Basic Bacteriology
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What are the structural differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
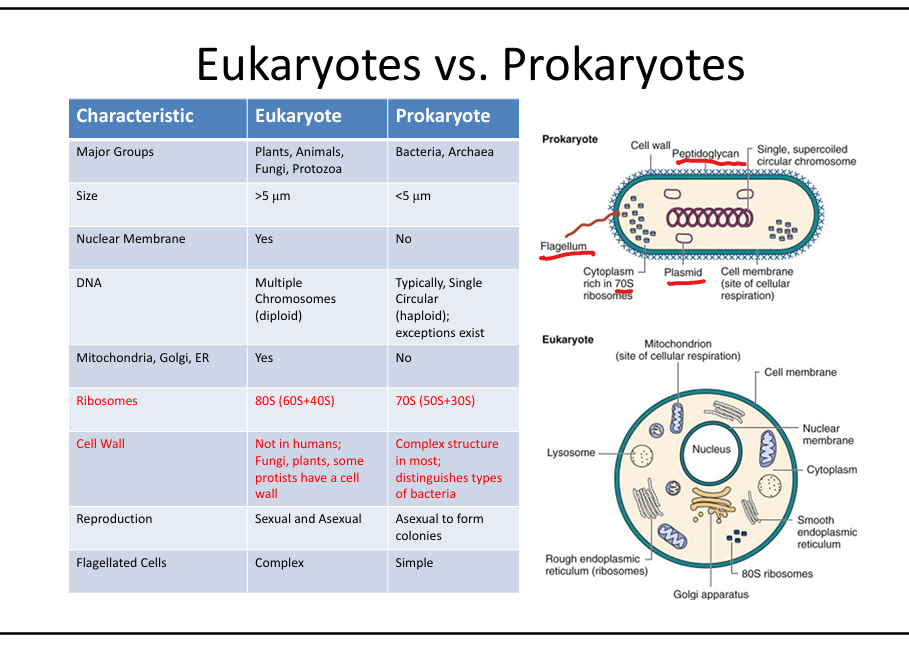
Eukaryotes: >5 µm, nuclear membrane, multiple linear chromosomes, mitochondria/ER/Golgi, 80S ribosomes, sexual/asexual reproduction. Prokaryotes: <5 µm, no nuclear membrane, single circular chromosome, no organelles, 70S ribosomes, binary fission.

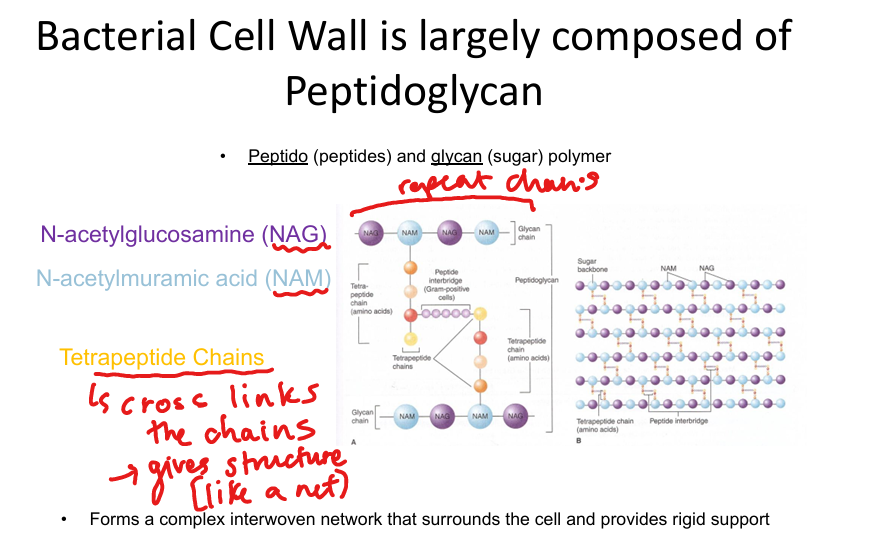
What is the major structural component of bacterial cell walls?
Peptidoglycan: alternating NAG/NAM sugars with tetrapeptide cross-links; provides rigidity and shape.

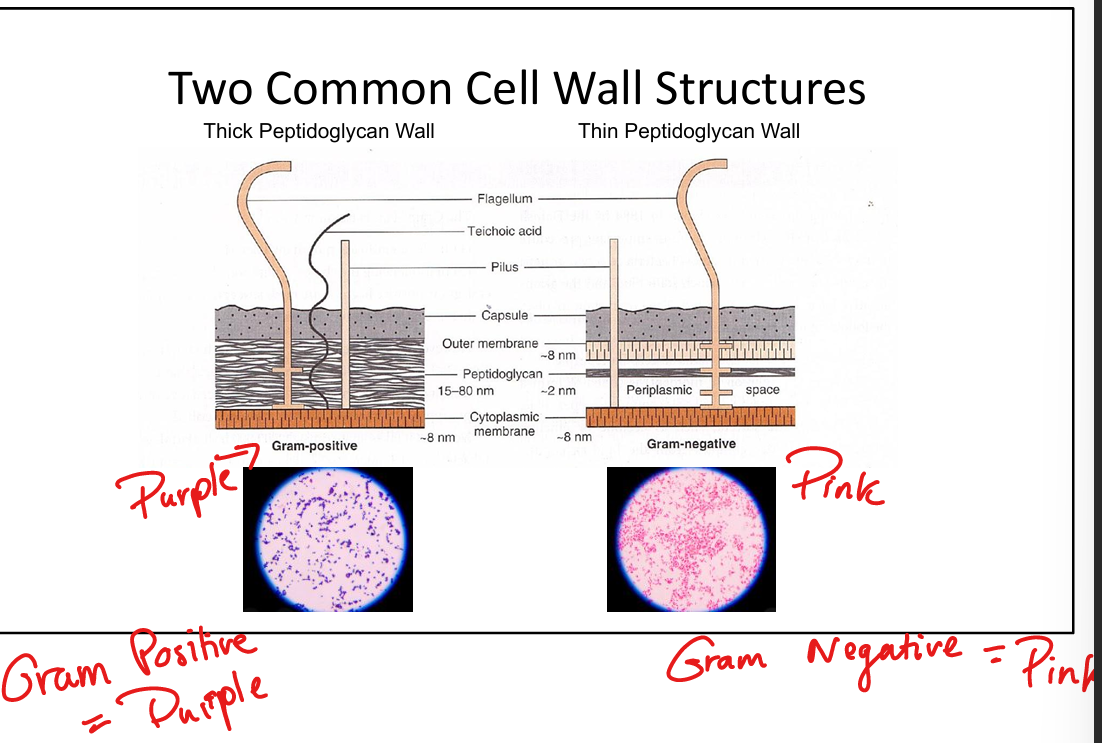
How do Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls differ?
Gram-positive: thick peptidoglycan, teichoic(flexibility)/lipoteichoic acids(adhesion), retain crystal violet → purple.
Gram-negative: thin peptidoglycan, outer membrane with LPS (O-antigen, core polysaccharide, Lipid A endotoxin), porins, periplasmic enzymes → lose crystal violet, take up safranin → pink/red.

What is the clinical significance of Lipid A in Gram-negative bacteria?
Lipid A is endotoxin; released during bacterial lysis; binds TLR4 → cytokine storm (IL-1, TNF) → septic shock.


What is the role of teichoic and lipoteichoic acids in Gram-positive bacteria?
Teichoic acid=provide rigidity, resistance to osmotic stress, confer negative charge,
Lipoteichoic acid= aid adhesion/colonization, activate TLR2 → NF-κB → IL-1/TNF release.
What is the principle of Gram staining?
Crystal violet stains all cells → iodine forms complex → alcohol decolorizes Gram-negative → safranin counterstains Gram-negative pink/red while Gram-positive remain purple.


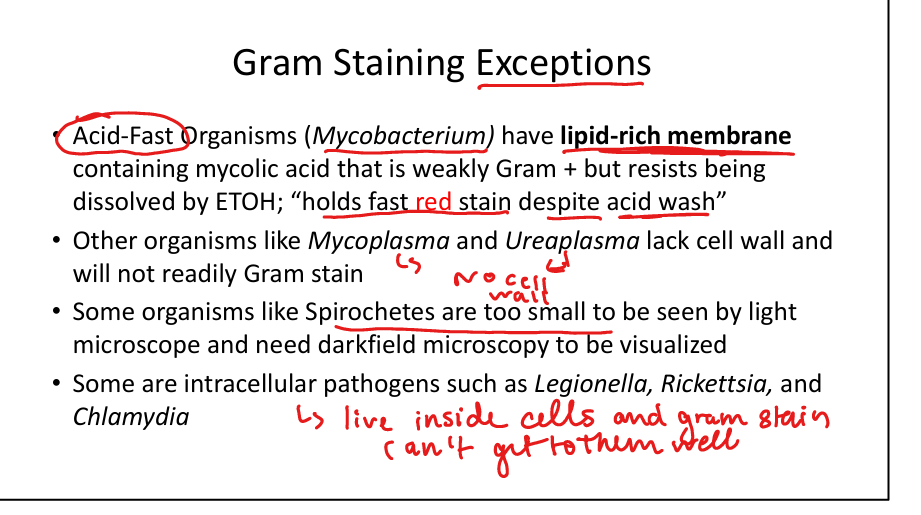
Which organisms are Gram stain exceptions?
Mycobacteria (acid-fast, lipid rich membrane with mycolic acids), Mycoplasma/Ureaplasma (no cell wall), Spirochetes (too thin, need darkfield), intracellular bacteria (Legionella, Rickettsia, Chlamydia).

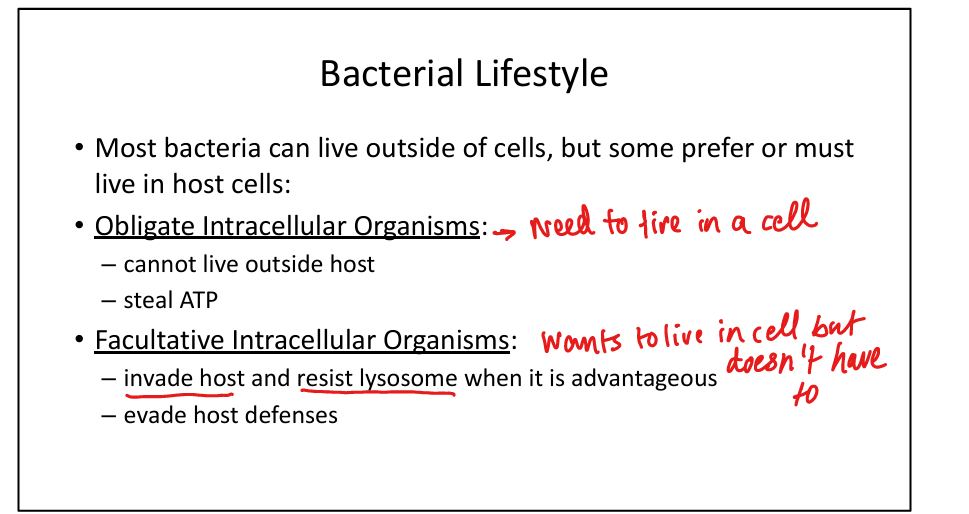
What are obligate intracellular organisms?
Rickettsia, Chlamydia → cannot survive outside host, steal ATP.
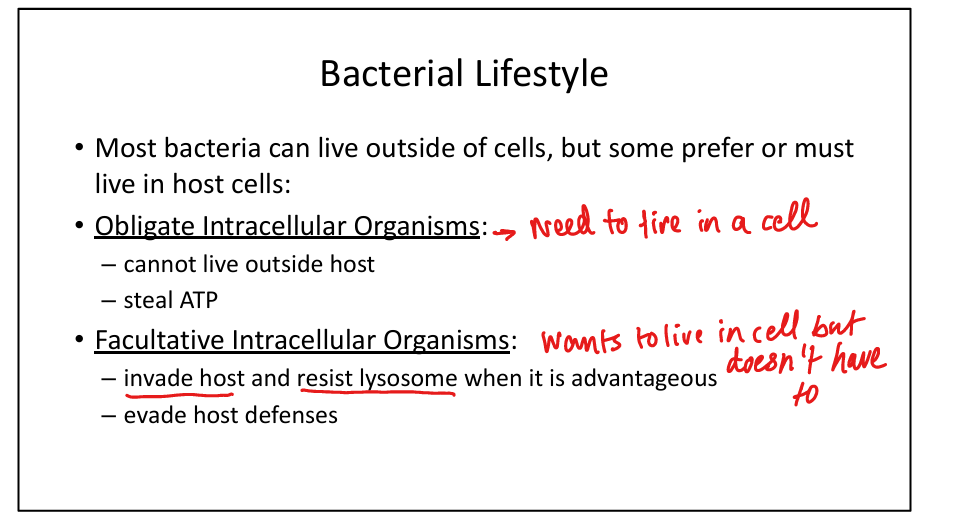

What are facultative intracellular organisms?
Listeria, Salmonella → invade host cells, resist lysosomal killing, evade immunity.

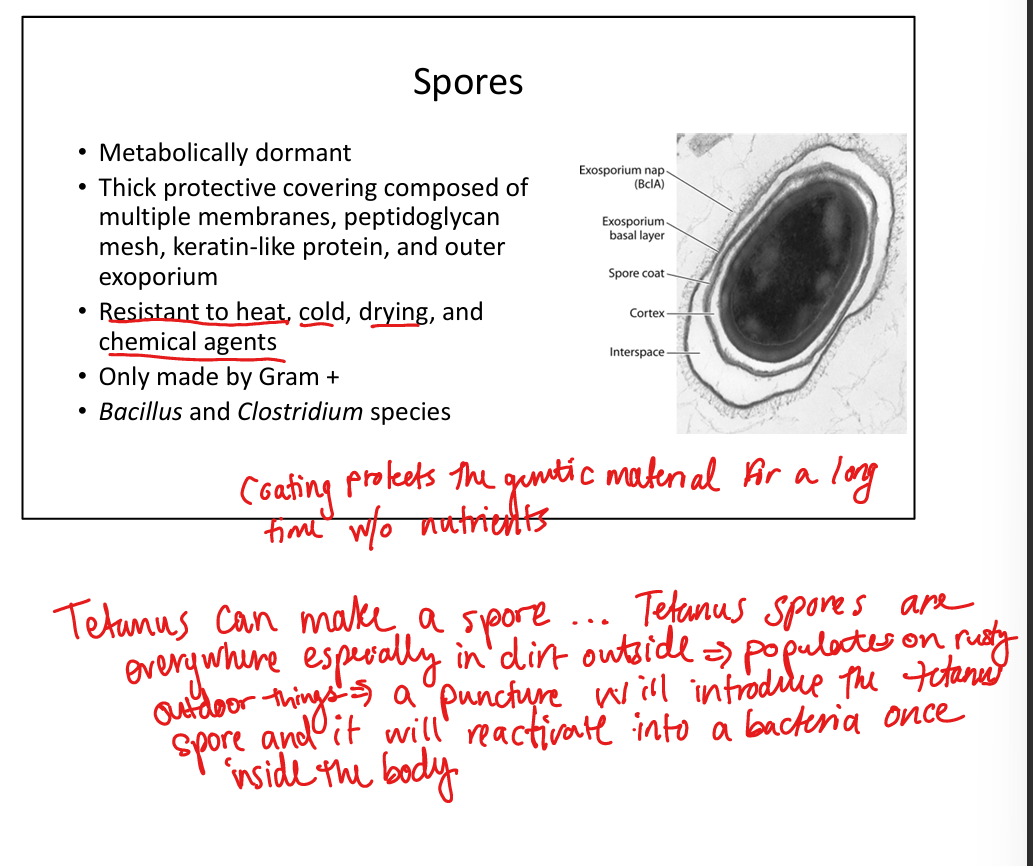
Which bacteria form spores?
Gram-positive Bacillus and Clostridium species → resistant to heat, chemicals, desiccation; clinically relevant in anthrax, tetanus, botulism, C. difficile.

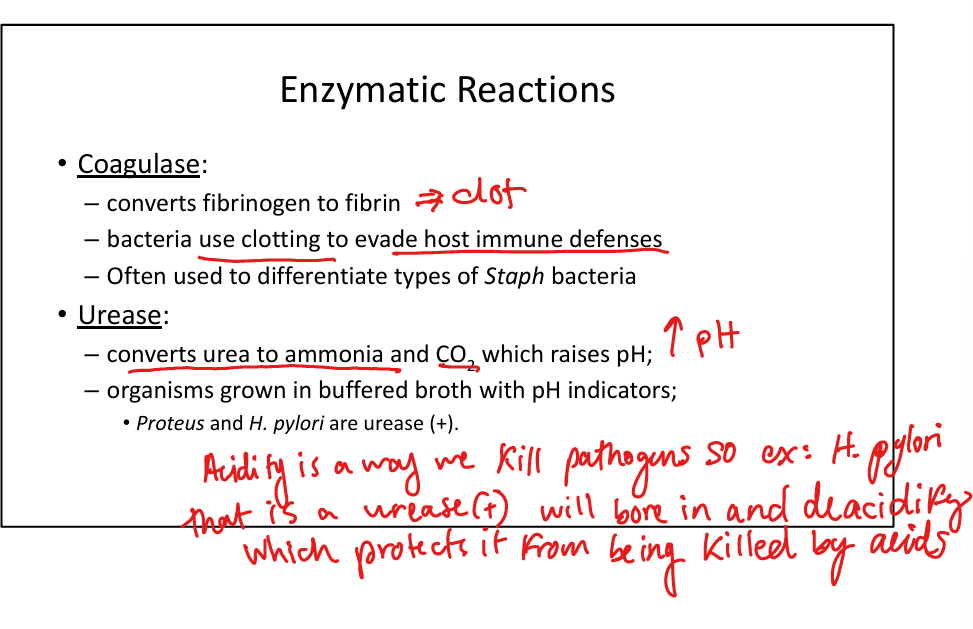
What is the role of coagulase in bacterial pathogenesis?
Converts fibrinogen → fibrin; cloaks bacteria in clot to evade immunity. Used to differentiate Staph aureus (coagulase +) from other staphylococci.
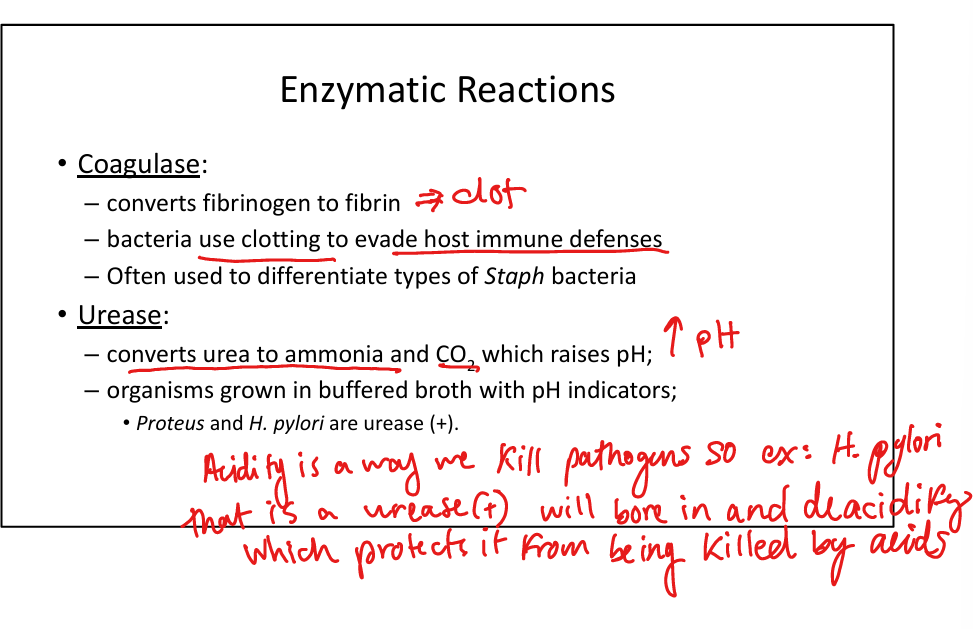

What is the role of urease in bacterial pathogenesis?
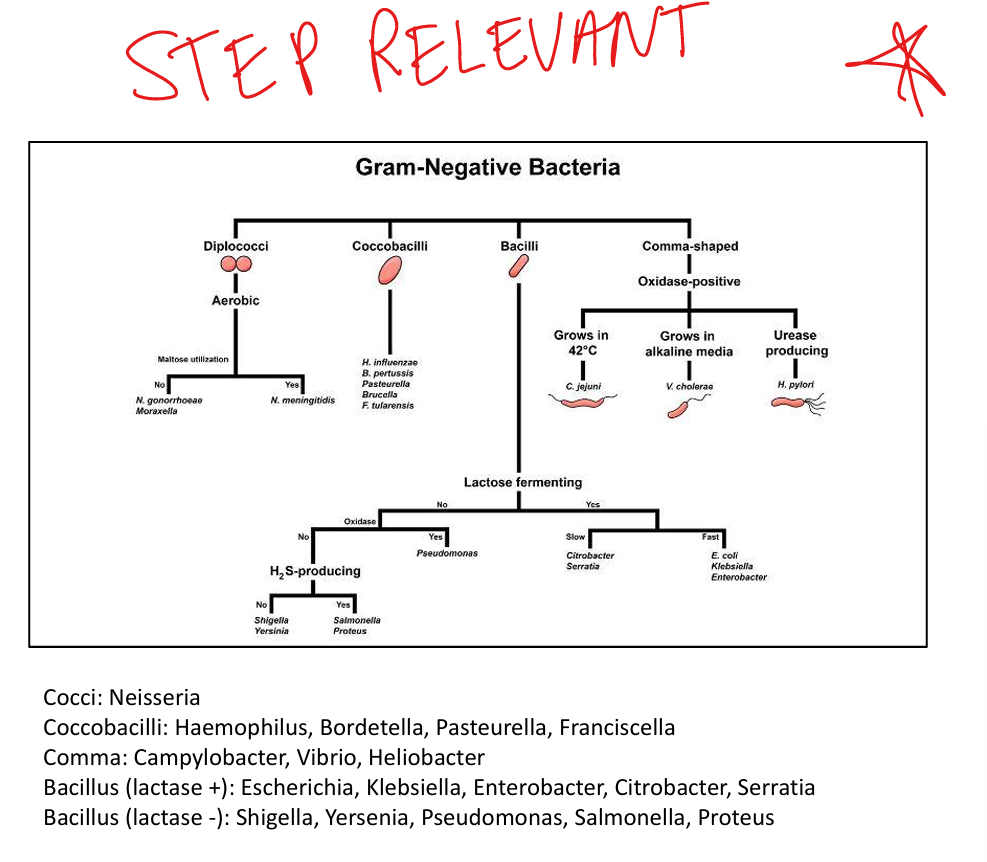
Converts urea → ammonia + CO₂ → raises pH, aids survival. Urease (+): Proteus, H. pylori. Used diagnostically in urease broth.

What are key bacterial virulence factors?
Capsule (anti-phagocytic, e.g. S. pneumoniae), exotoxins (protein toxins disrupting host), Protein A (Staph aureus, binds Fc of IgG to prevent opsonization), IgA protease (Neisseria, cleaves IgA allowing host to enter respiratory tract), M protein (Strep pyogenes, molecular mimicry → rheumatic fever).


What is the clinical importance of catalase in bacteria?
Catalase (+) organisms break down H₂O₂ and therefore lack ability to perform respiratory burst(killing of a pathogen); relevant in Chronic Granulomatous Disease (patients susceptible to catalase + infections).


What is Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)?
X-linked/AR NADPH oxidase deficiency → impaired respiratory burst → recurrent infections with catalase (+) organisms (Staph, Serratia, Aspergillus). WBCs can fight catalase (−) organisms by “borrowing” H₂O₂.


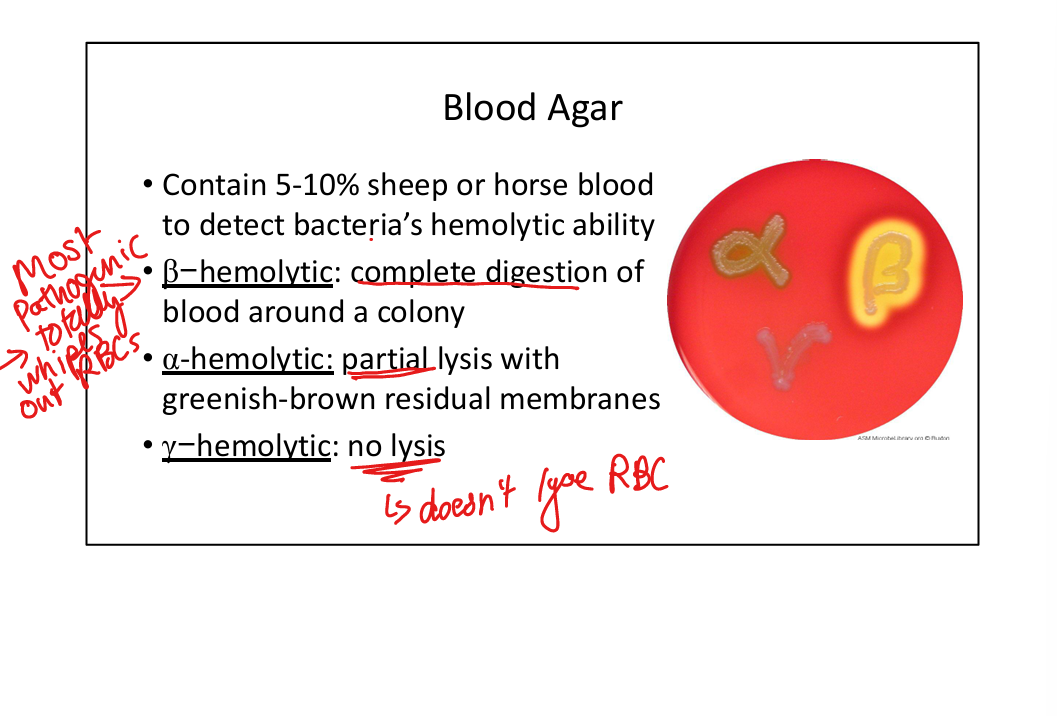
What is blood agar used for?
Detects hemolysis: β-hemolysis (complete clearing, e.g. Strep pyogenes), α-hemolysis (partial, greenish, e.g. Strep pneumoniae), γ-hemolysis (none).

What is chocolate agar used for?
Lysed RBCs → release growth factors (NAD, hemin); supports fastidious organisms (Neisseria, H. influenzae).


What is MacConkey agar used for?
Selective for Gram-negative rods; differentiates lactose fermenters (pink colonies: E. coli, Klebsiella) vs non-fermenters (colorless: Salmonella, Shigella).


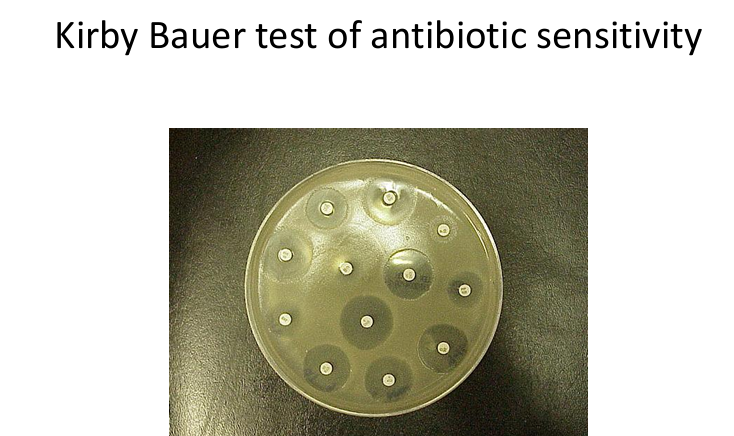
What is the Kirby-Bauer test?
Antibiotic sensitivity test using zones of inhibition around antibiotic discs.

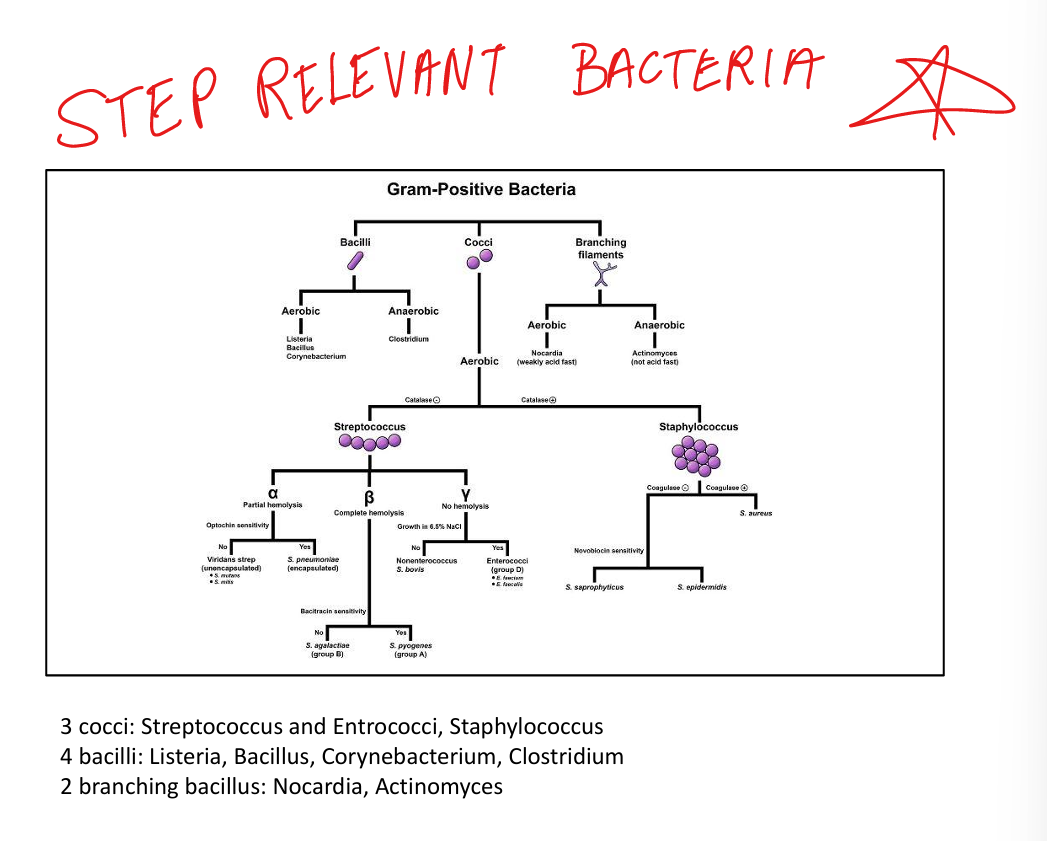
Step relevant Gram Positive Bacteria

Step Relevant Gram Negative Bacteria