PATIENT FACTORS & THE FAILURE OF RESTORATIONS
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what are (the groups of) risk factors that increase the risk of a disease from recurring or that increase the risk of a treatment failing
systemic conditions that impact on oral health
inherited or acquired oral conditions
habits or behaviours
list systemic conditions impacting on oral health/ operative treatment
cardiovascular disease
diabetes mellitus
epilepsy
autoimmune conditions
chemotherapy/ radiotherapy
anti-coagulant and anti-platelet drugs
anti-resorptive drugs/ bone metabolism drugs
how does cardiovascular disease impact on oral health/ operative treatment
CVD and drugs used to manage it impact on periodontitis, LA selection, prescription of antibiotics
there is increasing evidence that CVD may impact on oral soft and hard tissue healing
how does diabetes mellitus impact on oral health/ operative treatment
well established risk factor for periodontitis
drugs used to manage DM can lead to dry mouth which increases caries risk
how does epilepsy impact on oral health/ operative treatment
epilepsy and management can lead to gingival enlargement
seizures can lead to significant stress on dental tissues and increases risk of trauma i.e. tooth fractures and luxations
how do autoimmune conditions impact on oral health/ operative treatment
some can cause dry mouth e.g. Sjogren’s syndrome
how does chemotherapy/ radiotherapy impact on oral health/ operative treatment
can cause dry mouth if in head/ neck region
chemotherapy can lead to oral sores and timing of procedures
how do anti-coagulant and anti-platelets drugs impact on oral health/ operative treatment
impact on treatment planning with extractions being contraindicated in most situations
how do anti-resorptive drugs/ bone metabolism drugs impact on oral health/ operative treatment
e.g. bisphosphonates, Denosumab
extractions are contraindicated in most situations
what needs to be taken into consideration when planning complex restorations
if it can be cleaned well by the patient - adapt OH appliances to patient
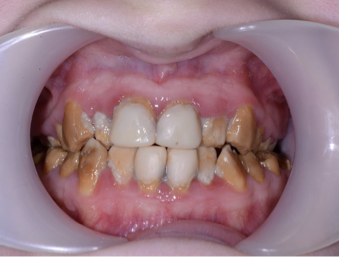
what condition is shown in this photo
amelogenesis imperfecta
what condition is shown in this photo
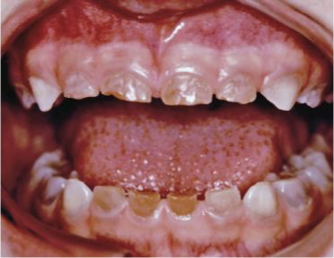
outline amelogenesis imperfecta
INHERITED/ HEREDITARY CONDITION
commonly presents with pitted and discoloured enamel
pain and sensitivity
affects all teeth in mouth so management typically involves full mouth restorations and often full coverage crowns from a young age
outline dentinogenesis imperfecta
INHERITED/ HEREDITARY CONDITION
discolouration of all teeth
all teeth appear to be significantly worn down
patients with more severe forms will typically wear dentures from a very young age
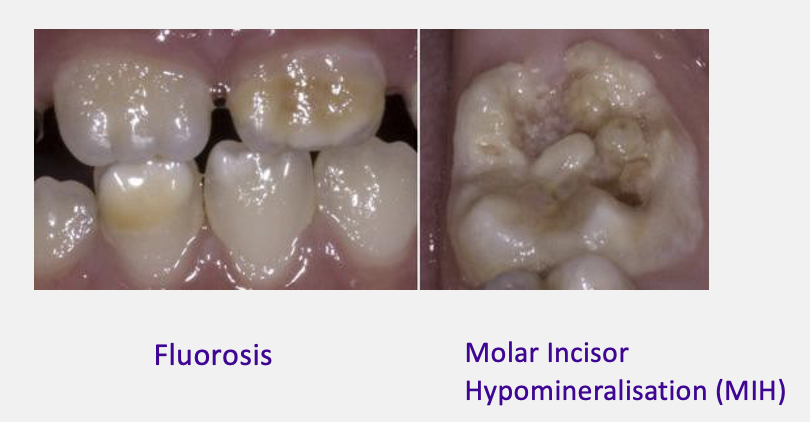
give examples of developmental oral conditions
fluorosis
molar incisor hypomineralisation (limited to first permanent molar teeth and incisors)
what occlusal factors impacts on treatment planning
anterior open bite
cross bites
heavy occlusal contacts
give examples of acquired diseases and conditions (after a tooth is fully erupted )
history of periodontal disease: gingival recession, loss of alveolar bone support, aesthetics
history of dental caries: increasing caries risk, restored teeth, impact on recall period
previous dental treatment: quality, complexity of maintenance and replacement
tooth surface loss: erosion, abrasion, attrition
what are the common causes of acquired diseases and conditions after a tooth is fully erupted
acquired diseases and conditions are typically the result of 3 common diseases of the tooth and surrounding structures:
caries
periodontitis
TSL
what are two general groups of patient factors that can cause restorations to fail
diet: cariogenic or erosive
lifestyle: impact on OH measures, smoking
how do restorations fail
secondary caries/ CARS
failure of restorative material
cracks and fractures
loss of vitality
outline secondary caries/ CARS
CARS = Caries Around a Restoration or Sealant
failure to eliminate underlying disease
continuation of the original disease
new episode of caries
outline failure of the restorative material
material thickness?
wear and tear?
occlusion?
outline cracks and fractures
cracks and fractures lead to loss of restoration or replacement of restoration
what can severe cases of cracks lead to
extraction
outline loss of vitality and its solution
pulp necrosis may occur after a previous deep lesion has been managed and restored or recurrent carious lesion may begin around an existing restoration
usual solution for loss of pulp vitality: RCT
what effect does the operator have on the longevity of restorations
assessment
diagnosis and prognosis
prevention
cavity preparation
restoration placement and finishing
maintenance

