Chapter 9 - Foundations of group behavior
Defining and classifying groups
- @@Group@@: two or more individuals, interacting and interdependent, who have come together to achieve particular objectives.
- @@Formal group@@: designated work group defined by an organization’s structure.
- @@Informal group@@: group that is neither formally structured nor organizationally determined, such a group appears in response to the need for social contact.
- Why do people form groups?
- @@Social identity theory@@: perspective that considers when and why individuals consider themselves members of groups.
- @@In-group favoritism@@: perspective in which we see members of our in-group as better than other people and not people in our group as all the same.
Stages of group development
@@Five-stage group-development model@@: five distinct stages groups go through; forming, storming, norming, performing and adjourning.
- Forming stage: first stage in group development characterized by much uncertainty.
- Storming stage: second stage in group development characterized by intra-group conflict.
- Norming stage: third stage in group development characterized by close relationships and cohesiveness.
- Performing stage: fourth stage in group development, during which the group is fully functional.
- Adjourning stage: final stage in group development for temporary groups, characterized by concern with wrapping up activities rather than task performance.
Alternative model for temporary groups with deadlines
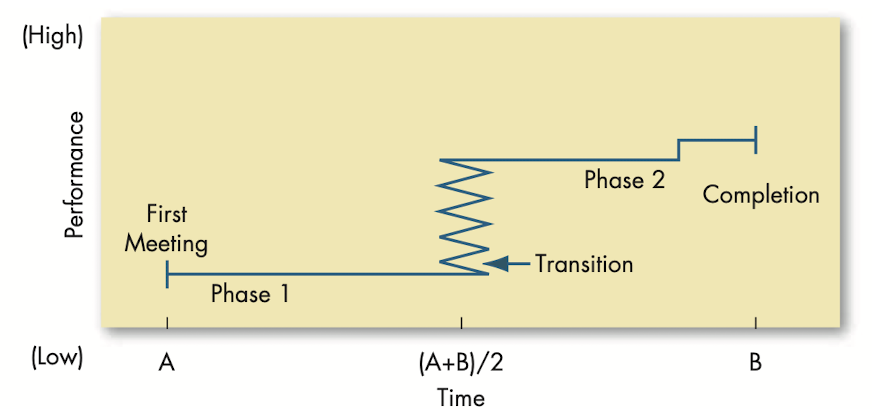
- @@Punctuated-equilibrium model@@: set of phases that temporary groups go through that involves transitions between inertia and activity.
Group properties: roles, norms, status, size, cohesiveness and diversity
- Group property 1: roles
- @@Role@@: set of expected behavior patterns attributed to someone occupying a given position in a social unit.
- @@Role perception@@: individual’s view of how he/she is supposed to act in a given situation.
- @@Role expectations@@: how other believe a person should act in a given situation.
- @@Psychological contract@@: unwritten agreement that sets out what management expects from an employee and vice versa.
- @@Role conflict@@: situation in which an individual is confronted by divergent role expectations.
- Group property 2: norms
- @@Norms@@: acceptable standards of behavior within a group that are shared by the groups members.
- @@Performance norms@@: level of output, time constraints.
- @@Appearance norms@@: dress code.
- @@Social arrangement norms@@: ability to form friendships within the workplace.
- @@Resource allocation norms@@: assignment of challenging jobs.
- The Hawthorne Studies concluded that the performance of individuals within the workplace is strongly influenced by work norms.
- @@Conformity@@: phenomenon of adjusting the behavior of an individual to align with the norms of the group.
- @@Reference groups@@: significant groups to which individuals belong or wish to belong and with whose work norms individuals are willing to conform.
- @@Deviant workplace behavior@@: voluntary behavior that violates significantly organizational norms.
- Group property 3: status
- @@Status characteristics theory@@: theory which states that differences in status characteristics create status hierarchies within groups.
- Group property 4: size
- @@Social loafing@@: tendency of individuals to extend less effort when they work collectively, then when they work individually.
- Group property 5: cohesiveness
- @@Cohesiveness@@: degree to which group members are attracted to each other and are motivated to stay in the group.
- Group property 6: diversity
- @@Diversity@@: extent to which members of a group are similar to, or different from another.
Group decision-making
- @@Groupthink@@: phenomenon in which norm for consensus overrides the realistic appraisal of alternative courses of action.
- @@Group-shift@@: phenomenon of changing the level of risk of a decision towards greater risk/conservatism.
- Group decision making techniques
- @@Interacting groups@@: typical groups in which members interact with each other face-to-face.
- @@Brainstorming@@: idea-generation process that specifically encourages any and all alternatives while withholding any criticism of those alternatives.
- @@Nominal group technique@@: group decision-making method in which individual members meet face-to-face to pool their judgements in a systematic but independent fashion.