Womens health
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Main hormones responsible for the changes that occur during puberty
Females- Estradiol and progesterone
Males- Testosterone
5 physical changes for females
Hips widen, breasts grow, pubic hair, taller, sweaty
5 physical changes for males
Voice drops, gains weight, gets taller, pubic hair, sweaty
5 emotional and social changes that occur for both males and females
Separates from family
Becomes closer to friends
Gets more anxious
Gets more emotional
Gets more embarrassed
PMS
A group of symptoms that occur in women, typically between ovulation and a period.
Mood swings, tender breasts, food cravings, fatigue, irritability and depression.
Sanitary items that females have available for them to use when they have their period
Pads
Tampons
Period undies
Menstrual cups
Menstruation
A normal vaginal bleeding that occurs as part of a woman's monthly cycle. Every month, your body prepares for pregnancy. If no pregnancy occurs, the uterus, or womb, sheds its lining.
Stage 1: Menstruation
Commonly known as ‘period’
Uterine lining sheds and exits out through the vagina
Average length lasts between 3-5 days; can last up to 7
Hormones: Estrogen and progesterone are at their lowest.
Stage 2: Follicular Phase
The dominant follicle in your ovaries matures an egg
This follicles prepared the egg to be released at the next stage
The lining of the uterus thickens in preparation for pregnancy
Occurs from the beginning of your period until ovulation
Hormones: Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and estrogen increases
Stage 3: Ovulation
The mature egg is released from the ovaries, through the fallopian tubes towards your uterus.
Lasts for 16-32 hours
Occurs around day 16
Once the mature egg is released, it will survive for 24 hours in the uterus.
Hormones: Dramatic increase in luteinizing hormone (LH), estrogen decreases right after ovulation.
Stage 4: Luteal
Lining thickens further in preparation for pregnancy
Occurs after ovulation, and ends at the start of menstruation.
If the egg is fertilised, it implants on the lining and the increase of progesterone maintains the thickness of the lining
If pregnancy does not occur, the egg dies, progesterone levels drop and the uterus lining sheds which is the beginning of menstruation
Hormones that control menstruation: FSH and LH
Released in the pituitary gland, which is a part of the brain
Hormones that control menstruation: Oestrogen
Development of the female secondary sexual characteristics
prepare the release of the ovum and the uterine lining thickens.
Hormones that control menstruation: Progesterone
Primarily responsible for preparing the uterus lining for a potential pregnancy
Follicle Stimulating Hormone’s (FSH) role in the menstrual cycle
The pituitary gland releases the FSH hormone.
FSH is secreted into the blood stream and enters the ovaries where the follicle then produces an ovum (egg).
The follicle then releases oestrogen to prepare the release of the ovum and the uterine lining thickens.
Luteinizing Hormone’s (LH) role in the menstrual cycle
After about 2 weeks the production of FSH stops and LH is produced.
LH is then transported through the blood stream to the ovaries to stimulate ovulation in the follicle.
Progesterone’s role in the menstrual cycle
If the ovum is not fertilized the the ovum degenerates and menstruation begins.
If the ovum is fertilized it embeds to the uterine wall and the overall hormone levels rise.
The remains of the follicle are then transported to the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland, where progesterone is secreted.
PCOS Key facts:
PCOS affects about %10 of women
Women with PCOS have partially formed follicles on the ovaries, each of which contains an egg.
These rarely grow to maturity or produce eggs that can be fertilised.
About 85% of women with PCOS have insulin resistance, which means the body blocks glucose from going into cells.
By age 40, 40% of women with PCOS will develop pre-diabetes or diabetes.
Fatty liver affects 15% to 55% of women with PCOS and can be improved by diet changes.
PCOS symptoms:
Irregular or no periods
Excessive hair (hirsutism) on the face or body
Hair loss (alopecia)
Skin conditions such as acne and skin tags
Weight problems
Reduced fertility
Stress, anxiety and depression
Female reproductve system
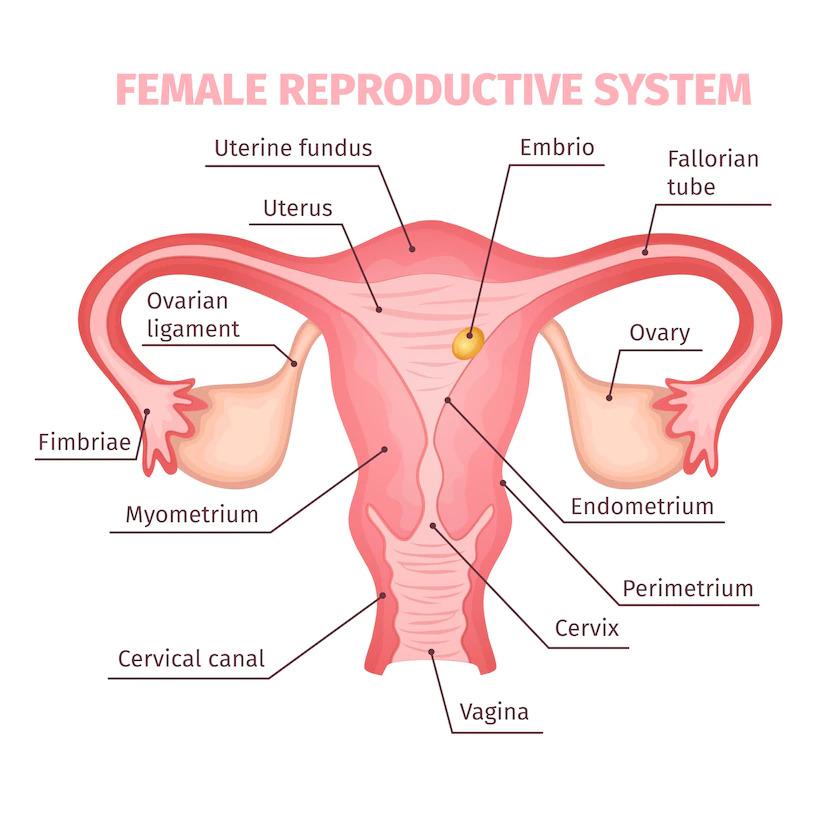
Cultural issues that impact women surrounding periods
It can be seen as
taboo
unclean
embarrassing
In some cultures there are
prohibitions on attending religious ceremonies
visiting religious spaces
handling food
sleeping in the home.