AP Psych Unit 11 (Intelligence)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:39 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
1
New cards
Intelligence
the mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
2
New cards
it is **SOCIALLY CONSTRUCTED** and used to rank people against one another
__eg__. which person is smarter, the VHS valedictorian, or the uneducated indigenous person from the Amazon?
__eg__. which person is smarter, the elderly person (high *crystalized intelligence*), or the young person (high *fluid intelligence*)?
__eg__. which person is smarter, the VHS valedictorian, or the uneducated indigenous person from the Amazon?
__eg__. which person is smarter, the elderly person (high *crystalized intelligence*), or the young person (high *fluid intelligence*)?
Why is the definition of intelligence a debated topic?
3
New cards
Crystalized Intelligence
knowing the cold, hard FACTS!!!
a person gains knowledge of factual information over the years
__eg__. an elderly person can recall exactly what it was like during World War 2 (who was involved, who was president, the economy, etc.)
a person gains knowledge of factual information over the years
__eg__. an elderly person can recall exactly what it was like during World War 2 (who was involved, who was president, the economy, etc.)
4
New cards
Fluid Intelligence
acquiring new skills!!!
__eg__. a young person is more likely to quickly figure out a new technological mechanism
__eg__. a young person is more likely to quickly figure out a new technological mechanism
5
New cards
1. *Spearman’s* g-factor theory
2. *Thurstone’s* 7 clusters theory
3. *Gardner’s* multiple intelligence theory
4. *Goleman’s* emotional intelligence (EQ) theory
5. *Sternberg’s* triarchic theory
What are all the **Theories of Intelligence**?
6
New cards
Spearman’s **General Intelligence Factor Theory**
* intelligence can be expressed by a single factor, or *g-factor*
* used **factor analysis** to conclude that underlying the many different specific abilities (mathematical vs. verbal intelligence) that people regard as types of intelligence is a SINGLE FACTOR
i.e. Mechanical, Verbal, Spatial, Numerical
* used **factor analysis** to conclude that underlying the many different specific abilities (mathematical vs. verbal intelligence) that people regard as types of intelligence is a SINGLE FACTOR
i.e. Mechanical, Verbal, Spatial, Numerical
7
New cards
1. Mechanical
2. Verbal
3. Spatial
4. Numerical
\
\*I looked at all the space on the road (*spatial*) and thought, I need a car to drive so I must fix it up (*mechanical*), but I need to make calculations to fix the car (*numerical*), so I will ask someone for help (*verbal*)
What are the 4 categories that blend into 1 single g-factor, according to Spearman?
8
New cards
Charles Spearman
Who created the **General Intelligence Factor Theory**?
9
New cards
Thurstone’s **7 Clusters Theory**
* there are 7 clusters of primary mental abilities
* i.e. word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory
* i.e. word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory
10
New cards
1. Perceptual speed
2. Inductive reasoning
3. Numerical ability
4. Spatial ability
5. Memory
6. Word fluency
7. Verbal comprehension
\
\*PINS Me With V
What are the 7 clusters of mental ability, according to Thurstone?
11
New cards
When other investigators studied Thurstone’s profiles, they found evidence of a g-factor.
A criticism of Thurstone’s 7 Clusters Theory?
12
New cards
LL Thurstone
Who created the **7 Clusters Theory**?
13
New cards
Gardner’s **Multiple Intelligence Theory**
* there are multiple, __unrelated__ intelligences, which include traditional and nontraditional categories
* i.e. musical, kinesthetic, interpersonal, linguistic, mathematics, naturalistic, interpersonal, visual
* i.e. musical, kinesthetic, interpersonal, linguistic, mathematics, naturalistic, interpersonal, visual
14
New cards
The Gardner theory only identifies “talents,” not intelligence
A criticism of Gardner’s Multiple Intelligence Theory?
15
New cards
Howard Gardner
Who created the **Multiple Intelligence Theory**?
16
New cards
Savant Syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill
17
New cards
People w/ **savant syndrome** are considered geniuses bc they excel in 1 specific area of intelligence
\
\*\*examples:
* __Alonzo Clemons__ \~ 2 year old who smacked his LH and caused brain damage; couldn’t speak, but RH *flourished* (he could SCULPT with clay an exact replica of a 2D picture of an animal)
* __Temple Gradin__ \~ designed paddles that press up against the side of cattle, calming them so work can be done on them
* __Kim Peek__ \~ if you hand him a book, he will remember EVERYTHING (i.e. remembers every address of “John Smith” in a phone book in order)
\
\*\*examples:
* __Alonzo Clemons__ \~ 2 year old who smacked his LH and caused brain damage; couldn’t speak, but RH *flourished* (he could SCULPT with clay an exact replica of a 2D picture of an animal)
* __Temple Gradin__ \~ designed paddles that press up against the side of cattle, calming them so work can be done on them
* __Kim Peek__ \~ if you hand him a book, he will remember EVERYTHING (i.e. remembers every address of “John Smith” in a phone book in order)
What does the Multiple Intelligence Theory suggest about *savant syndrome*?
18
New cards
Goleman’s **Emotional Intelligence Theory**
* the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
* makes you successful in life!!!
* IQ gets you the job, EQ makes you successful at it
* makes you successful in life!!!
* IQ gets you the job, EQ makes you successful at it
19
New cards
EQ stretches intelligence TOO FAR, despite the fact that higher EQ scores correlate to future success (career, marriage, parenting, etc.)
A criticism of Goleman’s Emotional Intelligence Theory?
20
New cards
Daniel Goleman
Who created the **Emotional Intelligence Theory**?
21
New cards
Sternberg’s **Triarchic Theory**
* includes 3 intelligences:
1. Analytical Intelligence
2. Creative Intelligence
3. Practical Intelligence
1. Analytical Intelligence
2. Creative Intelligence
3. Practical Intelligence
22
New cards
Analytical Intelligence
__Academic problem-solving__ as assessed by traditional intelligence tests; focuses on well-defined problems w/ a SINGLE correct answer
__eg__. SAT testing
__eg__. SAT testing
23
New cards
Creative Intelligence
Demonstrated in the reacting adaptivity to novel situations and generating novel ideas
__eg__. creative painting
__eg__. creative painting
24
New cards
Practical Intelligence
Your “street smarts”!!!
Required for everyday tasks, which may be ill-defined, w/ multiple solutions
__eg__. finding a flat tire, and figuring out what to do
Required for everyday tasks, which may be ill-defined, w/ multiple solutions
__eg__. finding a flat tire, and figuring out what to do
25
New cards
* Thurstone’s **7 Cluster Theory**
* Gardner’s **Multiple Intelligence Theory**
* Sternberg’s **Triarchic Theory**
* Gardner’s **Multiple Intelligence Theory**
* Sternberg’s **Triarchic Theory**
What are the 3 types of intelligence theories where you can excel in one thing, but perform poorly in another?
26
New cards
Are these categories (analytical, creative, practical) *really* independent?
A criticism of Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory?
27
New cards
1. Standardization
2. Reliability
3. Validity
What are the 3 criteria that must be met by psychological (intelligence) tests, in order to be widely accepted?
28
New cards
Standardization
Defining of uniform testing procedures and meaningful scores by comparison w/ the performance of a pre-tested group; “norms” have been established
Must create a STANDARD NORMAL CURVE
__eg__. the SAT *psyshometricians* use experimental sections and **standardization samples** to establish the norms for achievement
Must create a STANDARD NORMAL CURVE
__eg__. the SAT *psyshometricians* use experimental sections and **standardization samples** to establish the norms for achievement
29
New cards
Psychometrician
Person who makes/assesses a test
30
New cards
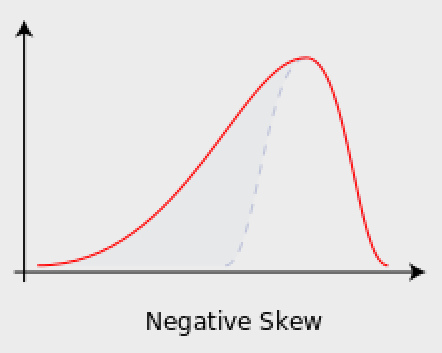
Negative Skew
tail points to the negatives
31
New cards
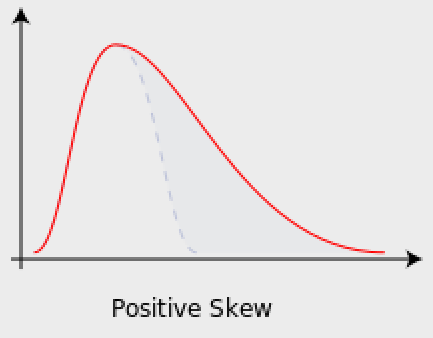
Positive Skew
tail points to the positives
32
New cards
The Flynn Effect
An INCREASE in intelligence test scores throughout the 20th century
\*\*results in an INCREASED need for **standardization** (i.e. new avg for IQ testing is 105 → must be shifted back to 100); items that everyone gets RIGHT AND WRONG are discarded
\*\*results in an INCREASED need for **standardization** (i.e. new avg for IQ testing is 105 → must be shifted back to 100); items that everyone gets RIGHT AND WRONG are discarded
33
New cards
Wechsler Intelligence Test
Measures IQ!!!
mean = 100
standard deviation = 15 points
mean = 100
standard deviation = 15 points
34
New cards
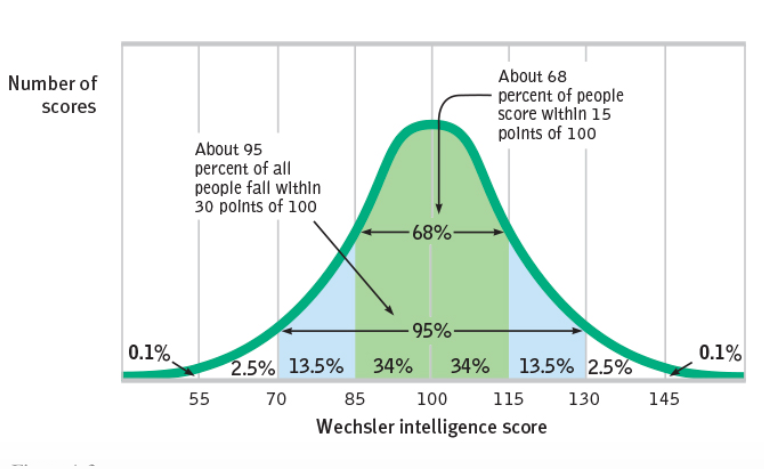
Normal Curve
Symmetrical, bell-shaped curve that describes the distribution of many physical and psychological attributes
68-95-99.7 !!!
68-95-99.7 !!!
35
New cards
Reliability
Extent to which a test yields __**CONSISTENT**__ results
36
New cards
Split-Half Reliability
Assesses consistency by dividing the test in two parts (i.e. odd-number questions vs. even-number questions), and assessing the accuracy of each part of the one test
\*\*Parts should be roughly EQUAL for optimum consistency!
\*\*Parts should be roughly EQUAL for optimum consistency!
37
New cards
Equivalent-Form Reliability
Assesses consistency through alternative forms of the test (i.e. taking the Unit X exam again, today, and getting roughly the same score)
38
New cards
Test-Retest Reliability
Assesses consistency through RETESTING (i.e. taking the same Unit X exam as last class, and getting roughly the same score)
39
New cards
Validity
The extent to which a test measures or predicts what it is supposed to; aka __**ACCURACY**__
__eg__. the SAT is supposed to predict how well you will do as an ungergrad
__eg__. the SAT is supposed to predict how well you will do as an ungergrad
40
New cards
Face Validity
A measure of the extent to which the content of the test measures all of the knowledge or skills that are supposed to be included within the domain being tested, __according to test-takers__
i.e. did you learn everything you were supposed to about Developmental Psych, aka Unit 9?
i.e. did you learn everything you were supposed to about Developmental Psych, aka Unit 9?
41
New cards
Content Validity
A measure of the extent to which the content of the test measures all of the knowledge or skill that is supposed to be included within the domain being tested, __according to expert judges__
i.e. rearranging blocks for the Wechsler Test… you would think, “what value does this have? this is easy,” BUT in actuality, the judges are timing you and it truly has value
i.e. rearranging blocks for the Wechsler Test… you would think, “what value does this have? this is easy,” BUT in actuality, the judges are timing you and it truly has value
42
New cards
Criterion-Related Validity
A measure of the extent to which a test’s results __correlate with other accepted measures__ (**criteria**) of what is being tested
i.e. colleges use your AP score (3, 4, 5) to excuse your engagement in a college course… looks at **criteria** of the college course, which is matched to that of the AP test
i.e. colleges use your AP score (3, 4, 5) to excuse your engagement in a college course… looks at **criteria** of the college course, which is matched to that of the AP test
43
New cards
Concurrent Validity
A measure of the extent to which the test provides __similar scores__ as other tests on the same subject
i.e. similar scores on **BOTH** the MCQ and FRQ portions of the AP Test
i.e. similar scores on **BOTH** the MCQ and FRQ portions of the AP Test
44
New cards
Predictive Validity
A measure of the extent to which the test accurately __forecasts a specific future result__
i.e. the SAT predicts how well you will do as an undergrad
i.e. the SAT predicts how well you will do as an undergrad
45
New cards
Construct Validity
The extent to which the test actually measures the __hypothetical construct__ behavior (*intelligence*) it is designed to assess
i.e. the MMPI-2 can discriminate between people with schizophrenia and those without
i.e. the MMPI-2 can discriminate between people with schizophrenia and those without
46
New cards
1. Aptitude Tests
2. Achievement Tests
What are the 2 most common types of tests?
47
New cards
Aptitude Tests
Tests designed to predict a person’s future performance
i.e. SAT (predicts how well you’ll do as an undergrad-student) and GRE (predicts how well you’ll do as a grad-student
i.e. SAT (predicts how well you’ll do as an undergrad-student) and GRE (predicts how well you’ll do as a grad-student
48
New cards
Achievement Tests
Tests designed to assess what a person has learned
i.e. the Unit X Exam in AP Psych
i.e. the Unit X Exam in AP Psych
49
New cards
VIRTUALLY IMPOSSIBLE
Making an exam that EXCLUSIVELY measures __one__ of these qualities (aptitude & achievement) is ______.
50
New cards
Speed Tests
Tests gauge how __quickly__ a person can solve problems
51
New cards
Power Tests
Tests gauge the __difficulty level__ of problems an individual can solve
i.e. a 500 question test gets progressively harder… if you miss 5 in a row, you’re done
i.e. a 500 question test gets progressively harder… if you miss 5 in a row, you’re done
52
New cards
Group Tests
A large # of people are tested at the same time
i.e. SAT in a room full of people
i.e. SAT in a room full of people
53
New cards
Individual Tests
A single person is tested by an examiner, allowing for greater depth
i.e. Wechler Test
i.e. Wechler Test
54
New cards
Francis Galton; James McKeen Cattell
In the 1880s, _____ and ______ used **psychomotor tasks** (strength, reaction time, sensitivity to pain, weight) as a “mental test” to identify intelligence
\*\*failed to validate their **eugenics**-based ideas of intelligence
\*\*failed to validate their **eugenics**-based ideas of intelligence
55
New cards
Psychomotor Tasks
* strength
* reaction time
* sensitivity to pain
* weight
* reaction time
* sensitivity to pain
* weight
56
New cards
Eugenics
A certain race of people deemed genetically inferior
57
New cards
Alfred Binet; Theodore Simon
In 1904, _____ and ______ were hired by the FRENCH gov to identify children who would **NOT** benefit from a traditional school setting and those who would benefit from special education
58
New cards
Compulsory School Attendance
What did the French gov implement in 1904?
59
New cards
Binet-Simon scale for class placement
Binet and Simon sampled **performance tasks** (memory, comprehension, and judgement) to assign children a **mental age** (mental level)
60
New cards
Suggested using the RATIO of mental age (MA) to chronological age (CA) to determine a child’s level of intelligence
* 1 = average
* >1 = above average
*
* 1 = average
* >1 = above average
*
What did **William Stern** suggest, based on the **Binet-Simon Scale**?
61
New cards
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale
In 1911, **Lewis Terman** developed this; reports results as an **IQ (intelligence quotient)**
62
New cards
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
* calculated by taking \[MA/CA x 100\]
* THIS CALCULATION IS ONLY USED FOR CHILDREN!!!
* Newest version assesses __5 ability areas__:
1. knowledge
2. fluid reasoning
3. verbal quantitative reasoning (ELA)
4. non-verbal quantitative reasoning (math)
5. visual-spacing processing (pattern recognition)
* THIS CALCULATION IS ONLY USED FOR CHILDREN!!!
* Newest version assesses __5 ability areas__:
1. knowledge
2. fluid reasoning
3. verbal quantitative reasoning (ELA)
4. non-verbal quantitative reasoning (math)
5. visual-spacing processing (pattern recognition)
63
New cards
100
What is the AVERAGE IQ?
64
New cards
Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale *for adults*
Uses a deviation IQ resulting from a __standardization process__
\*\*can’t use the children’s formula bc, according to research, intelligence stabilizes
\*\*can’t use the children’s formula bc, according to research, intelligence stabilizes
65
New cards
z-score
looks at standard deviation
* z=0 \~ NO deviation
* z=1 \~ 1 std *above* average
* z=-1 \~ 1 std *below* average
* z=0 \~ NO deviation
* z=1 \~ 1 std *above* average
* z=-1 \~ 1 std *below* average
66
New cards
G-factor
ONLY 1 score… connects all abilities
ONLY 1 score… connects all abilities
What kind of test is the Stanford-Binet?
67
New cards
David Wechsler
In 1939, _______ began developing alternatives to the Stanford-Binet
68
New cards
1. Wechsler Preschool and Primary Scale of Intelligence (WPPSI)
* preschool
2. Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC)
* age 6-16
3. Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
* older adolescents and adults
What are the alternatives to the Stanford-Binet Intelligence Scale, according to Wechsler?
69
New cards
AGE 7!!!
What is the most IDEAL time to test intelligence to predict future success?
70
New cards
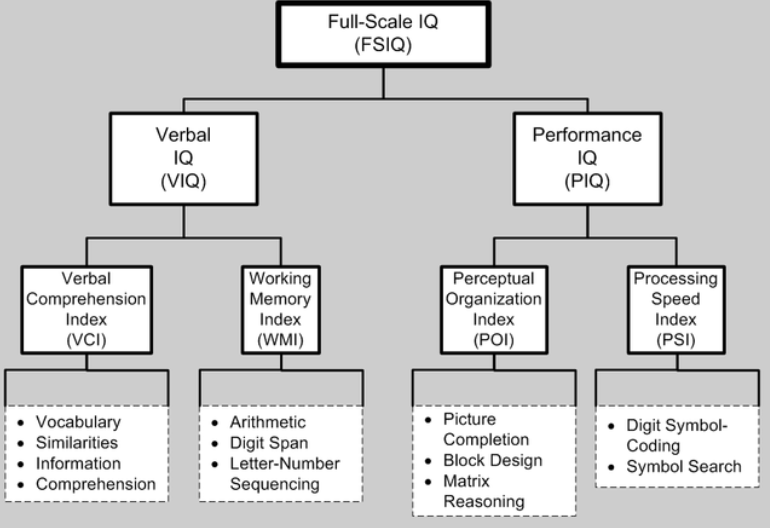
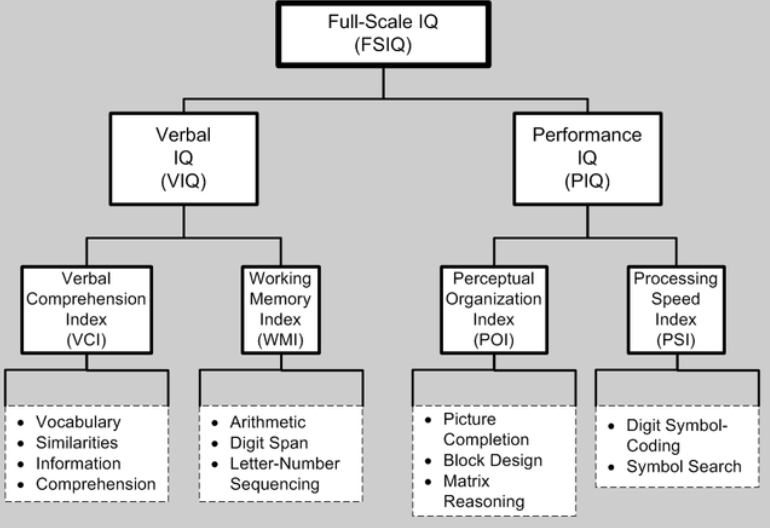
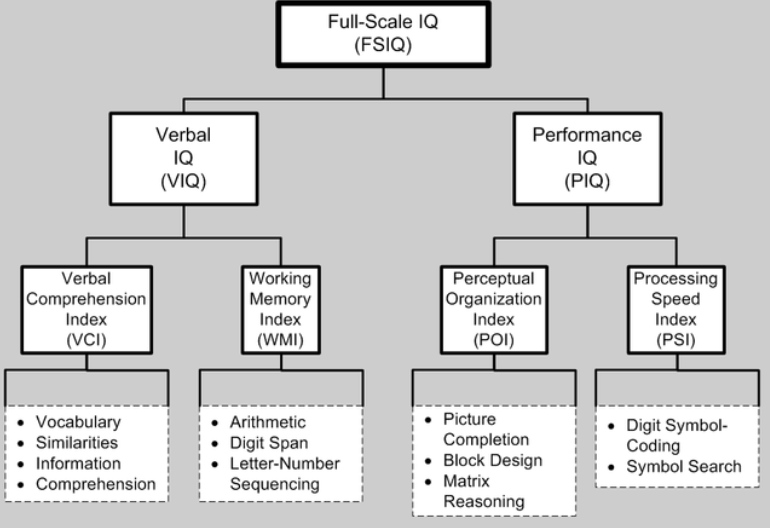
Full IQ Scale (FSIQ)
Verbal IQ + Performance IQ
71
New cards
Verbal IQ
* __Verbal Comprehension Index__ (vocab, similarities, info, comprehension)
* __Working Memory Index__ (arithmetic, digit span, letter #, sequencing)
* __Working Memory Index__ (arithmetic, digit span, letter #, sequencing)
72
New cards
Performance IQ
* __Perceptual Organization Index__ (picture completion, block design, matrix reasoning)
* __Processing Speed Index__ (digit symbol, coding, symbol search)
* __Processing Speed Index__ (digit symbol, coding, symbol search)
73
New cards
Intelligence DECLINES w/ age
According to **cross-sectional evidence**, will a person’s intelligence score remain stable over the course of their life?
74
New cards
Intelligence remains STABLE w/ age
\*\*maybe goes up w/ crystalized intelligence
\*\*maybe goes up w/ crystalized intelligence
According to **longitudinal evidence**, will a person’s intelligence score remain stable over the course of their life?
75
New cards
4 years old
When is the **earliest** you can test intelligence for maximum benefit?
76
New cards
7 years old
When is the **latest** you can test intelligence for maximum benefit?
77
New cards
Low Extreme of Intelligence
People w/ an IQ < 70 (2 standard deviations *below* mean); labeled as having an **intellectual disability**
78
New cards
Mild Intellectual Disability
* 85% of ID population
* mentally in 6th grade
* mentally in 6th grade
79
New cards
Moderate Intellectual Disability
* 10% of ID population
* mentally in 2nd grade
* mentally in 2nd grade
80
New cards
Severe Intellectual Disability
* 5% of ID population
* some vocational occupation, but must have supervision
* can learn self-help skills and routines
\*\*ICAP program at VHS
* some vocational occupation, but must have supervision
* can learn self-help skills and routines
\*\*ICAP program at VHS
81
New cards
Profound Intellectual Disability
* 1% of ID population
* require **intensive** support
* require **intensive** support
82
New cards
High Extreme of Intelligence
People w/ an IQ > 130 (2 standard deviations *above* mean); labeled as being intellectually gifted (genius)
\*\*Terman’s research showed that the stereotypes of high extreme of people are incorrect!!
\*\*Terman’s research showed that the stereotypes of high extreme of people are incorrect!!
83
New cards
YES.
* estimates **heritability** of intelligence range from 50-80%
* *Thomas Bouchard* calculated 70% after reviewing twin & adoption studies
* Researchers have created “smarter” mice by manipulating genes in **polygenic** studies
* estimates **heritability** of intelligence range from 50-80%
* *Thomas Bouchard* calculated 70% after reviewing twin & adoption studies
* Researchers have created “smarter” mice by manipulating genes in **polygenic** studies
Do people who share the same genes also share comparable mental abilities?
84
New cards
Heritability
A number that tells us how much of something you can attribute to a person’s genes (HIGHER = more nature, LOWER = more nurture)
85
New cards
Polygenetic
MANY genes contribute to the formation of intelligence, since there are so many factors that determine intelligence.
86
New cards
* Discovered delayed development in children
* Could NOT sit up unassisted at age 2, or walk at age 4
* Little sense of personal control over their environment since their cries, coos, or other behaviors went unacknowledged
* Called the Iranian children “**glum lumps**”
* Could NOT sit up unassisted at age 2, or walk at age 4
* Little sense of personal control over their environment since their cries, coos, or other behaviors went unacknowledged
* Called the Iranian children “**glum lumps**”
What did *J McVicker Hunt* observe in Iranian orphanages?
87
New cards
Began a program of __**tutored human enrichment**__ where he trained caregivers to play **language-fostering games** (VOCAL GAMES) with infants.
The results were a dramatic, unprecedented success for the orphanage. \*\*more adoption!!
The results were a dramatic, unprecedented success for the orphanage. \*\*more adoption!!
How did *J McVicker Hunt* address delayed development in Iranian orphanages?
88
New cards
YES and NO.
* YES bc the environment can prevent you from reaching your full potential for intelligence (i.e. Iranian orphanages)
* NO bc you can’t surpass what is genetically predisposed for intelligence (you can’t BECOME a genius, if you have the capacity for average intelligence)
* YES bc the environment can prevent you from reaching your full potential for intelligence (i.e. Iranian orphanages)
* NO bc you can’t surpass what is genetically predisposed for intelligence (you can’t BECOME a genius, if you have the capacity for average intelligence)
Regarding intelligence, can environmental conditions override one’s genes?
89
New cards
* less-qualified teachers vs. qualified teachers
* malnutrition
* malnutrition
What are some environmental factors that can influence intelligence?
90
New cards
Project Head Start
A US government-funded program for preschool for families below the poverty line (1965); prepares children for education to keep them from being held back
91
New cards
YES and NO.
* YES bc there is belief that there are long-term benefits, since genes and __experience__ together affect intelligence (i.e. you aren’t as embarrassed, if you aren’t held back, and you can reach your full potential for intelligence)
* NO bc, generally, the aptitude benefits dissipate over time
* YES bc there is belief that there are long-term benefits, since genes and __experience__ together affect intelligence (i.e. you aren’t as embarrassed, if you aren’t held back, and you can reach your full potential for intelligence)
* NO bc, generally, the aptitude benefits dissipate over time
Was Project Head Start effective?
92
New cards
1. Racial groups differ in their average scores on intelligence tests
2. High-scoring people are more likely to attain high levels of education and income
\
\*\*According to this, since the mean IQ scores for African-Americans is 85, essentially they will struggle in life as opposed to caucasian
What are the 2 disturbing facts about __ethnicity__ and __intelligence__?
93
New cards
Group differences may be rooted entirely in ENVIRONMENTAL differences, NOT genetics
\*think about the Iranian orphanages! where would those kids be if they were given the SAME opportunities as other kids?
\*think about the Iranian orphanages! where would those kids be if they were given the SAME opportunities as other kids?
What might cause differences between races in intelligence scores?
94
New cards
**Women**:
* spelling
* verbal ability
* non-verbal ability/object location
* sensory acuity
**Men**:
* spatial ability
* complex math
* intellectual extremes
\
\*equal math computation/overall math performance
* spelling
* verbal ability
* non-verbal ability/object location
* sensory acuity
**Men**:
* spatial ability
* complex math
* intellectual extremes
\
\*equal math computation/overall math performance
What are gender differences in mental ability scores?
95
New cards
IT DEPENDS…
* YES for the **Popular Meaning of Bias**
* NO for **Scientific Meaning of Bias**
* YES for the **Popular Meaning of Bias**
* NO for **Scientific Meaning of Bias**
If an intelligence test is *biased*, should it be used as an assessment tool?
96
New cards
Popular Meaning of Bias
* An intelligence test IS biased, if it measures your developed abilities, which reflect, in part, your education and experiences (ENVIRONMENT)
* __eg__. knowing what an iced tea saucer is
* __eg__. knowing what an iced tea saucer is
97
New cards
Yes
Should an exam w/ “popular bias” be continued?
98
New cards
Scientific Meaning of Bias
* An intelligence test IS biased, if it only assesses 1 group of test-takers, despite being presented as a VALID test for __all__ participants
* __eg__. the SAT test-makers weighted the test questions women did better on (as worth more points) in comparison to men … UNFAIR!! Doesn’t represent all demographics
* __eg__. the SAT test-makers weighted the test questions women did better on (as worth more points) in comparison to men … UNFAIR!! Doesn’t represent all demographics
99
New cards
No
Should an exam w/ “scientific bias” be continued?
100
New cards
Self-doubts and self-monitoring may hijack your working memory and impair your performance
How does the **stereotype threat** lead to a self-fulfilling prophecy?