Human Phys Exam III
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
1
New cards
Know this anatomy, label all parts
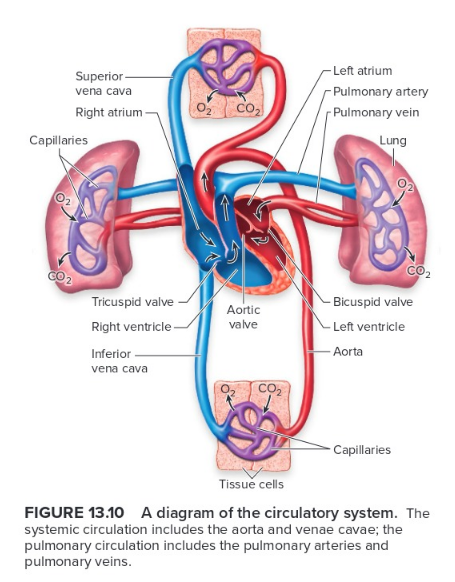
2
New cards
Know this anatomy, valves of the heart
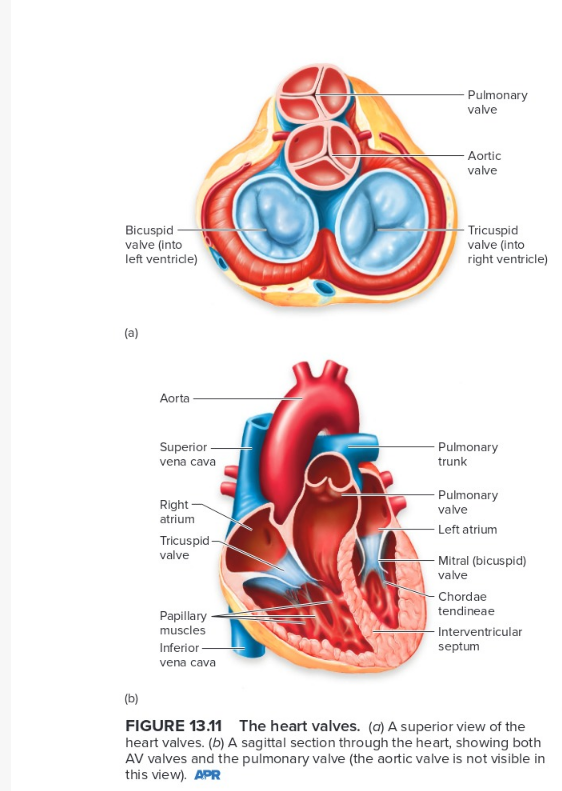
3
New cards
Know this anatomy, conduction system of the heart
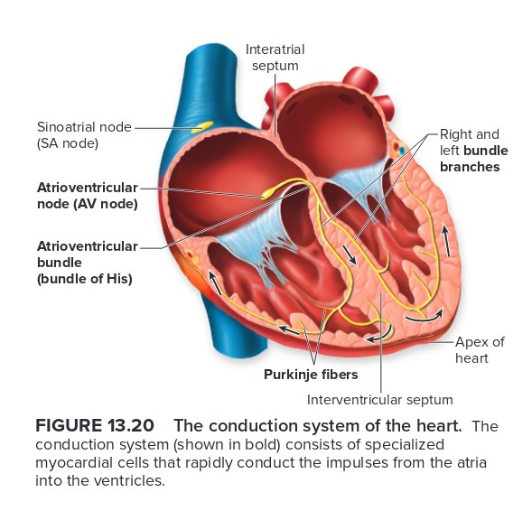
4
New cards
Know this anatomy, basic scheme of the lymphatic system
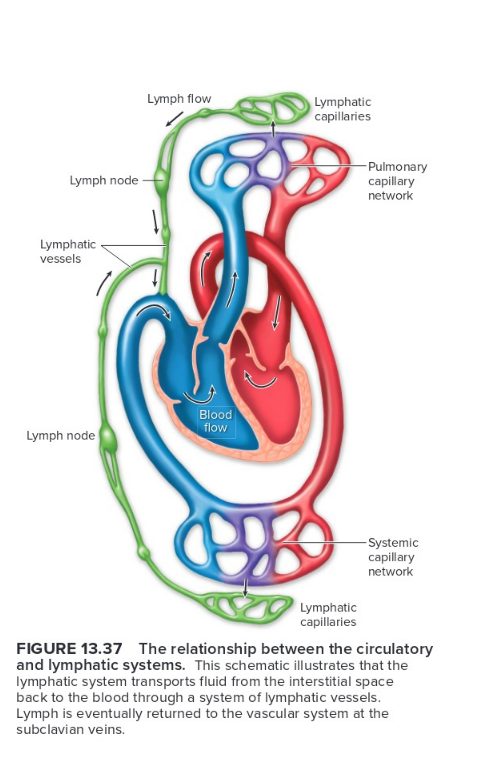
5
New cards
Exocrine
secretion outside the body (e.g. sweat glands)
6
New cards
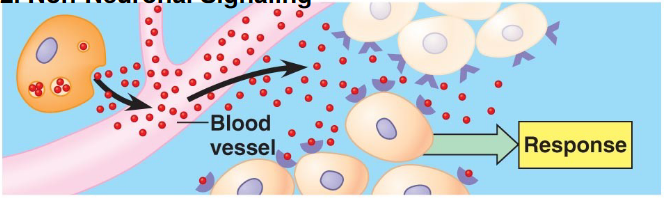
Endocrine
secretion into the blood, acting on distant tissues
7
New cards
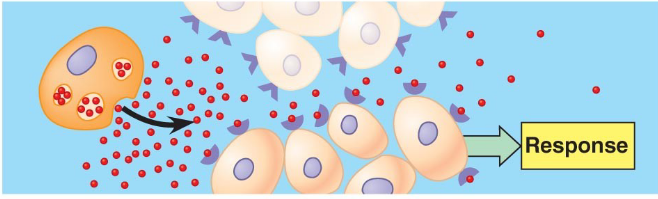
Paracrine
secretion acting on nearby cells
8
New cards
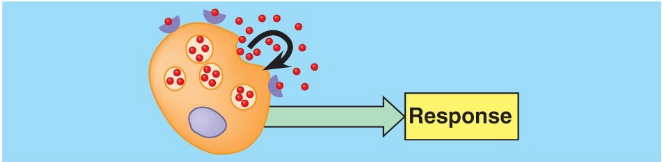
Autocrine
secretion acting on same cell
9
New cards
glands
Exocrine and Endocrine Cells that secrete chemicals
10
New cards
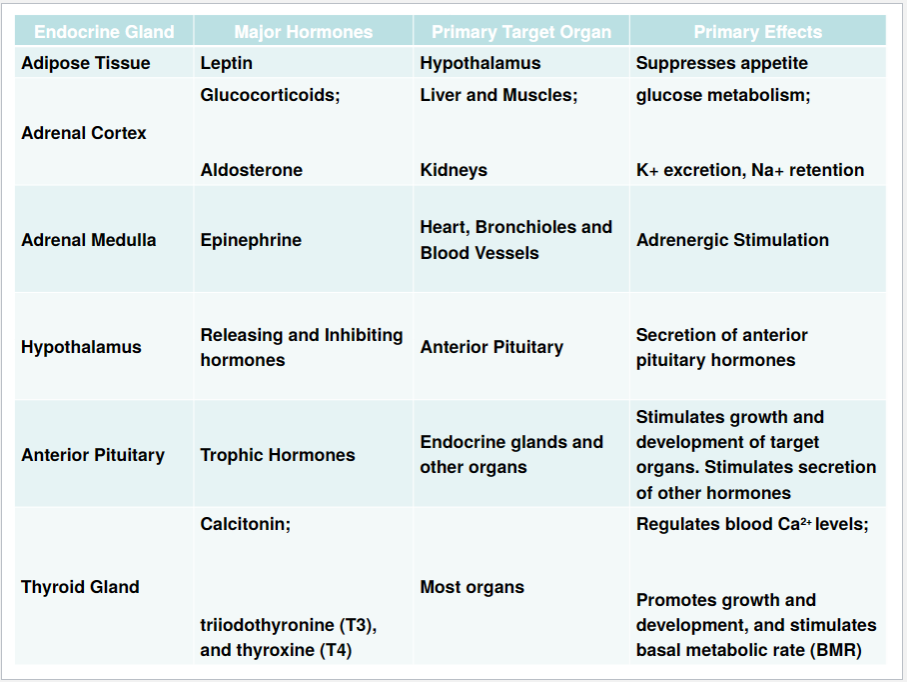
examples of endocrine glands
11
New cards
feedback loop
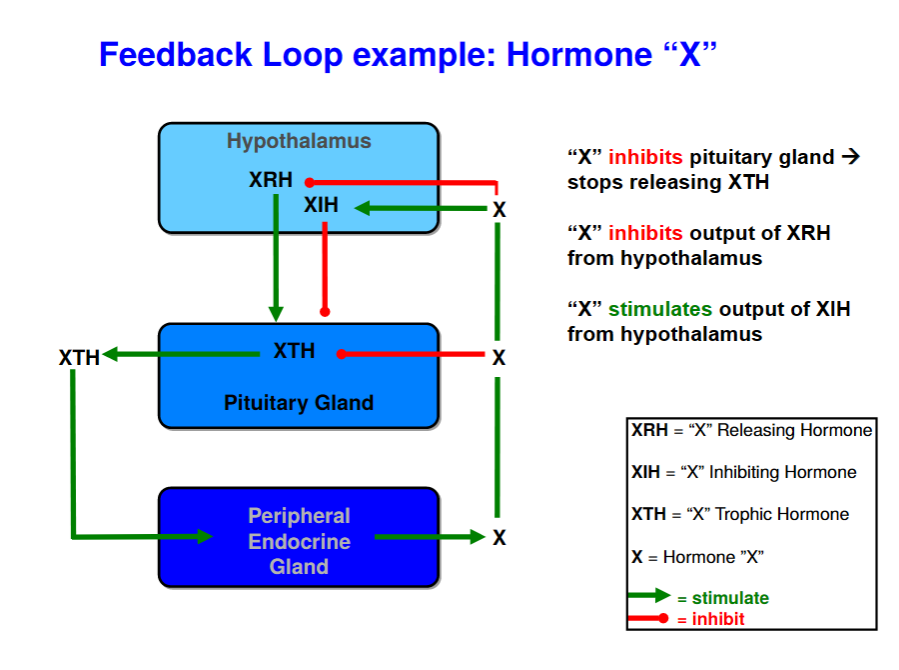
12
New cards
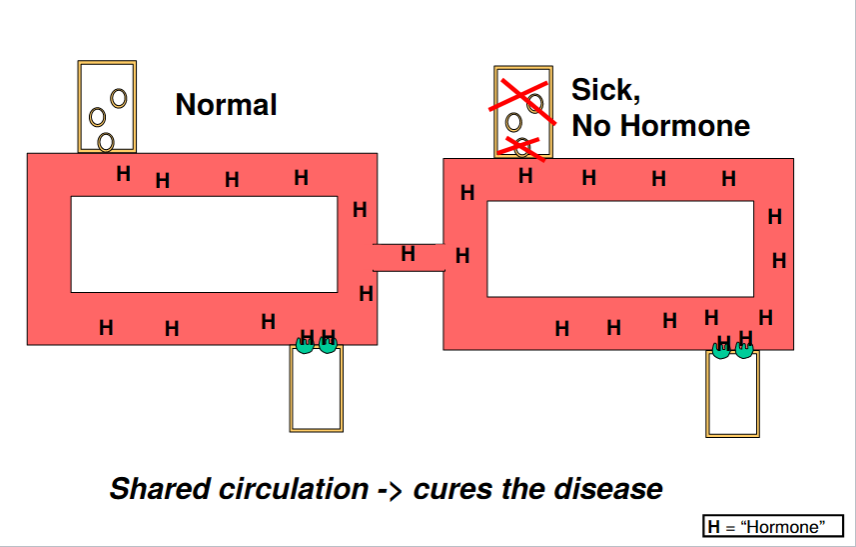
How to prove that abnormal loss of a hormone causes a disease?
Connect the circulatory systems of a normal and diseased individual.
13
New cards
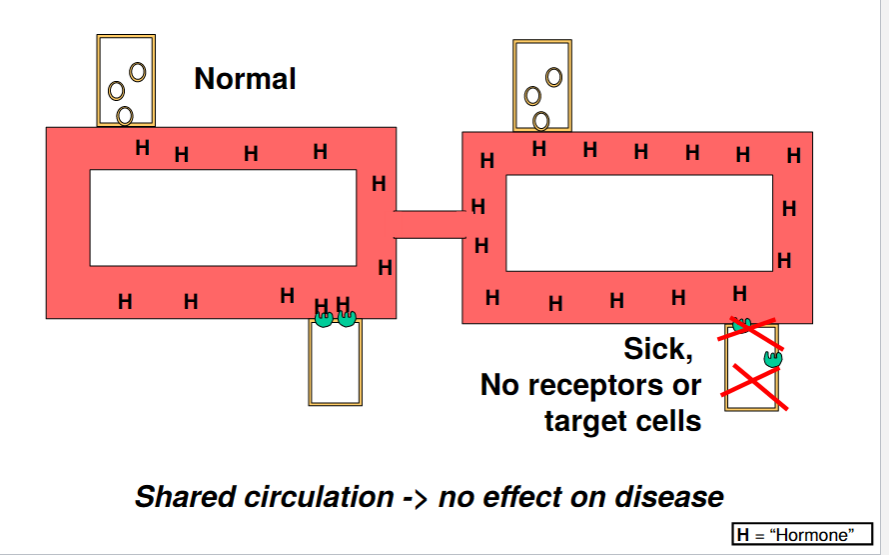
How to tell if the diseased person have no hormone receptors
Shared circulation -> no effect on disease
14
New cards
ob/ob mutation
extra stop codon terminates leptin transcript. –> hypoleptinemia
15
New cards
db/db mutation
extra stop codon terminates leptin receptor –> **functional** hypoleptinemia
16
New cards
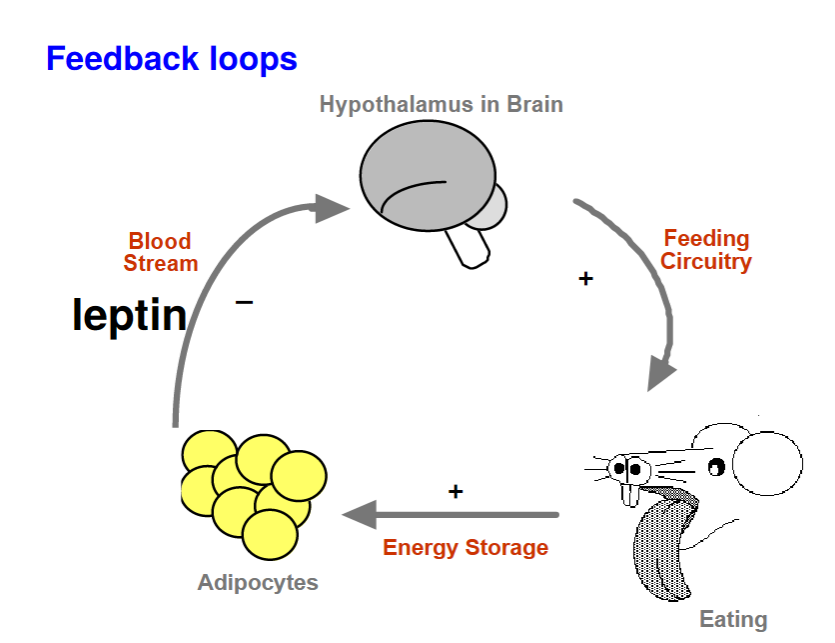
leptin feedback loop
Hypothalamus tells rat to eat, the fat cells secrete leptin to stop the hypothalamus from telling the rat to eat
17
New cards
ob/ob mutants look identical to db/db mice
**both** over eat, are obese, become diabetic
18
New cards
Parabiotic experiments
shared blood supply
19
New cards
What would happen if db/db blood mixes with ob/ob
db/db blood makes ob/ob anorexic
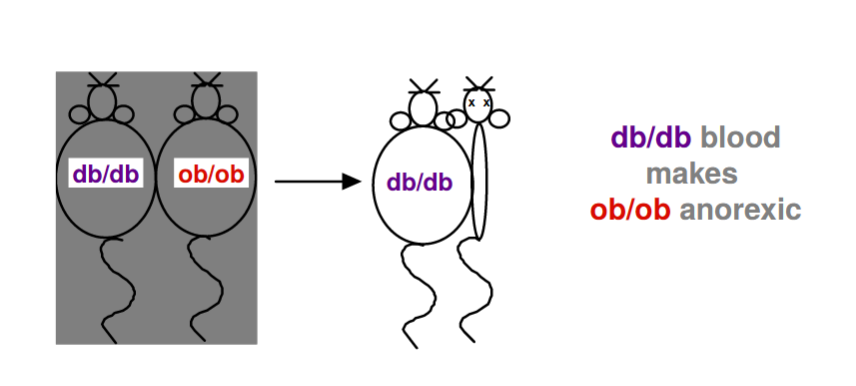
20
New cards
hypoleptinemia
no leptin hormone, so can’t produce negative feedback signal and keeps putting on fat
21
New cards
functional hypoleptinemia
no leptin receptors, so can’t detect negative feedback signal, and keeps putting on fat
22
New cards
anx mutant parabiotic experiments
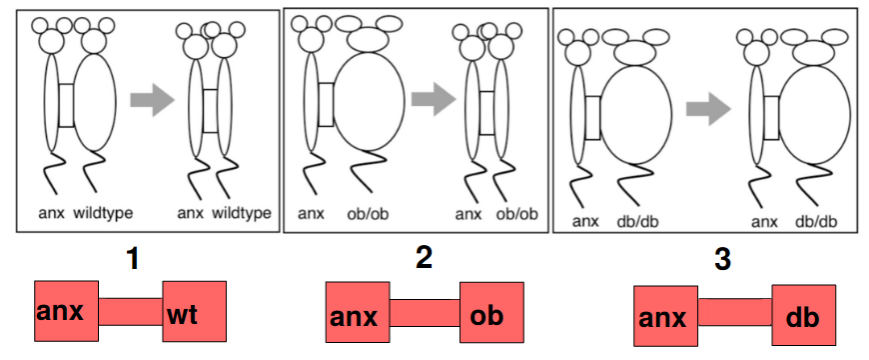
23
New cards
Nuclear Receptor Hormones
(Steroids, Thyroid Hormone, & Retinoic acid = lipophilic hormones)
(Steroids, Thyroid Hormone, & Retinoic acid = lipophilic hormones)
Can pass through membranes and skin due to being lipophilic and can **diffuse** across membrane and bind to receptors **inside** the cell. (can be bounded to carrier proteins in the blood to help move around).
Not easily contained in vesicles. Synthesized from lipid-soluble store by enzymes (so no gene for these hormones, although there are genes for synthesizing enzymes and for their receptors).
Receptors bind to specific sequences (response elements) in gene promoters. Because the nuclear receptors bind to DNA, their effects are necessarily genomic (e.g. not directly on ion channels or second messengers); i.e., they induce protein synthesis.
Not easily contained in vesicles. Synthesized from lipid-soluble store by enzymes (so no gene for these hormones, although there are genes for synthesizing enzymes and for their receptors).
Receptors bind to specific sequences (response elements) in gene promoters. Because the nuclear receptors bind to DNA, their effects are necessarily genomic (e.g. not directly on ion channels or second messengers); i.e., they induce protein synthesis.
24
New cards
Tamoxifen
displaces estrogen, inactivates receptor
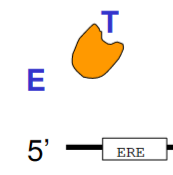
25
New cards
Polypeptide and Glycoprotein Hormones (Second-Messenger Coupled Hormones)
packaged in vesicles and secreted by endocytosis
Coded for by genes; processed in endoplasmic reticulum & Golgi apparatus; packaged in vesicles and secreted by endocytosis.
Hydrophilic molecules so soluble in blood; circulate and act on plasma membrane receptors (on the surface of the cell) to induce second messenger signaling in the target cells
Coded for by genes; processed in endoplasmic reticulum & Golgi apparatus; packaged in vesicles and secreted by endocytosis.
Hydrophilic molecules so soluble in blood; circulate and act on plasma membrane receptors (on the surface of the cell) to induce second messenger signaling in the target cells
26
New cards
3 Common Hormone Receptor Signaling Pathways
1\. GPCR linked to cAMP
2\. GPCR linked to phospholipase C and Ca++
3\. Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
2\. GPCR linked to phospholipase C and Ca++
3\. Tyrosine Kinase Receptors
27
New cards
GPCP linked to cAMP
1\.Hormone binds to receptor on target cell’s plasma membrane
2\. Hormone-receptor interaction acts by G-proteins to stimulate adenylate cyclase on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane
3\. Activated adenylate cyclase catalyzes conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the cytoplasm
4\. Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase enzymes in the cytoplasm
5\. Activated cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates (transfers phosphate groups) to **activate/inhibit** other enzymes in the cell.
6. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
\
2\. Hormone-receptor interaction acts by G-proteins to stimulate adenylate cyclase on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane
3\. Activated adenylate cyclase catalyzes conversion of ATP to cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the cytoplasm
4\. Cyclic AMP activates protein kinase enzymes in the cytoplasm
5\. Activated cAMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates (transfers phosphate groups) to **activate/inhibit** other enzymes in the cell.
6. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
\
28
New cards
Intracellular Ca++ as a Second Messenger
1\. Hormone binds to receptor on target cell’s plasma membrane
2. Hormone-receptor interaction acts by G-proteins to stimulate phospholipase C enzyme in the membrane
3\. Activated phospholipase C catalyzes the conversion of phospholipids in the membrane to inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
4. IP3 enters the cytoplasm and diffuses to the endoplasmic reticulum, binds to IP3 receptors, and causes Ca++ channels to open
5\. Endoplasmic reticulum has high \[Ca++\]; Ca++ rushes out of endoplasmic reticulum unto cytoplasm.
6. Ca++ in the cytoplasm binds to calmodulin protein.
7. Activated calmodulin activates protein kinases, which phosphorylate (transfers phosphate groups) to activate/inhibit other enzymes in the cell.
8. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
2. Hormone-receptor interaction acts by G-proteins to stimulate phospholipase C enzyme in the membrane
3\. Activated phospholipase C catalyzes the conversion of phospholipids in the membrane to inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
4. IP3 enters the cytoplasm and diffuses to the endoplasmic reticulum, binds to IP3 receptors, and causes Ca++ channels to open
5\. Endoplasmic reticulum has high \[Ca++\]; Ca++ rushes out of endoplasmic reticulum unto cytoplasm.
6. Ca++ in the cytoplasm binds to calmodulin protein.
7. Activated calmodulin activates protein kinases, which phosphorylate (transfers phosphate groups) to activate/inhibit other enzymes in the cell.
8. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
29
New cards
Tyrosine Receptor Kinases
1\. Hormone binds to receptor on target cell’s plasma membrane
2. Receptors dimerize (form pairs)
3. Receptors phosphorylate each other (the receptors themselves are kinases)
4. Activated receptors phosphorylate target proteins (“tyrosine kinases” because add phosphate groups to tyrosine residues in target proteins)
5. 5. Phosphorylated proteins activate/inhibit other pathways in the cell.
6. 6. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
2. Receptors dimerize (form pairs)
3. Receptors phosphorylate each other (the receptors themselves are kinases)
4. Activated receptors phosphorylate target proteins (“tyrosine kinases” because add phosphate groups to tyrosine residues in target proteins)
5. 5. Phosphorylated proteins activate/inhibit other pathways in the cell.
6. 6. Enzyme activity mediates the target cell’s response to the hormone.
30
New cards
Anterior Lobe of pituitary gland
contains endocrine cells that secrete tropic hormones into the circulation that stimulate target organs in the body.
31
New cards
Posterior Lobe of pituitary gland
contains axon terminals of ADH and oxytocin neurons that originate in the hypothalamus; releases ADH (water retention) and oxytocin (uterine contractions, milk release) into the blood stream
32
New cards
Where is ADH and oxytocin created?
Antidiuretic Hormone & Oxytocin synthesized in hypothalamus
33
New cards
anterior pituitary gland
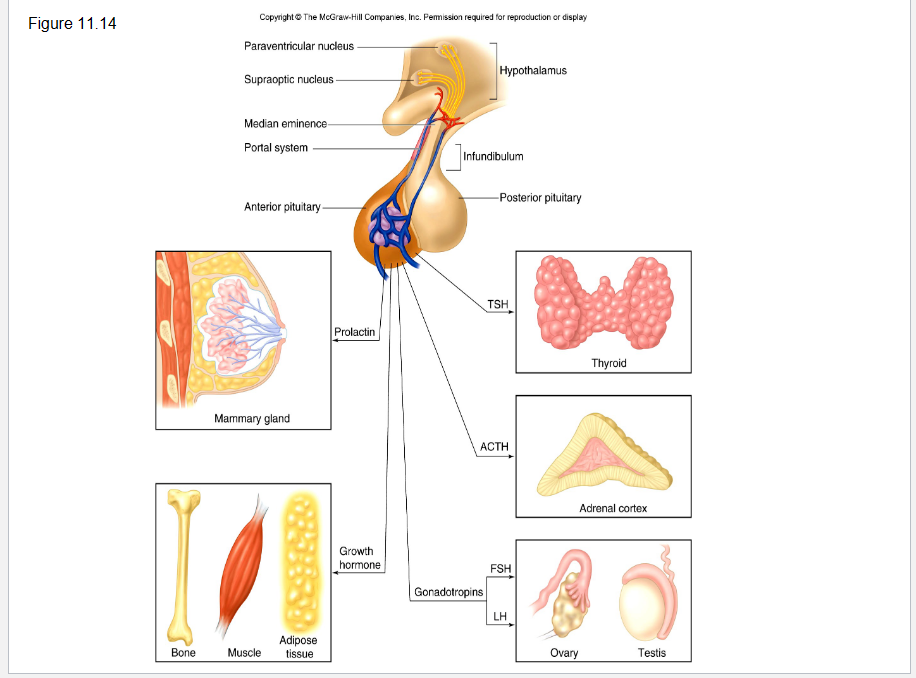
34
New cards
Transection of infundibulum
decrease of all pituitary hormones except prolactin increases.
35
New cards
releasing hormone
hypothalamus→ pituitary gland
36
New cards
tropic hormone
pituitary gland → target gland
37
New cards
examples of Hypothalamic Pituitary Axes
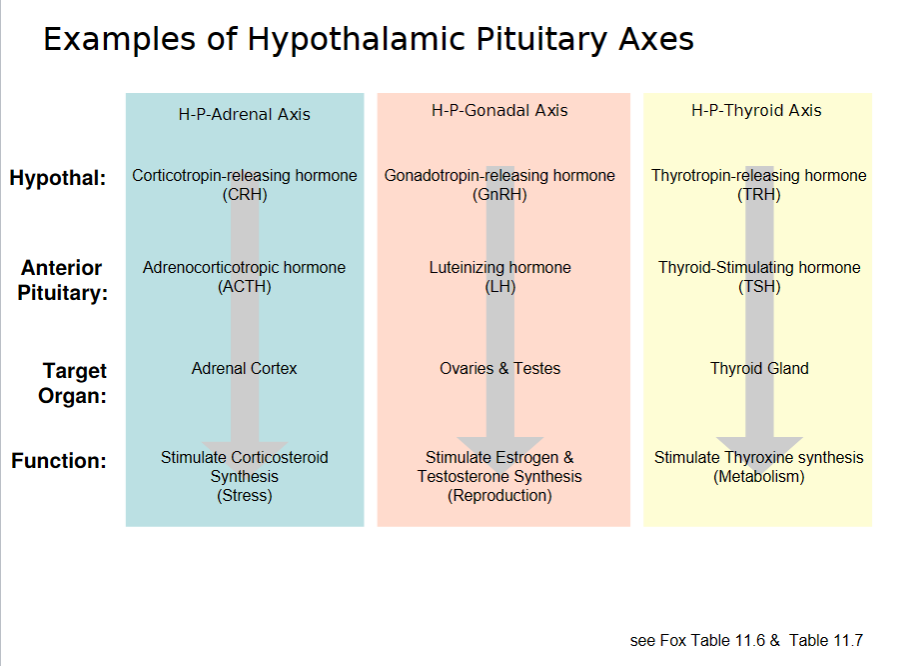
38
New cards
Immediate Endocrine Response to Stress
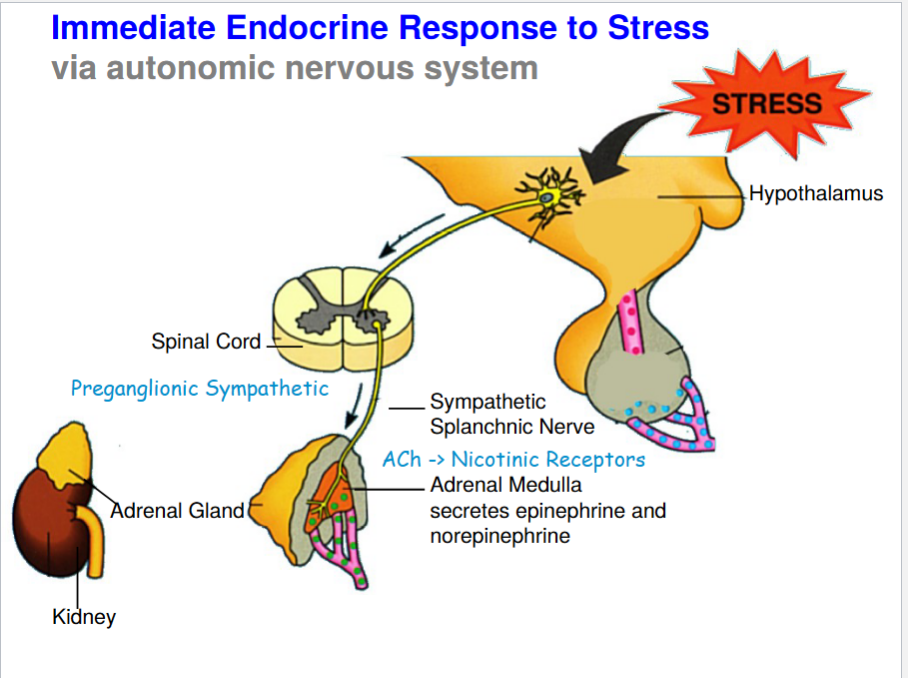
39
New cards
Long-Term Response to Stress
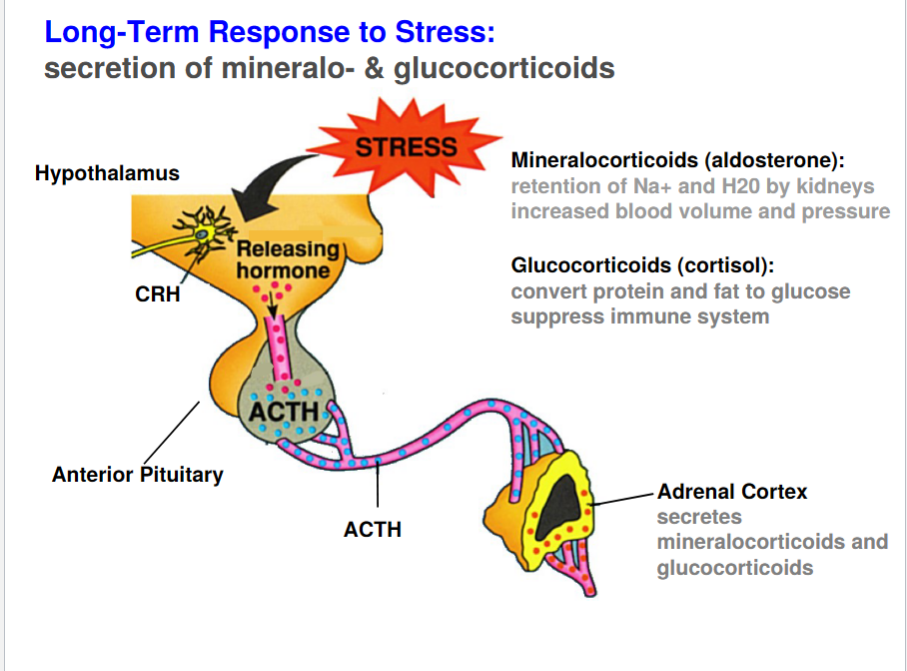
40
New cards
Enhanced Stress Response
Depressed women with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (childhood abuse) show enhanced cortisol release in response to social stress.
41
New cards
If cortisol synthesis is **blocked**
(by drug that blocks synthetic enzyme, or by a disease that damages adrenal cortex), then ACTH levels stay **elevated** (trying to elevate cortisol levels)
42
New cards
If excess glucocorticoids are administered
HPA detects high negative feedback, so then ACTH and cortisol levels should **fall**
43
New cards
Dexamethasone suppression test
administers an artificial glucocorticoid to confirm that HPA responds to negative feedback
44
New cards
metyrapone blocks conversion of 11-deoxycortisol -> cortisol; so cortisol levels fall;
pituitary responds by increasing ACTH levels
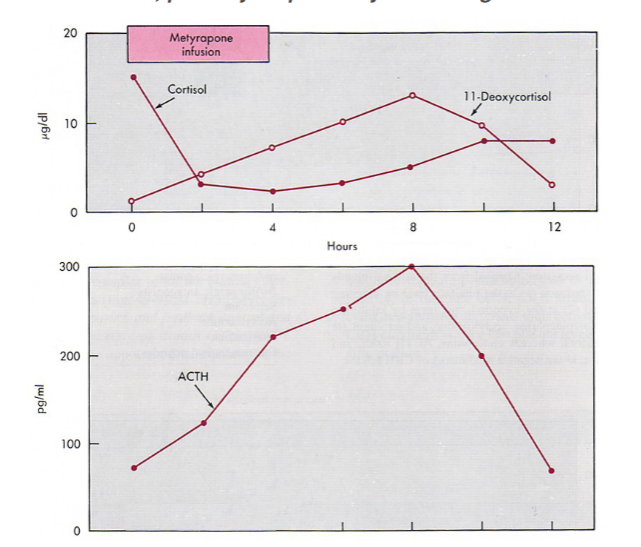
45
New cards
Addison’s Disease
autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortex causes loss of corticosteroids, but excess ACTH
46
New cards
Pheochromacytoma
Tumors can oversecrete hormones. Tumors of adrenal medulla -> elevated epinephrine
47
New cards
Cushing’s Syndrome: elevated cortisol
Tumors of Pituitary Gland (adenoma) or Lung (lung carcinoma) can produce too much ACTH
Tumors of Adrenal Gland can produce too much cortisol
Tumors of Adrenal Gland can produce too much cortisol
48
New cards
anatomy of pituitary gland
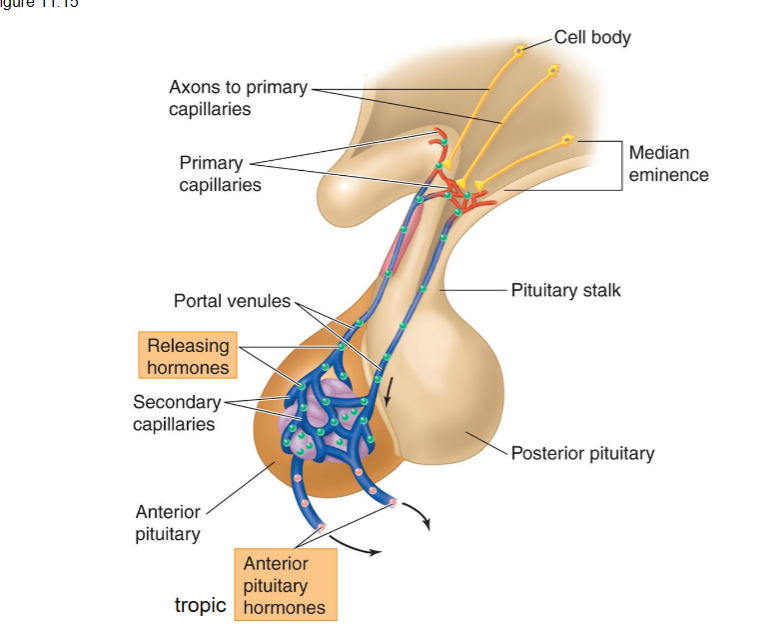
49
New cards
Dexamethasone suppression test
preRX with artificial GC (dexamethasone) suppresses cortisol response to CRH injection
\
\
50
New cards
iodine is important because
the thyroid needs it to create T3 and T4
51
New cards
Obesity: After the circulatory systems of two mice are surgically connected, one mouse remains obese while the second mouse becomes anorexic. One mouse is _____ and the anorexic mouse is _____.
db/db; wildtype
52
New cards
Hormone Receptors: Steroid hormones must dissociate from _________ in order to pass through the cell membrane. Inside the cytoplasm, steroid hormones bind to the __________ of receptor proteins in order to influence gene expression.
carrier proteins; ligand binding domain
53
New cards
Obesity: ____________, excreted by adipocytes, serve as negative feedback to the ________ in order to reduce feeding behavior.
Leptin; hypothalamus
54
New cards
Obesity: Which of the following is **NOT** a characteristic of a db/db mouse?
No leptin hormone
55
New cards
Hormone Receptors: This second messenger molecule releases Ca++ from the endoplasmic reticulum after it is converted from phospholipids by phospholipase C.
IP3
56
New cards
Pituitary: After transection of the infundibulum, the secretion of most pituitary hormones goes down, but secretion of _____________ increases.
prolactin
57
New cards
Lidocaine
blocks voltage-gated Na+ channels
58
New cards
Propranolol
beta blocker”: blocks norepi from binding beta-adrenergic receptors
59
New cards
Verapamil
blocks the voltage-gated Ca++ channels
60
New cards
The ______________________ is the origin of the action potential that spreads from the pacemaker cells located at the top of the right atria. Due to the fibrous skeleton of the heart, this action potential must then pass through the _________________________ in order to depolarize the ventricles of the heart.
sinoatrial node; atrioventricular node
61
New cards
The auditory sound referred to as a heart beat is produced by pressure differences between the ____________________ that closes the AV valve. Likewise, the pressure difference between __________________________ closes the semilunar valves
atria and ventricle; the ventricles and aorta/pulmonary artery
62
New cards
The pacemaker cells are different than neurons because (choose the best answer):
in pacemaker cells, depolarization results from voltage-gated ion channels that open in response to hyperpolarization, as opposed to depolarization in neurons.
63
New cards
The opening of _____________________ channels result in the rapid depolarization of myocardial cells in the ventricles; whereas the opening of ________________channels results in the slow plateau of the action potential. __________________ efflux then hyperpolarizes the cell.
Fast Na+ channels; slow Ca2+ channels; K+
64
New cards
According to an electrocardiogram, the ____ wave is created by atrial depolarization, the ______ wave is due to the spread of depolarization to the ventricles, and the S-T interval is due to the _______________.
P; QRS; plateau phase of the cardiac action potential
65
New cards
A fenestrated capillary is _________________ to compounds found in the blood; however, the majority of capillaries in the brain have _______________.
Permeable; tight junctions
66
New cards
Blood pressure, measured by mm Hg, is lowest in the _______________ ; however, blood is prevented from back flow by ________________ .
veins; valves
67
New cards
Lidocaine and Verapamil are different from Propranolol in which of the following ways?
Lidocaine and Verapamil directly influence ion channel permeability; whereas Propranolol indirectly influences ion channel permeability.
68
New cards
HCN channels open ______________ in response to Acetylcholine; which ________ heart rate due to the opening of more ______channels.
Slower; slows; K+
69
New cards
Damage to Pukinje fibers due to ischemia can result in:
Death,
Circus rhythms
Lack of proper coordination of refractory periods,
Out of synch heart contractions
Circus rhythms
Lack of proper coordination of refractory periods,
Out of synch heart contractions
70
New cards
Venous Return
\
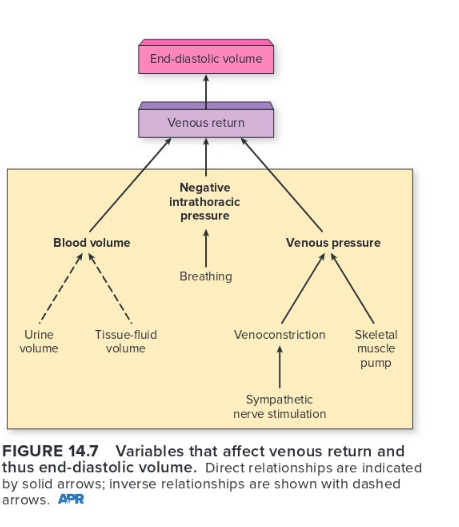
71
New cards
Increased blood in the ventricles of the heart results in greater strength during contraction (Frank Starling Law) because
The actin and myosin in the sarcromere have less overlap due to the stretch
72
New cards
A healthy heart has an ejection volume that is maintained at _____ of end-diastolic volume (EDV)
60%
73
New cards
After lying down, you sit up and notice that your vision starts turning black. You come to the conclusion that your blood pressure was too low to adequately supply your brain with oxygenated blood. Which of the following is NOT a part of orthostatic regulation of blood pressure?
osmoreceptors in the hypothalamus
74
New cards
Which of the following does not contribute to an increase in end-diastolic volume?
tissue-fluid volume and urine volume
75
New cards
Which of the following is true about the lymphatic system?
lymph is dumped into subclavian veins via he thoracic duct and right lymphatic duct
76
New cards
Exercise ______________ blood flow to skeletal muscles, _______________ blood flow to the gastrointestinal tract and liver, and _______________________ blood flow to the brain.
Increases; decreases; does not change
77
New cards
An increase in the following will decrease the resistance of a blood vessel.
radius
78
New cards
Baroreceptors detect changes in _________________; whereas osomoseceptors detect changes in_________________________.
Blood pressure; blood concentration
79
New cards
Arteries (arterial blood)
vessels carrying blood from heart towards the capillaries. Thick muscular walls to keep pressure up. High in oxygen (except for pulmonary arteries)
80
New cards
Veins (venous blood)
vessels carrying blood from capillaries back to heart. Very thin flabby walls with low pressure, but have one-way valves to prevent blood from backing up. Low in oxygen (except for pulmonary veins).
81
New cards
How does blood flow through the cardiac system
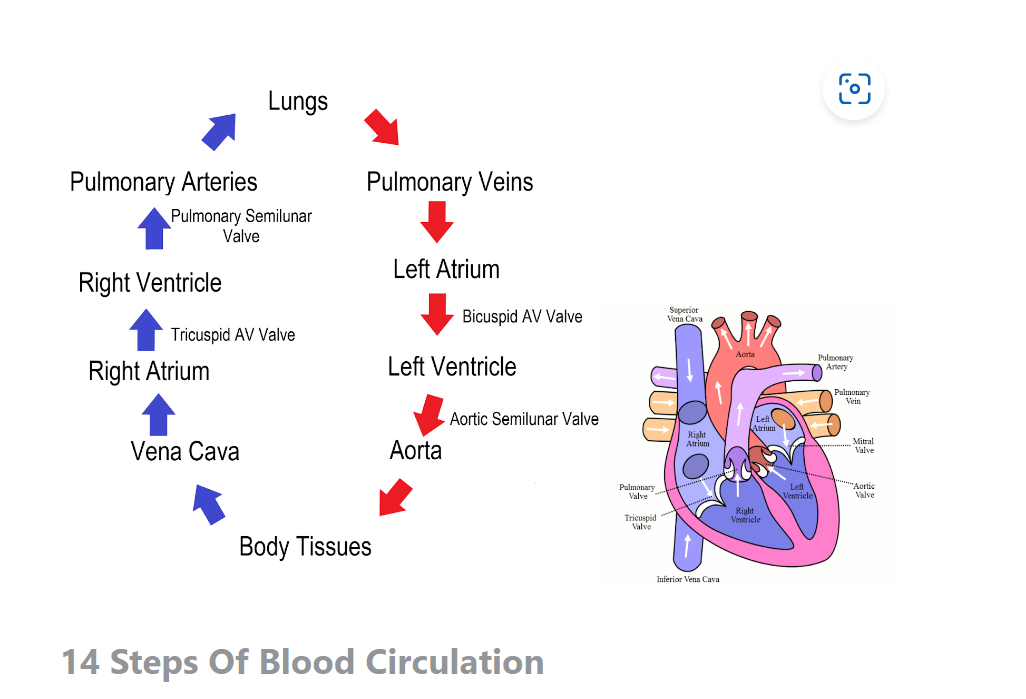
82
New cards
lub
closing of AV valves = S1
83
New cards
dub
closing of semilunar valves = S2
84
New cards
Diastole
chambers are relaxed, blood can flow in
85
New cards
Atrial Systole
atria contract, pushing blood into ventricles
86
New cards
Ventricular Systole
ventricles contract with high pressure, pushing blood into the lungs and systemic circulation
87
New cards
Diastolic pressure (bottom number)
arterial pressure when ventricle is relaxed
88
New cards
Systolic pressure (top number)
arterial pressure when ventricle contracts and pumps
89
New cards
Action Potential starts from pacemaker cells in
sinoatrial node (SA node) HCN channels open when hyperpolarized (Hyperpolarization-activated Cyclic Nucleotide-gated channels)
90
New cards
Myocardial Action Potential is longer than neural action potential
fast Na+ channels -> fast depolarization slow Ca++ channels -> plateau phase voltage-gated K+ channels cause repolarization
91
New cards
\[P wave\]
AP spreads rapidly across atria to cause depolarization and atrial systole (contraction)
92
New cards
\[QRS wave\]
Ventricles depolarize and contract
93
New cards
\[T wave\]
Ventricles repolarize
94
New cards
how the action potential spreads across the heart
From SA node to AV node, from AV node through bundle of His and along Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles
95
New cards
P-R/ P-Q
time for AP to spread from atria to ventricles
96
New cards
cardiac muscle contraction
"Excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Depolarization of the plasma membrane during action potentials, when voltage-gated Na+ channels are opened, causes voltage-gated Ca2+channels to open in the transverse tubules. (1) This allows some Ca2+ to diffuse from the extracellular fluid into the cytoplasm, which (2) stimulates the opening of Ca2+ release channels in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This process is called Ca2+-stimulated Ca2+release. (3) **The Ca2+ released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum binds to troponin and stimulates contraction**. (4) A Ca2+ (ATPase) pump actively transports Ca2+ into the (5) cisternae of the sarcoplasmic reticulum**, allowing relaxation of the myocardium** and producing a concentration gradient favoring the outward diffusion of Ca2+for the next contraction
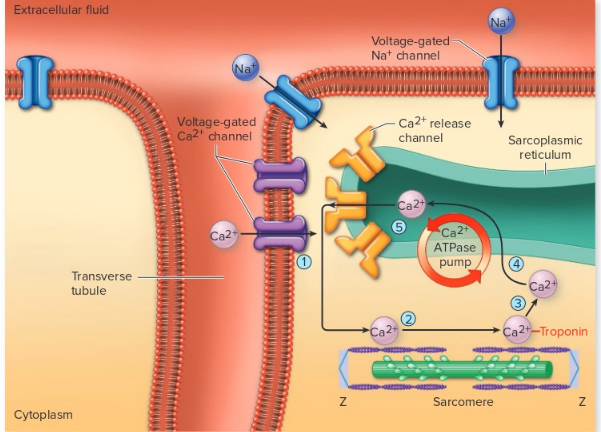
97
New cards
abnormal EKG
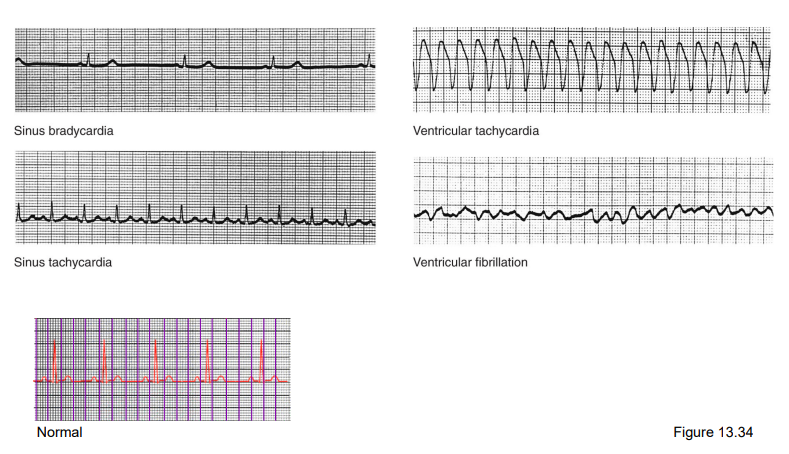
98
New cards
degrees of AV blocks
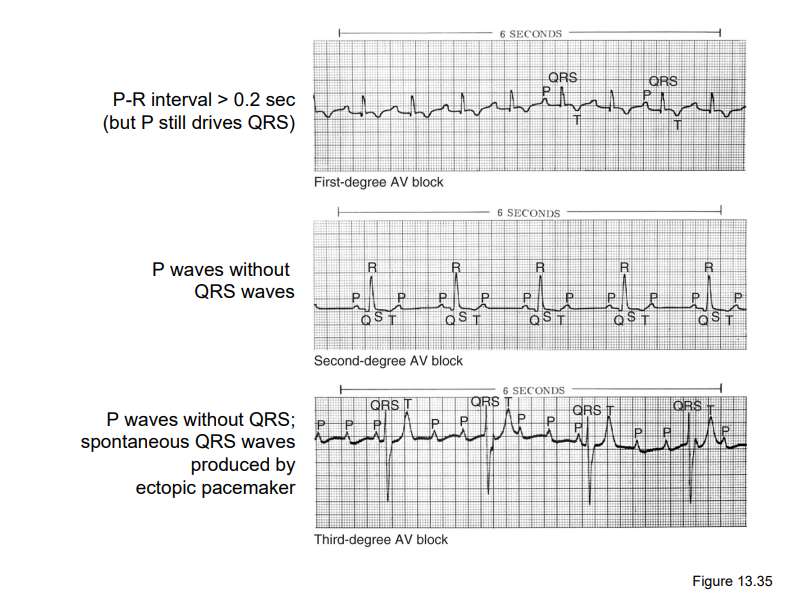
99
New cards
Sympathetic NS raises HR
sympathetic chain ganglia -> norepinephrine release onto pacemaker cells -> beta-adrenergic receptors -> increased cAMP -> open HCN channels, open Ca++ channels.
100
New cards
Parasympathetic NS slows HR
Vagus nerve -> acetylcholine release onto pacemaker cells -> muscarinic receptors -> decreased cAMP -> close HCN channels, open K+ channels