A level OCR Biology - Biological Molecules
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Name 5 roles of water
It is a reactant in lots of chemical reactions
It is a solvent
It transports substances
It helps with temperature control
It is a habitat
Describe the structure of a water molecule
One atom of oxygen
Two atoms of hydrogen
What makes water polar?
It has a partially negative charge on one side due to the negative oxygen
It has a partially positive side due to the positive hydrogen
What is hydrogen bonding?
The partially negative oxygen atoms attract the partially positive hydrogen atoms of other molecules
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celsius
How do hydrogen bonds give water a high specific heat capacity?
The hydrogen bonds between water molecules can absorb a lot of energy, so it takes a lot of energy to heat up the water
How does having a high specific heat capacity make water a good habitat?
It means that the water does not experience rapid temperature changes
Why does water have a high latent heat of evaporation?
It Takes a lot of energy to break the hydrogen bonds between water molecules, so a lot of energy is used up when it evaporates
Why is it useful that water has a high latent heat of evaporation for living organisms?
It means that water is great for cooling things, for example, some mammals sweat when they are hot to cool the surface of the skin
What is cohesion?
The attraction between molecules of the same type
Why are water molecules very cohesive?
because they are polar
What are the advantages of water being cohesive?
It helps water flow, making it great for transporting substances
It helps water be transported up plant stems in the transpiration stream
Why is water a good solvent?
it is polar, the slightly positive end will be attracted to the negative ion, and the slightly negative end will be attracted to the positive ion
This means that it will get totally surrounded by water molecules and dissolve
Why is water less dense as a solid than a liquid?
Water molecules are held further apart in ice than they are in water because each water molecule forms four hydrogen bonds to other water molecules, making a lattice shape
Why is it useful that ice floats on water?
In cold temperatures, ice forms an insulating layer on top of water and so the water below does not freeze.
What are the monomers that make up carbohydrates?
monosaccharides
How many carbon atoms does glucose have?
6 - hexose monosaccharide
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
Alpha glucose hydroxyl group on c1 is down
Beta glucose hydroxyl group on c1 is up
What is the function of glucose?
It is the main energy source in animals and plants
Why can glucose easily be transported?
It is soluble
How many carbon atoms does ribose have?
5 - pentose monosaccharide
What elements are in carbohydrates?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
What is the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen in carbohydrates?
1 carbon : 2 hydrogen : 1 oxygen
How do monosaccharides join together?
By glycosidic bonds
What is a condensation reaction?
a hydrogen atom on one monosaccharide bonds to an OH group on the other, releasing a molecule of water
What is a hydrolysis reaction?
When a molecule of water reacts with the glycosidic bond, breaking it apart
What is a disaccharide?
two monosaccharides joined together
How is maltose formed?
Alpha glucose + Alpha glucose
How is sucrose formed?
Alpha glucose + fructose
How is lactose formed?
Either alpha or beta glucose + galactose
What is a polysaccharide?
When more than two monosaccharides are joined together
What is the function of starch?
It is the main energy storage material in plants
What do plants store excess glucose as?
Starch
What two polysaccharides make up starch?
amylose and amylopectin
Describe amylose
A long unbranched chain of alpha glucose
Coiled structure
Compact - good for storage
Joined by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Describe amylopectin
Made by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Some 1-6 glycosidic bonds
Branched structure
Very compact
Free ends where glucose can be added or removed
Insoluble
What bonds form between two glucose molecules?
1-4 glycosidic bonds
What molecules make up cellulose?
Beta glucose molecules
How do beta glucose molecules join together?
They join by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
Every other molecules is flipped 180 degrees
Describe cellulose
Long
Unbranched
How do cellulose molecules become fibres?
They form hydrogen bonds with each other, forming microfibrils, microfibrils then join together forming microfibrils which combine to produce fibres
What elemts are lipids made up of?
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
What are triglycerides composed of?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids
Why are lipids insoluble in water?
Hydrophobic hydrocarbon tails
What is an ester bond?
A condensation reaction between the glycerol and the fatty acids, releasing water
What is a saturated fatty acid?
no double bonds between carbons
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?
At least one double bond between carbon atoms
What is the function of triglycerides?
They are energy storage molecules
Describe the structure of a triglyceride
Long hydrocarbon fatty acid tails (a lot of energy is released when broken down)
Insoluble as the hydrophobic tails face inwards shielding themselves from the water with their hydrophilic glycerol heads
Describe the structure of phospholipids
Hydrophilic phospholipid heads face out towards the water and the hydrophobic tails face in away from the water
What are the functions of phospholipids?
They are a component of the plasma membrane
They make up the phospholipid bilayer
They prevent water-soluble substances from passing through
Describe the structure of cholesterol
Small flattened shape
Has a carbon ring structure attached to a hydrocarbon tail
What is the function of cholesterol?
Strengthen the cell membrane
makes the cell membrane more rigid and less fluid
What are the monomers of proteins?
amino acids
What is a dipeptide?
2 amino acids
What is a polypeptide?
more than 2 amino acids joined together
Describe the structure of an amino acid
A carboxyl group
an amine group attached to a carbon atom
a single hydrogen
A variable R group
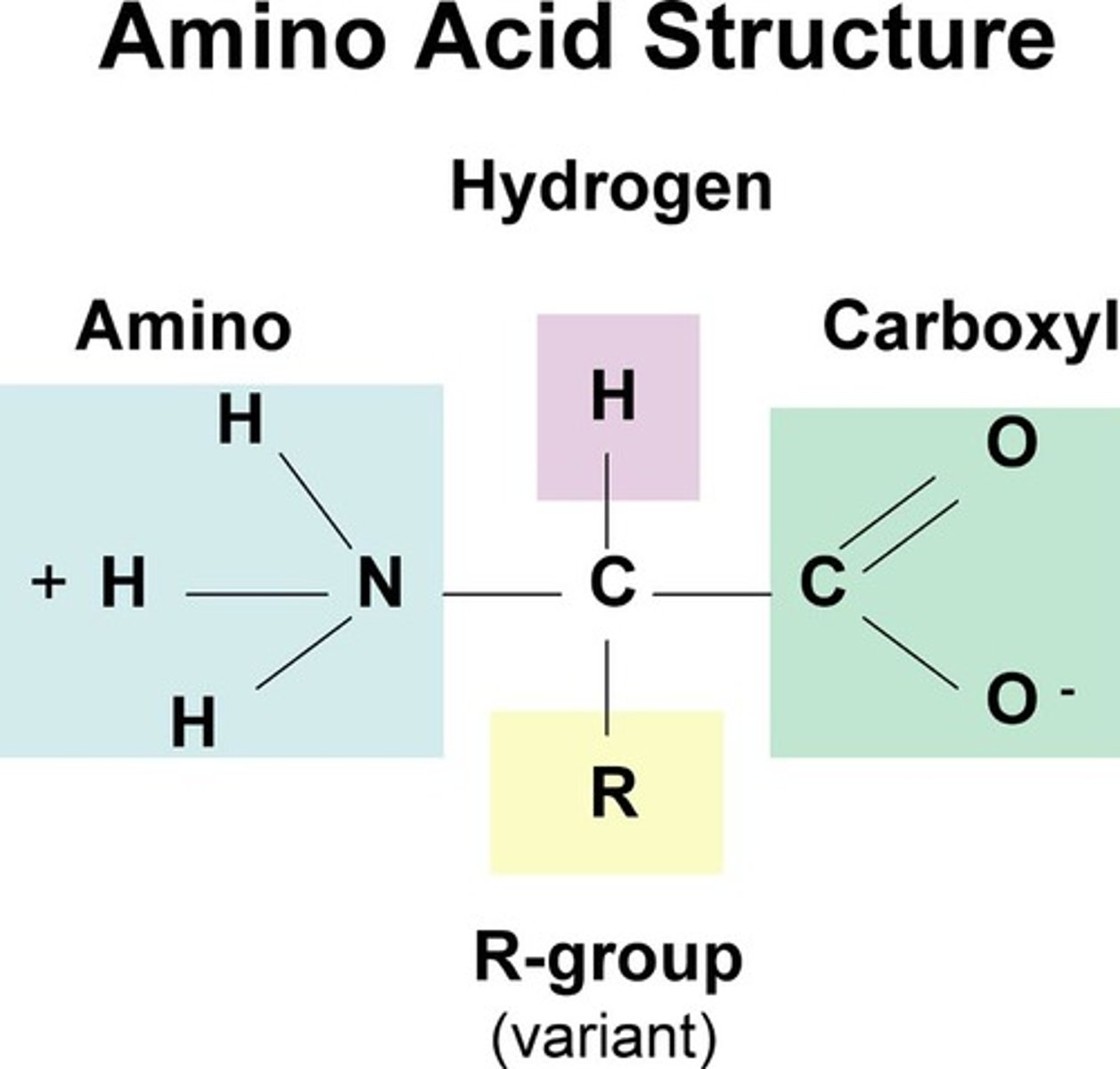
What R group does glycine have?
H
How do amino acids join together?
peptide bonds (condensation reaction)
What elements are in amino acids?
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen
Describe the primary structure of a protein
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
held together by peptide bonds
Describe the secondary structure of a protein
Hydrogen bonds form between amino acids in the chain
Folds into beta pleated sheet or coils into an alpha helix