Intro to Memory
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Cognition
mental activity involving thinking, knowing, forming and recalling memories, and communicating

Memory
learning that has endured a long period of time, through storing and recalling info

Information-Processing Model
3 processes involved in forming memories
Encoding
Storage/Rehearsal
Retrieval
Encoding
getting the actual info in our brain bruh
Storage/Rehearsal
holding onto info
Retrieval
being able to recall info when it’s needed
Connectionism Model
memories are seen as products of interconnected neural pathways and networks
specific memories come for specific neural activiation
Atkinson-Shiffrin (AS) Model of Memory
Human memories have 3 separate parts
sensory memory
short-term(active/working) memory
Long-term memory
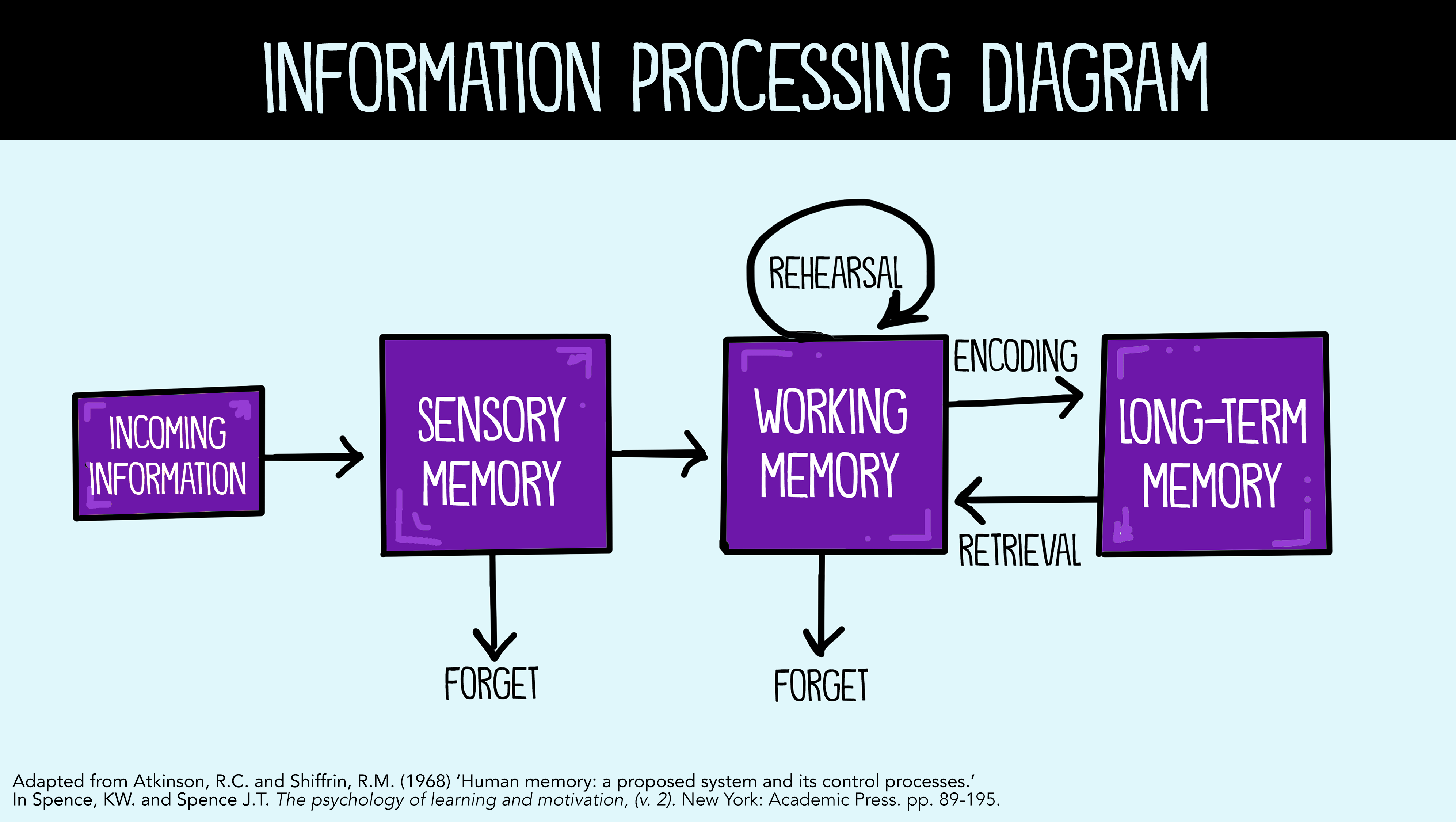
Sensory Memory
a very short recording of sensory info, which is almost forgotten immediately you’re not paying attention
Short-term (active/working) memory
memory function that can hold onto a few items pretty shortly
can be turned into long-term memory through rehearsal
no rehearsal usually = forgotten
hippocampus
Short-term memory is associated with the ?
Long-term memory
a permanent and unlimited storage for your memories
includes knowledge, skills, and experiences
typically outside of immediate thinking, but can be recalled (preconsciousness)
cerebral cortex
long-term memory is associated with the ?
Explicit (declarative) memories
The Atkinson-Shiffrin model puts an emphasize on the processing of ?
intentionally
Explicit memories are memories where you are ? recollecting
such as facts, events, and experiences
effortful processing
Explicit memories are created through ?
hippocampus, frontal lobes
Explicit memories are associated with the ? and ?
working memory (explicit)
short-term memory that allows us to hold onto limited amounts of info
actively processes
a type of explicit memory
episodic memory
long-term memory system that holds onto info about specific events (episodes) related to someone’s own life
a type of explicit memory
semantic memory
long-term memory system that holds onto general knowledge
facts
a type of explicit memories
Baddeley Model of Working Memory
An updated version of the Atkinson-Shiffrin model
adds two components
Working memory (Baddeley)
stresses the active processing in short-term memory
short-term memories are like desktops
brain processes info and links it to long-term memories
part of Baddeley Model
Automatic Processing
processing of info outside of our conscious awareness
skips the conscious encoding part of memories
part of Baddeley Model
Implicit (nondeclarative) memories
skills we acquired and classically conditioned associations
outside our awareness
difficult to explain to others
walking, balancing, riding a bike
type of automatic processing
cortical areas, cerebellum, basal ganglia
implicit memories are associated with ?, ?, and ?
Priming
automatic/unconscious processing that can speed up responses
a cue used to trigger associated concepts/memories, makes retrieval easier
type of implicit memory
Procedural memory
memory for the process of completing a task
hitting a baseball, typing, making cereal, riding a bike
after you learn it, it’s kinda hard to forget…
type of implicit memory
Classical Conditioning
memory of associations between stimuli
type of implicit memory
Selective Attention
consciously process a very limited part of incoming sensory info
everything else gets blocked out
we need to focus in on a task to complete it
not automatic
Divided Attention
involves completing tasks via auotmatic processing while completing another task at the same time
relies on automatic processing
space, time, frequency
We automatically process info such as
? (we can mentally note where we left off while reading a book)
? (we can replay events and retrace steps pretty easily)
? (keeping track of how many times something happens)
attention
We have to pay ? for our sensory memory to begin encoding
Sensory Register
holds onto a record of info received by sensory receptor cells until it’s processed, used, or discarded
there’s practically no limit, but info here is pretty useless unless it’s used in one of the 3 things named
Iconic Memory
a very short (few tenths of a second) sensory memory of visual stimuli
Echoic Memory
3 or 4 second sensory memory of auditory stimuli
7 items (plus or minus 2)
our short-term memory capacity is about ? but it disappears from our memory pretty quickly
age, intelligence
Working memory capacity varies on ?, ?, and other factors
Levels of Processing
the depth of processing affects long term-retention
Shallow Processing (maintenance rehearsal)
encoding words based on just their structure but not the actual meaning
actual appearance
color, length, font, etc
Deep Processing (elaborative rehearsal)
encoding words based on their meaning and associations between old/new knowledge
application, relationships, real-life examples, definitions
best way to hold onto long term info
Metacognition
The act of thinking about thinking
how we manage and understand our own thinking processes
Examples of Metacognition
Cognitive processes (I’m not that good at psychology)
Monitoring of cognitive processes (I’m not paying attention, so I need to pay attention)
Control of cognitive processes (I’ll use flash cards to study since they work best for me)