Physics 1 Term Test
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
1
New cards
**Momentum**
* quantity of motion that an object has
* “mass in motion”
describes an object's __resistance__ to stopping
* “mass in motion”
describes an object's __resistance__ to stopping
2
New cards
mass and velocity
The amount of momentum that an object has is dependent upon two variable
3
New cards
directly proportional
momentum is ___________ to both mass and speed
4
New cards
**IMPULSE**
a certain amount of force you apply for a certain amount of time to cause a change in momentum.
5
New cards
p=mv
momentum formula
6
New cards
J=ft
impulse formula
7
New cards
**IMPULSE-MOMENTUM THEOREM**
states that the change in momentum of an object equals the impulse applied to it.
8
New cards
**LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM**
* In the __absence__ of an external force, the momentum of a system __does not__ change.
9
New cards
**LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM**
* states when a system of interacting objects is not influenced by outside forces (like friction), the total momentum of the system can not change
* the total momentum of all objects interacting with one another remains constant regardless of the nature of the forces between the objects
the total momentum of a system will stay the __same__ before and after a collision
* the total momentum of all objects interacting with one another remains constant regardless of the nature of the forces between the objects
the total momentum of a system will stay the __same__ before and after a collision
10
New cards
m1v1= -m2v2
**LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MOMENTUM equation**
11
New cards
**RECOIL**
a term that refers to moment when a gun moves backwards after it is shot
12
New cards
__uniformly accelerated motion__
The motion of an object with __constant acceleration__ is also known as ___________
13
New cards
**COLLISIONS**
any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time.
14
New cards
equals
In any collision, the total net momentum before the collision **___** the total net momentum after the collision
15
New cards
**ELASTIC**
When objects collide __without__ being permanently **deformed** and __without__ generating **heat**
16
New cards
**ELASTIC**
* Perfectly ___ collisions almost never occur
* Heat is usually generated with collisions, so energy is transformed out of the system
* Heat is usually generated with collisions, so energy is transformed out of the system
17
New cards
**ELASTIC**
* Momentum AND Kinetic energy is conserved
* No permanent deformation, no sound, no friction
* Different direction
* No permanent deformation, no sound, no friction
* Different direction
18
New cards
**INELASTIC**
* When colliding objects __stick__ together and travel off as one object
Momentum is conserved, but Kinetic energy is **NOT**
Momentum is conserved, but Kinetic energy is **NOT**
19
New cards
**INELASTIC**
* Possible permanent deformation, sound, or friction between objects
* Work done by non-conservative forces
* Same direction
* Work done by non-conservative forces
* Same direction
20
New cards
**PROJECTILE**
neglects air resistant
21
New cards
__**ONE-DIMENSIONAL MOTION**__
motion along a straight line or in a single direction
22
New cards
**MOTION**
a __change__ in position with respect to a reference point.
23
New cards
**DISPLACEMENT**
the __straight-line__ distance between an object’s initial and final positions, with direction toward the final position
24
New cards
**DISTANCE**
* the __total__ length of path taken by an object in moving from its initial to final position
25
New cards
**SPEED**
A __measure__ of how fast an object moves; Rate at which distance is covered; The distance traveled by a moving object per unit time
26
New cards
**VELOCITY**
includes the __speed__ of an object and the direction of its motion.
27
New cards
**ACCELERATION**
rate of __change of velocity__; Because velocity is a vector quantity, a change in velocity can be a change in magnitude, a change in direction, or a change in both magnitude and direction
28
New cards
**FREE FALL MOTION**
* Objects that fall **ONLY** due to __gravity__.
* the state wherein a falling object is __free__ from air resistance and falls under the influence of gravity **alone**
* Projectile’s downward acceleration when it is on air (-9.8 m/s^2)
* Initial velocity is always 0 m/s
* the state wherein a falling object is __free__ from air resistance and falls under the influence of gravity **alone**
* Projectile’s downward acceleration when it is on air (-9.8 m/s^2)
* Initial velocity is always 0 m/s
29
New cards
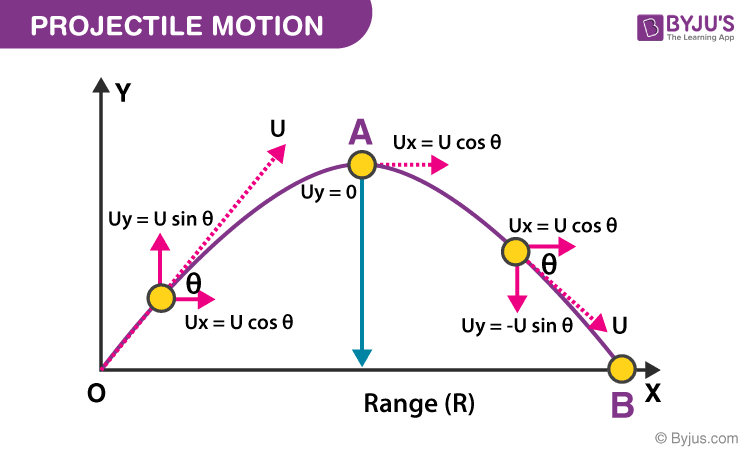
**PROJECTILE MOTION**
a motion in which an object is thrown near the earth’s surface, and it moves along the __curved path__ under the action of gravity only
30
New cards
**PROJECTILE MOTION**
Traces a curved (__parabolic__) line because at the same time that the ball is moving horizontally, it is also moving vertically under the effect of gravity.
31
New cards
**PROJECTILE MOTION**
Object that is initially thrown into the air and continues to move on its trajectory acted upon by gravity.
32
New cards
**HORIZONTAL**
one of the components of projectile motion
\
remains **constant**
entirely **independent**
\
remains **constant**
entirely **independent**
33
New cards
**VERTICAL**
one of the components of projectile motion
\
velocity of a projectile changes
\
\
velocity of a projectile changes
\
34
New cards
Time of Flight
* __Time__ taken by the projectile to cover the entire trajectory
35
New cards
Range
* the __horizontal__ (x) distance traveled by the projectile during entire motion
36
New cards
Trajectory
The parabolic __path__ followed by a projectile in air
37
New cards
Type I
* Horizontal, then vertical; there is an initial velocity
* a rock is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff 88 m high, with a horizontal speed of 25m/s.
* a rock is thrown horizontally from the top of a cliff 88 m high, with a horizontal speed of 25m/s.

38
New cards
Type II
* Ground -> up -> down
* a golf ball was struck from the first tee at Lunar Golf. It was given a velocity of 50m/s at an angle of 42o to the horizontal. On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is 1.6m/s2
* a golf ball was struck from the first tee at Lunar Golf. It was given a velocity of 50m/s at an angle of 42o to the horizontal. On the moon, the acceleration due to gravity is 1.6m/s2
39
New cards
Type III
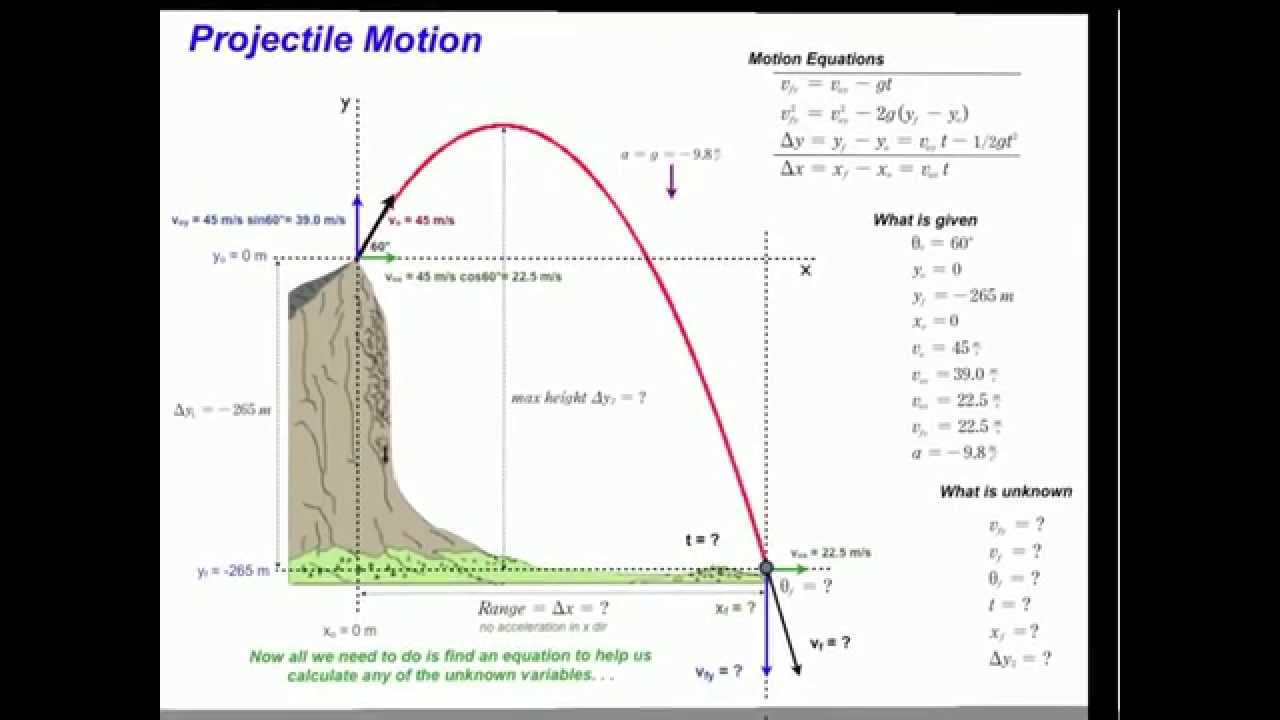
* Initial velocity;
* a diver takes off with a speed of 10 m/s from a 5 m high diving board at 30 above the horizontal.
* a diver takes off with a speed of 10 m/s from a 5 m high diving board at 30 above the horizontal.
40
New cards
45
best angle to fire to reach the largest distance
41
New cards
zero
Velocity in both highest and lowest points will always be __