Psychology (Placement Test)
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Older Brain Structures
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
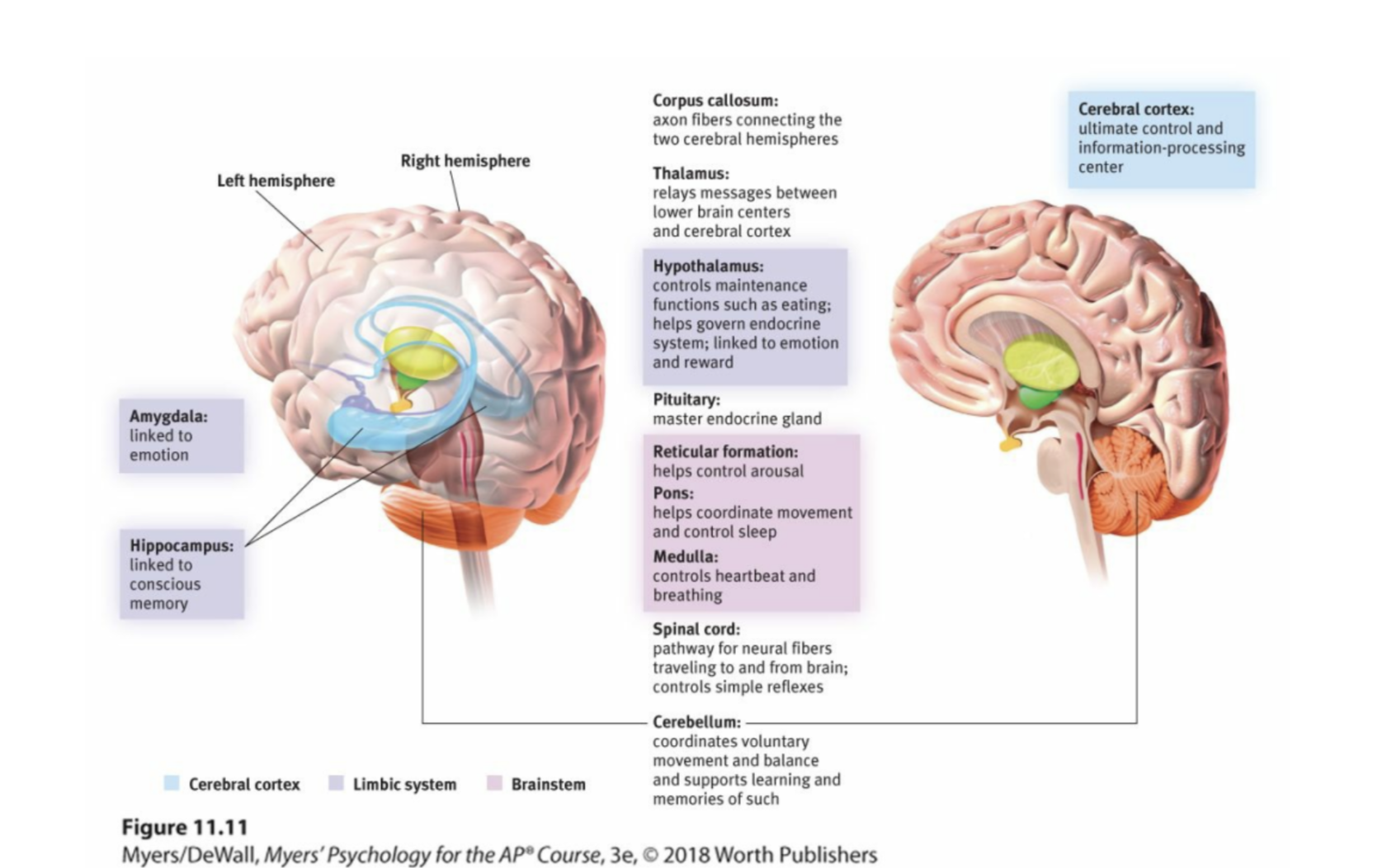
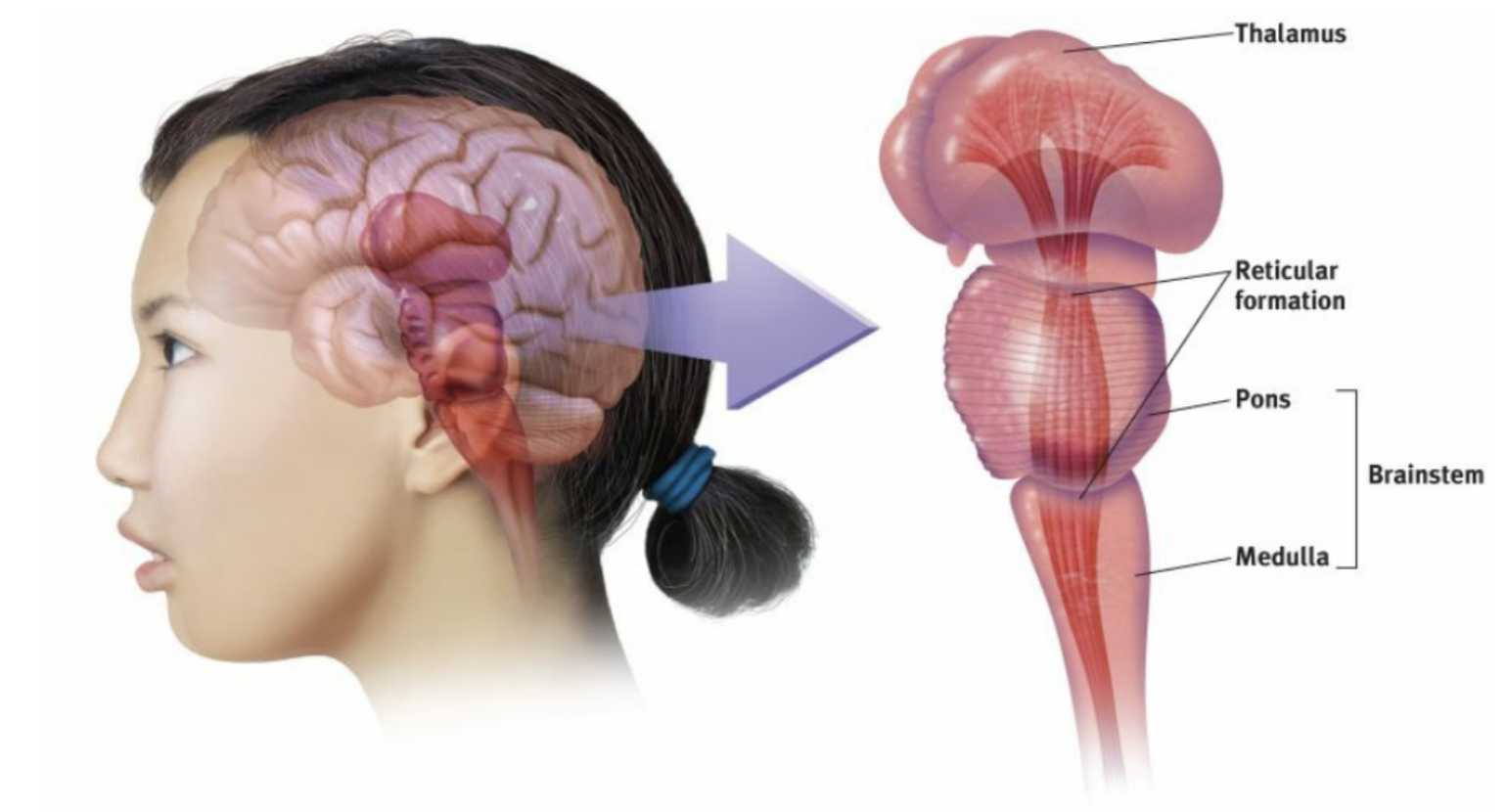
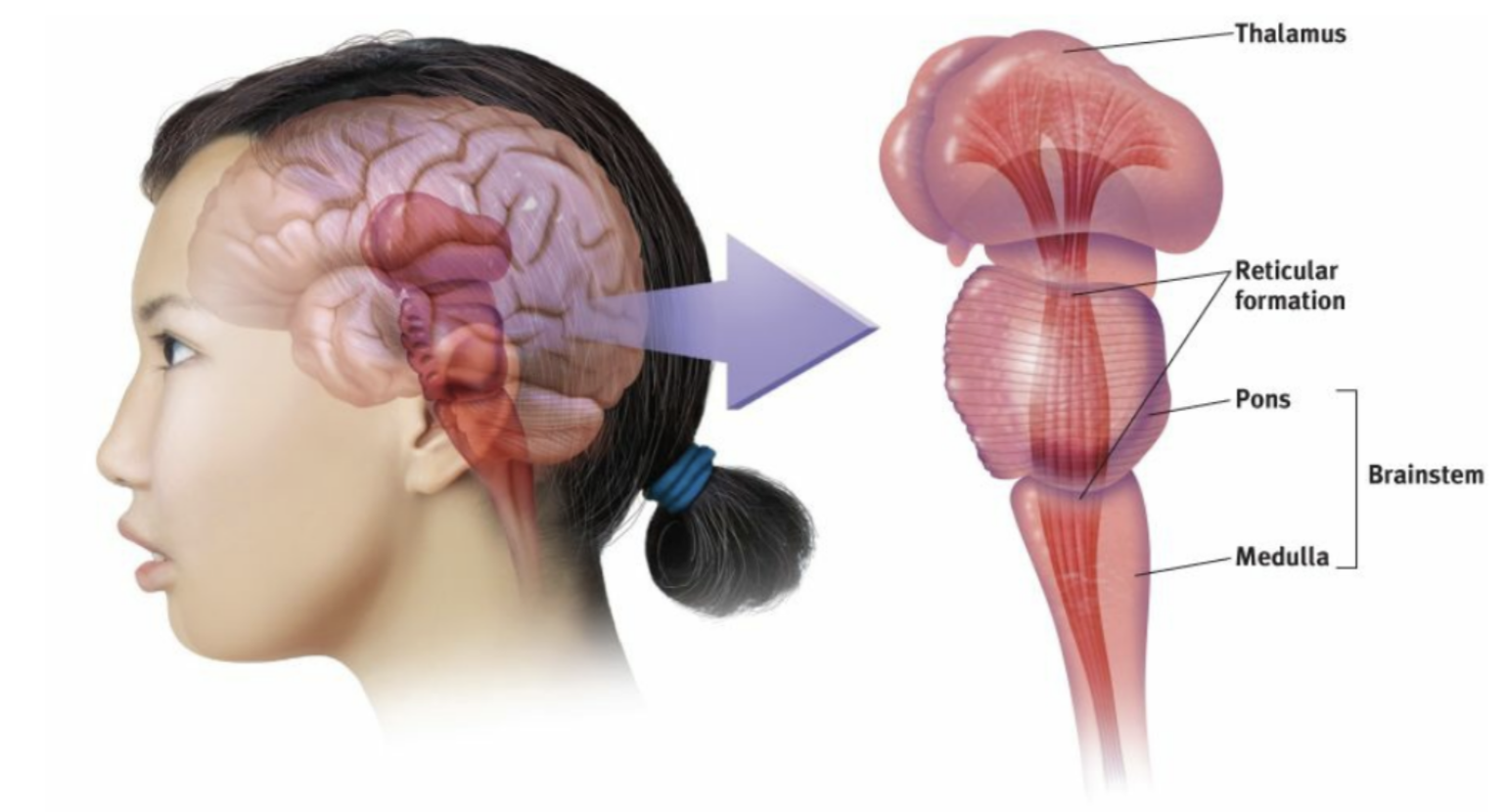
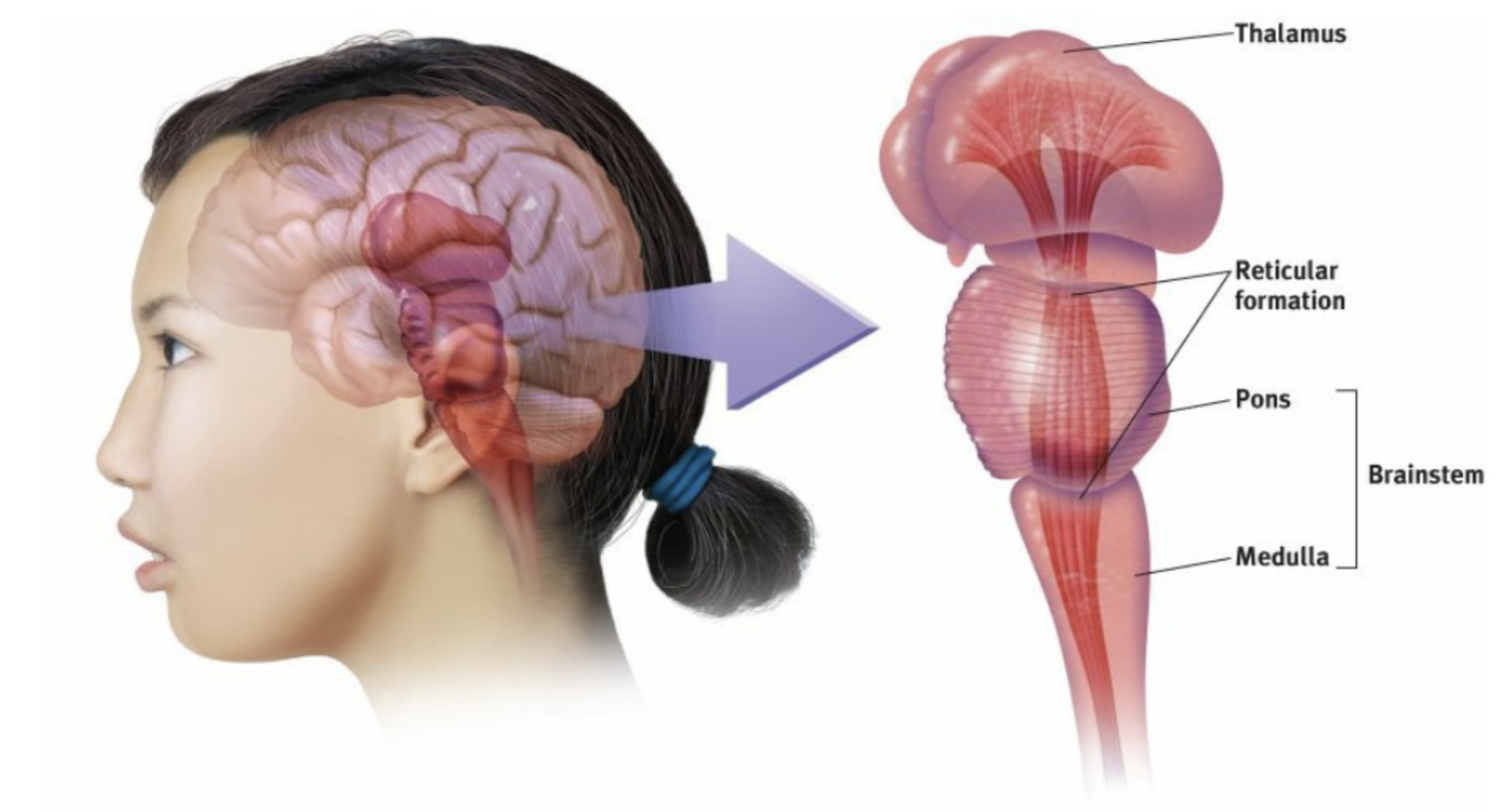
Brainstem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions.
medulla
The base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing.
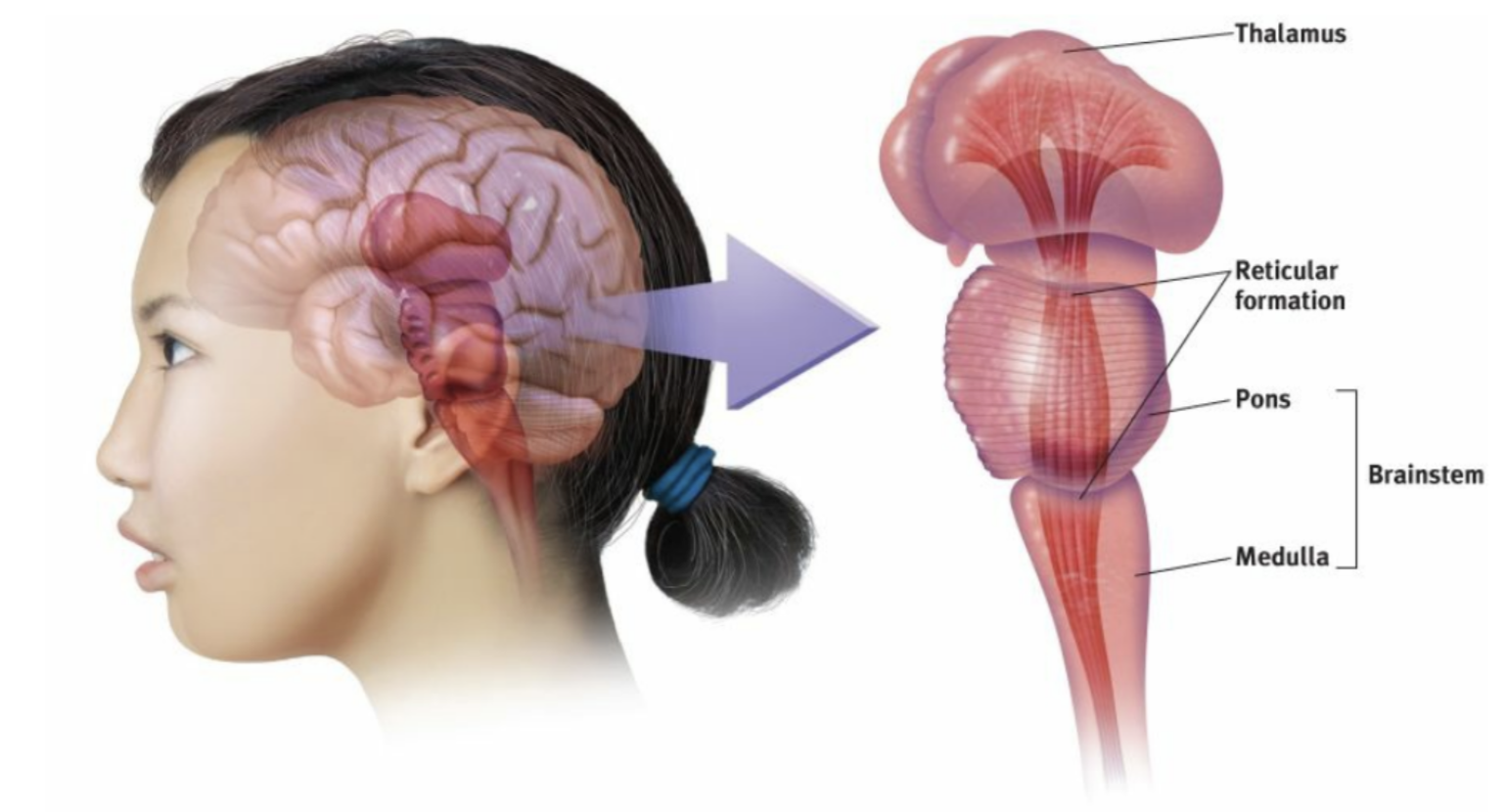
the reticular formation
A nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus and plays an important role in controlling arousal. It also controls the amount of information your brain can receive, limiting and filtering out sensory information that we don't want to pay.
cerebellum
the “little brain” at the rear of the brainstem; functions include processing sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory.
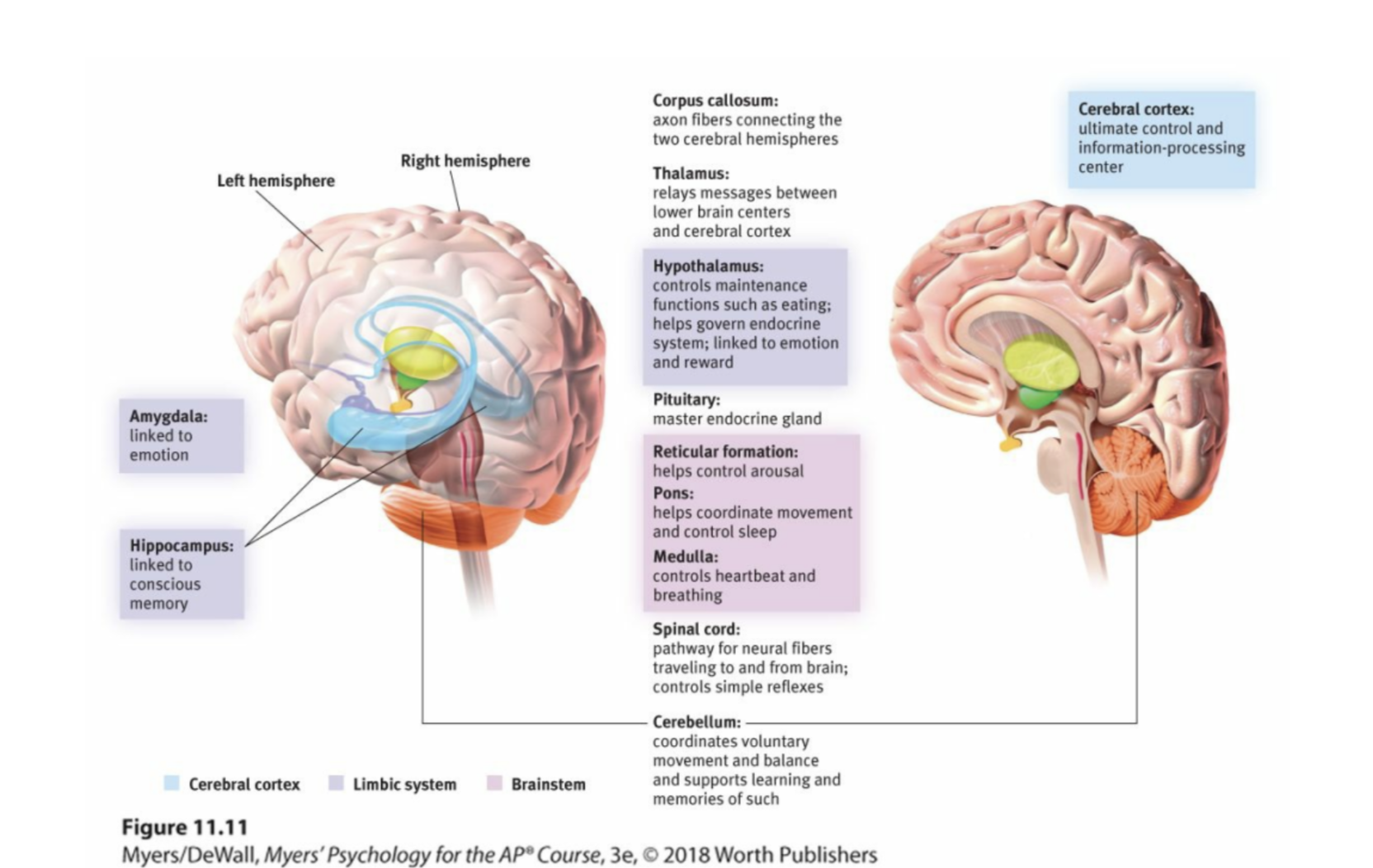
limbic system
neural system (including the amygdala, hypothalamus, and hippocampus) located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives.
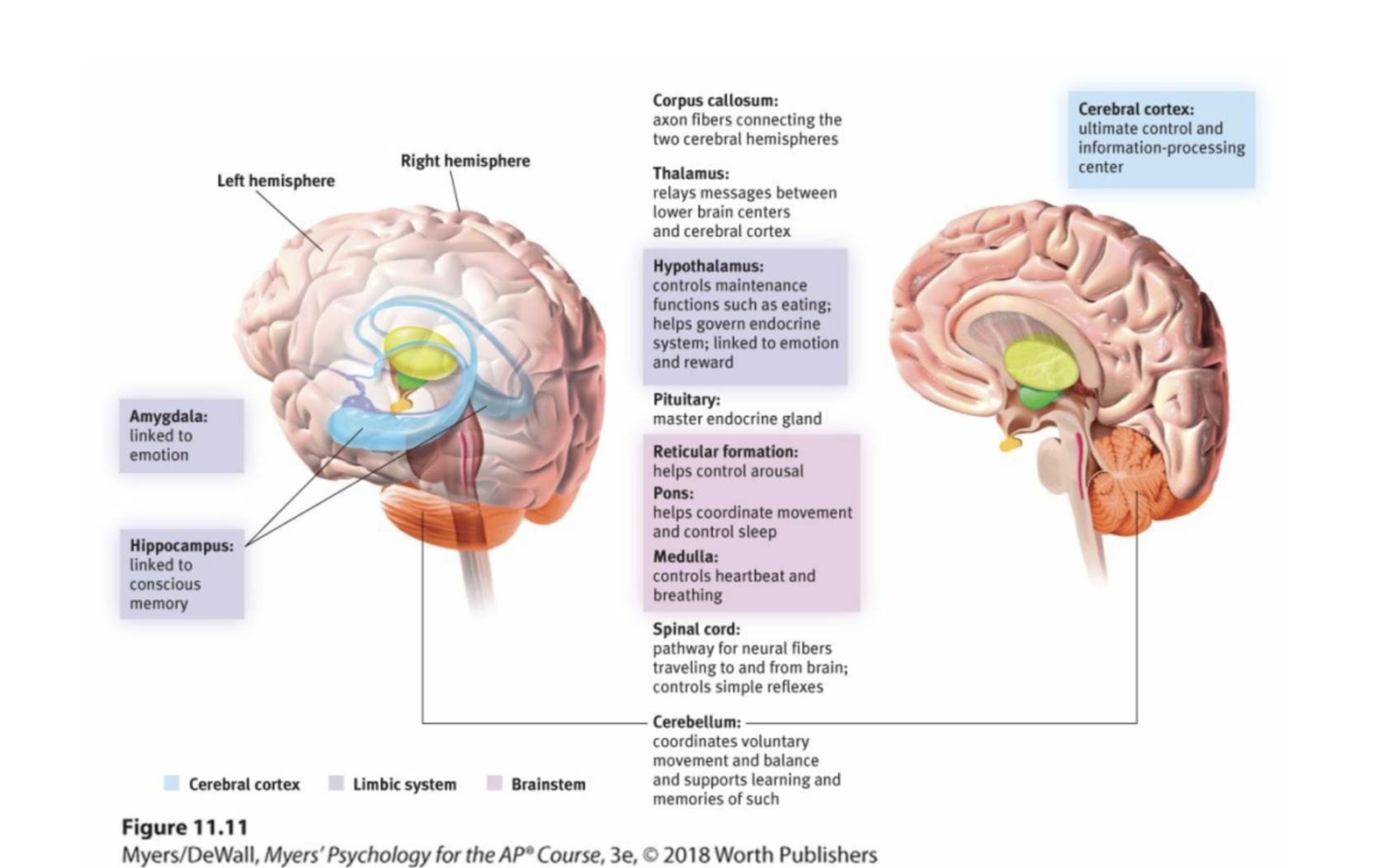
thalamus
the brain’s sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla.
amygdala
Two lima-bean-sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion.
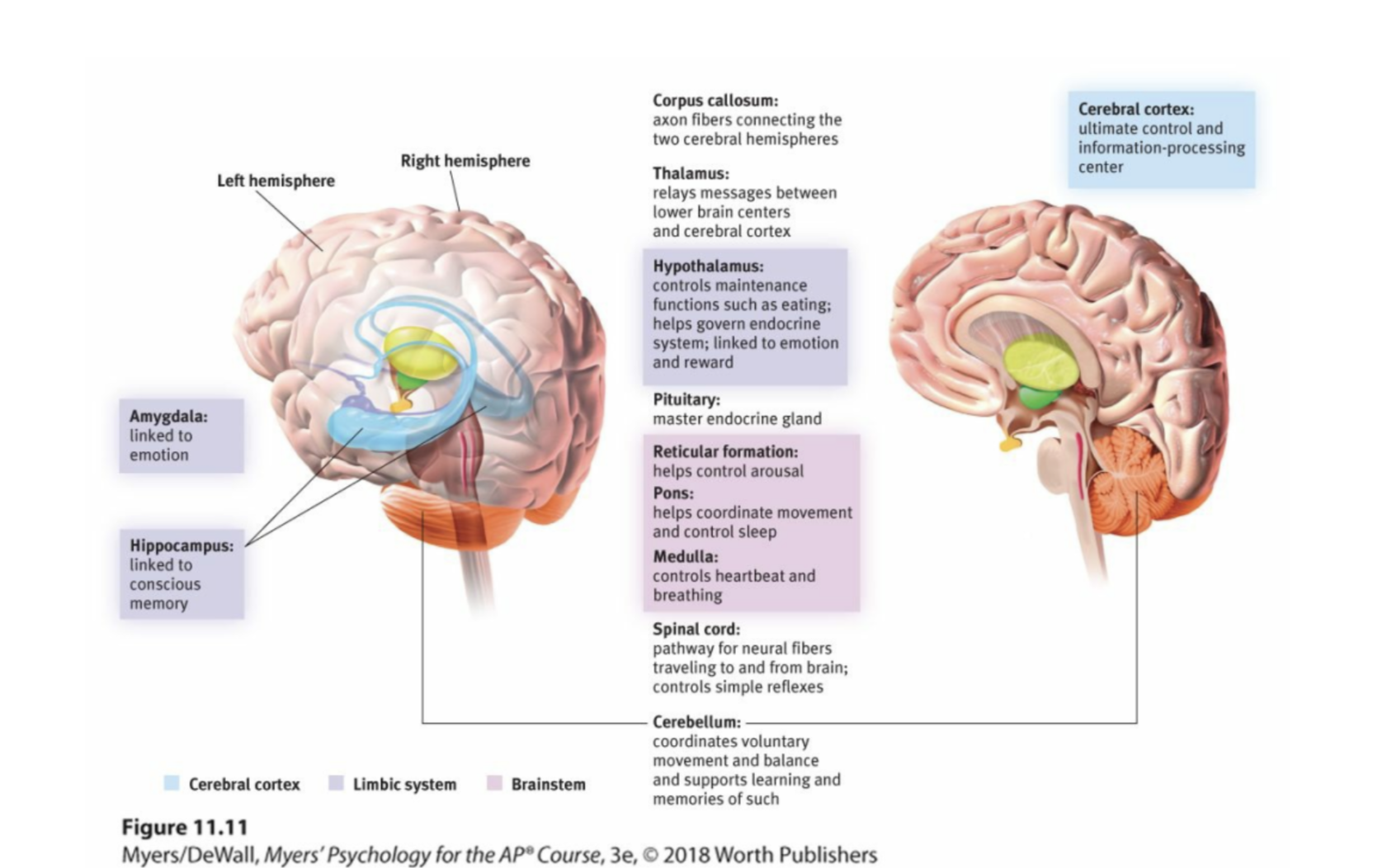
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
ex: brain cerebral cortex think abt sex→hypothalamus send signals for brain to secret hormones to pituitary (“master” gland)→intensify thoughts of sex
nucleus accumbens (in front of the hypothalamus)
another reward system to the hypothalamus
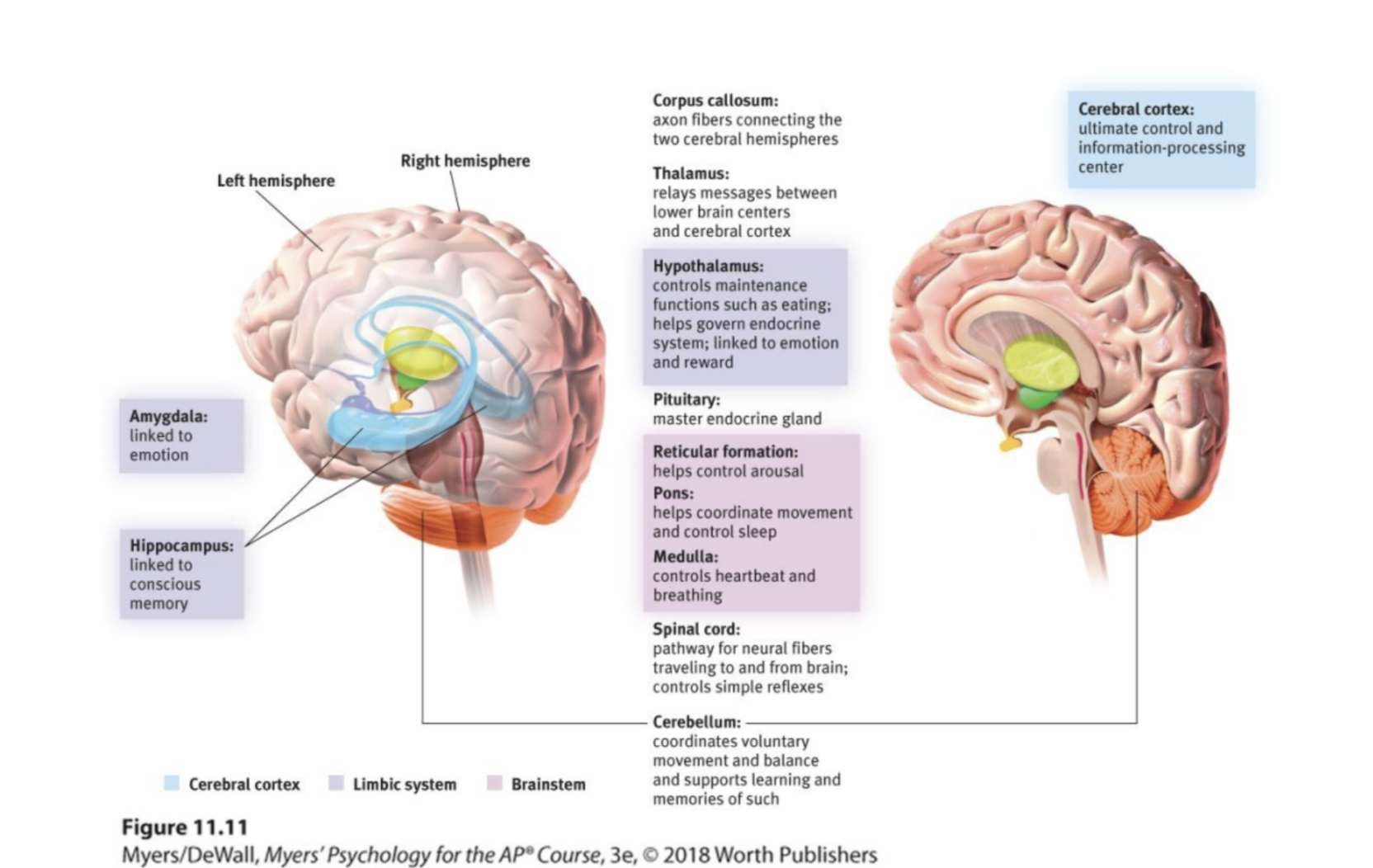
hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system that is in the shape of a seahorse; helps process for storage explicit (conscious) memories of facts and events.