Midterm Reviewer - Pre Calculus
LESSON 1: Conic Section (Conics) |
|---|
Conic Section
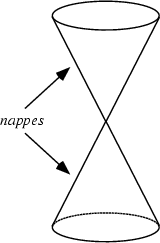
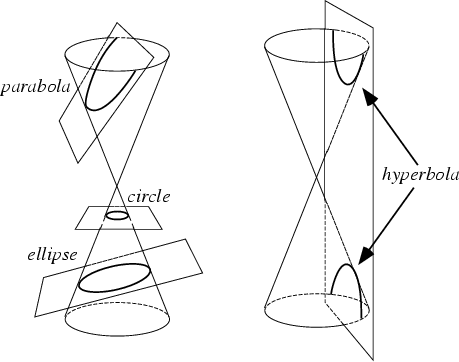
- These are generated by intersections of a plane with one or two nappes of a cone.
- Depending on the plane's angle with respect to the cone, a conic section may be a circle. A parabola, ellipse, and hyperbola. These are also called non-degenerate conics.
Non-degenerate Conics
|
|---|
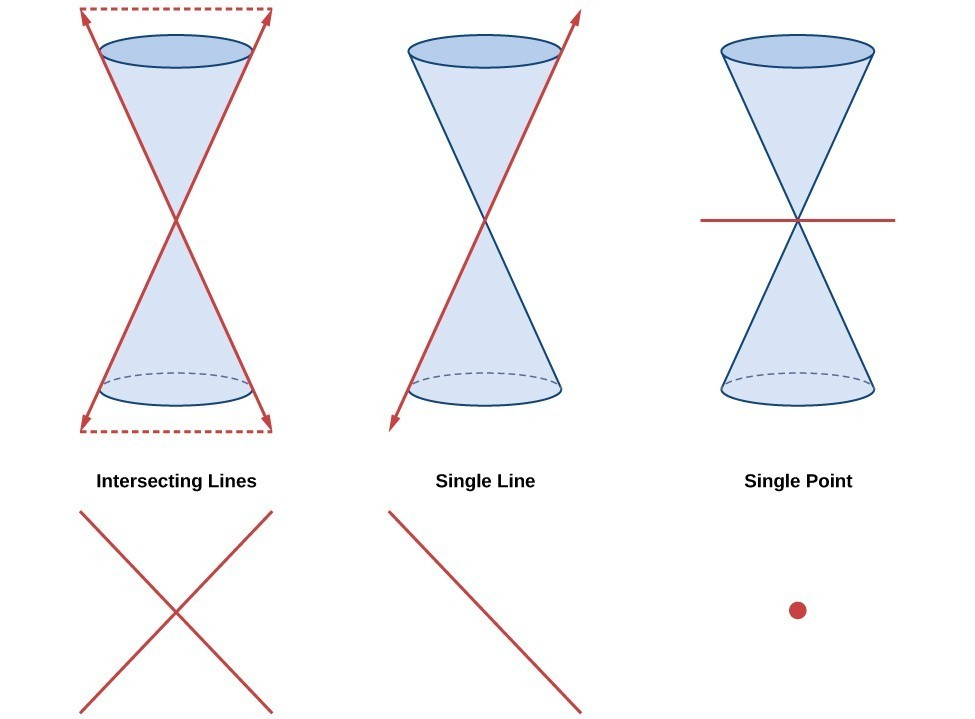
Degenerate Conics
- A degenerate conic results when a plane interests the double cone and passes through the apex
- Depending on the angle of the plane, three types of degenerate conic sections are possible: a point, a line, or two intersecting lines.
![]()
![]()
![]()
General Form of Non-degenerate Conics
- A conic section has the general form
- Where A, B, and C are not all zero,
- When the coefficient B is nonzero, it means that the graph of the conic is rotated.
- Note that in the general form of nondegenerate conics - no rotation, B = 0, A and C are real numbers, and A and C cannot both be zero at the same time.
Conic Sections | Coefficient |
|---|---|
Circle | A = C ≠ 0 |
Parabola | AC = 0 |
Ellipse | AC > 0 |
Hyberbola | AC < 0 |
Examples:
|
|---|
Circle
- A circle is the set of all points in a plane that are equidistant from the fixed point called the center of the circle.
- The constant distance between the center and any point on the circle is called the radius.
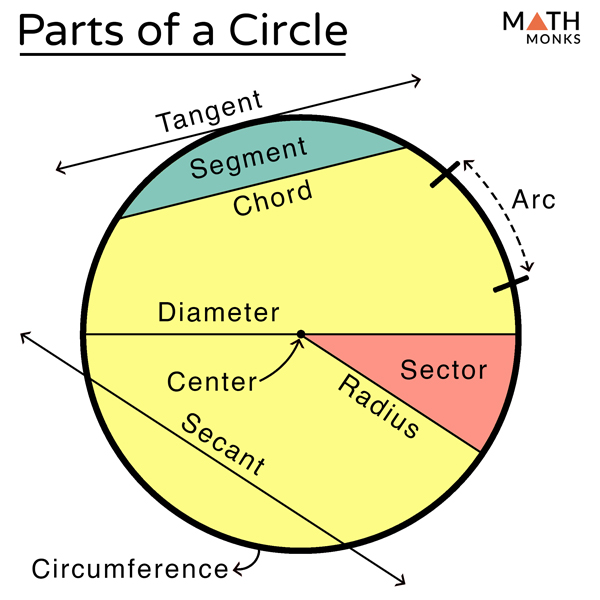
Arc - Is a portion of the circumference Chord - A chord connects 2 points on the circle. A Line Segment, a line has no boundaries. It ends at 2 points on the circle. Diameter - A diameter is a chord because it connects 2 points in the circle. It is called the longest circle, the difference between the diameter and chord is that the diameter passes through the center. Radius - Is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its circumference. Usually denoted by "R" or "r". Half the diameter. Secant Line - A straight line that intersects a circle in two points Tangent Line - A line that touches the circle at a single point. Sector - A portion of the area of the circle. The region bounded by an arc of the circle to the two radii to the arc’s endpoint |
|---|
Equations of a Circle
A circle with its center at the origin, (0,0) and radius r has an equation,
A circle with its center at (h, k) and radius r has an equation,
General form of the equation
Midpoint Formula:
Examples:
LESSON 2 : CONIC SECTIONS: PARABOLA |
|---|
Definition of Parabola
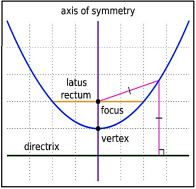
- A parabola is the locus of all points in the plane whose distances from a fixed point F and a fixed line l (not passing through F) are the same. The fixed point is called the focus, while the fixed line is called the directrix.
- A parabola always opens in the direction where the focus is situated. The focus is always on the concave side (the “inside”, the enclosing side).
- The line that passes through the focus and is perpendicular to the directrix is called the axis of symmetry of the parabola. A parabola is always symmetric about its axis. Also, the axis will always hit the parabola at exactly one point, the vertex.
- Latus Rectum is a line segment that passes through a focus, perpendicular to the axis of symmetry.
Equations of a Parabola
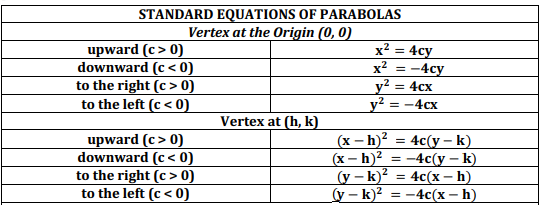
Focus = (h, k + c) Directrix = y = k - c
Axis of symmetry = X = h 4c = C/4 2c = 2(C)
Endpoints:
Lr1 = (h + 2c, k + c)
Lr2 = (h - 2c, k + c)
4c = the length of the latus rectum c = the distance from the vertex to the focus and from the vertex to the directrix 2c = the distance from the focus to the endpoints of the latus rectum |
|---|
Examples:
LESSON 3: CONIC SECTIONS: ELLIPSE |
|---|
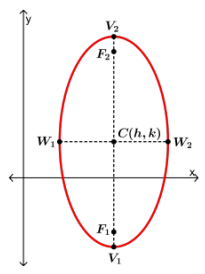
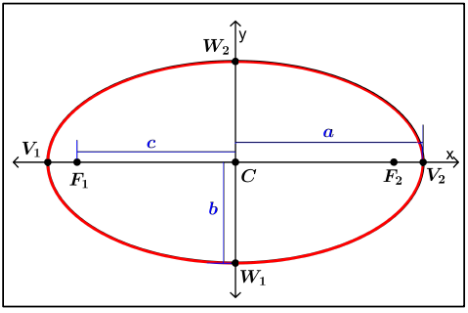
Ellipse
- An ellipse is the set of all points , the sum of whose distance from two specific points and is a constant number.
- The points and are called foci (each is the focus) of the ellipse.
Properties of Ellipse
- The Center C of the ellipse is the midpoint of the foci.
- The Major Axis (longest diameter) is the segment through the foci, with endpoints on the ellipse. These endpoints and are called vertices.
- The Minor Axis (shortest diameter at the narrowest part of the ellipse) is the segment perpendicular to the major axis at C, with endpoints on the ellipse. The endpoints and are the covertices.
- The Semi-major axis is half of the Major axis, and the semi-minor axis is half of the Minor axis.
Equations of Ellipse:
Center: 0,0 Equation: Corresponding Graph: 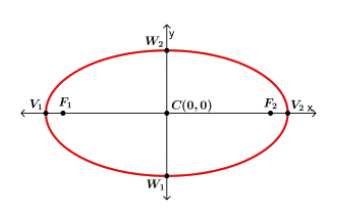 |
|---|
Center: 0,0 Equation: Corresponding Graph: 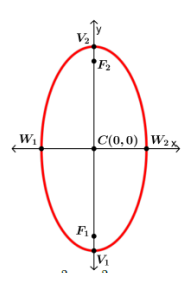 |
Center: (h,k) Equation: Corresponding Graph: 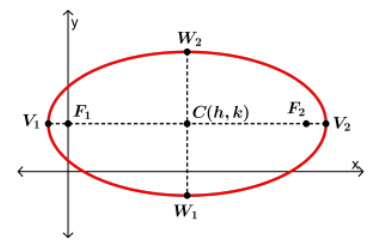 |
Center: (h,k) Equation: Corresponding Graph: |
Examples:
LESSON 4: CONIC SECTIONS: HYPERBOLA |
|---|
Hyperbola
- Is the set of all points in a plane whose distances from the fixed points, called foci, has an absolute difference that is equal to a positive constant.
- A hyperbola is formed by the intersection of a cone with an oblique plane that intersects the base. It consists of two separate curves, called branches.
- The points on the separate branches of the graph where the distance is at a minimum are called vertices.
- The midpoint between a hyperbola’s vertices is its center.
- A hyperbola is asymptotic to certain lines drawn through the center. Note that asymptotes are essential for determining the shape of any hyperbola.
- Given any hyperbola, the transverse axis is the line segment formed by its vertices.
- The conjugate axis is the line segment perpendicular to the transverse axis through the center.
- An asymptote is a line that a curve approaches, as it heads towards infinity.
- The transverse axis is the axis of a hyperbola that passes through the two foci.
- The conjugate axis is the axis of a hyperbola perpendicular to the transverse axis at a point equidistant from the foci.