Rates and order
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Rate of reaction can be found by:
Measuring decrease in conc. of reactant over time
Measuring increase in conc. of product over time
Units for rate of reaction
mol dm-3 s-1
What is the overall order of reaction?
sum of powers of reactants in rate equations
conc-time graph; 0 order
reactant conc deacrease while time increases
straight line
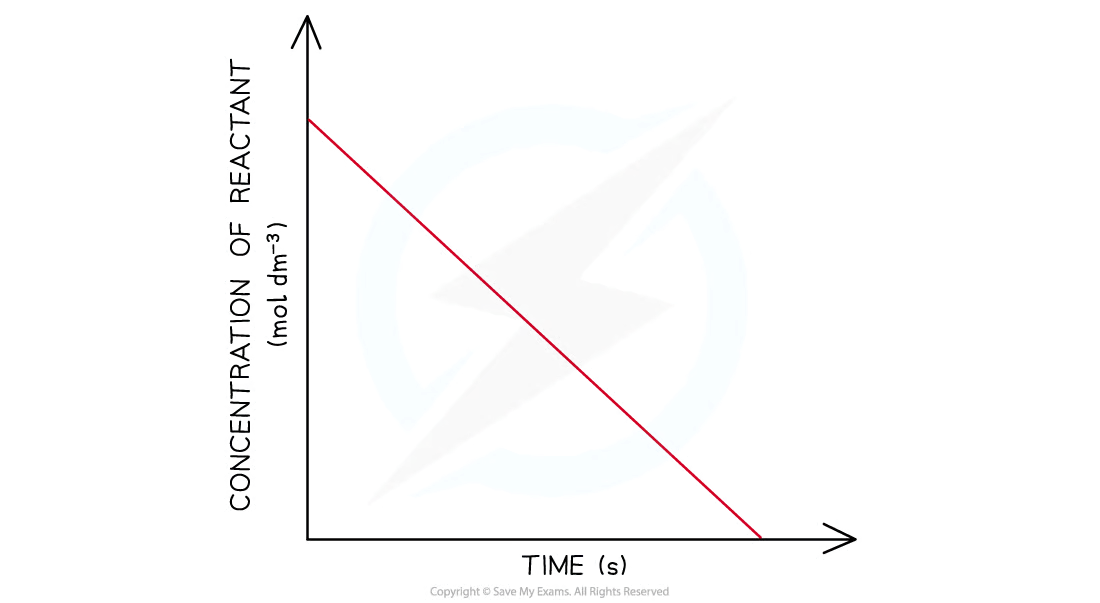
What does grad of line =
rate of reaction / rate constant k
conc-time graph: 1st order
curve going downwards and eventually plateaus
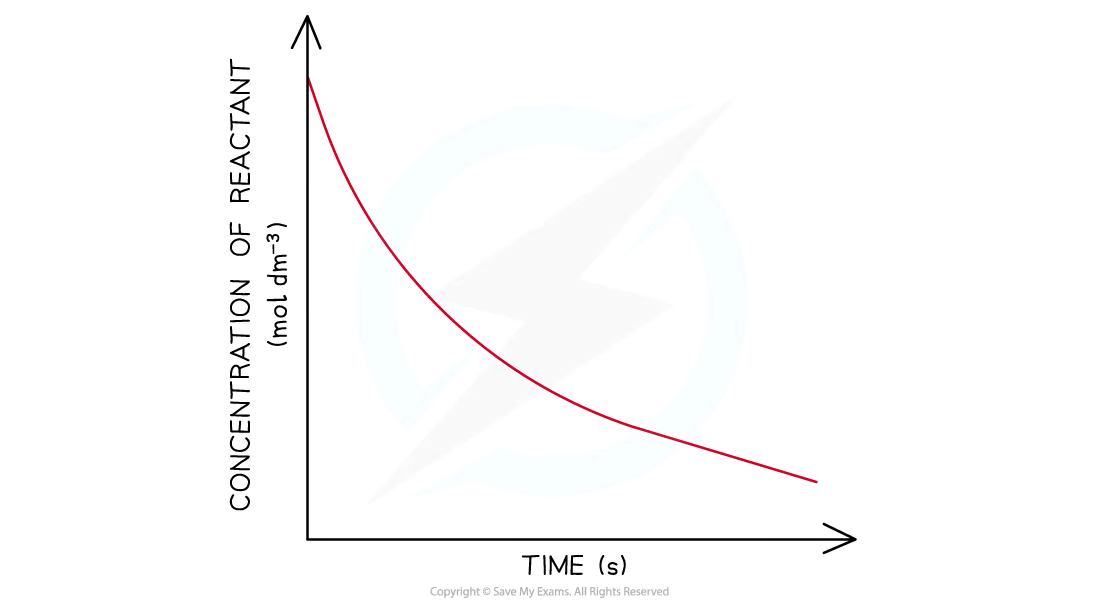
conc-time graph: 2nd order
concentration of the reactant decreases more steeply with time

For a zero-order reaction the successive half-lives decrease with time
∴ would take less time for the concentration of reactant to halve as the reaction progresses
half-life of a first-order reaction remains constant throughout the reaction
amount of time required for the concentration of reactants to halve will be the same during the entire reaction
second-order reaction, the half-life increases with time
as the reaction is taking place, it takes more time for the concentration of reactants to halve

rate v conc graph: o order

rate v conc graph: 1st order
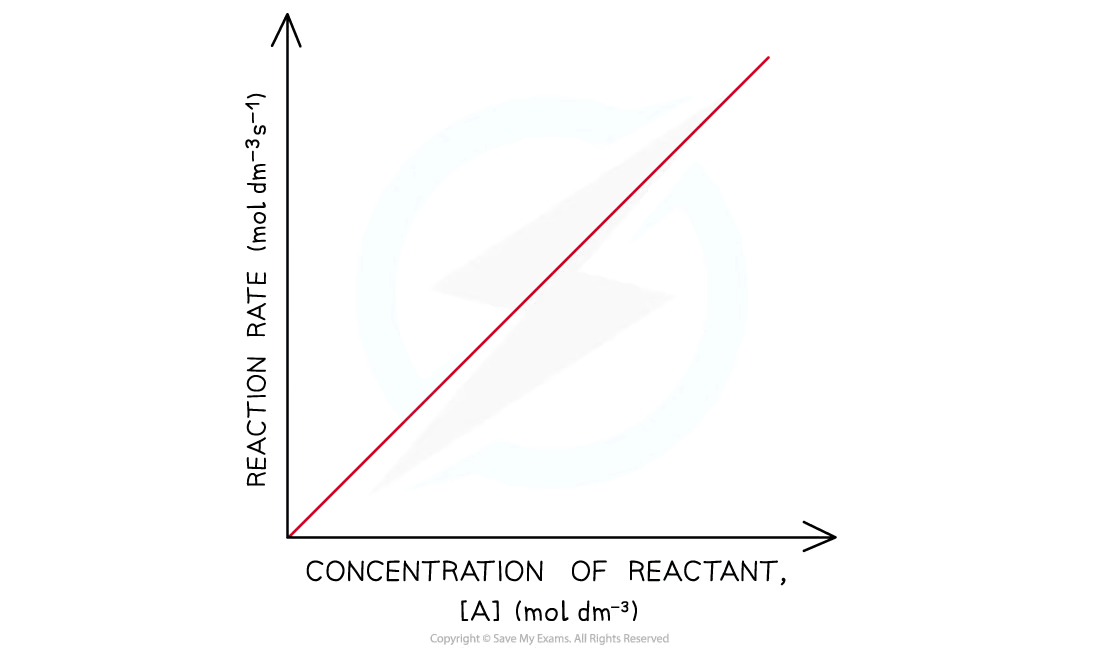
rate v conc graph: 1st order
The rate of the reaction increases more as the concentration of the reactant increases
This means that the rate of the reaction decreases more as the concentration of the reactant decreases when it gets used up during the reaction
The graph is a curved line

effect of temperature on the rate constant, k:
A + B → C + D
Rate of reaction = k[A][B]
rate of reaction depends on the rate constant, k, and the concentration of the reactants
Increasing the ____ of a reaction increases the rate of a chemical reaction
temp

rate=
K (_)
How find from second order k with graph?
plot rate v conc2
grad=k
equation relating half life to rate constant, for for first order
k=In2/ t1/2
rate determining step is ___
slow

rate constant and rate of reaction are directly proportional to the _____, then at higher temperatures:
fraction of molecules with energy equal to or greater than the activation energy
The rate of reaction increases
The rate constant increases
effect of the higher temperature on the rate constant, k.
increases