Anatomy Ch. 10
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:26 PM on 1/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
what happens when blood is centrifuged
formed elements (eukaryocytes, leukocytes, and platelets) sink to the bottom (45%), buffy layer in middle with leukocytes and platelets, plasma is at the top (55%)
2
New cards
what is in plasma
90% water, nutrients, salt (electrolytes), respiratory gases (oxygen, co2), hormones, plasma proteins, waste products from kidneys filtering,
3
New cards
plasma proteins
most abundant substance in plasma, made by liver, 3 kinds- albumin, clotting proteins (fibrinogens), antibodies (globulins)
4
New cards
albumin
plasma protein, regulates osmotic pressure
5
New cards
fibrinogen (clotting proteins)
plasma protein, converted to fibrin during clotting process, helps stem blood loss when a blood vessel is injured
6
New cards
globulins (antibodies)
plasma proteins, help protect the body from pathogens
7
New cards
formed elements
erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets, cellular fragments
8
New cards
erythrocytes
most abundant formed element, 4-6 million per mm3, red biconcave disks, anucleate, sacs of hemoglobin, most organelles are ejected, transport oxygen to hemoglobin molecules, also move small amounts of o2
9
New cards
leukocytes
white blood cells, five kinds; neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils, 4-11,000 per mm3
10
New cards
platelets
50-500,000 per mm3, irregularly shaped deep purple cell fragments, needed for normal blood clotting, initiate clotting cascade by clinging to torn area, help control blood loss from broken blood vessels
11
New cards
hematocrit
the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the total volume of blood
12
New cards
average number of hemoglobin
250 million per erythrocyte
13
New cards
red blood cell disorders
anemia, sickle cell anemia, polycythemia
14
New cards
anemia
decrease in oxygen-carrying ability of blood, 3 types- decrease in RBC \#, inadequate hemoglobin content in RBC, abnormal hemoglobin in RBC
15
New cards
sickle cell anemia
abnormally shaped hemoglobin in RBC
16
New cards
polycythemia
excessive or abnormal increase in number of erythrocytes
17
New cards
hemoglobin
iron containing protein, binds strongly but can be reversed to oxygen, has four binding sites for oxygen, each erythrocyte has 250 million, normal blood has 12-18 g per 100 ml of blood
18
New cards
types of anemia from decrease in RBC
hemorrhagic anemia, hemolytic anemia, pernicious anemia, aplastic anemia
19
New cards
iron deficiency anemia
inadequate hemoglobin content in RBC
20
New cards
positive chemotaxis
response of leukocytes to chemicals released by damaged tissues
21
New cards
leukocytosis
WBC above 11,000 leukocytes per mm3, usually indicates an infection
22
New cards
leukopenia
abnormally low leukocyte level, commonly caused by certain drugs like corticosteroids or chemotherapy
23
New cards
leukemia
excessive WBC causes bone marrow to become dangerous
24
New cards
granulocytes
granules in cytoplasm, lobed nuclei; neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils
25
New cards
agranulocytes
no granules, spherical, oval, or kidney shaped nuclei; lymphocytes and monocytes
26
New cards
never let monkeys eat bananas
list of WBC from most to least abundant; neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
27
New cards
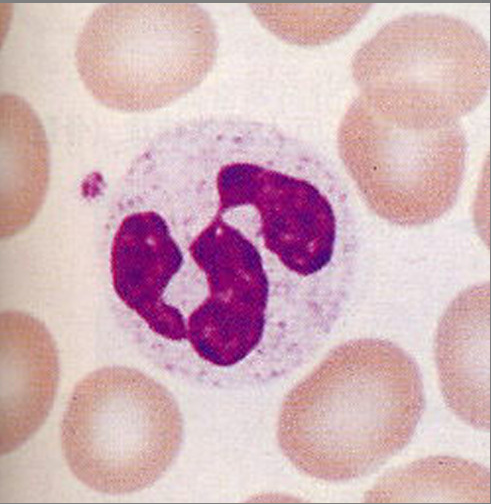
neutrophils
multilobed nucleus with fine granules, destroy infection by ingesting them and killing them
28
New cards
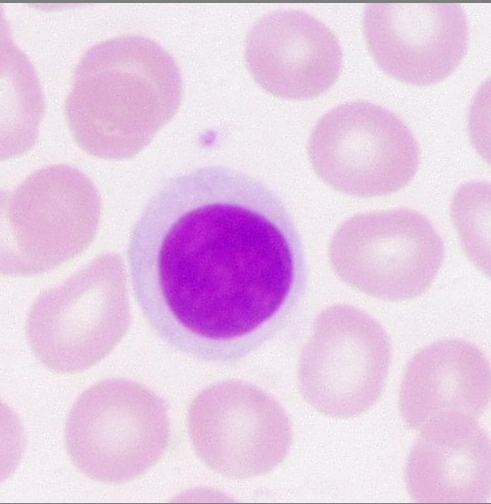
lymphocytes
part of immune system, produces antibodies to fight infection
29
New cards
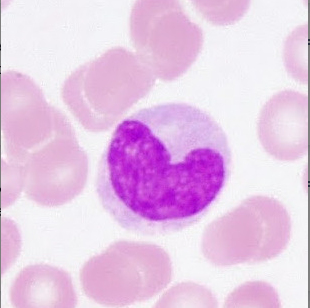
monocytes
agranular leukocyte that can migrate into tissues and transform into a macrophage.
30
New cards
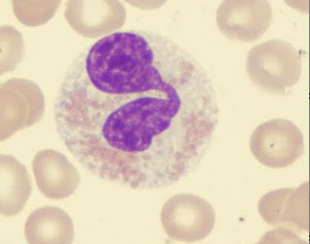
eosinophils
large red cytoplasmic granules, found in response to allergies and worms
31
New cards
basophils
have histamine containing granules, initiate inflammation
32
New cards
hematopoiesis
blood cell formation, occurs in red bone marrow, all blood cells are derived from a hemocytoblast (common stem cell), lymphoid cells produce lymphocytes, myeloid stem cells produce everything else
33
New cards
formation of red blood cells
formation happens when erythrocytes are unable to grow, divide, or synthesize proteins (100-120 days), then are eliminated by the phagocytes in the liver and spleen, they are then replaced by division of hemocytoblasts in the red bone marrow
34
New cards
how is the rate of formation of red blood cells controlled
erythropoietin, a hormone produced by kidneys as a response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood, homeostasis is maintained by a negative feedback from blood oxygen levels
35
New cards
how are platelets formed
produced by cell fragments from a hormone called thrombopoietin controlling the production
36
New cards
thrombocytopenia
a bleeding disorder in which platelets are deficient, even normal movements can cause bleeding from small blood vessels that require platelets for clotting
37
New cards
when does shock begin in blood loss
15-30% causes weakness, over 30% causes hypovolemic shock
38
New cards
thrombus
a clot in an unbroken blood vessel, can potentially be deadly if it is in the heart area
39
New cards
embolus
thrombus that breaks away into the blood stream, can clog vessels in critical areas like the brain
40
New cards
hemophilia
hereditary bleeding disorder, noraml clotting factors are missing
41
New cards
ABO blood group
based on presence/absence of two antigens; type A or type B, if someone has neither they are called blood type O
42
New cards
agglutination
how blood is typed, put antibodies in a sample of blood, if the blood clumps up then they have that antigen in their body
43
New cards
antibody
part of immune system, searches for antigens, if they are bad then an immune response is triggered
44
New cards
antigen
marker on outside of cell, tells "what am i :)?"
45
New cards
universal donor
type O; they have no antigens and therefore cannot trigger any antibodies in other bodies
46
New cards
universal recipient
type AB; they have all antigens so no antibodies in their body are triggered
47
New cards
cross matching
testing for agglutination of donor RBCs by the recipients serum and vice versa
48
New cards
hemolytic disease of newborn
in second pregnance if the mother if Rh-, and the baby is Rh+, the mothers immune system creates antibodies to attack the second babies Rh+ blood
49
New cards
physiologic jaundice
in infants when the liver cannot rid the body of hemoglobin breakdown fast enough
50
New cards
Rh blood group
named by presence or absence of one of eight Rh antigens (agglutinogen D) that was in Rhesus monkeys, Rh+ blood doesnt make antibodies, Rh- blood does, but only after it is exposed to Rh+
51
New cards
RhoGam
shot given to pregnant mothers to prevent buildup of anti-Rh+ antibodies when the baby is Rh+ and mother is Rh-
52
New cards
hemostasis
vascular spasms contract blood vessel, platelets stick to damaged site on endothelium, they then release serotonin which attracts more platelets to form a platelet plug, then PF3 is released from platelets, tissue factor in damaged tissue and calcium and other clotting factors in blood plasma are released that create the prothrombin activator, which converts prothrombin into thrombin, which then joins soluble fibrinogen that converts into insoluble fibrin which forms the mesh