The Retina
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is the retina
the retina is the light sensitive part of the eye which is responsible for visual transduction
which is responsible for converting light energy into electrical signal into neurons
describe what photoreceptors are
they are sensory receptors of the retina that detect light and convert it into electrical signals.
There are two main types: rods and cones.
what are rods and cones
rods are sensory receptors of the retina which are responsible for black & white (greyscale) vision
cones are sensory receptors that detect color and are responsible for high acuity vision in bright light conditions.
why are we able to see the EM spectrum
because the wavelength of our photoreceptors transduce into electrical transduction
describe the structure of the retina
the retina is made up of layers of neuronal cells with photoreceptors at the back of the retina
Photoreceptors synapse with the bipolar cell which then synapse with retinal ganglion cells which takes the electrical signal from the retinal to the brain via the axon (yellow) which goes across the front of the retina & leave at the optic nerve to take the information onto the brain
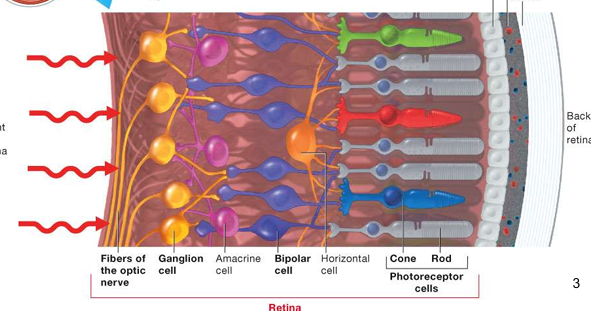
name 2 types of neuronal in the retina
the horizontal cells
amacrine cells
they are important to lateral processing
describe the structure of the photoreceptor
it is divided into 3 segment : outer segments, the inner segment, & synaptic terminal
The outer segment contains the photopigments that absorb light,
the inner segment contains the cell's metabolic machinery,
the synaptic terminal transmits signals to bipolar cells.
Approximately how may rods & cones in the retina
there is 100 million rods
and 6 million cones
why at night are we unable to distinguish colours
At night, we primarily rely on rods for vision, which has a high sensitive to light so are unable to distinguish between color,
cones have low sensitivity to light because they require bright light for colour to function effectively.
what does the fovea allow
it allows us to see fine detail and colour due to the high density of cones.
what does the peripheral vision allow
it allows us to detect motion and see in low light conditions, as it relies primarily on a higher density of rods , so we are unable to detect colour
why are rods highly convergent and cone not
because up to 100 rods feed into one ganglion cells, allowing for greater sensitivity to light but less detail in visual information.
cones are less convergent, with one or a few cones connecting to a single ganglion cell, providing high resolution images.
what is the fovea
the fovea is the area where lens focuses the imageson the retina,
providing the highest visual acuity and color perception due to a high density of cones.
what is photopigment
it is the outer segment of the photorecepetor
it consist of the protein opsin and a chromophore called retinal
what is opsin
it is a GPCR and the retinal is the ligand
what are the 4 photopigmentrs
There are four types of photopigments in the retina: rhodopsin (found in rods)
three types in cone which are sensitive to red, green and blue light
what happens when the retinal is activated by light
it changes shape from 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinal
this tiggers a conformational change in opsin, initiating the phototransduction cascade which results in hyperpolarisation of the photoreceptor cells.
describe photoreceptor activity in the dark
the outer segment of the photoreceptor contains a cGMP-gated cation channel
next the cGMP opens the cation channel which allows sodium ion to move inot the cell down its electrochemical gradient
because in the dark cGMP levels are high due to the action of guanylate cyclase which coverts GTP to cGMP, the cGMP-gated cation channels are kept open
movement of sodium into the cell then depolarisation (to approx -40mV)
depolarisation then causes the opening of the voltage gate calcium channels in the synaptic terminal
so, in the dark, the photoreceptors are depolarized, releasing neurotransmitters and maintaining a steady signal
describe photoreceptor activity in the light
light causes the 11-cis-retinal to change conformation to all-trans-retinal which causes a conformational change when the G protein is stimulated
transducin is also a g protein associated with the receptor inactive (inactive bound to gdp, activated to gtp exchange)
activation of transducin causes the activation of phosphodiesterase (PDE), which decreases cGMP levels.
This causes cGMP levels to fall, and cGMP-gated channels close the cGMP gated cation channel
closure of this means that sodium ion is no longer moving into the cell,
leading to hyperpolarization of the membrane potential.
Hyperpolarization then causes a closure of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels, and decreases the amount of neurotransmitter released
•Therefore in the light, the photoreceptor is hyperpolarized and neurotransmitter release decreases