1 accoustics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Architectural Acoustics
is the art and technique of designing spaces, structures and mechanical systems to meet hearing needs
Architectural Acoustics
The art and science of designing a room or building that insures both comfort and communications, and provide special features as to purpose and use of the building
1.To control echoes
2.To reduce sound
3.To isolate noise
three main objectives for acoustics in buildings
Sound
1. The oscillation in pressure of the atmosphere which is capable of being detected by the human ear.
2. Form of energy propagated in waves which continues to subsist until filtered through a material turning into heat by friction.
3. The sensation produced through the ear resulting from fluctuations in the pressure of the air.
1. Source of sound
2. Medium or Transmission Path
3. Receiver
The nature of sound, in order to be heard, requires the following elements
transducer
often used as a generic term for devices used in converting some form of energy into sound such as loudspeakers and microphones
Source of Sound
normally a vibrating body, which converts some other form of energy into vibration. The source can be made quieter.
Transmission Path
is any substance that allows the vibration to be transmitted in the form of a wave motion.
Airborne Sounds
sounds that are transmitted by air.
Structure borne Sounds
sounds that are transmitted through solid bodies
Receiver
pertains with the human ear.
1. Music – sounds organized to have melody, rhythm, harmony and dynamics.
2. Speech – to express with the voice. Music and Speech can be classified as ordered sounds since they are integrated.
3. Noise – sound, especially, of the loud and harsh kind. Noise is classified as disordered sound, as in a street noise.
Types of Sound
Sound waves
e longitudinal wave motion with which sound energy travels through a medium.
Cycle – full circuit by the particle.
2. Frequency – number of complete cycles per second measured in Hertz (Hz).
3. Amplitude – maximum displacement of a particle to either side of its normal position during vibration. 4. Period – the time required for one complete vibration, measured in seconds per cycle
Sound waves
Significance of Room Acoustics
-Direct Sound
-Reverberant Sound (reflections)
-Useful and harmful reflections
-Sound attenuation and absorption,
diffusion
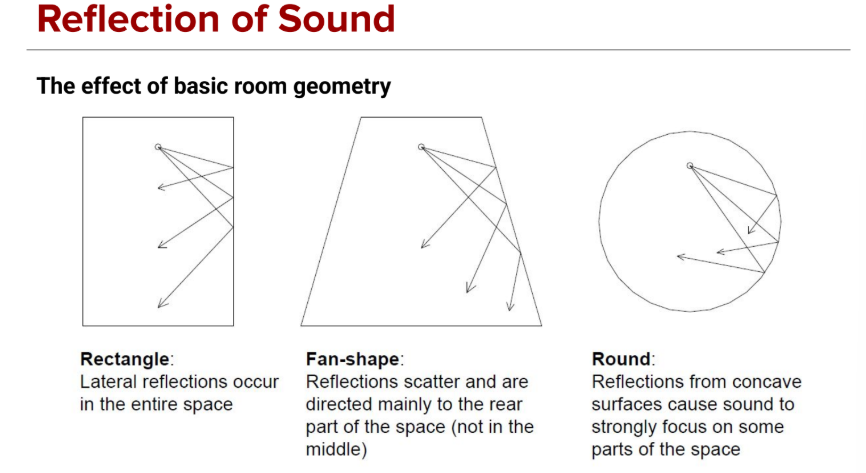
Fanshape good for theatre
Echoes
is produced when the reflected sound wave reaches the ear just when the original sound from the same source has been already heard. Thus, there is repetition of sound
Reverberation
is the persistence of sound in the enclosed space, after the source of sound has stopped
Prolonged Reverberation
due to large amounts of highly reflective surfaces and/or to large volume of space which will take considerable time for reflected sound to die out.
effect is blurring which is harmful to both speech and music.
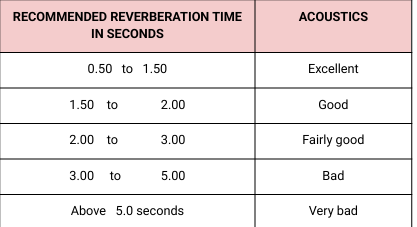
reverberation time
The time during which the sound persists
Reverberation time is influenced by:
a.Volume of the room
b. Sound absorbing qualities of the room’s surfaces
c. Number of people and furniture in the room
Flutter Echoes
a rapid but repetitive succession of sounds caused by highly reflective parallel surfaces (wall to wall, or ceiling to floor). Flutter is often heard as a high frequency ringing or buzzing
Undue Focused Soun
caused by concave surfaces which causes sound to converge at certain points with resulting loss of energy in other parts of the room
angle of incidence
this applies when Sound wavelength is adequately smaller than the dimensions of the object causing the reflection The reflecting surface is even (not sound scattering) and hard (not sound absorbing
Resonance
the emphasis of sound energy at a particular frequency
External Noise
vehicles, traffic engines, factories, machines etc.
Raked seating
refers to seating which is positioned
on an upwards slope away from the stage, in order to
give those in the audience at the back a better view
than if the seats were all on the same level.
Why 60 dB?
decibel measurememt is based on a logarithmic scale
Noise
to unwanted, annoying, or discordant sounds as noise.
Noise from outside of a space can be controlled in the following ways:
Isolate the noise at its source.
• Locate noisy areas as far away as possible from quiet areas.
• Reduce the transmission of sound from one space to another.
Sound behaves within a space
Reflected, Transmitted, Absorbed
Noise reduction
refers to the perceived
difference in sound levels between two
enclosed spaces.
Noise reduction
depends on the following:
1.absorptive qualities of the receiving space
Transmission loss
The level of masking or background
sound,
Transmission loss (TL)
measure of
the performance of a building material
or construction assembly in
preventing the transmission of
airborne sound.
NOISE REDUCTION
Background or ambient sound from
both exterior and interior sources is
normally present in an environment.
white noise
A type of background sound sometimes deliberately introduced into a
space to mask or obliterate unwanted
sound.
THE ABC’s of acoustic design
Absorb, Block, Cover