IT Security & Information Assurance
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Computer Security
The protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable objectives of preserving the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of information system resources.
Information Security (aka IT Security)
process of implementing measures and systems designed to securely
Anything Involving Security of
electronic
Anything Involving Security of
electronic or
information or Information
Systems Regardless of Realm
But Anything that Occurs in
information or into sustems
Cyber Security
Anything Security-Related inThe cyber realm
All about protecting data in its electronic form
Information security performs four important functions for an organization:
Protects the organization's ability to function
Enables the safe operation of applications implemented on the organization's IT systems
Protects the data the organization collects and uses
Safeguards the technology assets in use at the organization
1 - Protecting the Ability to Function
Management is responsible
Information security is
a management issue
a people issue
Communities of interest must argue for information security in terms of impact and cost
Access vs Security
2 - Enabling Safe Operation
Organizations must create integrated, efficient, and capable applications
Organization need environments that safeguard applications
Management must not abdicate to the IT department its responsibility to make choices and enforce decisions
3 - Protecting Data
One of the most valuable assets is data
Without data, an organization loses its record of transactions and/or its ability to deliver value to its customers
An effective information security program is essential to the protection of the integrity and value of the organization's data
4 - Safeguarding Technology Assets
Organizations must have secure infrastructure services based on the size and scope of the enterprise
Additional security services may have to be provided
More robust solutions may be needed to replace security programs the organization has outgrown
Circle of risks
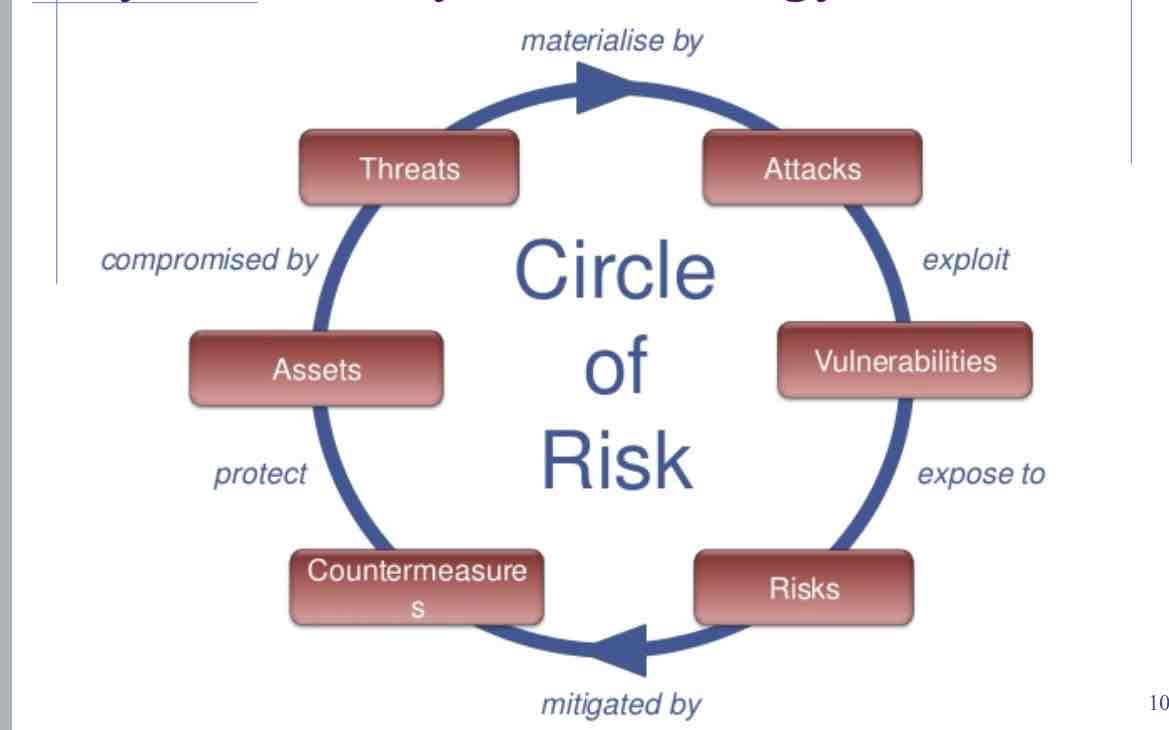
Assets
Asset - People, property, and information.
People may include employees, customers and other persons such as contractors or guests.
Property assets consist of both tangible and intangible items that can be assigned a value.
Intangible assets include reputation and proprietary information.
Information may include databases, software code, critical company records, and many other intangible items.
An Asset is what we are trying to protect
Threat
Threat - Anything that can exploit a vulnerability, intentionally or accidentally, and obtain, damage, or destroy or make unauthorized use of an asset.
An threat / attack is what we are trying to protect against.
Attack
An threat / attack is what we are trying to protect against.
Attack is a threat put into action
A threat agent
an individual or group of attackers that carry out an attack
Vulnerability
Weaknesses or gaps in a security program that can be exploited by threats to gain unauthorized access to an asset.
A vulnerability is a weakness or gap in our protection efforts.
Risk
Risk - The potential for loss, damage or destruction of an asset as a result of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
IT Security attempts to mitigate (reduce) risk
Risk is the intersection of assets, threats, and vulnerabilities.
Attacks
An attack is the deliberate act that exploits vulnerability
It is accomplished by a threat-agent to damage or steal an organization's information or physical asset
An exploit is a technique to compromise a system
A vulnerability is an identified weakness of a controlled system whose controls are not present or are no longer effective
An attack is then the use of an exploit to achieve the compromise of a controlled system
A+T+V= Risk
• Asset + Threat + Vulnerability = Risk.
R= T x V
Risk= threat times vulnerabilities
Risk examples
business disruption
financial losses
loss of privacy
damage to reputation
loss of confidence
legal penalties
impaired growth
loss of life
Threat examples
angry employees
dishonest employees
criminals
governments
terrorists
the press
competitors
hackers
nature
Vulnerability examples
software bugs
broken processes
ineffective controls
hardware flaws
business change
legacy systems
Inadequate BCP
human error
Countermeasures
Countermeasure - An action, process, device, or system that can prevent, or mitigate the effects of, threats to a computer, server or network.
IT Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment identifies biggest vulnerabilities and external threats
Highly Complex
Rely upon Risk Frameworks
NIST
ISO
By examining each threat category and associated risks, an organization protects information assets through:
policy,
education and training,
technology controls
IT Risk Assessment Other slide
Essential that the risk assessment is understood and supported at the highest level of the organization
Only 44% of boards are actively participating in their security strategy.
Without buy-in from the board and senior leaders, a risk assessment is likely to end up being little more than a series of recommendations that are never actually implemented.
9 Biggest Threats Today
Cybercrime syndicates
Smalltime cons, money launderers
Hacktivists
Intellectual property theft & corp espionage
Malware mercenaries
Botnets as a service
All-in-one malware
Increasingly compromised web
Cyber warfare
Sources of Threats - Categories
Human Error
Computer Crime
Natural Events and Disasters
Sources of threat examples
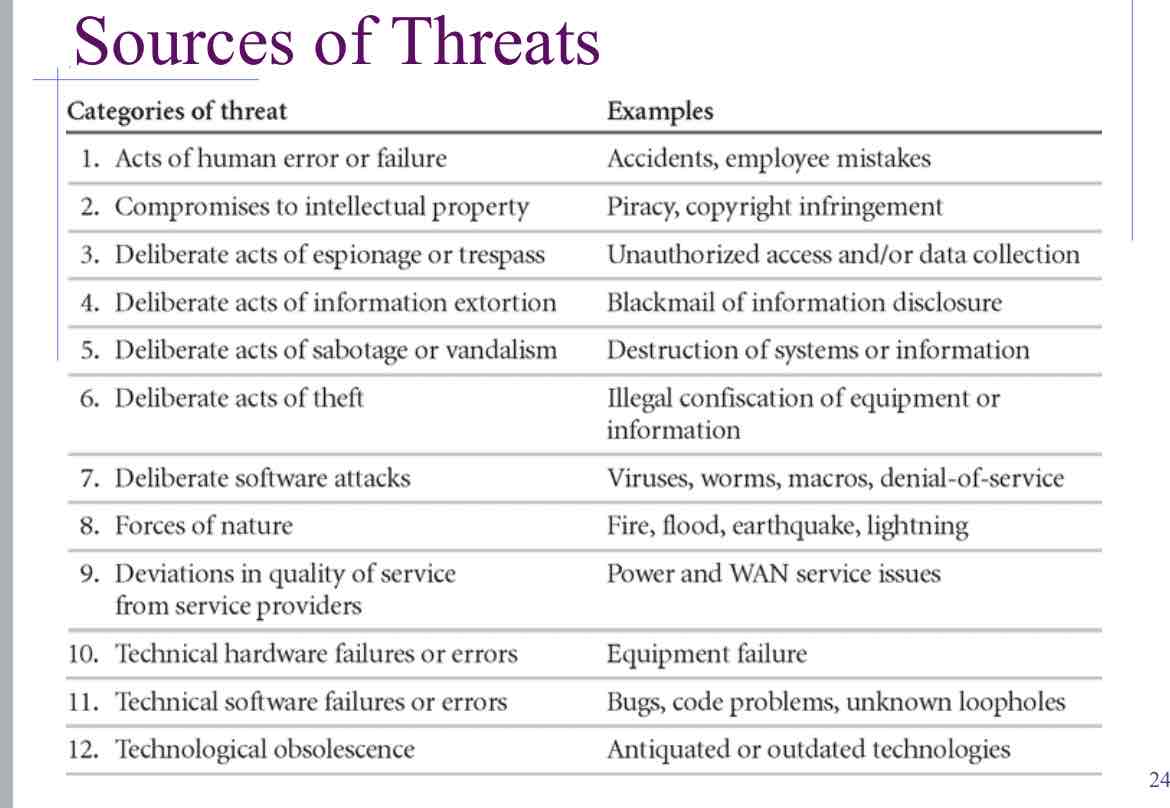
Human Error
>90% of breaches occur due to human error!
Sending sensitive docs to unintended recipients
Falling for Social engineering ploys
Lost/stolen devices
Use of removable
95% of advanced and targeted attacks involved spear-phishing scams
emails contain malicious attachments that can cause malware to be downloaded
Computer crime and examples
Is a very broad category of offenses
Includes larceny or fraud when aided by a computer or internet technologies
Examples
Improperly accessing a computer, system, or network;
Modifying, damaging, using, disclosing, copying, or taking programs or data;
Introducing a virus or other contaminant into a computer system;
Using a computer in a scheme to defraud;
Interfering with someone else's computer access or use;
Using encryption in aid of a crime;
Falsifying email source information; and
Stealing an information service from a provider.
Computer Viruses
Virus - Software written with malicious intent to cause annovance or damage
Backdoor program
Denial-of-service attack (DoS)
Distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS)
Polymorphic virus
Trojan-horse virus
Worm
Common Threats to Users
Botnets
DDoS
Hacking
Malware
Pharming
Phishing
Ransomware
Spam
Spoofing
Spyware / Adware
Trojan Horses
Viruses
Wi-Fi Eavesdropping
Worms
WPA2 Handshake
Vulnerabilities
Crime and no punishment
Some victims never recover from exploitation.
credit record is forever scarred
malware uses the victim's address book list to forward itself to friends and family members
victims of intellectual property theft spend tens of millions of dollars in repair and prevention.
Very few attackers are successfully prosecuted.
professional criminals on the Internet are living large because the Internet isn't good at producing court-actionable evidence.
suspects are living outside the victim's court jurisprudence.
hacking is anonymous by default, and tracks are lost and covered up in milliseconds.
Natural Events and Disasters
Mitigating Risk of Data Loss due to
Natural disasters include:
Backup and Recovery Procedures
Replicated Data
Business continuity plan
Training & Testing Exercises
Countermeasures: Personal Security Safeguards
Take security seriously
Create strong passwords
Use multiple passwords
Send no PID or financial data via email
Use HTTPS sites
Clear browsing history, temp files & cookies
Update antivirus software
Follow organizational security directives & guidelines
Use caution when using public wi-fi or kiosks
Countermeasures: Organizational Measures
Establish Policies & Guidelines
Information Security Policies
Information Security Plan
Acceptable Computer Use Policy
Internet Use Policy
BYOD Policies
Train Employees on Threats / Risks
Unattended devices
Password controls
Countermeasures
Organizational Measures: Prevention and Resistance Technologies
Prevention and Resistance Technologies
Identification, Authentication and Authorization
Passwords
Smart Cards
Personal Identification Number (PINs)
Biometric Authentication
Content Filtering
Malware protection
Encryption
Firewalls
IF countermeasures fail
Mitigate damage with detection and response technologies
Security monitoring
Intrusion detection software
Handling a "Breach":
.Secure physical areas
Stop additional data loss
Remove improperly posted info from the web
Contact Law Enforcement local, FBI or US Secret Service)
Cost of a Data Breach(5)
Remediation:
Avg. 46 days to resolve a data breach @ $21,155 / day =
$973,130
Loss of Customers:76% adults surveyed said they would move away from company with high record of data breach
Business Disruption:Accounts for 39% of total external costs
Regulatory Fines: Fines from FCC, FTC, HHS, PCIDSS...
Legal Costs
Cost of a Data Breach (5more)
Public Relations
Breached Client Records: The avg cost for each lost or stolen record = $221
Direct financial loss
Notification costs: Most states require private and public sector entities to
notify individuals when PID is involved - average cost = .59
millionCredit card reissues, identity theft repair, and monitoring: Average $10 / victim for theft repair and monitoring. Card replacement = $172 million for Target
Information Assurance Obiectives: 1 - Confidentiality
Data confidentiality: assure confidential information is not made available to unauthorized individuals
Privacy: assure individuals can control what information related to them is collected, stored and distributed
Information Assurance Obiectives
2 - Integrity
Data integrity: assure information and programs are changed only in an authorized manner
System integrity: assure system performs intended function
Information Assurance Obiectives
3 - Availability
Assure that systems work promptly and service is not denied to authorized users
Information Assurance Objectives
4 - Accountability
Actions of an entity can be traced uniquely to that entity
Supports: non-repudiation, deterrence, fault isolation, intrusion detection and prevention, after-action recovery and legal action
For example, the use of unique user identification and authentication supports accountability; the use of shared user IDs and passwords destroys accountability.
Good Security Standards follow the 90 / 10" Rule:
10% of security safeguards are technical
90% of security safeguards rely on the computer user ("YOU") to adhere to good computing practices
Example: The lock on the door is the 10%. You remembering to lock the lock, checking to see if the door is closed, ensuring others do not prop the door open, keeping control of the keys, etc. is the 90%. You need both parts for effective security.
Responsibility of IT Security
This means that everyone who uses a computer or mobile device needs to understand how to keep their computer, devices and data secure.
• Information Security is everyone's responsibility
Key Takeaways: 4
Use good, cryptic passwords that can't be easily guessed - and keep them secret
Make sure computer, devices & apps are
current
Make sure your computer is protected with up-to-date anti-virus and anti-spyware
Don't click on unknown or unsolicited links or attachments - don't download unknown files or programs
Key takeaways: 2
Remember that information and passwords sent via standard, unencrypted wireless are easy for hackers to intercept
Remember that Public Wi-Fi's can be unsecure and avoid using PID's