and lone pairs in a trigonal planar molecule
3 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
bond angle of a trigonal planar
120
number of bonding and lone pairs in a triangular pyramid
3 bonding pairs
1 lone pair
bond angle of a triangular pyramid
107
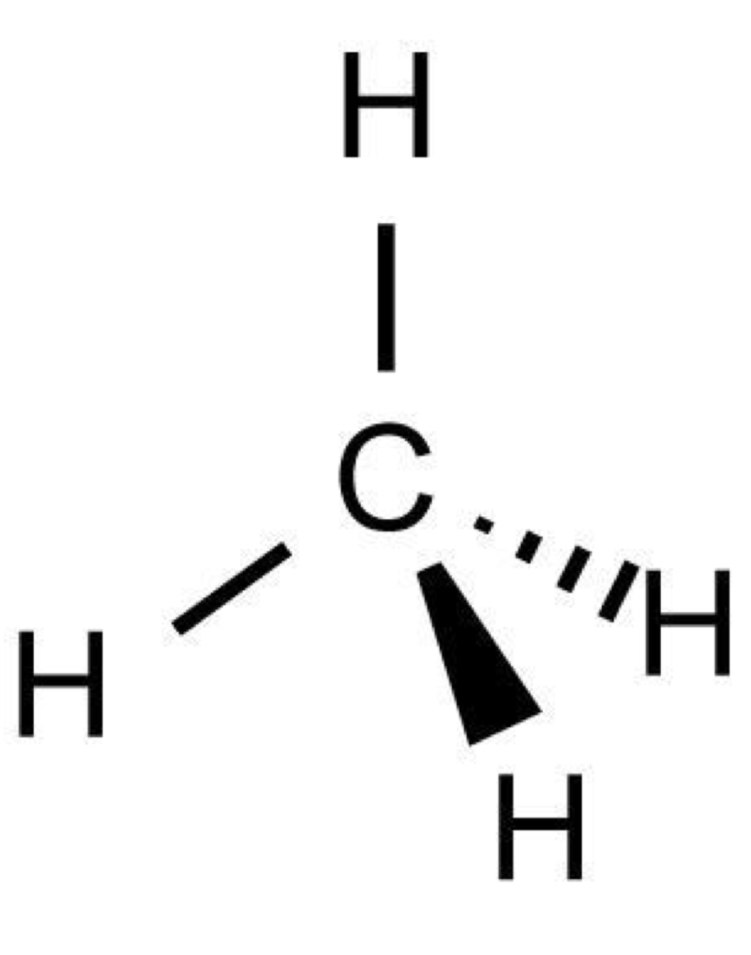
number of bonding and lone pairs in a tetrahedral
4 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
bond angle in a tetrahedral
109.5
number of bonding pairs and lone pairs in a trigonal bipyramid
5 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
bond angle in a trigonal bipyramid
90 and 120
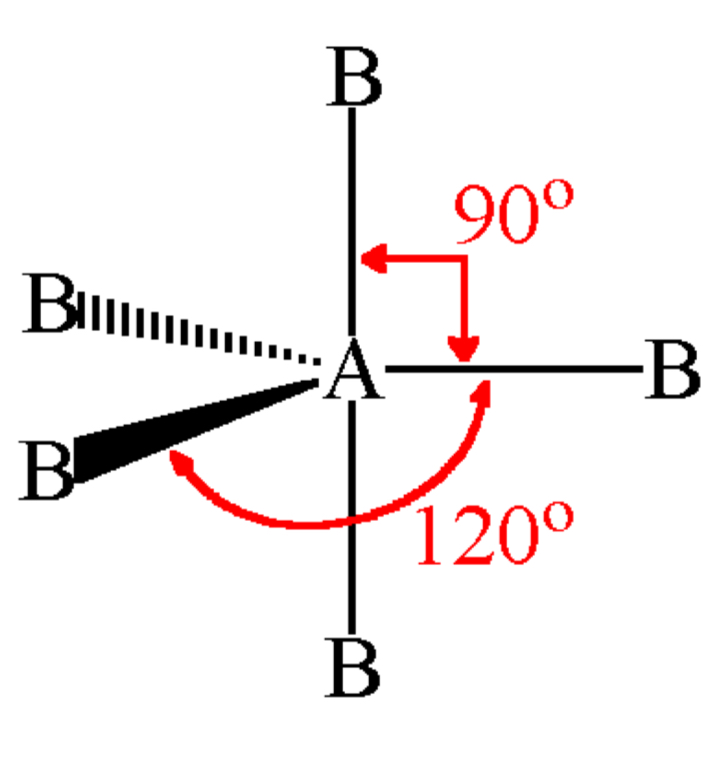
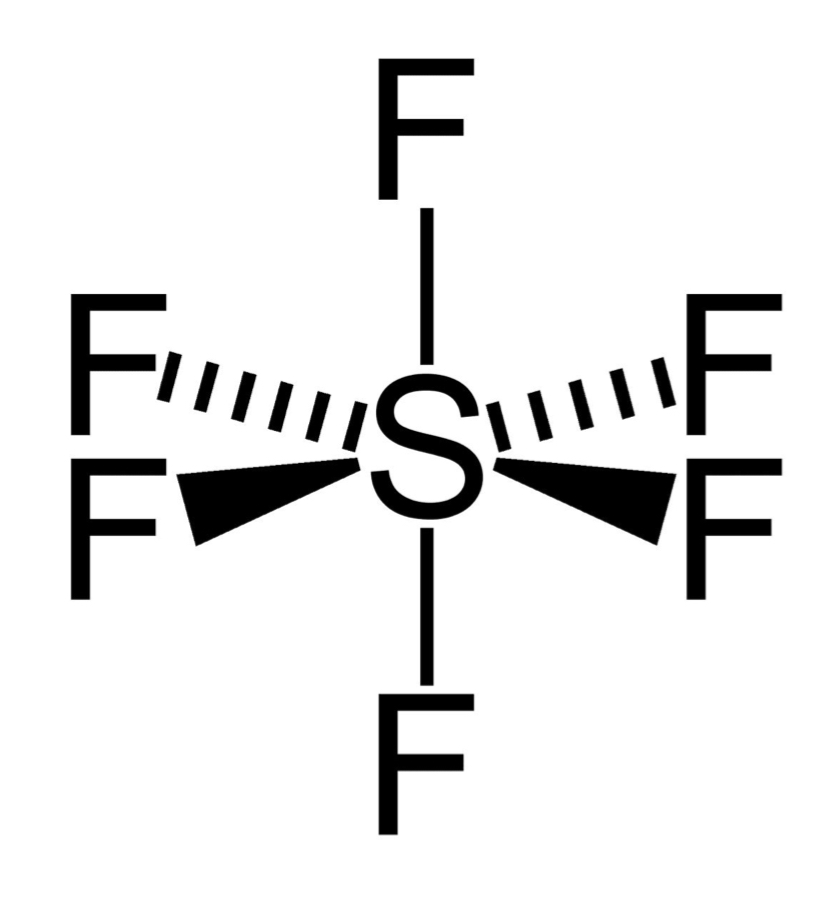
number of bonding and lone pairs in an octahedral
6 bonding pairs
0 lone pairs
bond angle of an octahedral
90
what is bond polarity
negative charge around a covalent bond is not evenly spread around the orbitals of the bonded atoms
define electronegativity
the power of an atom to attract a pair of electrons towards itself within a covalent bond
what does electronegativity depend on
size
nuclear charge
trend of electronegativity along a period
increases along a period as atomic radius decreases and atomic charge
trend of electronegativity down a group
decreases down a group as shielding and atomic radius increases
define a permanent dipole
two atoms with different electronegativities bond
more electronegative draws more of the negative charge towards itself and away from other atom
delta negative and delta positive region created
when does a polar bond form
if two atoms with different electronegativity bond
what can polar molecules with a permanent dipole align to form
a lattice of molecules, similar to an ionic lattice
when do induced dipoles form
when the electron orbitals around a molecule are influenced by another charged particle
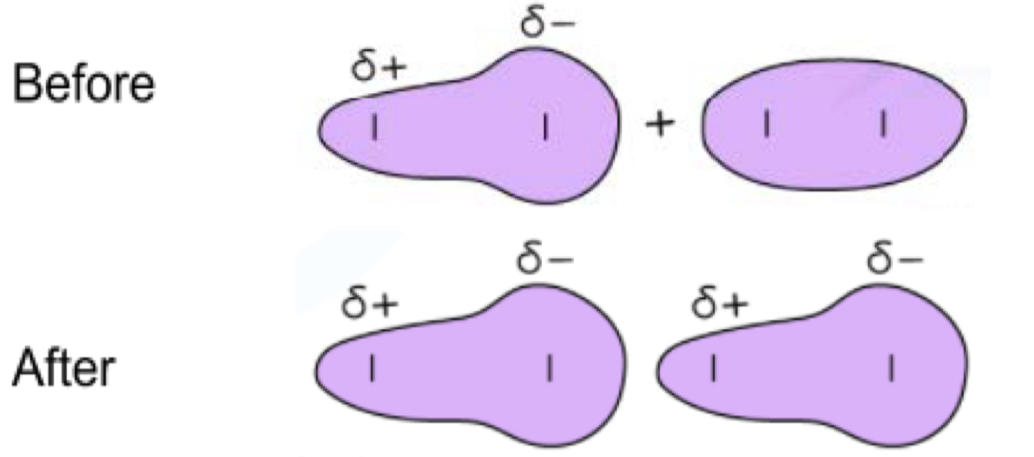
3 types of intermolecular forces
van der waals
permanent dipole
hydrogen bonding
describe van der waals forces
weakest type
acts as an induced dipole
what does the strength of van der waals forces depend on
Mr of the molecule/number of electrons
Shape
how does number of electrons impact strength of van der waals
more electrons = stronger molecular forces
more = increased polarisability of a molecule, making it more likely for temporary induced dipoles to form
how does electronegativity impact bonding
small electronegativity difference wil be purely covalent
very large difference = ionic
when does a polar covalent bond form
when the elements in the bond have different electronegativities
unequal distribution of electrons in the bond and produces a dipole
define symmetric molecules
all bonds are identical and no lone pairs
are symmetric molecules polar or non polar
non polar, even if individual bonds are polar
individual dipoles cancel out
how does shape (straight chain and branched) impact strength of van der waals
straight chain molecules = stronger than branches as they can pack closer together,
reduces distance over which the force acts
describe hydrogen bonding
strongest force
only form between hydrogen and the 3 most electronegative atoms: nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine
which atoms form hydrogen bonds
hydrogen with the most electronegative atoms:
nitrogen, oxygen and fluorine
how do hydrogen bonds form
the lone pair on the atoms (nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine) for a bond with a hydrogen atom from another molecule
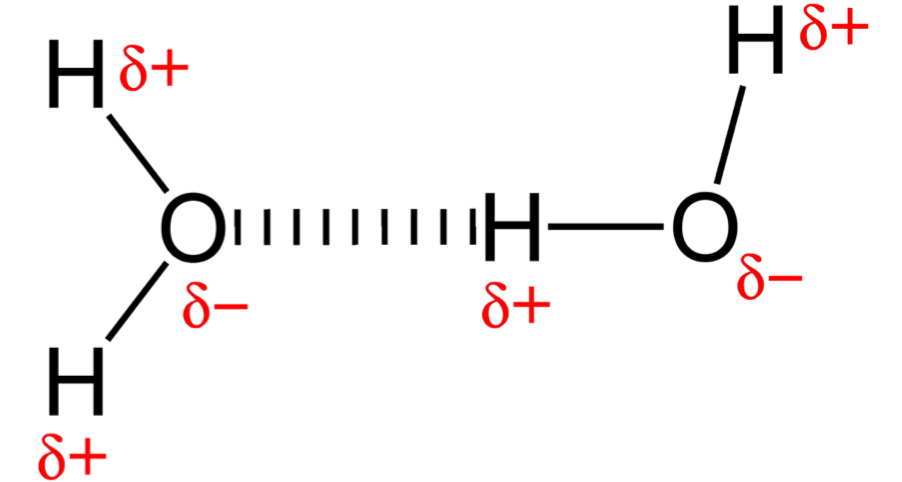
physical properties of molecules with hydrogen bonds
higher melting and boiling points