Genetics E1- Overview
1/51
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is the comprehensive analysis of entire genomes, all genes and their interactions?
*uses advanced tech to study complete DNA sequences and genome wide patterns
Genomics
What is the study of individual genes, heredity, and genetic variation that focuses on how traits are inherited & how specific genes function at the molecular level?
Genetics
What is a double helix structure that is organized into functional units called genes?
DNA
What bases are seen in RNA?
Purines: Adenine (A) & Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C) & Uracil (U)
What bases are seen in DNA?
Purines: Adenine (A) & Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines: Cytosine (C) & Thymine (T)
How do uracil & thymine differ?
By a single methyl group (CH3)
What structure is responsible for passing genetic information from one generation to the next, composed of tightly packed DNA and associated proteins?
Chromosomes
How many total chromosomes are there?
46
How many chromosome pairs are there?
23 → 22 autosome pairs & 1 sex chromosome pair
What primarily drives sex determination in humans?
SRY gene on Y chromosome→ initiates male gonadal/ testis development
absence of SRY → ovary formation
What encodes proteins for oxidative metabolism and essential RNA molecules (tRNA, rRNA) required for protein synthesis w/in the mitochondrion?
mtDNA
What is the specific physical location of a gene or other DNA sequence on a chromosome?
Locus
What is an allele?
One of two or more variants of a gene that arise by mutation & are found at the same locus on homologous chromosomes
What term describes a genotype or individual having 2 identical alleles for a particular gene (one on each homologous chromosome)?
Homozygous
What term describes a genotype or individual having 2 different alleles for a particular gene (one on each homologous chromosome)?
Heterozygous
What is a gene map?
Diagram showing relative locations of genes & other identifiable DNA sequences on chromosomes
What is the process of determining the specific locations of genes on chromosomes and the relative distances between them?
*also includes methods to ID genetic loci associated w/ particular traits or diseases
Gene mapping
What is genotype?
Genetic makeup of an individual; contains genes that may or may not be expressed
What is phenotype?
Observable expression of genes
Ex: hair & eye color, height, blood type
What is the shorter arm of a chromosome?
p-arm
What is the longer arm of a chromosome?
q-arm
What separates the arms of a chromosome?
Centromere
What is each arm of a chromosome further subdivided into?
Regions, bands (numbered outward from the centromere) & sub-bands
What do the terms p telomere or “ptel” & q telomere or “qtel” refer to?
Ends of the p-arm & q-arm
How is the nomenclature “3p22.1” read?
Chromosome 3, short arm, region 2, band 2, sub-band 1
What is the process where genetic information is transcribed from DNA to mRNA?
Transcription
What is the process of converting the sequence of a mRNA molecule to a sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis?
Translation
During translation, what component of the cell is responsible for reading the sequence of mRNA in groups of 3 bases (codons) to assemble the protein?
Ribosome
What is the triplet of nucleotide bases in the mRNA that codes for a particular amino acid?
Codon
What is a reading frame?
Order of triplet codons, which codes for specific amino acids
What is the reading frame for glutamine (Gin)?
CAA or CAG
What is the reading frame for tyrosine (Tyr)?
UAC
What is the reading frame for isoleucine (Ile)?
AUA
What does the reading frame UAA encode?
Nothing
What is a change in DNA that may aversely affect the host, occurring spontaneously through errors in DNA duplication and repair (MC) or exposure to mutagenic agents?
Mutation
What type of mutation replaces a single nucleotide with another nucleotide?
*MC type of mutation
Substitution
What term refers to replacing pyrimidine for pyrimidine or purine for purine in substitution mutations?
ex: C for T, A for G
Transition
What term refers to replacing pyrimidine for purine or purine for pyrimidine in substitution mutations?
Ex: A for T, C for G
Transversion
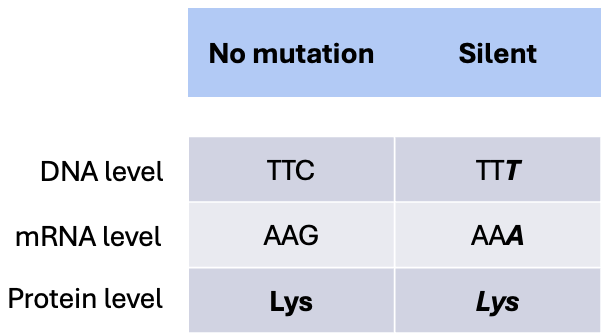
What type of substitution mutation occurs when the base pairs get swapped out, but the mutated RNA sequence produces the same amino acid?
Silent mutation
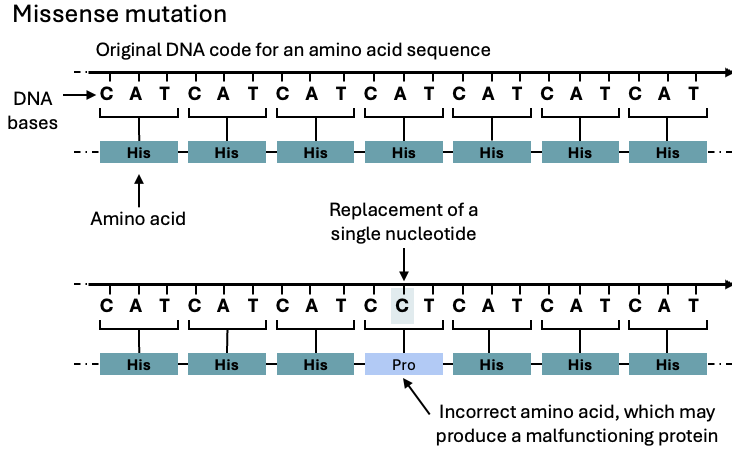
What type of substitution mutation occurs when a nucleotide gets changed and results in a different amino acid in the protein?
Ex: Sickle Cell Anemia
Missense mutation
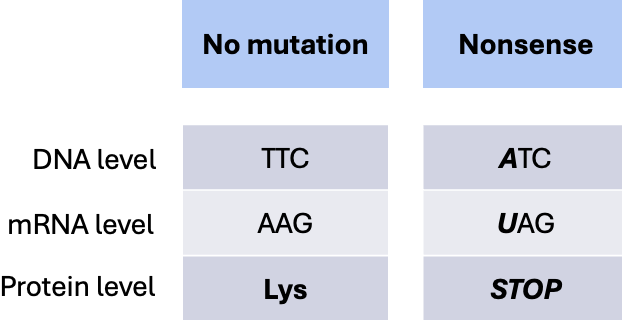
What type of substitution mutation occurs when a base change causes an early stop codon, resulting in the protein being too short and almost always nonfunctioning?
*worst type of substitution mutation
Nonsense mutation
What type of mutation involves the loss of a section of DNA?
Deletion
What type of mutation involves the addition of one or more nucleotides to a gene?
Insertion
What is the loss or gain of chromosomes?
Aneuploidy
What is the gain of 1 or more complete haploid complements?
Polyploidy
What is the loss/ absence of a single chromosome from a diploid pair?
*results in 2n-1 chromosomes (ex- 45 chromosomes in humans)
Monosomy
What is the gain of 1 chromosome?
Trisomy
What is the failure of chromosomes to separate (disjoin) and move to opposite poles of the division spindle?
Nondisjunction
What condition can result from non-disjunction?
Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome)
What is the general viability of monosomy?
Typically incompatible with life, resulting in early embryonic loss
Exception: Turner syndrome
What condition results when individuals are missing 1 X chromosome (absence of second sex chromosome)?
Karyotype: 45,X or X0
Turner syndrome
What is the presence of 2 or more cell lines that differ in genetic makeup?
Mosaicism