FRNSC 410 Quiz #1
4.7(3)
Card Sorting
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:03 AM on 11/3/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
1
New cards
Reflective Ultraviolet Imaging System
Backronym of RUVIS and is used to illuminate small items and/or surfaces.
2
New cards
Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation
Backronym of LASER and has the advantages of having high intensity and defined operational wavelengths, but has the disadvantages of having limited flexibility with wavelength settings and is typically expensive.
3
New cards
High-Intensity Tunable-Wavelength Light Source
The backronym of HITWLS, this light source that has the advantages of a greater flexibility of wavelength settings and is less expensive than a laser, but has the disadvantage of a lower intensity than a laser.
4
New cards
Forensic Light Source
The backronym of FLS, it is another name used for a HITWLS.
5
New cards
Alternate Light Source
The backronym of ALS, it is another name used for a HITWLS.
6
New cards
lamp
A component of a HITWLS, this object offers an intense, white illumination source using xenon and produces wavelengths in the UV and VIS ranges.
7
New cards
cold mirror
A component of a HITWLS, this object is able to transmit UV and VIS light, but blocks IR.
8
New cards
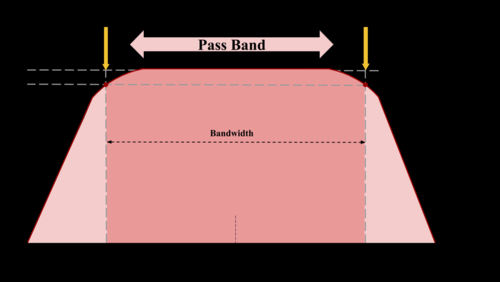
bandpass filter
A component of a HITWLS, this item is able to "tune" wavelengths, which passes frequencies within a certain range and rejects frequencies outside that range.
9
New cards
collimation lens
A component of a HITWLS, this object focuses light into a light guide.
10
New cards
light guide
A component of a HITWLS, this object is composed of a single-core liquid or fiber optic bundles.
11
New cards
focusing lens
A component of a HITWLS, this object is able to provide uniform illumination with sharp edges. It permits range changes, also known as spot size, from being distant to close up.
12
New cards
central wavelength
This is the selected wavelength that describes the wavelength that is at the center of the range of a filter being used.
13
New cards
bandwidth
This is measured at half maximum and referred to as the full width at half maximum.
14
New cards
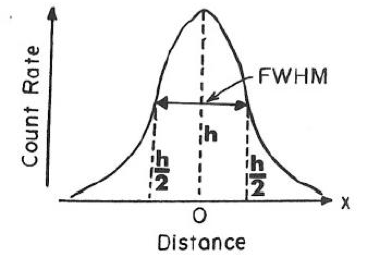
full width at half maximum
The backronym of FWHM. It is associated with the bandwidth of a HITWLS device. It is where the filter transmits at least 50% of light at the central wavelength.
15
New cards
dark
The type of lighting environment a HITWLS should be used in.
16
New cards
415 nm
The wavelength where blood exhibits the strongest absorption.
17
New cards
common IR sources
Incandescent lamps (tungsten and quartz-halogen), HITWLS (requires IR port), and sunlight are all considered this.

18
New cards
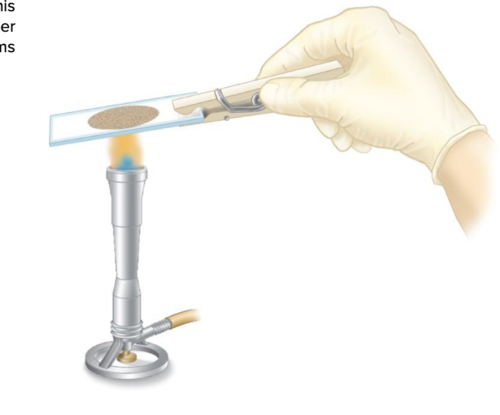
heat fixation
This type of blood fixing is challenging to perform at a scene and aids the adherence of a specimen to its underlying surface.
19
New cards
chemical fixation
This type of blood fixing is more frequently used and is less challenging to perform at a scene. Common fixatives are 5-sulfosalicylic acid and menthol, ethanol, and acetone.
20
New cards
ballistics
The study of the dynamics or flight characteristics of projectiles. It is primarily concerned in reconstruction of shooting events.
21
New cards
interior ballistics
The study of projectile behavior from propellant ignition to barrel exit.
22
New cards
transitional ballistics
The study of projectile behavior from barrel exit to point where pressure behind the projectile is equalized. It is the intermediate stage between interior and exterior ballistics.
23
New cards
exterior ballistics
The study of projectile behavior from the point where pressure behind the projectile is equalized to substrate interaction.

24
New cards
terminal ballistics
The study of projectile interaction with objects and other materials.

25
New cards
firearm safety rules
The following numbered list refers to this:
1) Treat all firearms as if they were loaded
2 Never let the muzzle cover anything you are not willing to destroy
3) Keep your finger off the trigger until your sights are on the target
4) Identify your target, and what is behind it.
1) Treat all firearms as if they were loaded
2 Never let the muzzle cover anything you are not willing to destroy
3) Keep your finger off the trigger until your sights are on the target
4) Identify your target, and what is behind it.
26
New cards
Jeff Cooper
The name of the man who created the "firearm safety rules."
27
New cards
loaded
The gun is considered this when there are one or more bullets in the cartridge.
28
New cards
unloaded
The gun can only be considered this when there are no bullets in the cartridge.
29
New cards
rifled barrel
This type of firearm is designed to fire one projectile. It includes gun types such as: pistols, rifles, submachine guns, and machine guns. The barrels of these guns have lands and grooves.
30
New cards
smooth-bore barrel
This type of firearm is designed to fire multiple projectiles. It includes a shotgun as the type of gun. The barrels of these guns are smooth.
31
New cards
pistol
This type of gun is a single-shot gun and includes subtypes such as: revolvers, self-loading guns, and automatics.

32
New cards
swing-out cylinder
Some revolvers have this feature where the cylinder of the gun can be reloaded by swinging out the cylinder to the left or right.

33
New cards
blowback
A semi-automatic operation where the bolt and barrel of the gun are not locked and are held together by recoil spring pressure.
34
New cards
recoil operation
A semi-automatic operation where the bolt and barrel are locked and remain locked for some distance after discharge.
35
New cards
hammer
This is a component of the firing mechanism, which strikes the firing pin.

36
New cards
firing pin
This is a component of the firing mechanism, which strikes the primer or ridge of the cartridge.

37
New cards
striker
This is a spring-driven rod-like firing pin, or a component that impacts the firing pin, which travels in linear path to strike the primer.
38
New cards
single action only
This is an action type where the hammer must be cocked to discharge firearm.
39
New cards
double action only
This is an action type where the firearm can be discharged only with a trigger pull. If the hammer of the gun is present, it cannot be cocked.
40
New cards
single action/double action
This is an action type where the firearm can be discharged using either single action or double action. In semiautomatic firearms that have a hammer present, it is cocked during slide movement.
41
New cards
rifle
This type of firearm is either a single shot, pump action, lever action, or bolt action
42
New cards
single shot rifle
This is a firearm that holds only a single round of ammunition, and must be reloaded manually after every shot.
43
New cards
lever action
This is a design wherein the breech mechanism is cycled by an external lever generally below the receiver.
44
New cards
bolt action
This type of rifle is a type of manual firearm action that is operated by directly manipulating the bolt via a bolt handle, which is most commonly placed on the right-hand side of the weapon (as most users are right-handed).
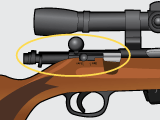
45
New cards
turn bolt
This is another term for "bolt action."
46
New cards
gas operated semi-automatic
With this type of rifle, the expanding gases from the shell move up the barrel into a gas port that regulates how much pressure is exerted against a piston under the fore end. This piston drives back the bolt to cycle the shotgun for the next shot.
47
New cards
clip
This is a device that is used to store multiple rounds of ammunition together as a unit for insertion into the magazine or cylinder of a firearm. Some styles of this device are stripper, full moon, and half-moon.
48
New cards
magazine
This is a container that holds cartridges under spring pressure to be fed into the gun's chamber. It is not the same as a clip.
49
New cards
submachine gun
This firearm is an automatic gun and fires pistol ammunition. These firearms are normally compact, and intended to be used at close combat ranges.
50
New cards
machine gun
This firearm is an automatic gun that fires bullets in rapid succession for as long as the trigger is pressed. This firearm is for military use and needs to be propped on steady ground and fires rifle ammunition.
51
New cards
shotgun
This type of firearm has a long barrel designed to shoot a straight-walled cartridge known as a shotshell, which usually discharges numerous small pellet-like spherical sub-projectiles called shot, or sometimes a single solid projectile called a slug.
52
New cards
aperture sight
This sighting device is a combination of a bead or post front sight and a round hole set on the rifle's receiver close to the shooter's eye.
53
New cards
telescopic sight
This sighting device consists of a main tube with lenses to magnify distant objects, it has line reticles for lining up the center of a target. This sight is mounted on top of the barrel or action of a firearm.
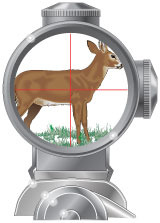
54
New cards
holographic sight
This sighting device uses a non-magnifying gunsight that allows the user to look through a glass optical window and see a holographic reticle image superimposed at a distance on the field of view.
55
New cards
broaching
This type of barrel rifling method that uses a toothed tool to remove material, resulting in lands and grooves inside the barrel of the firearm.

56
New cards
swaging
This is a rifling method in which a rifling button is forced down a drilled-out barrel blank. The button simultaneously expands the barrel to its final diameter and embosses the lands and grooves on the interior.
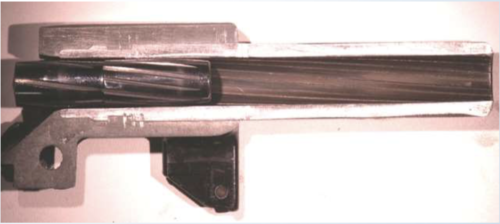
57
New cards
hammer forging
This is a rifling method in which a barrel blank is hammered down over a mandrel. This method is used to make polygonal rifling.

58
New cards
electrochemical etching
This is a rifling method in which the grooves of the rifling are produced by an electrochemical process. The barrel and probe are immersed in an electrolyte (NaNO3) solution.
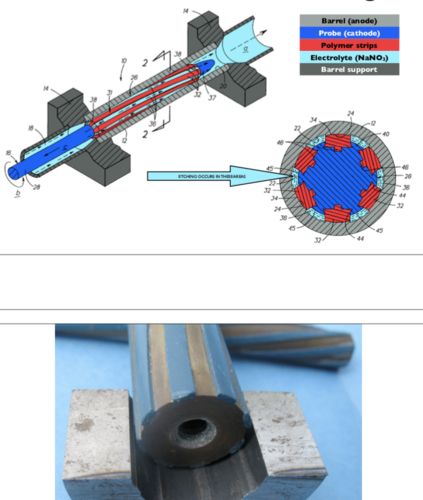
59
New cards
gauge
The bore diameter of a barrel is expressed as this form of measurement, determined by the number of lead balls of size equal to the approximate diameter of the bore that it takes to weigh one pound.
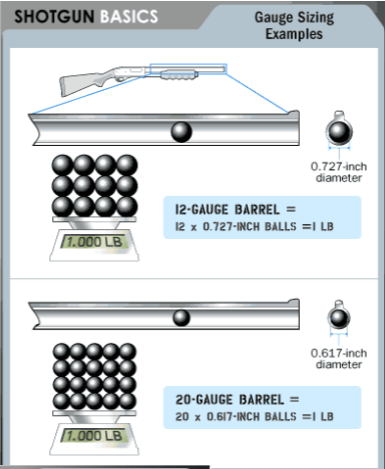
60
New cards
choke
This is an interior constriction placed at or near the muzzle end of a shotgun's barrel to control shot dispersion. The tighter this is constriction is, the more controlled the shot dispersion is and the further distance it will travel.
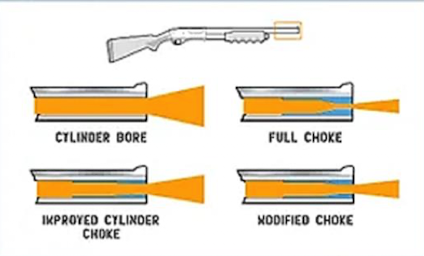
61
New cards
bore diameter
This is the diameter of the circle formed by the tops of the lands inside the barrel of a rifled firearm.
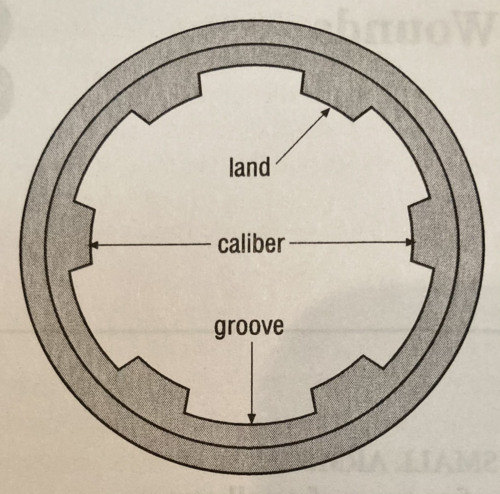
62
New cards
caliber
The diameter of the bore measured from land to land. Not the same thing as bore diameter.
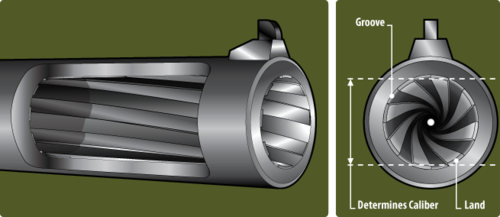
63
New cards
410
What is the only shotgun that doesn't use gauge?
64
New cards
ammunition
Designed to be fired out of rifled barrels and smooth-bore barrels. Cartridges can be rifled and shot out of shotguns.

65
New cards
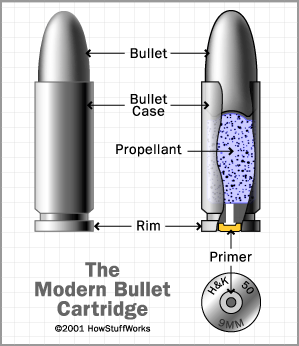
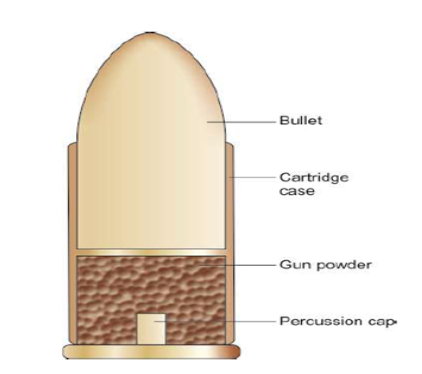
primer
An explosive chemical compound that ignites gunpowder when struck by a firing pin. May be placed in rim of the case of in the center of the base.
66
New cards
projectile
The object expelled from the barrel. A bullet is one of these. Commonly is a copper jacket.
67
New cards
propellant
Sometimes called gunpowder. Classified as an explosive. Produces thick vapor, draws moisture, and thus rusts parts of a gun. Combusts rapidly, but does not detonate. More of this is added than needed in order to make sure the projectile is ejected fully from the barrel.
68
New cards
cartridge
Also called a round. A type of pre-assembled firearm ammunition packaging a projectile and its components.
69
New cards
single-base
A type of smokeless powder composed of nitrocellulose, stabilizers, and additional additives. Manufactured by the nitration of cellulose.
70
New cards
double-base
A type of smokeless powder composed of nitrocellulose, nitroglycerin, stabilizers, and additional additives.
71
New cards
triple-base
A type of smokeless powder utilized by the military.
72
New cards
powder granules
Ball, disc, rod, and lamel are all used to describe geometries of what? These shapes are used to control burn rate.

73
New cards
modern primers
Lead styphnate, antimony sulfide, and barium nitrate are all common constituents of what?
74
New cards
Sintox
This lead-free primer is designed to eliminate lead vapors.
75
New cards
head stamp
These indicate the manufacturer of a bullet among other information.
76
New cards
wad
This is part of a shot shell that is designed to produce more consistent patterns by protecting the shot and ensuring reliable powder combustion.
77
New cards
birdshot pellets
Another term for smaller shot sizes.
78
New cards
buckshot pellets
Another term for larger shot sizes.
79
New cards
unload it
What should you do with a firearm before packaging it as evidence?
80
New cards
if gun is loaded
What is the first thing you should check for when you see a firearm on scene?
81
New cards
recorded and photographed
Condition of firearm upon discovery must be ______ and _______
82
New cards
gunshot residue
The backronym of GSR. This includes all residue produced from firearm discharge. Some sources include primer, propellants, and projectiles.
83
New cards
lead styphnate
This chemical is the most common initiating explosive in primer and is a source of GSR.
84
New cards
barium nitrate
This chemical is the most common oxidizing agent in primer and is a source of GSR.
85
New cards
antimony sulfide
This chemical is the most common fuel in primer and is a source of GSR.
86
New cards
Tetracene
This chemical is the most common sensitizer in primer and is a source of GSR.
87
New cards
organic and inorganic
GSR components are separated into two chemical categories. What are they?
88
New cards
SEM/EDX
The most commonly used instrumental method to detect GSR in the lab.
89
New cards
light background
This type of background should be used when using and intense, white illumination to visualize GSR patterns. Stereomicroscopy or other magnification can be used with this type of illumination as well.
90
New cards
dark background
This type of background should be used when using IR illumination techniques, HITWLS, and radiography to visualize GSR patterns.
91
New cards
400-555 nm
This wavelength range (VIS) from a HITWLS should be used for visualizing GSR patterns in order to cause the substance to fluoresce.
92
New cards
nondestructive
If you want to try and visualize GSR on a dark background, what type of techniques should you use first?
93
New cards
diphenylamine
This is a test that tests for nitrates and nitrites, resulting in a product that is blue in color. Some disadvantages include it being very corrosive and not only reacting to one oxidizing agent.
94
New cards
modified Griess test
The backronym of MGT, this is a test for nitrites only. To perform this test, test it on patterns and spots.
95
New cards
sodium rhodizonate test
This test is used to detect lead. It is conducted by dampening filter paper with 15% acetic acid and pressing it onto material, producing a scarlet color if it is positive.
96
New cards
dithiooxamide test
This is a test for copper and nickel. To perform this test, first dampen filter paper with ammonium hydroxide and press it to material. A color change will occur. Green indicates copper, blue or pink indicate nickel.
97
New cards
bullet impact mark
The backronym of BIM. Based on Locard's exchange principle in the way that material from the projectile it transferred to the substrate and vice versa.
98
New cards
ejecta cloud
Produced upon impact between projectile and substrate. May contain material from both the projectile and substrate.
99
New cards
two hours
Within what time frame can significant amounts of GSR be lost from the skin?
100
New cards
swabbing
A method of GSR collection that involves different types of swabs and filter paper moistened with solvent to sample areas. Materials are then extracted and analyzed.